Abstract
Abstract
Parkinson disease (PD) is associated with a variety of motor and non-motor clinical manifestations, including cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (nOH) is a potentially serious manifestation of cardiovascular sympathetic failure that occurs in approximately 30% of patients with PD. Here we review the pathophysiology and effects of the condition as well as treatment considerations for patients with PD and nOH. Screening for nOH using orthostatic symptom questionnaires, orthostatic blood pressure measurements, and specialized autonomic testing is beneficial for the identification of symptomatic and asymptomatic cases because cardiac sympathetic denervation and nOH can occur even at early (premotor) stages of PD. Symptoms of nOH, such as orthostatic lightheadedness, in patients with PD, have been shown to adversely affect patient safety (with increased risk of falls) and quality of life and should prompt treatment with non-pharmacologic and, occasionally, pharmacologic measures. Patients with nOH are also at increased risk of supine hypertension, which requires balancing various management strategies.
Funding
Lundbeck (Deerfield, IL).
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
An introduction and overview of the article. (MP4 198563 kb)
Parkinson disease (PD) is commonly defined by its motor symptoms, including bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and postural instability, but it is also a systemic disease with multiple non-motor clinical manifestations. Patients with PD frequently experience disturbances of olfaction, cognition, sleep, and mood (e.g., depression, anxiety, apathy), as well as gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and cardiovascular dysfunction [1,2,3,4]. The motor and non-motor features of PD are the result of dysregulation within components of the central and peripheral nervous systems [5,6,7], and several non-motor symptoms result from dysfunction within the sympathetic cholinergic, parasympathetic cholinergic, sympathetic noradrenergic, and adrenomedullary hormonal pathways of the autonomic nervous system [5, 8]. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (nOH), a sustained drop in blood pressure (BP) upon achieving an upright posture, is a manifestation of cardiac sympathetic noradrenergic failure that can result in dizziness, syncope, and falls [5, 9, 10]. nOH is common in patients with PD because Lewy body pathology commonly involves the peripheral (and less so the central) autonomic structures, causing both dysfunction and neurodegeneration of these structures [7]. Although nOH frequently occurs among patients with PD and other neurodegenerative disorders [5, 9, 11], the condition is often unrecognized or undertreated among individuals with PD. Because nOH can increase fall risk, negatively affect patients’ ability to perform daily activities, and decrease quality of life [12], timely diagnosis and management are critical. The aim of this review is to aid clinicians treating patients with PD by providing an overview of nOH in these patients, including discussions of the pathophysiologic features, clinical impact, appropriate diagnosis (including distinguishing nOH from other types of orthostatic hypotension [OH]), and treatment considerations.
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Clinical Features
Orthostatic Hypotension and Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension
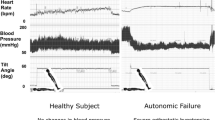
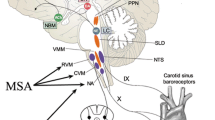
By consensus definition [10], OH is a sustained decrease in systolic BP by ≥ 20 mmHg or in diastolic BP by ≥ 10 mmHg within 3 min of standing or a ≥ 60° head-up tilt on a tilt table (Table 1 [5, 9, 10, 13,14,15,16,17,18,19]; Fig. 1). OH can be due to neurogenic and non-neurogenic causes. nOH is a subtype of OH that occurs in a variety of neurodegenerative disorders, including PD, multiple system atrophy (MSA), pure autonomic failure, and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and in peripheral autonomic neuropathies (e.g., diabetes, amyloidosis) as a consequence of the autonomic failure associated with these conditions [9, 11, 17]. This subtype is due to inadequate compensatory neurocirculatory responses to postural change caused by baroreflex failure and impaired release of norepinephrine [9, 11, 17, 20, 21]. The most common cause of non-neurogenic OH is the use of certain medications, particularly tricyclic antidepressants and antihypertensive agents (e.g., vasodilators, diuretics), but it also may be caused by hypovolemia and cardiac pump failure [13,14,15, 22, 23].
The symptoms of nOH/OH result from inadequate perfusion of target organs upon standing and are similar regardless of the underlying etiology [17, 24]. The most frequent symptoms of the condition include postural lightheadedness or dizziness, presyncope, and falls (occurring with or without loss of consciousness) [9, 10]. Less common symptoms include visual disturbances, fatigue, generalized weakness, cognitive dysfunction, neck pain or discomfort (coat hanger pain), and orthostatic dyspnea [9, 10].
