Abstract
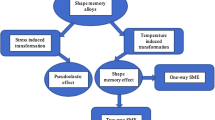
In this review, the research during the 50-year career in shape memory and superelasticity of Kazuhiro Otsuka is discussed, with a focus on his most cited publications. Not only did his research, in collaboration with many fellow scientists, explain the scientific basis for these phenomena, but also it has led to the realisation of a new aspect of the science of shape memory, particularly with regard to the physics of the most important Ti–Ni alloys, from the point of view of shape memory applications, as the result of the discovery of strain glass materials as a subset of shape memory behaviour for off-stoichiometric Ti50-xNi50+x compositions.





Copyright 1978, with permission from Elsevier

Copyright 1981, with permission from Elsevier

Copyright 1983, with permission from Elsevier

Copyright 1990, with permission from Elsevier


Copyright 2005 by the American Physical Society

Copyright 2006 by the American Physical Society

Copyright 2006 by the American Physical Society

Copyright 2010 by the American Physical Society
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not Applicable.
References
Otsuka K, Wayman CM (eds) (1988) Shape memory materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Otsuka K, Wayman CM (1967) Epitaxial growth of vacuum-evaporated Co on NaCl I. Conditions leading to epitaxy. Phys Stat Sol 22:559–578
Otsuka K, Wayman CM (1967) Epitaxial growth of vacuum-evaporated Co on NaCl II. Analysis of diffraction patterns. Phys Stat Sol 22:579–592
Shimizu K, Wayman CM (1966) Discussion of “Factors determining twinning in martensites.” Acta Metall 14:1390–1391
Rachinger WA (1958) A “super-elastic” single crystal calibration bar. Brit J Appl Phys 9:250–252
Duggin MJ, Rachinger WA (1964) The nature of the martensitic transformation in a copper-nickel-aluminium alloy. Acta Met 12:529–535
Otsuka K, Shimizu K (1969) Morphology and crystallography of thermoelastic γ´ Cu–Al–Ni martensite. Jap J Appl Phys 8:1196–1204
Otsuka K, Shimizu K (1970) Memory effect and thermoelastic martensitic transformation in Cu–Al–Ni alloy. Scripta Metall 4:469–472
Otsuka K (1971) Origin of the memory effect in Cu–Al–Ni alloy. Japan J Appl Phys 10(5):571–579
Otsuka K, Shimizu K (1974) Morphology and crystallography of thermoelastic Cu–Al–Ni martensite analysed by the phenomenological theory. Trans Jpn Inst Metals 15:103–108
Wechsler MS, Lieberman DS, Read TA (1953) On the theory of the formation of martensite. Trans AIME 197:1503–1515
Bowles JS, McKenzie JK (1954) The crystallography of martensitic transformations I. Acta Met 2:129–137
McKenzie JK, Bowles JS (1954) The crystallography of martensitic transformations II. Acta Met 2:138–147
Sakamoto H, Otsuka K, Shimizu K (1977) Rubber-like behaviour in a Cu–Al–Ni alloy. Scripta Met 11:607–611
Otsuka K, Wayman CM, Nakai K, Sakamoto H, Shimizu K (1976) Superelastic effects and stress-induced martensitic transformations in Cu–Al–Ni alloy. Acta Met 24:207–226
Otsuka K, Sakamoto H, Shimizu K (1976) Two stage superelasticity effects and stress-induced martensitic transformations in Cu–Al–Ni alloy. Scripta Met 10(11):983–988
Shimizu K, Sakamoto H, Otsuka K (1978) Phase diagram associated with stress-induced martensitic transformation in a Cu–Al–Ni alloy. Scripta Met 12(9):771–776
Otsuka K, Sakamoto H, Shimizu K (1979) Stress-induced martensitic transformations and associated transformation pseudoelasticity in Cu–Al–Ni alloys. Acta Met 27:585–601
Otsuka K, Tokonami M, Shimizu K, Iwata Y, Shibuya I (1979) Structure analysis of stress-induced β1“ martensite in a Cu–Al–Ni alloy by neutron diffraction. Acta Met 27:965–972
Baron A (2022) A brief history of nitinol – Kellogs Research Labs. https://www.kelloggsresearchlabs.com/2018/01/10/brief-history-of-nitinol/. Accessed 27 Sept 2022
Otsuka K, Sawamura T, Shimizu K (1971) Crystal structure and internal defects of equiatomic TiNi martensite. Phys Stat Sol (a) 5:457–470
