Abstract
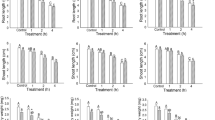
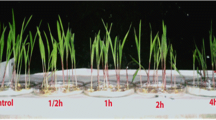
Communication technologies are moving toward higher microwave frequencies and bandwidths to satisfy the growing demand for high data rates. The concern about the possible effects of microwaves on plants and animals has increased recently. There is still uncertainty concerning the effects of microwaves on plants. The present study was conducted to investigate the effect of industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio band microwaves on seedlings and seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.). In vitro growing A. thaliana wild-type seedlings and seeds were exposed to 2.45 GHz continuous-wave microwaves at a power flux density of 1.0 ± 0.1 W m−2 for 48 h. Microwave exposure increased the hydrogen peroxide content, photosynthetic pigments, nonphotochemical quenching and fluorescence of the seedlings, while peroxidase activity and Fv/Fm values were unchanged. Anthocyanin and malondialdehyde were decreased. Seed germination rate, fresh weight and photosynthetic pigment contents of 10-day-old seedlings obtained from microwaves exposed seeds remained unchanged. Results confirmed the inexistence of oxidative stress but a stimulatory effect of microwave on A. thaliana seedlings. The increased hydrogen peroxide content and nonphotochemical quenching suggest acceptance of extra photon energy and a portion of the excess captured photon passing through the photosystem, while a portion of energy dissipated as heat.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JM, Chow WS, Il Park Y (1995) The grand design of photosynthesis: acclimation of the photosynthetic apparatus to environmental cues. Photosynth Res 46:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020423
Atapaththu KSS, Asaeda T (2015) Growth and stress responses of Nuttall’s waterweed Elodea nuttallii (Planch) St. John to water movements. Hydrobiologia 747:217–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2141-9
Bayat L, Arab M, Aliniaeifard S et al (2018) Effects of growth under different light spectra on the subsequent high light tolerance in rose plants. AoB Plants. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/ply052
DeRose-Wilson L, Gaut BS (2011) Mapping salinity tolerance during Arabidopsis thaliana germination and seedling growth. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022832
Duysen ME, Freeman TP (1974) Effects of moderate water deficit (stress) on wheat seedling growth and plastid pigment development. Physiol Plant 31:262–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1974.tb03702.x
Force L, Critchley C, Van Rensen JJS (2003) New fluorescence parameters for monitoring photosynthesis in plants 1. The effect of illumination on the fluorescence parameters of the JIP-test. Photosynth Res 78:17–33. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026012116709
Halgamuge MN, Yak SK, Eberhardt JL (2015) Reduced growth of soybean seedlings after exposure to weak microwave radiation from GSM 900 mobile phone and base station. Bioelectromagnetics 36:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/BEM.21890
ICNIRP (1998) Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz). International commission on non-ionizing radiation protection. Heal Phys 74:494–522
Jennings P, Saltveit ME (1994) Temperature and chemical shocks induce chilling tolerance in germinating Cucumis sativus (cv. Poinsett 76) seeds. Physiol Plant 91:703–707. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1994.tb03008.x
Johkan M, Shoji K, Goto F et al (2010) Blue light-emitting diode light irradiation of seedlings improves seedling quality and growth after transplanting in red leaf lettuce. HortScience 45:1809–1814. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.45.12.1809
Kalaji HM, Carpentier R, Allakhverdiev SI, Bosa K (2012) Fluorescence parameters as early indicators of light stress in barley. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 112:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2012.03.009
Kitajima K, Hogan KP (2003) Increases of chlorophyll a/b ratios during acclimation of tropical woody seedlings to nitrogen limitation and high light. Plant Cell Environ 26:857–865. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2003.01017.x
Kouřil R, Wientjes E, Bultema JB et al (2013) High-light vs. low-light: effect of light acclimation on photosystem II composition and organization in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.12.003
Kovinich N, Kayanja G, Chanoca A et al (2015) Abiotic stresses induce different localizations of anthocyanins in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2015.1027850
Kume A, Akitsu T, Nasahara KN (2018) Why is chlorophyll b only used in light-harvesting systems? J Plant Res 131:961–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-018-1052-7
MacAdam JW, Nelson CJ, Sharp RE (1992) Peroxidase activity in the leaf elongation zone of tall fescue: I. Spatial distribution of ionically bound peroxidase activity in genotypes differing in length of the elongation zone. Plant Physiol 99:872–878. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.99.3.872
Miller RA, Zalik S (1965) Effect of light quality, light intensity and temperature on pigment accumulation in barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 40:569–574. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.40.3.569
Murata N, Allakhverdiev SI, Nishiyama Y (2012) The mechanism of photoinhibition in vivo: re-evaluation of the roles of catalase, α-tocopherol, non-photochemical quenching, and electron transport. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1817:1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.02.020
Nakata M, Mitsuda N, Herde M et al (2013) A bHLH-type transcription factor, ABA-inducible BHLH-type transcription factor/JA-associated MYC2-LIKE1, acts as a repressor to negatively regulate jasmonate signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.111112
Pe W, Hill MJ, Johnston MEH (1975) I. Acid treatment and mechanical scarification. N Z J Exp Agric 3:81–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/03015521.1975.10425778