The prevalence of nOH in patients with PD reported in studies that defined nOH by BP reduction criteria ranges widely in individual studies from 10 to 65% [25,26,27]), and a meta-analysis of 25 studies identified an estimated point prevalence of 30% [25]. Similarly, the prevalence estimates of symptomatic nOH in patients with PD are diverse, with reported rates ranging from 16 to 89% in individual studies [26,27,28,29]. However, not all patients who have an orthostatic BP drop meeting the criteria for nOH will report orthostatic symptoms. Results from studies in PD populations have suggested that a substantial portion of patients meet the BP criteria for OH but are asymptomatic—that is, they report no symptoms typical of cerebral hypoperfusion (e.g., dizziness, lightheadedness, impaired vision, head/neck pain) [26, 29, 30].
The characteristic symptoms of OH occur when mean arterial pressure falls below an individual’s threshold of cerebral autoregulation [26, 31]. Notably, chronic episodes of hypotension may induce mechanistic changes in cerebral autoregulation that ultimately allow patients with nOH to tolerate lower mean pressure without experiencing symptoms (compared with healthy individuals) [26, 31]. These findings underscore the notion that the presence or absence of orthostatic symptoms in patients with PD may not be a reliable indicator of nOH. A recent survey of patients with nOH revealed that they often hide or minimize nOH symptoms and are reluctant to discuss symptoms with their healthcare providers [12]. Therefore, additional objective evaluations (e.g., orthostatic BP measurements) are necessary to recognize nOH [24, 26].
Temporal Variants of Orthostatic Hypotension
In addition to OH defined as a BP drop within 3 min of standing (often referred to as “classical” OH) [10, 24], there are two other temporally defined forms of OH that can be identified by clinical BP measurements. Initial OH is a transient drop in BP that occurs immediately upon standing and resolves within 30–60 s of active standing, and delayed OH is a sustained drop in BP that occurs beyond 3 min of standing (Table 1) [10, 16, 19]. One large study of delayed OH monitored BP during 45 min of head-up tilt; however, there is currently no accepted standard for the length of time to test in the upright position for this condition [32].
Initial OH differs from classical and delayed OH in several ways. Initial OH is defined by a greater magnitude of BP decrease (systolic BP drop of ≥ 40 mmHg; diastolic BP drop of ≥ 20 mmHg) within 15 s of active standing, with restoration of normotensive BP within 30–60 s [14, 16, 19]. Signs and symptoms of initial OH are similar to those of the classical form of OH (e.g., lightheadedness, visual disturbances, syncope) [14, 16, 19]. However, initial OH is not associated with a particular disease state or with autonomic failure, and the prevalence of initial OH in patients with PD is currently unknown [24, 33].
Delayed OH occurs in some patients with PD (Table 1) and is thought to be related to, or a precursor of, classical OH [9, 10, 24]. In one study, more than half (54%) of patients with delayed OH developed classical OH during 10 years of follow-up [32]. Delayed OH may be a mild or early form of sympathetic adrenergic failure and has been associated with the development of neurodegenerative disorders (especially synucleinopathies) and increased mortality [32].
Clinical Relevance
Natural History
Because PD is a progressive neurodegenerative disease, it is perhaps not surprising that symptomatic manifestations of autonomic failure, including nOH, have been shown to be more likely in patients with more advanced disease [28, 34]. nOH is not only a late-stage complication of PD, however; OH is now included as a diagnostic marker of prodromal PD in the most recent Movement Disorder Society research criteria [35]. Supportive evidence that nOH can occur in the early stages of PD or as a prediagnostic feature of the disease is also found in clinical data [36,37,38,39,40]. In one study, 60% of patients (n = 21/35) had nOH in the early stages of PD [37]. A large case–control study using longitudinal medical record data found that patients who were subsequently diagnosed with PD had a higher incidence of hypotension complaints 5 years before diagnosis when compared with healthy controls [40]. Similarly, there are several reports of patients with symptoms of OH prior to demonstration of the motor features of PD [8, 39, 41, 42]. Pathophysiologic data also support the clinical observations of nOH onset before motor manifestations. For example, cardiac sympathetic denervation was demonstrated by neuroimaging assessment in a patient 4 years before the onset of motor parkinsonism [38].
