Abstract
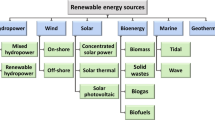
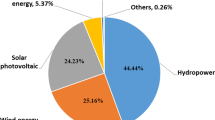
Recently, low-emission energy models have been rapidly developed in Jordan to cope with population growth and the limited availability of resources. One of the low-emission energy models refers to wind energy as increasingly becoming an essential source of renewable energy. As a result, a thorough examination of long-term wind data of small-scale wind power generating is critical to assess the potentiality of wind energy output in a region. For this purpose, this research presents an assessment of wind energy potentiality in Al-Salt city of Jordan. To understand the wind energy potentiality that is produced from the selected site, two parameters are utilized by the Weibull distribution model. As a result, the shape parameter k and the scale parameter c were utilized to calculate the wind potential and its yearly frequencies. According to the findings, the peak values of k and c in 2016 were 1.65 and 4.4, respectively, where the wind speed repetition is within 1–4 m/s with a probability of 76%. Furthermore, the findings indicated that the scale parameters and typical form were 3.14 and 1.40, respectively, and that there is little change in wind speed and wind potential growth over time as such December has the lowest wind power intensity, while November has the highest. In conclusion, the findings indicated that Al-Salt city has scarce wind resources by international standards. However, it is still an appropriate location for small-scale power generation, according to the current findings.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Authors can confirm that all relevant data are included in the article.
References
Al-Ghriybah M (2022) Assessment of wind energy potentiality at Ajloun, Jordan using weibull distribution function. Evergreen Joint J Novel Carbon Resour Sci Green Asia Strateg 09(01):10–16
Al-Ghriybah M, Zulkafli MF, Didane DH, Mohd S (2019) Wind energy assessment for the capital city of Jordan, Amman. J Appl Eng Sci 17(3):310–319
Al Hazaimeh I, Alnsour M (2022) Developing an assessment model for measuring roads infrastructure sustainability in Jordan. Innov Infrastruct Solut 7(5):1–26
Alkubaisi A, Alnsour MA (2022) Using AHP method for development of existing building green assessment system in Jordan. Asian J Civ Eng 23(8):1231–1250
Al-Salaymeh A, Al-Hamamre Z, Sharaf F, Abdelkader MR (2010) Technical and economical assessment of the utilization of photovoltaic systems in residential buildings: the case of Jordan. Energy Convers Manag 51(8):1719–1726
Balat M (2009) A review of modern wind turbine technology. Energy Sources Part A: Recovery Util Environ Effects 31(17):1561–1572. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567030802094045
Bani Yaseen A, Al-Hyari L, Almahmoud O, Hammad M (2020) Performance of a new solar water heater design with natural circulation. Energy Sources Part A: Recov Util Environ Effects. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1785590
Bickerton IJ, Jaber KS, Abu, Irvine VE (2022) “Jordan”. Encyclopedia Britannica, 18 Oct. https://www.britannica.com/place/Jordan. Accessed 23 Oct 2022
Biswas S, Sraedhar BN, Singh YP (1990) A simplified statistical technique for wind turbine energy output estimation. Wind Eng 19(3):147–155
Celik AN (2003) Energy output estimation for small-scale wind power generators using Weibull-representative wind data. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 91(5):693–707
Charabi Y, Al Hinai A, Al-Yahyai S, Al Awadhi T, Choudri BS (2019) Offshore wind potential and wind atlas over the Oman Maritime Zone. Energy Ecol Environ 4(1):1–14
Department of Meteorological DoM (2022) Yearly report of the DoM, Amman Jordan
Hammad M, Ebaid MS, Al-Hyari L (2014) Green building design solution for a kindergarten in Amman. Energy Build 76:524–537
Hilpert S, Dettner F, Al-Salaymeh A (2020) Analysis of cost-optimal renewable energy expansion for the near-term Jordanian electricity system. Sustainability 12(22):9339
Hrayshat ES (2007) Analysis of renewable energy situation in Jordan. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 11(8):1873–1887
