Abstract
Background and purpose
Sonoelastography (SE) is a new technique that can assess differences in tissue stiffness. This study investigated the performance of SE for the differentiation of supraspinatus (SSP) tendon alterations of tendinopathy compared to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and conventional ultrasonography (US).
Methods
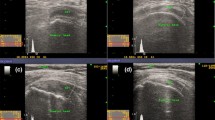
One hundred and eighteen consecutively registered patients with symptoms and MRI findings of SSP tendinopathy were assessed with US and SE. Coronal images of the SSP tendon were obtained using US and SE. Increased signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the coronal planes were graded according to the extent of the signal changes from ventral to dorsal. SE images were evaluated by reviewers using an experimentally proven color grading system.
Results
Using SE, 7.6 % of the SSP tendons were categorized as grade 0, 30.5 % as grade 1, 19.5 % as grade 2, and 42.4 % as grade 3. Evaluation of the interobserver reliability of the SE findings showed “almost perfect agreement”, with a weighted kappa coefficient of 0.83. By comparing the MRI findings with the SE findings, grades of MRI and SE had a positive correlation (r = 0.829, p = <0.001). Furthermore, grades of US and SE also had a positive correlation (r = 0.723, p = <0.001).
Conclusions
SE is valuable in the detection of the intratendinous and peritendinous alterations of the SSP tendon and has excellent interobserver reliability and excellent correlation with MRI findings and conventional ultrasonography findings.
Riassunto
Obiettivi
La sonoelastografia (SE) è una nuova tecnica in grado di valutare le differenze di rigidità dei tessuti. Questo studio ha valutato le capacità della SE nella differenziazione delle alterazioni tendinee da tendinopatia del sovraspinato (SSP) rispetto a risonanza magnetica (MRI) ed ecografia convenzionale (US).
Materiali e Metodi
Centoventuno pazienti con sintomi e reperti MRI di tendinopatia del SSP sono stati valutati con US e SE. Si sono realizzate immagini coronali del tendine SSP utilizzando US e SE. Sono state valutate immagini T2-pesate, per la maggiore intensità del segnale, nei piani coronali, da ventrale a dorsale. Immagini di SE sono state valutate da revisori che utilizzavano un sistema di grading di colore sperimentale.
Risultati
Utilizzando la SE, 7,4 % dei tendini SSP sono stati classificati come di grado 0, 29,8 % di grado 1, 19,8 % di grado 2, e 43,0 % di grado 3. La valutazione inter-osservatori dei risultati SE ha mostrato “accordo quasi perfetto”, con un coefficiente kappa pesato di 0,83. Confrontando i risultati della risonanza magnetica con i risultati della SE, risonanza magnetica e SE hanno avuto una correlazione positiva (r = 0,849, p = < 0.001). Inoltre, anche US e SE hanno avuto una correlazione positiva (r = 0,706, p = < 0,001).
Conclusioni
La SE è valida nella rilevazione delle alterazioni intra-tendinee e peri-tendinee del tendine SSP e ha un’ottima affidabilità inter-osservatori e un’eccellente correlazione con RM e reperti di ecografia convenzionale.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chard MD, Hazleman R, Hazleman BL, King RH, Reiss BB (1991) Shoulder disorders in the elderly: a community survey. Arthritis Rheum 34:766–769
Vecchio P, Kavanagh R, Hazleman BL, King RH (1995) Shoulder pain in a community-based rheumatology clinic. Br J Rheumatol 34:440–442
Iannotti JP (1994) Full-thickness rotator cuff tears: factors affecting surgical outcome. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2:87–95
Milgrom C, Schaffler M, Gilbert S, van Holsbeeck M (1995) Rotator-cuff changes in asymptomatic adults. The effect of age, hand dominance and gender. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77:296–298
Neer CS, 2nd (1983) Impingement lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 173:70–77
Almekinders LC (1998) Tendinitis and other chronic tendinopathies. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 6:157–164
Fredberg U, Stengaard-Pedersen K (2008) Chronic tendinopathy tissue pathology, pain mechanisms, and etiology with a special focus on inflammation. Scand J Med Sci Sports 18:3–15
Sher JS, Uribe JW, Posada A, Murphy BJ, Zlatkin MB (1995) Abnormal findings on magnetic resonance images of asymptomatic shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:10–15
Miniaci A, Mascia AT, Salonen DC, Becker EJ (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder in asymptomatic professional baseball pitchers. Am J Sports Med 30:66–73
Worland RL, Lee D, Orozco CG, SozaRex F, Keenan J (2003) Correlation of age, acromial morphology, and rotator cuff tear pathology diagnosed by ultrasound in asymptomatic patients. J South Orthop Assoc 12:23–26
Connor PM, Banks DM, Tyson AB, Coumas JS, D’Alessandro DF (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging of the asymptomatic shoulder of overhead athletes: a 5-year follow-up study. Am J Sports Med 31:724–727
