Abstract
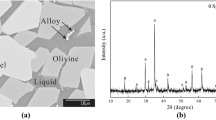
Phosphate rocks mainly contain Ca3(PO4)2, SiO2, and MgO. The vacuum carbothermal reduction of Ca3(PO4)2 with different MgO contents was investigated to determine the maximum volatilization rate of P2 and the transformation of phases in a SiO2–C–Ca3(PO4)2–MgO-based system. The application of reduced slag in the dephosphorization of a converter was discussed. The carbon excess coefficient (CEC), reduction temperature, and equilibrium phase were calculated using FactSage 8.1. The quinoline phosphomolybdate weight method, scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction were used to characterize the volatilization rate of P2, phases, and micromorphology of the reduced slag. The volatilization rate of P2 first increased and then decreased, with the highest volatilization rate of 93.77% obtained at n(MgO/CaO) = 0.50. The reduced slag phase changed from CaSiO3 to 2CaO·SiO2·MgO·SiO2, CaO·SiO2·MgO·SiO2, and 3CaO·P2O5·2CaO·SiO2 solid solutions with increasing MgO content. The diffusion of graphite was hindered by an excessive MgO solid phase when n(MgO/CaO) > 0.50, resulting in the reaction of unreacted Ca3(PO4)2 with 2CaO·SiO2·MgO·SiO2 to form 2CaO·SiO2·3CaO·P2O5 (C2S–C3P2) during the holding process, thus reducing the reduction rate of Ca3(PO4)2. Reduced slag with a small amount of phosphorus can be used in converter smelting to achieve low-temperature dephosphorization.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sengul H, Ozer AK, Gulaboglu MS (2006) Beneficiation of Mardin-Mazıdaği (Turkey) calcareous phosphate rock using dilute acetic acid solutions. Chem Eng J 122:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2006.06.005
Ait-Ouakrim EIH, Chakhchar A, Modafar CEI, Douira A, Amir S, Ibnsouda-Koraichi S, Belkadi B, Filali-Maltouf A (2023) Valorization of Moroccan phosphate sludge through isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and assessment of their growth promotion effect on Phaseolus vulgaris. Waste Biomass Valoriz 14:2673–2690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02054-2
Liu WB, Huang WX, Ma H, Chi XP, Rao F (2020) China’s phosphate ore resources distribution and the progress of phosphate ore dressing technology. Ind Miner Process 49:19–25. https://doi.org/10.16283/j.cnki.hgkwyjg.2020.12.005. (in Chinese)
Cui RG, Zhang FY, Guo J, Guo ZH, Xiao YP (2019) Development strategy of phosphate rock in China under global allocation of resources. Strateg Study CAE 12:128–132. https://doi.org/10.15302/J-SSCAE-2019.01.018. (in Chinese)
Jia H, Liu JX, Jiao S, Shang PQ, Wang CG, Chi HX (2021) Situation analysis and countermeasures of phosphate rock resources exploitation and ecological protection in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Min Mag 30:67–72. https://doi.org/10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2021.02.028. (in Chinese)
Wang B, Zhou ZX, Xu DH, Wu JH, Yang XS, Zhang ZY, Yan ZJ (2022) A new enrichment method of medium-low grade phosphate ore with high silicon content. Miner Eng 181:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107548
Wu FF, Wang JX, Liu JT, Zeng GP, Xiang P, Hu P, Xiang WS (2021) Distribution, geology and development status of phosphate resources. Geol China 48:67–72. https://doi.org/10.12029/gc20210106. (in Chinese)
Zrelli RE, Rabaoui L, Daghbouj N, Abda H, Castet S, Josse C, Beek PV, Souhaut M, Michel S, Bejaoui N, Courjault-Radé P (2018) Characterization of phosphate rock and phosphogypsum from Gabes phosphate fertilizer factories (SE Tunisia): high mining potential and implications for environmental protection. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:14690–14702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1648-4
Wu QH, Huang R, Lv XD, Qian X, Liu L, Zhang JZ (2019) Effect of temperature on the vacuum carbothermal reduction of low-grade phosphate ore. Mater Res Express 6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab17a6
Shang DL, Geissler B, Mew M, Satalkina L, Zenk L, Tulsidas H, Barker L, El-Yahyaoui A, El-Yahyaoui A, Tahhusseina M, Zheng YH, Wang ML, Yao Y, Liu XD, Deng HD, Zhong J, Li ZY, Steiner G, Bertau M, Haneklaus N (2021) Unconventional uranium in China’s phosphate rock: review and outlook. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 140:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110740
Haneklaus N, Sun YJ, Bol R, Lottermoser B, Schnug E (2017) To extract, or not to extract uranium from phosphate rock, that is the question. Environ Sci Technol 51:753–754. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05506
Abouzeid AZM (2008) Physical and thermal treatment of phosphate ores—an overview. Int J Miner Process 85:59–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2007.09.001
Aydin I, Imamoglu S, Aydin F, Saydut A, Hamamci C (2009) Determination of mineral phosphate species in sedimentary phosphate rock in Mardin, SE Anatolia, Turkey by sequential extraction. Microchem J 91:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2008.08.001