Islam MR, Saidur R, Rahim NA (2011) Assessment of wind energy potentiality at Kudat and Labuan, Malaysia using Weibull distribution function. Energy 36(2):985–992
Jadallah AA, Ibrahim TK (2022) Performance and economic evaluation of a wind energy system: a case study. Energy Sources Part A: Recov Util Environ Effects 44(3):7365–7377
Jamil M, Parsa S, Majidi M (1995) Wind power statistics and evaluation of wind energy density. Renew Energy 6(5):623–628
Jenkins J, Malho M, Hyytiäinen K (2022) Regionally extended shared socioeconomic pathways for the offshore wind industry in Finland. Energy Ecol Environ 7:533–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-022-00252-7
Kainkwa RMR (2000) Wind speed pattern and the available wind power at Basotu, Tanzania. Renew Energy 21:289–295
Kenfack-Sadem C, Tagne R, Pelap FB, Nfor Bawe G (2021) Potential of wind energy in Cameroon based on Weibull, normal, and lognormal distribution. Int J Energy Environ Eng 12(4):761–786
Khan MA, Çamur H, Kassem Y (2019) Modeling predictive assessment of wind energy potential as a power generation sources at some selected locations in Pakistan. Model Earth Syst Environ 5(2):555–569
Li Q, Wang J, Zhang H (2021) Comparison of the goodness-of-fit of intelligent-optimized wind speed distributions and calculation in high-altitude wind-energy potential assessment. Energy Convers Manag 247:114737
Mahmood FH, Resen AK, Khamees AB (2020) Wind characteristic analysis based on Weibull distribution of Al-Salman site, Iraq. Energy Rep 6:79–87
Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources MEMR (2022) Summary of Jordan energy strategy
Ministry of Environment MoE (2013) The National Climate Change Policy of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan 2013–2020. Retrieved from http://www.moenv.gov.jo/AR/PDFs/Climatechangepolicy.pdf. 15. Accessed on 16 Nov 2022 from https://www.climatelinks.org/sites/default/files/asset/document/2017_USAID_ClimateChangeRiskProfile_Jordan.pdf
Ministry of Interior MOI, The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan (2021) Governorates and sectors. https://moi.gov.jo/EN/ListDetails/Governorates_and_Sectors/57/3. Accessed 15 Jan 2022. https://moi.gov.jo/EN/ListDetails/Governorates_and_Sectors/57/3
Mohammadi K, Mostafaeipour A, Dinpashoh Y, Pouya N (2014) Electricity generation and energy cost estimation of large-scale wind turbines in Jarandagh, Iran. J Energy 2014:613681. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/613681
Osinowo AA, Okogbue EC, Eresanya EO, Akande OS (2017) Evaluation of wind potential and its trends in the mid-Atlantic. Model Earth Syst Environ 3(4):1199–1213
Pratiwi S, Juerges N (2020) Review of the impact of renewable energy development on the environment and nature conservation in Southeast Asia. Energy Ecol Environ 5(4):221–239
Puri V, Kumar N (2022) Wind energy forecasting using artificial neural network in himalayan region. Model Earth Syst Environ 8(1):59–68
Schmidt J, Cancella R, Pereira AO Jr (2016) An optimal mix of solar PV, wind and hydro power for a low-carbon electricity supply in Brazil. Renew Energy 85:137–147
Serban A, Paraschiv LS, Paraschiv S (2020) Assessment of wind energy potential based on Weibull and Rayleigh distribution models. Energy Rep 6:250–267
Soulouknga MH, Doka SY, Revanna N, Djongyang N, Kofane TC (2018) Analysis of wind speed data and wind energy potential in Faya-Largeau, Chad, using Weibull distribution. Renew Energy 121:1–8
UNFCCC (2014) Jordan’s Third National Communication on Climate Change. Retrieved from https://unfccc.int/resource/docs/natc/jornc3.pdf. Irrigation in the Middle East region in figures-AQUASTAT Survey (2008) Retrieved from http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/countries_regions/jor/JOR-CP_eng.pdf
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Ghriybah, M., Alnsour, M.A. & Al-Hyari, L. Using Weibull distribution model for wind energy analysis of small-scale power generation at Al-Salt city in Jordan. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 9, 2651–2661 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01643-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01643-9