Abstract
Purpose
Aim of the present review is to analyze the most relevant achievements of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) in neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) management, focusing on treatment efficacy as well as toxicity and taking into account the innovative applications and future perspectives.
Methods
A comprehensive literature review of PubMed/Medline (last updated January 2021) was performed using a combination of the following keywords: PRRT, NEN/NET treatment, somatostatin analogues, PET/CT [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-peptides (DOTATATE, DOTATOC, DOTANOC), [18F]FDG. Case reports, editorials, letters to the editor and articles not specifically addressing PRRT achievements were excluded. Only papers in English were considered.
Results
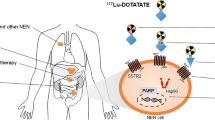
Published data showed that PRRT has been increasingly used for treatment of well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumours (NETs). Preliminary results from early studies were difficult to compare due to different treatment regimens in often small and heterogeneous patients’ populations. Recently, the regulatory agencies approved [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE for treatment of well-differentiated gastro-entero-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours G1-G2 (GEP-NET). Patients treated with PRRT show good response rates (range 66–95% considering total objective response and stable disease). Regarding toxicity, a significant reduction of renal absorbed dose (ranging from 9 to 53%) has been reported using kidney protection strategies. Moreover, the incidence of haematological long-term toxicity has been reported in many studies but toxicity is mild and transient in most patients while severe toxicity, such as acute leukemia (AL) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), were reported in less than 3% of patients. However, several issues are still under debate including dose schemes personalization, selection of eligible patients, evaluation of treatment response and treatment sequencing.
Conclusion
PRRT is now recognized as an effective treatment strategy for well-differentiated SSTR-positive NETs with a very high disease control and overall limited toxicity. Further optimization of PRRT employment is warranted to further increase efficacy and reduce toxicity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oronsky B, Ma PC, Morgensztern D, Carter CA (2017) Nothing but NET: a review of neuroendocrine tumors and carcinomas. Neoplasia N Y N 19(12):991–1002
Gut P, Komarowska H, Czarnywojtek A, Waligórska-Stachura J, Bączyk M, Ziemnicka K et al (2015) Familial syndromes associated with neuroendocrine tumours. Contemp Oncol Poznan Pol 19(3):176–183
Williams ED, Sandler M (1963) The classification of carcinoid tum ours. Lancet Lond Engl 1(7275):238–239
Păun I, Becheanu G, Costin AI, Constantin VD, Mihai GM, Radu L et al (2018) Aspects regarding nomenclature, classification and pathology of neuroendocrine neoplasms of the digestive system—a review. Romanian J Morphol Embryol Rev Roum Morphol Embryol 59(3):673–678
Taal BG, Visser O (2004) Epidemiology of neuroendocrine tumours. Neuroendocrinology 80(Suppl 1):3–7
Cives M, Strosberg JR (2018) Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):471–487
Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, Dagohoy C, Leary C, Mares JE et al (2008) One hundred years after “carcinoid”: epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol 26(18):3063–3072
WHO Classification of Tumours [Internet]. https://whobluebooks.iarc.fr/publications/index.php. Accessed 25 Feb 2021
Farrell JM, Pang JC, Kim GE, Tabatabai ZL (2014) Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: accurate grading with Ki-67 index on fine-needle aspiration specimens using the WHO 2010/ENETS criteria. Cancer Cytopathol 122(10):770–778
Rindi G, Klimstra DS, Abedi-Ardekani B, Asa SL, Bosman FT, Brambilla E et al (2018) A common classification framework for neuroendocrine neoplasms: an International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and World Health Organization (WHO) expert consensus proposal. Mod Pathol 31(12):1770–1786
Laskaratos F-M, Caplin M (2019) Treatment challenges in and outside a network setting: Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Surg Oncol J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol 45(1):52–59