Because cardiovascular autonomic failure and nOH can occur before motor symptoms, the differentiation of PD from other neurodegenerative diseases with nOH (e.g., pure autonomic failure, MSA, DLB) may be clinically challenging [37]. Furthermore, it is increasingly apparent that a substantial proportion of patients initially diagnosed with pure autonomic failure will progress to PD, MSA, or DLB, with reported phenoconversion rates of between 32 and 48% [43,44,45]. Various clinical characteristics, including normal circulating norepinephrine levels (supine or change from supine to standing), early bladder dysfunction, rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder (RBD), and preserved cardiovagal function, have been identified as predictors of phenoconversion [43,44,45]. Progression to a PD diagnosis specifically has been associated with RBD, decreased olfaction, increase in heart rate of < 10 bpm during head-up tilt, and orthostatic norepinephrine increase of > 65 pg/mL [43, 45]. Among patients with PD, the presence of nOH, mild cognitive impairment, or RBD is associated with more rapid disease progression and worse prognosis [46]. nOH in patients with PD is also associated with reduced 5- and 10-year survival rates [47].
Supine Hypertension
In patients with autonomic failure and nOH, supine hypertension is an important and often coexistent comorbidity. Supine hypertension has been defined by consensus criteria as a systolic BP of ≥ 140 mmHg and/or a diastolic BP of ≥ 90 mmHg after ≥ 5 min of supine rest [48]. It has been estimated that approximately one-third to one-half of patients with nOH related to parkinsonian disorders have comorbid supine hypertension, although inconsistent definition criteria and ascertainment methods limit a full understanding of the epidemiology [48, 49]. The autonomic nervous system dysfunction that underlies the pathogenesis of nOH also contributes to supine hypertension because both conditions result from baroreflex failure due to autonomic dysfunction and the inability of hemodynamic control mechanisms to buffer BP upon postural change [48, 50, 51].
Although the morbidity and mortality impacts of supine hypertension are not nearly as well understood as those for essential hypertension, an increased risk of renal impairment has been found in patients with supine hypertension [52], and some studies have indicated that patients with autonomic failure have similar markers of cardiovascular damage (e.g., left ventricular hypertrophy, arterial stiffness) as patients with essential hypertension [53,54,55]. A recent prospective study in an nOH patient cohort found that individuals with nOH and supine hypertension had increased markers of cardiovascular, renal, and brain damage (as measured by left ventricular hypertrophy, blood urea nitrogen, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and white matter hyperintensities) and a greater risk of adverse cardiovascular events and death when compared with patients with nOH only [56].
Additionally, altered circadian BP patterns (most often a lack of the diastolic BP decrease during sleep) are prevalent in patients with autonomic failure, with studies reporting this finding in 66–90% of patients with PD, MSA, and pure autonomic failure [57,58,59]. Nocturnal “reverse dipping” patterns also are associated with autonomic failure in patients with PD [60]. Deviations from normal diurnal BP patterns are clinically important because of the relationship to poor cardiovascular outcomes and end-organ damage [61]; however, studies examining effects exclusively in patients with autonomic failure or PD populations are lacking.
Functional, Psychosocial, and Healthcare Resource Use Impacts
Falls and their consequences are of high clinical concern in patients with PD. Falls increase the risk of injuries and increase healthcare resource use [62,63,64,65,66]. In patients with PD, symptoms of nOH are associated with increased risk of falls and impairment of activities of daily living [36, 67, 68]. An increased rate of falls has been demonstrated even in patients with asymptomatic nOH when compared with patients with PD without nOH (odds ratio 6.726; P = 0.005) [27]. The greater risk of falls in patients with nOH results in more emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and use of outpatient services [65, 69]. In a retrospective cohort study, unadjusted medically attended fall-related costs were significantly higher for patients with PD and nOH than for patients with PD alone (P = 0.0002) [65]. Similarly, another retrospective study found that overall healthcare costs were more than 250% higher in patients with PD and nOH than in those with PD alone (P = 0.037), even after adjusting for confounding factors [69].
In addition to risks posed by falls, nOH affects patients’ abilities to function and their sense of well-being. In a survey of 363 patients and 128 caregivers that assessed nOH symptom impact (in which approximately 90% of the patients had clinical diagnoses of PD), most patients and caregivers (≥ 87%) indicated that the symptoms of nOH had an overall negative impact on the ability to perform everyday activities [12]. Furthermore, substantial percentages of patients and caregivers reported that nOH negatively impacted quality of life, robbed the patient of a sense of independence, and drastically changed the patient’s life [12]. In another prospective study, more than half of patients with PD reported that orthostatic dizziness affected their activities of daily living “a lot to very much” [67].