Otsuka K, Sawamura T, Shimizu K, Wayman CM (1971) Characteristics of the martensitic transformation in TiNi and the memory effect. Met Trans 2:2583–2588
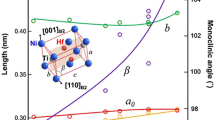
Kudoh Y, Tokonami M, Miyazaki S, Otsuka K (1985) Crystal structure of the martensite in Ti-49.2 at.%Ni alloy analysed by the single crystal X-ray diffraction method. Acta Metall 33(11):2049–2056
Miyazaki S, Otsuka K, Suzuki Y (1981) Transformation pseudoplasticity and deformation behaviour in a Ti-50.6at.% Ni alloy. Scripta Metall 15:287–292
Takei F, Miura T, Miyazaki S, Kimura S, Otsuka K, Suzuki Y (1983) Stress-induced martensitic transformation in a Ti–Ni single crystal. Scripta Met 17:987–992
Miyazaki S, Otsuka K (1986) Deformation and transition behaviour associated with the R-phase in Ti–Ni alloys. Met Trans A 17A:53–63
Miyazaki S, Igo Y, Otsuka K (1986) Effect of thermal cycling on the transformation temperature of Ti–Ni alloys. Acta Metall 34(10):2045–2051
Miyazaki S, Imai T, Igo Y, Otsuka K (1986) Effect of cyclic deformation on the pseudoelasticity characteristics of Ti–Ni alloys. Met Trans A 17A:115–120
Matsumoto O, Miyazaki S, Otsuka K, Tamura H (1987) Crystallography of martensitic transformation in Ti–Ni single crystals. Acta Metall 35(8):2537–2144
Miyazaki S, Kimura S, Otsuka K (1988) Shape-memory effect and pseudoelasticity associated with the R-phase transition in Ti-50.5at%Ni single crystals. Phil Mag A 57(3):467–478
Miyazaki S, Otsuka K, Wayman CM (1989) The shape memory mechanism associated with the martensitic transformation in Ti–Ni alloys – I. Self accommodation Acta Metall 37(7):1873–1884
Miyazaki S, Otsuka K, Wayman CM (1989) The shape memory mechanism associated with the martensitic transformation in Ti–Ni alloys – II. Variant coalescence and shape recovery. Acta Metall 37(7):1885–1890
Hara T, Ohba T, Okunishi E, Otsuka K (1997) Structural study of R-phase in Ti-50.23at%Ni and Ti-47.75at%Ni-1.50at%Fe alloys. Mater Trans JIM 38(1):11–17
Tanner LE, Soffa WA (1988) Foreward. Met Trans 19(4):760
Tanner LE, Wayman CM (1981) Foreward. Met Trans 12A(4):558
Otsuka K, Kubo H, Wayman CM (1981) Diffuse electron scattering and “streaming” effects. Met Trans 12A(4):595–605
Tanner LE, Schryvers D, Shapero SM (1990) Electron microscopy and neutron scattering studies of premartensitic behaviour in ordered Ni-Al β2 phase. Mater Sci Eng A127:205–213
Tanner LE (1966) Diffraction contrast from elastic shear strains due to coherent phases. Phil Mag 14:111–130
Otsuka K (1990) Crystallography of martensitic transformations and lattice invariant shears. Mater Sci Forum 56–58:393–404
Shapiro SM (1990) Neutron scattering studies of premartensitic phenomena. Mater Sci Forum 56–58:33–44
Finlayson TR, Liu M, Smith TF (1994) Thermal expansion and phonon anomalies near martensitic transformations. Advanced materials ’93 V/B. In: Otsuka K, Fuka Y (eds) Shape memory materials and hydrides, vol 18B. Elsevier Science Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, Amsterdam, pp 835–838
Dianoux A-J, Lander G (eds) (2002) Neutron data booklet. Institute Laue-Langevin, Grenoble, pp 11–12
Ohba T, Shapiro SM, Aoki S, Otsuka K (1994) Phonon softening in Au-49.5at%Cd alloy. Jpn J Appl Phys 33:L631–L633
Ohba T, Finlayson TR, Otsuka K (1995) Diffraction profile change in Au-Cu-Zn alloy with aging. ICOMAT 95, eds R. Gotthardt and J. Van Humbeeck, J. de Physique IV (Colloque C8) suppl. J Physique III 5:C8-1083-C8-1086
Toyoshima N, Harada K, Abe H, Ohshima K, Suzuki T, Wuttig M, Finlayson T (1994) X-ray diffraction study of martensitic phase transformation in In-23at%Tl alloy. J Phys Soc Jpn 63:1803–1813
Otsuka K, Kakeshita T (2002) Science and technology of shape-memory alloys: new developments. MRS Bull 27(2):91–98
Duerig T (2002) The use of superelasticity in modern medicine. MRS Bull 27(2):101–104
Otsuka K, Ren X (2005) Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Progress in Mater Sci 50:511–678