Posmyk MM, Bałabusta M, Wieczorek M et al (2009) Melatonin applied to cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seeds improves germination during chilling stress. J Pineal Res 46:214–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00652.x
Pospíšil P (2016) Production of reactive oxygen species by photosystem II as a response to light and temperature stress. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01950
Răcuciu M, Miclăuş S (2007) Low-level 900 MHz electromagnetic field influence on vegetal tissue. Rom J Biophys 17:149–156
Rodríguez VM, Soengas P, Alonso-Villaverde V et al (2015) Effect of temperature stress on the early vegetative development of Brassica oleracea L. BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0535-0
Roux D, Vian A, Girard S et al (2008) High frequency (900 MHz) low amplitude (5 V m−1) electromagnetic field: a genuine environmental stimulus that affects transcription, translation, calcium and energy charge in tomato. Planta 227:883–891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0664-2
Ruban AV (2016) Nonphotochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching: mechanism and effectiveness in protecting plants from photodamage. Plant Physiol 170:1903–1916. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01935
Satterfield CN, Bonnell AH (1955) Interferences in the titanium sulfate method for hydrogen peroxide. Anal Chem 27:1174–1175. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60103a042
Scialabba A, Tamburello C (2002) Microwave effects on germination and growth of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seedlings. Acta Bot Gall 149:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/12538078.2002.10515947
Senavirathna MDHJ, Asaeda T (2014) The significance of microwaves in the environment and its effect on plants. Environ Rev 22:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1139/er-2013-0061
Senavirathna MDHJ, Asaeda T (2017) Microwaves affect Myriophyllum aquaticum plants differently depending on the wave polarization. Biol Plant 61:378–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0660-0
Senavirathna MDHJ, Takashi A, Kimura Y (2014) Short-duration exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation alters the chlorophyll fluorescence of duckweeds (Lemna minor). Electromagn Biol Med 33:327–334. https://doi.org/10.3109/15368378.2013.844705
Shibayev PP, Pergolizzi RG (2011) The effect of circularly polarized light on the growth of plants. Int J Bot 7:113–117. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijb.2011.113.117
Skiles JW (2006) Plant response to microwaves at 2.45 GHz. Acta Astronaut 58:258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2005.12.007
Tafforeau M, Verdus MC, Norris V et al (2006) Memory processes in the response of plants to environmental signals. Plant Signal Behav 1:9–14. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.1.1.2164
Takács A, Horváth J, Gáborjányi R et al (2014) Hosts and non-hosts in plant virology and the effects of plant viruses on host plants. Plant Virus Host Interact. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-411584-2.00005-6
Techawongstien S, Nawata E, Shigenaga S (1992) Effect of water stress at various stages of plant development on growth and yield of chilli pepper. Jpn J Trop Agric 36:51–57. https://doi.org/10.11248/jsta1957.36.51
Teng S, Keurentjes J, Bentsink L et al (2005) Sucrose-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis requires the MYB75/PAP1 gene. Plant Physiol 139:1840–1852. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.066688
Tkalec M, Malarić K, Pevalek-Kozlina B (2007) Exposure to radiofrequency radiation induces oxidative stress in duckweed Lemna minor L. Sci Total Environ 388:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.07.052
Trimborn S, Thoms S, Petrou K et al (2014) Photophysiological responses of Southern Ocean phytoplankton to changes in CO2 concentrations: short-term versus acclimation effects. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 451:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2013.11.001
Velez-Ramirez AI, Van Ieperen W, Vreugdenhil D, Millenaar FF (2011) Plants under continuous light. Trends Plant Sci 16:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2011.02.003
Vian A, Roux D, Girard S et al (2006) Microwave irradiation affects gene expression in plants. Plant Signal Behav 1:67–70. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.1.2.2434
Von Arnim A, Deng X-W (1996) Light control of seedling development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:215–243. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.47.1.215
Weber H, Chételat A, Reymond P, Farmer EE (2004) Selective and powerful stress gene expression in Arabidopsis in response to malondialdehyde. Plant J 37:877–888. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2003.02013.x
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81192-2
Zhang Z, Huang R (2016) Analysis of malondialdehyde, chlorophyll proline, soluble sugar, and glutathione content in Arabidopsis seedling. Bio-Protocol. https://doi.org/10.21769/bioprotoc.817
Ziegelberger G, The International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (2009) ICNIRP statement on the “Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz)”. Health Phys 97:257–258. https://doi.org/10.1097/HP.0b013e3181aff9db
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Yuichi Kimura and Mr. Sakuyoshi Saito (Saitama University, Japan) for their support in the preparation of the microwave exposure system. This work was supported by the annual budget allocations of Saitama University, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MDHJS originally formulated the idea. MDHJS and ISPN developed methodology. MDHJS, ISPN and GM conducted research work. MDHJS and GM collaborated in data analysis. MDHJS wrote the manuscript. MDHJS, ISPN and GM performed editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senevirathna, M.D.H.J., Nagahage, I.S.P. & Muhetaer, G. Stimulatory effect of exposure to low-power-density 2.45 GHz microwaves on Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings in vitro. Braz. J. Bot 43, 459–467 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-020-00618-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-020-00618-3