Modlin IM, Moss SF, Chung DC, Jensen RT, Snyderwine E (2008) Priorities for improving the management of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(18):1282–1289
Singh S, Law C (2010) Multidisciplinary reference centers: the care of neuroendocrine tumors. J Oncol Pract 6(6):e11-16
Uri I, Grozinsky-Glasberg S (2018) Current treatment strategies for patients with advanced gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs). Clin Diabetes Endocrinol 4:16
Oberg KE, Reubi J-C, Kwekkeboom DJ, Krenning EP (2010) Role of somatostatins in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor development and therapy. Gastroenterology 139(3):742–753 (753.e1)
Eychenne R, Bouvry C, Bourgeois M, Loyer P, Benoist E, Lepareur N (2020) Overview of radiolabeled somatostatin analogs for cancer imaging and therapy. Mol Basel Switz. 25(17):4012
Anthony LB, Woltering EA, Espenan GD, Cronin MD, Maloney TJ, McCarthy KE (2002) Indium-111-pentetreotide prolongs survival in gastroenteropancreatic malignancies. Semin Nucl Med 32(2):123–132
Kwekkeboom DJ, Krenning EP (2016) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am 30(1):179–191
Sabet A, Haslerud T, Pape U-F, Sabet A, Ahmadzadehfar H, Grünwald F et al (2014) Outcome and toxicity of salvage therapy with 177Lu-octreotate in patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41(2):205–210
Kwekkeboom DJ, Teunissen JJ, Bakker WH, Kooij PP, de Herder WW, Feelders RA et al (2005) Radiolabeled somatostatin analog [177Lu-DOTA0, Tyr3]octreotate in patients with endocrine gastroenteropancreatic tumors. J Clin Oncol 23(12):2754–2762
Pauwels S, Barone R, Walrand S, Borson-Chazot F, Valkema R, Kvols LK et al (2005) Practical dosimetry of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with (90)Y-labeled somatostatin analogs. J Nucl Med 46(Suppl 1):92S-S98
Menda Y, Madsen MT, O’Dorisio TM, Sunderland JJ, Watkins GL, Dillon JS et al (2018) 90Y-DOTATOC dosimetry-based personalized peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. J Nucl Med 59(11):1692–1698
Hindorf C, Chittenden S, Causer L, Lewington V, Maecke H, Flux G (2007) Dosimetry for Y-90-DOTATOC therapies in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 1(22):130–135
Vinjamuri S, Gilbert TM, Banks M, McKane G, Maltby P, Poston G et al (2013) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 90Y-DOTATATE/90Y-DOTATOC in patients with progressive metastatic neuroendocrine tumours: assessment of response, survival and toxicity. Br J Cancer 108(7):1440–1448
Sundlöv A, Sjögreen-Gleisner K, Svensson J, Ljungberg M, Olsson T, Bernhardt P et al (2017) Individualised 177Lu-DOTATATE treatment of neuroendocrine tumours based on kidney dosimetry. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44(9):1480–1489
Bodei L, Mueller-Brand J, Baum RP, Pavel ME, Hörsch D, O’Dorisio MS et al (2013) The joint IAEA, EANM, and SNMMI practical guidance on peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRNT) in neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 40(5):800–816
Waldherr C, Pless M, Maecke HR, Schumacher T, Crazzolara A, Nitzsche EU et al (2002) Tumor response and clinical benefit in neuroendocrine tumors after 7.4 GBq (90)Y-DOTATOC. J Nucl Med 43(5):610–6
Valkema R, Pauwels S, Kvols LK, Barone R, Jamar F, Bakker WH et al (2006) Survival and response after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with [90Y-DOTA0, Tyr3]octreotide in patients with advanced gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Semin Nucl Med 36(2):147–156
Filice A, Fraternali A, Frasoldati A, Asti M, Grassi E, Massi L et al (2012) Radiolabeled somatostatin analogues therapy in advanced neuroendocrine tumors: a single centre experience. J Oncol 2012:320198
Mariniello A, Bodei L, Tinelli C, Baio SM, Gilardi L, Colandrea M et al (2016) Long-term results of PRRT in advanced bronchopulmonary carcinoid. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43(3):441–452
Bodei L, Cremonesi M, Grana CM, Fazio N, Iodice S, Baio SM et al (2011) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE: the IEO phase I-II study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38(12):2125–2135
Kwekkeboom DJ, de Herder WW, Kam BL, van Eijck CH, van Essen M, Kooij PP et al (2008) Treatment with the radiolabeled somatostatin analog [177 Lu-DOTA 0, Tyr3]octreotate: toxicity, efficacy, and survival. J Clin Oncol 26(13):2124–2130