Beyond studies describing the symptomatic burden of nOH, there is also evidence that patients with asymptomatic nOH may experience functional impairment [27, 30]. A prospective cohort study of patients with PD-associated autonomic dysfunction found that those with asymptomatic OH were more likely than those without OH to experience greater deterioration in measures of activities of daily living and health-related quality of life (nine- and five-fold higher odds of deterioration, respectively; both P ≤ 0.01) [27]. These findings support earlier work on the functional consequences of asymptomatic OH [30] and underscore the importance of screening for OH in all patients with PD.
Cognitive Effects
Although the consequences of nOH, such as fall risk and negative effects on function, are generally recognized, other impacts of the condition are currently less well appreciated. There is growing evidence that OH (regardless of cause) may negatively affect cognition [70]. Among data restricted to PD populations, a 2016 systematic review found a positive association between OH and cognitive impairment in patients with PD in seven of ten studies, with attentional/executive and visuospatial cognitive domains most affected [71]. Currently, it is uncertain whether the relationship between OH and cognitive decline is one of causation or association [72]. One potential mechanism could be reduced blood flow to areas of the brain responsible for executive and visuospatial function (e.g., frontotemporal and parieto-occipital regions) [71]. This hypothesis is supported by findings that patients with PD and OH had greater cognitive deficits in an upright position versus when supine. These postural effects on cognition were not noted in patients with PD without OH [73]. Further, repeated BP fluctuations over time may lead to cerebrovascular injury [71]. Alternatively, nOH may reflect greater effects of the overall neurodegenerative processes and more severe disease [71]. Finally, synergistic effects of hypoperfusion and neurodegeneration may be responsible for cognitive impairment in patients with nOH [71]. Further work is needed to confirm the association between nOH and cognitive impairment and the potential impacts on outcomes. In the meantime, recognition and appropriate diagnosis of nOH are important to mitigate risk from falls and to improve patients’ functional abilities and maintain quality of life.
Screening and Diagnosis
Patients presenting with a synucleinopathy (e.g., suspected or confirmed PD, MSA, DLB, or pure autonomic failure), peripheral neuropathy, unexplained falls or syncope, those who are elderly and taking multiple medications, and those with any symptoms of orthostatic intolerance are at increased risk for nOH [9]. As such, evaluation for nOH is appropriate when treating patients with any of these characteristics. Although there are no standardized, recommended screening protocols for OH and nOH, an expert consensus panel has developed a list of screening questions that may be a useful assessment tool for clinicians (Fig. 2a) [9]. Other screening instruments include the 5-item Self-Report Orthostatic Grading Scale questionnaire [74] and the Orthostatic Hypotension Questionnaire [75], both of which are validated measures of OH symptom severity.
Screening questions (a), diagnostic assessment (b), and treatment options (c) for orthostatic hypotension (OH) and neurogenic OH (nOH) [9, 10, 77, 108, 113, 114]. BP Blood pressure, FDA US Food and Drug Administration. Screening panel (a) was adapted from Gibbons et al. [9], under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Although screening questions can be suggestive of nOH, the usefulness of these patient-reported evaluations is limited by the non-specific nature of orthostatic symptoms and by some patients’ lack of recall of such symptoms if nOH progresses to syncope. Therefore, orthostatic BP testing is warranted in all patients identified as being at risk for nOH [9, 27]. The primary assessment method for OH is the measurement of change in BP from supine (after ≥ 5 min of rest) to upright position (standing or head-up tilt); upright BP measurements are taken after 1 and 3 min of standing (Fig. 2b) [9]. The standard criteria for diagnosis of OH are a sustained systolic BP decrease of ≥ 20 mmHg or diastolic BP decrease of ≥ 10 mmHg during postural change [10]. Some autonomic testing laboratories, including the Mayo Clinic where the authors practice, evaluate for OH using the passive head-up maneuver on a tilt table and thus require stricter OH diagnostic criteria of a drop of ≥ 30 mmHg in systolic BP or of ≥ 15 mmHg in diastolic BP (as measured using a manual sphygmomanometer). We do this because this passive tilt-testing reduces the muscle-pumping action of the lower limbs that occurs during active standing. Consequently, a greater drop in orthostatic BP can be normal when the contribution from this physiologic compensatory mechanism is minimized. In the clinic, orthostatic BP testing can also be used to detect supine hypertension (i.e., if the patient’s systolic BP increases to > 140 mmHg or diastolic BP increases to > 90 mmHg after 5 min of supine rest) [48]. For patients with supine hypertension, the more conservative OH diagnosis criteria of ≥ 30-mmHg drop in systolic BP or ≥ 15-mmHg drop in diastolic BP during a supine-to-standing test may also be more appropriate for diagnosing OH [9, 10].
