Abstract
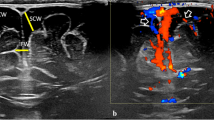
Bacterial meningitis is a severe and life-threatening disease that rapidly progresses in neonates and infants; prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are lifesaving. Magnetic resonance imaging remains the primary imaging technique for diagnosing meningitis; however, due to its limited availability and cost, ultrasound is often used for initial screening. Microvascular imaging ultrasound (MVI) is an emerging technique that offers insight into the brain microvasculature beyond conventional ultrasound. Here we present three patients with confirmed bacterial meningitis and associated cerebral microvascular findings on brain MVI to instigate further validation of cerebral microvascular imaging markers of bacterial meningitis for early detection and intervention.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Oliveira CR, Morriss MC, Mistrot JG, Cantey JB, Doern CD, Sánchez PJ (2014) Brain magnetic resonance imaging of infants with bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr 165:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.02.061
Hwang M, Haddad S, Tierradentro-Garcia LO, Alves CA, Taylor GA, Darge K (2022) Current understanding and future potential applications of cerebral microvascular imaging in infants. Br J Radiol 95:20211051. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20211051
Barletta A, Balbi M, Surace A, Caroli A, Radaelli S, Musto F et al (2021) Cerebral superb microvascular imaging in preterm neonates: in vivo evaluation of thalamic, striatal, and extrastriatal angioarchitecture. Neuroradiology 63:1103–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02634-w
Goeral K, Hojreh A, Kasprian G, Klebermass-Schrehof K, Weber M, Mitter C et al (2019) Microvessel ultrasound of neonatal brain parenchyma: feasibility, reproducibility, and normal imaging features by superb microvascular imaging (SMI). Eur Radiol 29:2127–2136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5743-1
Tierradentro-Garcia LO, Onyango L, Dennis R, Freeman CW, Haddad S, Kozak B et al (2023) Evaluation of the cerebrospinal fluid flow dynamics with microvascular imaging ultrasound in infants. Children (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020245
Hwang M, Tierradentro-García LO, Kozak BL, Darge K (2022) Cerebrospinal fluid flow detection in post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus with novel microvascular imaging modality. J Ultrasound Med 41:1013–1017. https://doi.org/10.1002/jum.15781
van Dinther M, Voorter PH, Jansen JF, Jones EA, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Staals J et al (2022) Assessment of microvascular rarefaction in human brain disorders using physiological magnetic resonance imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 42:718–737. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X221076557
Amtul Z, Yang J, Lee T-Y, Cechetto DF (2019) Pathological changes in microvascular morphology, density, size and responses following comorbid cerebral injury. Front Aging Neurosci 11:47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00047
Lowerison MR, Sekaran NVC, Zhang W, Dong Z, Chen X, Llano DA et al (2022) Aging-related cerebral microvascular changes visualized using ultrasound localization microscopy in the living mouse. Sci Rep 12:619. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-04712-8
Funding
No specific funding was received for the development of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
(Misun Hwang): Bracco Diagnostics Inc. Investigator Initiated Grant. Cell and Gene Therapy Grant, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. Seed Grant, Society of Pediatric Radiology. R01 Grants, NIH. Lecture invitation Honorarium, Korean Society of Ultrasound Medicine. Equipment support, Siemens.
Ethics statement
This research study was approved by our Institutional Review Board.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Foran, A.T., Tierradentro-Garcia, L.O., Haddad, S. et al. Microvascular imaging findings in infants with bacterial meningitis: a case series. J Ultrasound (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-023-00867-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-023-00867-4