Brabander T, van der Zwan WA, Teunissen JJM, Kam BLR, Feelders RA, de Herder WW et al (2017) Long-term efficacy, survival, and safety of [177Lu-DOTA0, Tyr3]octreotate in patients with gastroenteropancreatic and bronchial neuroendocrine tumors. Clin Cancer Res 23(16):4617–4624
Sitani K, Parghane RV, Talole S, Basu S (2021) Long-term outcome of indigenous 177Lu-DOTATATE PRRT in patients with metastatic advanced neuroendocrine tumours: a single institutional observation in a large tertiary care setting. Br J Radiol 94(1117):20201041
Sistani G, Sutherland DEK, Mujoomdar A, Wiseman DP, Khatami A, Tsvetkova E et al (2020) Efficacy of 177Lu-dotatate induction and maintenance therapy of various types of neuroendocrine tumors: a phase II registry study. Curr Oncol Tor Ont 28(1):115–127
Kunikowska J, Zemczak A, Kołodziej M, Gut P, Łoń I, Pawlak D et al (2020) Tandem peptide receptor radionuclide therapy using 90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE for neuroendocrine tumors efficacy and side-effects—polish multicenter experience. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 47(4):922–933
Zandee WT, Brabander T, Blažević A, Kam BLR, Teunissen JJM, Feelders RA et al (2019) Symptomatic and radiological response to 177Lu-DOTATATE for the treatment of functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 104(4):1336–1344
Demirci E, Kabasakal L, Toklu T, Ocak M, Şahin OE, Alan-Selcuk N et al (2018) 177Lu-DOTATATE therapy in patients with neuroendocrine tumours including high-grade (WHO G3) neuroendocrine tumours: response to treatment and long-term survival update. Nucl Med Commun 39(8):789–796
Rudisile S, Gosewisch A, Wenter V, Unterrainer M, Böning G, Gildehaus FJ et al (2019) Salvage PRRT with 177Lu-DOTA-octreotate in extensively pretreated patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumor (NET): dosimetry, toxicity, efficacy, and survival. BMC Cancer 19(1):788
Kim S-J, Pak K, Koo PJ, Kwak JJ, Chang S (2015) The efficacy of (177)Lu-labelled peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in patients with neuroendocrine tumours: a meta-analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42(13):1964–1970
Dannoon SF, Alenezi SA, Elgazzar AH (2017) The efficacy of the available peptide receptor radionuclide therapy for neuroendocrine tumors: a meta-analysis. Nucl Med Commun 38(12):1085–1093
Strosberg J, El-Haddad G, Wolin E, Hendifar A, Yao J, Chasen B et al (2017) Phase 3 trial of 177Lu-dotatate for midgut neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med 376(2):125–135
Strosberg J, Wolin E, Chasen B, Kulke M, Bushnell D, Caplin M et al (2018) Health-related quality of life in patients with progressive midgut neuroendocrine tumors treated with 177Lu-dotatate in the phase III NETTER-1 trial. J Clin Oncol 36(25):2578–2584
van der Zwan WA, Bodei L, Mueller-Brand J, de Herder WW, Kvols LK, Kwekkeboom DJ (2015) GEPNETs update: radionuclide therapy in neuroendocrine tumors. Eur J Endocrinol 172(1):R1-8
Bodei L, Cremonesi M, Ferrari M, Pacifici M, Grana CM, Bartolomei M et al (2008) Long-term evaluation of renal toxicity after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 90Y-DOTATOC and 177Lu-DOTATATE: the role of associated risk factors. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35(10):1847–1856
Imhof A, Brunner P, Marincek N, Briel M, Schindler C, Rasch H et al (2011) Response, survival, and long-term toxicity after therapy with the radiolabeled somatostatin analogue [90Y-DOTA]-TOC in metastasized neuroendocrine cancers. J Clin Oncol 29(17):2416–2423
Bergsma H, van Lom K, Raaijmakers MHGP, Konijnenberg M, Kam BLBLR, Teunissen JJM et al (2018) Persistent hematologic dysfunction after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE: incidence, course, and predicting factors in patients with gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Nucl Med 59(3):452–8
Sansovini M, Severi S, Ianniello A, Nicolini S, Fantini L, Mezzenga E et al (2017) Long-term follow-up and role of FDG PET in advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine patients treated with 177Lu-D OTATATE. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44(3):490–499
Emami B, Lyman J, Brown A, Coia L, Goitein M, Munzenrider JE et al (1991) Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21(1):109–122
Benua RS, Cicale NR, Sonenberg M, Rawson RW (1962) The relation of radioiodine dosimetry to results and complications in the treatment of metastatic thyroid cancer. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 87:171–182