Pelton AR, Berg BT, Saffari P, Stebner AP, Bucsek AN (2022) Pre-strain and mean strain effects on the fatigue behaviour of superelastic nitinol medical devices. Shape Mem Superelasticity 8:64–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-022-00377-y
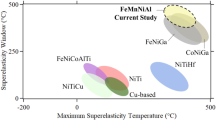
Sarkar S, Ren X, Otsuka K (2005) Evidence for strain glass in the ferroelastic-martensitic system Ti50-xNi50+x. Phys Rev Lett 95:205702. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.205702
Kartha S, Castan T, Krumhansl JA, Sethna JP (1991) Spin-glass nature of tweed precursors in martensitic transformations. Phys Rev Lett 67(25):3630–3633
Kartha S, Krumhansl JA, Sethna JA, Wickham LK (1995) Disorder-driven pretransitional tweed pattern in martensitic transformations. Phys Rev B 52(2):803–822
Ren X, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Wang D, Fan G, Otsuka K, Suzuki T, Ji Y, Zhang J, Tian Y, Hou S, Ding X (2010) Strain glass in ferroelastic systems: Premartensitic tweed versus strain glass. Phil Mag. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786430903074771
Wang Y, Ren X, Otsuka K (2006) Shape memory effect and superelasticity in a strain glass alloy. Phys Rev Lett 97:225703. https://doi.org/10.12103/PhysRevLett.97.225703
Zhang Z, Wang Y, Wang D, Zhou Y, Otsuka K, Ren X (2010) Phase diagram of Ti50-xNi50+x: crossover from martensite to strain glass. Phys Rev B 81:224102. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.81.224102
Zhou Y, Xue D, Tian Y, Ding X, Guo S, Otsuka K, Sun J, Ren X (2014) Direct evidence for local symmetry breaking during a strain glass transition. Phys Rev Lett. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.025701
Wang W, Ji Y, Fang M, Wang D, Ren S, Otsuka K, Wang Y, Ren X (2022) Reentrant strain glass transition in Ti–Ni-Cu shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.act.mat.2022.117618
Otsuka K, Saxena A, Deng J, Ren X (2011) Mechanism of the shape memory effect in martensitic alloys: an assessment. Phil Mag. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786435.2011.608735
Duerig TW (1990) Applications of shape memory. Mater Sci Forum 56–58:679–692
Balasubramanian M, Srimath R, Vignesh L, Rajesh S (2021) Application of shape memory alloys in engineering—A review. J Phys Conf Ser. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2054/1/012078
Ohba T (ed) (2002) A tribute to the work of Professor Kazuhiro Otsuka. University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba
Krumhansl JA (2000) Multiscale science: Materials in the 21st century. In: Saburi T (ed.) Shape Memory Materials, – Proceedings of the International Symposium and Exhibition on Shape Memory Materials (SMM ’99) held in Kanazawa, Japan, in May 1999, Mater. Sci. Forum vol 327–328, pp 1–8
Acknowledgments
I wish to acknowledge the hospitality of the research group of Professor George Franks, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Melbourne, which enables me to continue my research. I am also most grateful to Kizuku Kushimoto, a visitor to the George Franks Research Group from Tohoku University, Japan, for his translations of the text of the Preface of the booklet, “A Tribute to the Work of Professor Kazuhiro Otsuka” [61].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This invited article is part of a special issue of Shape Memory and Superelasticity honoring Professor Kazuhiro Otsuka for his 50 years of research on shape memory alloys and his 85th birthday. The special issue was organized by Dr. Xiaobing Ren, National Institute for Materials Science; Prof. Antoni Planes, University of Barcelona; and Dr. Avadh Saxena, Los Alamos National Lab.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Finlayson, T.R. The Contributions by Kazuhiro Otsuka to “Shape Memory and Superelasticity”: A Review. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 9, 217–230 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-022-00406-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-022-00406-w