In clinical settings where a supine-to-standing test is not practical, a seated-to-standing BP measurement may be a convenient alternative. The seated-to-standing technique may be modestly less sensitive and specific for detecting OH [9, 76]; a lower BP reduction threshold may be indicative of OH (systolic BP drop of ≥ 15 mmHg; diastolic BP drop of ≥ 7 mmHg) [77]. Ambulatory and home BP monitoring can supplement data obtained by in-clinic BP measurements. These types of BP monitoring can help patients and physicians correlate BP drops or supine BP spikes with specific times of day, medication use (i.e., pharmacodynamic effects), and activities [9]. For example, patients with PD and similar autonomic failure disorders are prone to post-prandial hypotension [78, 79]; thus, BP testing after meals is recommended [9, 10]. Additionally, 24-h ambulatory BP monitoring can identify supine hypertension and establish nocturnal BP patterns, including “reverse dipping” profiles [60].
To evaluate for temporal variants of OH (i.e., delayed or initial OH), modifications to the standard in-clinic supine-to-standing BP testing protocol are required. For delayed OH, the period of standing or head-up tilt is extended beyond 3 min before the final BP measurement is taken [10]. For initial OH, BP changes may occur too rapidly to be detected using standard, intermittent BP measurements; thus, detection requires the use of a beat-to-beat BP monitoring device [80]. Initial OH is defined specifically as OH that occurs during active standing, so a tilt-table test is not an appropriate evaluation method when initial OH is suspected [80].
Diagnosis of Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension
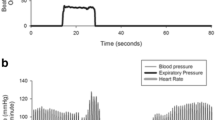
Once a BP drop indicating OH is identified, further investigation into the underlying cause is warranted. Patients with nOH can often be distinguished clinically from patients with non-neurogenic OH by a blunted orthostatic heart rate response [9], although this single variable is not a perfectly sensitive or specific marker (Table 1). OH accompanied by a minimal increase in heart rate from the supine- and/or seated-to-standing position (< 15 bpm) may be suggestive of nOH, whereas compensatory heart rate increases of ≥ 15 bpm are usually observed when OH is due to non-neurogenic causes [9]. The results of a recent study suggest that a heart rate increase of < 17 bpm has better sensitivity and specificity for detecting nOH; however, the rate of the orthostatic change in heart rate with falling systolic BP (called baroreflex gain, < 0.5 bpm/mmHg) may be an even better indicator of nOH than the absolute change in heart rate alone [81, 82]. As part of the diagnostic evaluation for nOH, exclusion of potentially confounding factors, such as dehydration, acute bleeding, and non-neurogenic causes, is necessary [83]. An electrocardiogram, cardiac history, and medication review should be performed to rule out cardiogenic causes (e.g., pacemakers, dysrhythmias) that may affect postural heart rate [9].
Specialized autonomic reflex tests may be used to confirm a diagnosis of nOH (Fig. 2b). Among these, BP and heart rate monitoring during the Valsalva maneuver distinguish nOH from other forms of OH when an exaggerated and sustained BP decrease in the absence of a compensatory increase in heart rate during straining, absence of reflex vasoconstriction, or delayed recovery of BP is observed (Fig. 1d) [9, 22, 84]. Continuous monitoring of the BP response to prolonged head-up tilt is also useful in the identification of nOH [9, 84], as is measurement of supine and standing fractionated plasma catecholamine levels to identify lower than normal norepinephrine levels when supine or a less than appropriate increase upon standing [9, 84, 85]. Additional evaluations may identify the specific autonomic failure condition associated with nOH. For example, the Composite Autonomic Severity Scale (CASS; an instrument developed to grade autonomic failure based on evaluations of sudomotor, adrenergic, and cardiovagal dysfunction) and measurement of the anhidrosis percentage during a thermoregulatory sweat test are useful tools for distinguishing PD from MSA [86, 87]. PD is typically associated with normal norepinephrine levels, a CASS score of < 6, and anhidrosis of < 40%, whereas MSA is more often associated with a normal supine norepinephrine level but less than expected orthostatic increase, a CASS score of > 6, and anhidrosis of > 40% [84].