Del Prete M, Buteau F-A, Arsenault F, Saighi N, Bouchard L-O, Beaulieu A et al (2019) Personalized 177Lu-octreotate peptide receptor radionuclide therapy of neuroendocrine tumours: initial results from the P-PRRT trial. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46(3):728–742
Garske-Román U, Sandström M, Fröss Baron K, Lundin L, Hellman P, Welin S et al (2018) Prospective observational study of 177Lu-DOTA-octreotate therapy in 200 patients with advanced metastasized neuroendocrine tumours (NETs): feasibility and impact of a dosimetry-guided study protocol on outcome and toxicity. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45(6):970–988
Ilan E, Sandström M, Wassberg C, Sundin A, Garske-Román U, Eriksson B et al (2015) Dose response of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors treated with peptide receptor radionuclide therapy using 177Lu-DOTATATE. J Nucl Med 56(2):177–182
Jahn U, Ilan E, Sandström M, Garske-Román U, Lubberink M, Sundin A (2020) 177Lu-DOTATATE peptide receptor radionuclide therapy: dose response in small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Neuroendocrinology 110(7–8):662–670
Konijnenberg M, Herrmann K, Kobe C, Verburg F, Hindorf C, Hustinx R et al (2021) EANM position paper on article 56 of the Council Directive 2013/59/Euratom (basic safety standards) for nuclear medicine therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48(1):67–72
Severi S, Sansovini M, Ianniello A, Bodei L, Nicolini S, Ibrahim T et al (2015) Feasibility and utility of re-treatment with (177)Lu-DOTATATE in GEP-NENs relapsed after treatment with (90)Y-DOTATOC. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42(13):1955–1963
Zacho MD, Iversen P, Villadsen GE, Baunwall SMD, Arveschoug AK, Grønbaek H et al (2021) Clinical efficacy of first and second series of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in patients with neuroendocrine neoplasm: a cohort study. Scand J Gastroenterol 20:1–9
Vaughan E, Machta J, Walker M, Toumpanakis C, Caplin M, Navalkissoor S (2018) Retreatment with peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in patients with progressing neuroendocrine tumours: efficacy and prognostic factors for response. Br J Radiol 91(1091):20180041
Strosberg J, Leeuwenkamp O, Siddiqui MK (2021) Peptide receptor radiotherapy re-treatment in patients with progressive neuroendocrine tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev 93:102141
Seregni E, Maccauro M, Chiesa C, Mariani L, Pascali C, Mazzaferro V et al (2014) Treatment with tandem [90Y]DOTA-TATE and [177Lu]DOTA-TATE of neuroendocrine tumours refractory to conventional therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41(2):223–230
Sharma N, Naraev BG, Engelman ES, Zimmerman MB, Bushnell DL, O’Dorisio TM et al (2017) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) outcomes in a North American cohort with metastatic well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors. Pancreas 46(2):151–156
Ezziddin S, Attassi M, Yong-Hing CJ, Ahmadzadehfar H, Willinek W, Grünwald F et al (2014) Predictors of long-term outcome in patients with well-differentiated gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177Lu-octreotate. J Nucl Med 55(2):183–190
Nilica B, Waitz D, Stevanovic V, Uprimny C, Kendler D, Buxbaum S et al (2016) Direct comparison of (68)Ga-DOTA-TOC and (18)F-FDG PET/CT in the follow-up of patients with neuroendocrine tumour treated with the first full peptide receptor radionuclide therapy cycle. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43(9):1585–1592
Nicolini S, Severi S, Ianniello A, Sansovini M, Ambrosetti A, Bongiovanni A et al (2018) Investigation of receptor radionuclide therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE in patients with GEP-NEN and a high Ki-67 proliferation index. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45(6):923–930
Aalbersberg EA, Huizing DMV, Walraven I, de der Veen BJW, Kulkarni HR, Singh A et al (2019) Parameters to predict progression-free and overall survival after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy: a multivariate analysis in 782 patients. J Nucl Med 60(9):1259–65
Baum RP, Kulkarni HR, Singh A, Kaemmerer D, Mueller D, Prasad V et al (2018) Results and adverse events of personalized peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 90Yttrium and 177Lutetium in 1048 patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms. Oncotarget 9(24):16932–16950