He X, Huang R (2022) Effect of different carbon sources on vacuum carbothermal reduction of low-grade phosphorus ore. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 28:29–37. https://doi.org/10.2298/CICEQ210219013H
Ma H, Feng X, Deng C (2018) Water–phosphorus nexus for wet-process phosphoric acid production. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:6968–6979. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b05399
Ma H, Feng X, Zeng B (2018) Self-anticorrosion for the combustion tower of heat recovered thermal process phosphoric acid production. Process Saf Environ 118:330–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.07.008
Liu Q, Liu WZ, Lü L, Li RH, Liang B, Yue HR, Tang SW, Li C (2018) Study on reactions of gaseous P2O5 with Ca3(PO4)2 and SiO2 during a rotary kiln process for phosphoric acid production. Chin J Chem Eng 26:795–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.11.016
Wu FH, Jin CY, Xie RS, Qu GF, Chen BJ, Qin J, Liu XX, Li HL, Kuang LR (2023) Extraction and transformation of elements in phosphogypsum by electrokinetics. J Clean Prod 385:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135688
Qin XT, Cao YH, Guan HW, Hu QS, Liu ZH, Xu J, Hu B, Zhang ZY, Luo R (2023) J Clean Prod 387:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.135858
Zheng GY, Cao RF, Li Y, Xia JP, Chen ZJ (2020) The additive effect of K2CO3–NiSO4 on the carbothermal reduction process of phosphate rock and SiO2. SILICON 12:1985–1994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00311-5
Jacob KD, Reynolds DS, Hill WL (1929) Reduction of tricalcium phosphate by carbon. J Ind Eng Chem 21:1126–1132. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50239a041
Li XF, Huang R, Wu QH, Xie SF, Li JQ (2021) Experimental approach for the characterization of low-grade phosphate ore performance in isothermal conditions. J Sustain Metall 7:1736–1747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00451-2
Yang MR, Lv XW, Bai CG, Wang HY (2022) Isothermal kinetics model for solid–solid reaction of powders through surface area and size distribution of particles. Metall Mater Trans B 53:968–980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02393-2
Phutke M, Raichur AR, Suresh AK (2022) Contact-point models for solid–solid reaction kinetics: a parameter estimation and derived insights. Ind Eng Chem Res 61:11636–11644. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.2c00513
Shimizu A, Hao YJ, Tanaka T (1998) Representation of the concentric spherical powder reaction model in the form of linear regression analysis. Can J Chem Eng 76:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450760109
Phutke M, Dedhia J, Suresh AK (2019) Modelling solid–solid reactions: contact-point approach. Chem Eng J 377:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.030
Dalvi VV, Suresh AK (2011) A contact-point based approach for the analysis of reactions among solid particles. AIChE J 57:1329–1338. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12347
Lv YC, Li HB, Liu Y, Wang HB (2022) Effects of dephosphorization from solid 2CaO·SiO2–3CaO·P2O5 of steelmaking slag. In: International conference on advanced manufacturing technology and manufacturing systems (ICAMTMS), Shijiazhuang, China, 2022, p 123091X-4. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2645818
Pahlevani F, Kitamura SY, Shibata H, Maruoka N (2010) Distribution of P2O5 between solid solution of 2CaO·SiO2–3CaO·P2O5 and liquid phase. ISIJ Int 50:822–829. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.50.822
Zhu B, Zhu MM, Luo J, Dou XF, Wang Y, Jiang HJ, Xie B (2020) Distribution behavior of phosphorus in 2CaO·SiO2–3CaO·P2O5 solid solution phase and liquid slag phase. Metals 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081103
Wang ML, Yang WY (2020) Dephosphorization in the early stage of converter steelmaking. Ironmak Steelmak 47:1127–1134. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2019.1673546
Sun H, Yang J, Lu XW, Liu WS, Ye GF, Zhang RH, Yang WK (2021) Dephosphorization in double slag converter steelmaking process at different temperatures by industrial experiments. Metals 11:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071030
Acknowledgements
The authors are especially grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52064010), Outstanding Young Scientists and Technologists Program of Guizhou Province, China (Grant No. [2021]5644), the Key Nurturing Projects of Guizhou University (Grant No. [2019]07), and the Natural Science Research Project of Guizhou Provincial Department of Education ([2022]041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was M. Akbar Rhamdhani.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Zhu, R., Huang, R. et al. Effect of MgO on Vacuum Carbothermal Reduction Mechanism of Ca3(PO4)2 in SiO2–C–Ca3(PO4)2–MgO-Based System. J. Sustain. Metall. 9, 1429–1443 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-023-00735-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-023-00735-9