Varghese T, Ophir J, Konofagou E, Kallel F, Righetti R (2001) Tradeoffs in elastographic imaging. Ultrason Imaging 23:216–248
Ophir J, Cespedes I, Ponnekanti H, Yazdi Y, Li X (1991) Elastography: a quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason Imaging 13:111–134
Pesavento A, Perrey C, Krueger M, Ermert H (1999) A time-efficient and accurate strain estimation concept for ultrasonic elastography using iterative phase zero estimation. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 46:1057–1067
Itoh A, Ueno E, Tohno E, Kamma H, Takahashi H, Shiina T et al (2006) Breast disease: clinical application of US elastography for diagnosis. Radiology 239:341–350
Frey H (2003) Realtime elastography. A new ultrasound procedure for the reconstruction of tissue elasticity. Radiologe 43:850–855
Garra BS, Cespedes EI, Ophir J, Spratt SR, Zuurbier RA, Magnant CM et al (1997) Elastography of breast lesions: initial clinical results. Radiology 202:79–86
Lyshchik A, Higashi T, Asato R, Tanaka S, Ito J, Mai JJ et al (2005) Thyroid gland tumor diagnosis at US elastography. Radiology 237:202–211
Pallwein L, Mitterberger M, Struve P, Horninger W, Aigner F, Bartsch G et al (2007) Comparison of sonoelastography guided biopsy with systematic biopsy: impact on prostate cancer detection. Eur Radiol 17:2278–2285
Lyshchik A, Higashi T, Asato R, Tanaka S, Ito J, Hiraoka M et al (2007) Cervical lymph node metastases: diagnosis at sonoelastography–initial experience. Radiology 243:258–267
Kjellin I, Ho CP, Cervilla V, Haghighi P, Kerr R, Vangness CT et al (1991) Alterations in the supraspinatus tendon at MR imaging: correlation with histopathologic findings in cadavers. Radiology 181:837–841
Zanetti M, Hodler J (2000) Imaging of degenerative and posttraumatic disease in the shoulder joint with ultrasound. Eur J Radiol 35:119–125
De Zordo T, Lill SR, Fink C, Feuchtner GM, Jaschke W, Bellmann-Weiler R et al (2009) Real-time sonoelastography of lateral epicondylitis: comparison of findings between patients and healthy volunteers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:180–185
Alfredson H (2005) Conservative management of Achilles tendinopathy: new ideas. Foot Ankle Clin 10:321–329
Alfredson H (2003) Chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy: an update on research and treatment. Clin Sports Med 22:727–741
Andres BM, Murrell GA (2008) Molecular and clinical developments in tendinopathy: editorial comment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:1519–1520
Seitz AL, McClure PW, Finucane S, Boardman ND 3rd, Michener LA (2011) Mechanisms of rotator cuff tendinopathy: intrinsic, extrinsic, or both? Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 26:1–12
Bouffard JA, Lee SM, Dhanju J (2000) Ultrasonography of the shoulder. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 21:164–191
Sein ML, Walton J, Linklater J, Harris C, Dugal T, Appleyard R et al (2007) Reliability of MRI assessment of supraspinatus tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med 41:e9
Godefroy D, Sarazin L, Rousselin B, Dupont AM, Drape J, Chevrot A (2001) Shoulder imaging: what is the best modality? J Radiol 82:317–332 quiz 33–4
Khan KM, Forster BB, Robinson J, Cheong Y, Louis L, Maclean L et al (2003) Are ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of value in assessment of Achilles tendon disorders? A two year prospective study. Br J Sports Med 37:149–153
Parameswaran K, Willems-Widyastuti A, Alagappan VK, Radford K, Kranenburg AR, Sharma HS (2006) Role of extracellular matrix and its regulators in human airway smooth muscle biology. Cell Biochem Biophys 44:139–146
Khoury V, Cardinal E (2009) “Tenomalacia”: a new sonographic sign of tendinopathy? Eur Radiol 19:144–146
De Zordo T, Chhem R, Smekal V, Feuchtner G, Reindl M, Fink C et al (2010) Real-time sonoelastography: findings in patients with symptomatic achilles tendons and comparison to healthy volunteers. Ultraschall Med 31:394–400
Drakonaki EE, Allen GM, Wilson DJ (2012) Ultrasound elastography for musculoskeletal applications. Br J Radiol 85:1435–1445
Conflict of interest
The authors (Joong-Bae Seo, Jae-Sung Yoo, and Jee-Won Ryu) have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 (5). All patients provided written informed consent to enrolment in the study and to the inclusion in this article of information that could potentially lead to their identification.
Human and animal studies
The study conducted in accordance with all institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, JB., Yoo, JS. & Ryu, JW. Sonoelastography findings of supraspinatus tendon in rotator cuff tendinopathy without tear: comparison with magnetic resonance images and conventional ultrasonography. J Ultrasound 18, 143–149 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-014-0148-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-014-0148-8