Dj K, Wh B, Bl K, Jj T, Pp K, de Ww H et al (2003) Treatment of patients with gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) tumours with the novel radiolabelled somatostatin analogue [177Lu-DOTA(0), Tyr3]octreotate. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30(3):417–422
Sabet A, Haug AR, Eiden C, Auernhammer CJ, Simon B, Bartenstein P et al (2017) Efficacy of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177Lu-octreotate in metastatic pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors: a dual-centre analysis. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 7(2):74–83
Tirosh A, Papadakis GZ, Millo C, Hammoud D, Sadowski SM, Herscovitch P et al (2018) Prognostic utility of total 68Ga-DOTATATE-avid tumor volume in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Gastroenterology 154(4):998-1008.e1
Hope TA, Bodei L, Chan JA, El-Haddad G, Fidelman N, Kunz PL et al (2020) NANETS/SNMMI consensus statement on patient selection and appropriate use of 177Lu-DOTATATE peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. J Nucl Med 61(2):222–227
Merola E, Prasad V, Pascher A, Pape U-F, Arsenic R, Denecke T et al (2020) Peritoneal carcinomatosis in gastro-entero-pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: clinical impact and effectiveness of the available therapeutic options. Neuroendocrinology 110(6):517–524
Albertelli M, Dotto A, di Dato C, Malandrino P, Modica R, Versari A et al (2020) PRRT: identikit of the perfect patient. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-020-09581-6
Hicks RJ, Kwekkeboom DJ, Krenning E, Bodei L, Grozinsky-Glasberg S, Arnold R et al (2017) ENETS consensus guidelines for the standards of care in neuroendocrine neoplasia: peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with radiolabeled somatostatin analogues. Neuroendocrinology 105(3):295–309
Bodei L, Kidd MS, Singh A, van der Zwan WA, Severi S, Drozdov IA et al (2018) PRRT genomic signature in blood for prediction of 177Lu-octreotate efficacy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45(7):1155–1169
Sundin A, Arnold R, Baudin E, Cwikla JB, Eriksson B, Fanti S et al (2017) ENETS consensus guidelines for the standards of care in neuroendocrine tumors: radiological. Nuclear Med Hybrid Imaging Neuroendocrinol 105(3):212–244
Ambrosini V, Kunikowska J, Baudin E, Bodei L, Bouvier C, Capdevila J et al (2021) Consensus on molecular imaging and theranostics in neuroendocrine neoplasms. Eur J Cancer Oxf Engl 1990 146:56–73
Choi H, Charnsangavej C, Faria SC, Macapinlac HA, Burgess MA, Patel SR et al (2007) Correlation of computed tomography and positron emission tomography in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated at a single institution with imatinib mesylate: proposal of new computed tomography response criteria. J Clin Oncol 25(13):1753–1759
Kulke MH, Blaszkowsky LS, Ryan DP, Clark JW, Meyerhardt JA, Zhu AX et al (2007) Capecitabine plus erlotinib in gemcitabine-refractory advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(30):4787–4792
Raymond E, Dahan L, Raoul J-L, Bang Y-J, Borbath I, Lombard-Bohas C et al (2011) Sunitinib malate for the treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med 364(6):501–513
Fazio N, Kulke M, Rosbrook B, Fernandez K, Raymond E (2021) Updated efficacy and safety outcomes for patients with well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors treated with sunitinib. Target Oncol 16(1):27–35
Liberini V, Huellner MW, Grimaldi S, Finessi M, Thuillier P, Muni A et al (2020) The challenge of evaluating response to peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: the present and the future. Diagn Basel Switz. 10(12):1083
Carlsen EA, Fazio N, Granberg D, Grozinsky-Glasberg S, Ahmadzadehfar H, Grana CM et al (2019) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in gastroenteropancreatic NEN G3: a multicenter cohort study. Endocr Relat Cancer 26(2):227–239
Thang SP, Lung MS, Kong G, Hofman MS, Callahan J, Michael M et al (2018) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) in European Neuroendocrine Tumour Society (ENETS) grade 3 (G3) neuroendocrine neoplasia (NEN) - a single-institution retrospective analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45(2):262–277
Severi S, Nanni O, Bodei L, Sansovini M, Ianniello A, Nicoletti S et al (2013) Role of 18FDG PET/CT in patients treated with 177Lu-DOTATATE for advanced differentiated neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 40(6):881–888
A phase III multi-center, randomized, open-label study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Lutathera in patients with grade 2 and grade 3 advanced GEP-NET [Internet]. Report no NCT03972488. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03972488. Accessed 24 Feb 2021
Delle Fave G, O’Toole D, Sundin A, Taal B, Ferolla P, Ramage JK et al (2016) ENETS consensus guidelines update for gastroduodenal neuroendocrine neoplasms. Neuroendocrinology 103(2):119–124
van Vliet EI, van Eijck CH, de Krijger RR, Nieveen van Dijkum EJ, Teunissen JJ, Kam BL et al (2015) Neoadjuvant treatment of nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors with [177Lu-DOTA0, Tyr3]octreotate. J Nucl Med 56(11):1647–53
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (2021) A pilot study investigating intrahepatic arterial and intravenous infusion of the radiolabeled somatostatin agonist 177Lu-DOTATATE in patients with liver-dominant metastatic gastroenteropancreatic (GEP), Bronchial or Unknown Primary Well Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors [Internet]. Report no NCT04544098. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04544098. Accessed 20 Apr 2021
Lam M (2020) Intra-arterial Lutetium-177-dotatate for treatment of patients with neuro-endocrine tumor liver metastases [Internet]. Report no NCT03590119. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03590119. Accessed 20 Apr 2021
Istituto Scientifico Romagnolo per lo Studio e la cura dei Tumori (2020) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177lu-dotatate associated with metronomic capecitabine in patients affected by aggressive gastro-etero-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors [Internet]. Report no NCT02736500. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02736500. Accessed 24 Feb 2021
Gustave Roussy, Cancer Campus, Grand Paris (2018) Antitumor efficacy of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177lutetium -octreotate randomized vs sunitinib in unresectable progressive well-differentiated neuroendocrine pancreatic tumor: first randomized phase II [Internet]. Report no NCT02230176. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02230176. Accessed 24 Feb 2021
A prospective, randomised, controlled, open-label, multicentre phase III study to evaluate efficacy and safety of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) With 177Lu-edotreotide compared to targeted molecular therapy with everolimus in patients with inoperable, progressive, somatostatin receptor-positive (SSTR+), neuroendocrine tumours of gastroenteric or pancreatic origin (GEP-NET) [Internet]. Report no NCT03049189. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03049189. Accessed 24 Feb 2021
Thakral P, Sen I, Pant V, Gupta SK, Dureja S, Kumari J et al (2018) Dosimetric analysis of patients with gastro entero pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NeTs) treated with PrCrT (peptide receptor chemo radionuclide therapy) using lu-177 DOTaTaTe and capecitabine/temozolomide (CaP/TeM). Br J Radiol 91(1091):1–7
Claringbold PG, Brayshaw PA, Price RA, Turner JH (2011) Phase II study of radiopeptide 177Lu-octreotate and capecitabine therapy of progressive disseminated neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38(2):302–311
Claringbold PG, Price RA, Turner JH (2012) Phase I-II study of radiopeptide 177Lu-octreotate in combination with capecitabine and temozolomide in advanced low-grade neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 27(9):561–569
Claringbold PG, Turner JH (2016) Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor control: durable objective response to combination 177Lu-octreotate-capecitabine-temozolomide radiopeptide chemotherapy. Neuroendocrinology 103(5):432–439
Campana D, Walter T, Pusceddu S, Gelsomino F, Graillot E, Prinzi N et al (2018) Correlation between MGMT promoter methylation and response to temozolomide-based therapy in neuroendocrine neoplasms: an observational retrospective multicenter study. Endocrine 60(3):490–498
Yadav MP, Ballal S, Bal C (2019) Concomitant 177Lu-DOTATATE and capecitabine therapy in malignant paragangliomas. EJNMMI Res 9(1):13
Kashyap R, Hofman MS, Michael M, Kong G, Akhurst T, Eu P et al (2015) Favourable outcomes of (177)Lu-octreotate peptide receptor chemoradionuclide therapy in patients with FDG-avid neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42(2):176–185
Zhang J, Kulkarni HR, Singh A, Niepsch K, Müller D, Baum RP (2019) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in grade 3 neuroendocrine neoplasms: safety and survival analysis in 69 patients. J Nucl Med 60(3):377–385
Özdirik B, Amthauer H, Schatka I, Goretzki PE, Mogl MT, Fehrenbach U et al (2021) A rare case of a patient with a high grade neuroendocrine tumor developing neutropenic sepsis after receiving PRRT combined with Capecitabine or Temozolomide: a case report. Mol Clin Oncol 14(1):20
Brieau B, Hentic O, Lebtahi R, Palazzo M, Ben Reguiga M, Rebours V et al (2016) High risk of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia after 177Lu-octreotate PRRT in NET patients heavily pretreated with alkylating chemotherapy. Endocr Relat Cancer 23(5):L17-23
Goncalves I, Burbury K, Michael M, Iravani A, Ravi Kumar AS, Akhurst T et al (2019) Characteristics and outcomes of therapy-related myeloid neoplasms after peptide receptor radionuclide/chemoradionuclide therapy (PRRT/PRCRT) for metastatic neuroendocrine neoplasia: a single-institution series. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46(9):1902–1910
Kong G, Thompson M, Collins M, Herschtal A, Hofman MS, Johnston V et al (2014) Assessment of predictors of response and long-term survival of patients with neuroendocrine tumour treated with peptide receptor chemoradionuclide therapy (PRCRT). Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41(10):1831–1844
Ginj M, Zhang H, Waser B, Cescato R, Wild D, Wang X et al (2006) Radiolabeled somatostatin receptor antagonists are preferable to agonists for in vivo peptide receptor targeting of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(44):16436–16441
Cives M, Strosberg J (2017) Radionuclide Therapy for Neuroendocrine Tumors. Curr Oncol Rep 19(2):9
Nicolas GP, Morgenstern A, Schottelius M, Fani M (2018) New developments in peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. J Nucl Med 60:167–171
Kratochwil C, Giesel FL, Bruchertseifer F, Mier W, Apostolidis C, Boll R et al (2014) 213Bi-DOTATOC receptor-targeted alpha-radionuclide therapy induces remission in neuroendocrine tumours refractory to beta radiation: a first-in-human experience. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41(11):2106–2119
Nonnekens J, van Kranenburg M, Beerens CEMT, Suker M, Doukas M, van Eijck CHJ et al (2016) Potentiation of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy by the PARP inhibitor olaparib. Theranostics 6(11):1821–1832
Bodei L, Pepe G, Paganelli G (2010) Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) of neuroendocrine tumors with somatostatin analogues. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 14(4):347–351
Jensen RT, Bodei L, Capdevila J, Couvelard A, Falconi M, Glasberg S et al (2019) Unmet needs in functional and nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Neuroendocrinology 108(1):26–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Every author contributed equally to this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors, Silvi Telo MD, Giuseppe Lamberti MD, Davide Campana MD, PhD and Diletta Calabrò MD, have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Valentina Ambrosini reports personal fees from ESMIT, EANM and AAA outside the submitted work and is a member of ENETS advisory board, EANM Oncology and theranostic committee, ESMO faculty staff for NET and of the scientific board of ITANET. Stefano Fanti reports personal fees from ANMI, Astellas, Bayer, BlueEarth Diagnostics, GE Healthcare, Jenssen, Novartis, Sofie Biosciences, non-financial support from AAA, Bayer, GE Healthcare, Curium, Tema Sinergie, Sanofi, Telix, outside the submitted work. Angelina Filice reports personal fees from AAA, Novartis, Bayer and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. Annibale Versari reports personal fees from Novartis and AAA outside the submitted work.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Telo, S., Filice, A., Versari, A. et al. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy for GEP-NET: consolidated knowledge and innovative applications. Clin Transl Imaging 9, 423–438 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-021-00443-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-021-00443-y