Treatment Considerations
Once an nOH diagnosis is confirmed, management of the condition should focus on alleviating symptoms, mitigating fall risk, increasing standing time, and maximizing the patient’s ability to perform daily activities independently [9]. Normalization of standing BP is not necessarily the goal of treatment, although the increased risks of falls, injuries, and cognitive dysfunction even with “asymptomatic” nOH suggest a symptom-driven treatment paradigm may be insufficient. Management can begin with a thorough medication review, followed by consideration of non-pharmacologic and pharmacologic treatments. Continued monitoring for and management of co-occurring supine hypertension is also recommended [9].
Confounding Medications
Treating nOH in patients with PD is complex because many of the medications used to manage PD symptoms, including levodopa, dopamine agonists, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and amantadine, are associated with hypotensive effects that can induce or worsen OH (Table 2) [29, 88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104]. The results of some studies have suggested, however, that OH occurs independently of levodopa use [105, 106]. Although the precise mechanism by which these medications induce hypotension is currently unknown, it is clear that careful management is necessary in patients with PD and nOH [107, 108]. In general, antihypertensive and antidepressant (especially tricyclic antidepressant) medications commonly cause OH, and the use of these medications should be carefully monitored in patients with PD [13, 14, 22, 109]. Polypharmacy (i.e., concomitant use of ≥ 5 medications) has also been associated with increased likelihood of nOH in patients with PD [110]. Although it may not be practical or safe to discontinue all medications that can contribute to OH, changes to dosage or dosing schedule may help some patients [9].
Non-pharmacologic Measures
Once medications that may induce or worsen nOH have been minimized, treatment interventions should be considered. Non-pharmacologic interventions should be implemented first to manage nOH symptoms; these include the liberal intake of fluid and salt, physical counterpressure maneuvers, use of compression garments on the abdomen and thighs, and lower-body strength training (Fig. 2c) [9, 108]. Of these non-pharmacologic strategies, the most effective at limiting an orthostatic systolic BP drop are bolus water ingestion (approximately 500 mL in 5 min) and abdominal compression (using an elastic belt) [111]. Physical counter maneuvers (standing cross-legged) have also been shown to limit diastolic BP drop [111].
Implementation of non-pharmacologic measures is a key component of nOH treatment but may be limited by circumstances and patient preference. For example, increased intake of fluids and salt may not be advisable for patients with kidney disease, hypertension, or heart failure [108]. Evaluation of the risks (worsening symptomology of the renal and cardiovascular conditions over the long term) and benefits (reduction in imminent fall risk and improved upright function) of increased fluid and salt intake and regular monitoring to ensure proper use is appropriate [83]. Further, although the use of waist-high compression garments to reduce venous pooling in the splanchnic circulation can be effective [9, 111, 112], patients may protest because of the difficulty and discomfort of wearing them [9]. Compression shorts are a reasonable alternative to prescription-strength hose and are much better tolerated. Non-pharmacologic therapies may not provide sufficient symptom relief for many patients, but their implementation is critical to the effectiveness of any subsequent BP-augmenting pharmacotherapy.
Pharmacologic Treatments
When medication adjustments and non-pharmacologic management strategies do not provide adequate relief of nOH symptoms, pharmacologic treatments to augment BP are appropriate (Fig. 2c). If patients report severe orthostatic symptoms, concurrent implementation of pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic management strategies (versus a stepwise approach) may be required.
Droxidopa, a norepinephrine prodrug, is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of symptomatic nOH (labeled indication for the treatment of orthostatic dizziness, lightheadedness, or the “feeling that you are about to black out” in adult patients with symptomatic nOH) with an underlying dysautonomia [113]. Midodrine is approved for the broader indication of symptomatic OH, including nOH [114]. Droxidopa’s approval in the USA is based on data from randomized clinical trials that demonstrated improvements in standing BP that were associated with patient-reported benefits on symptoms of nOH and their effect on daily activities [9, 113, 115, 116]. Integrated analyses of clinical trial data (including a sub-analysis limited to patients with PD) found that droxidopa significantly increased standing systolic BP in comparison to placebo [117, 118]. In both patients with PD and the wider population of patients with nOH, droxidopa has also been shown to improve symptoms of nOH, including dizziness/lightheadedness and weakness [115,116,117,118]. In a post hoc analysis of clinical trial data and a prospective open-label “real-world” patients study, a reduction in falls was found with droxidopa treatment [119, 120]. More rigorous trials are needed, however, to fully elucidate the effect of droxidopa on falls. Another area of future research on the use of droxidopa is differential efficacy based on baseline norepinephrine levels. The results of a recent small study (n = 20) suggest that droxidopa may elicit greater pressor effects in patients with low supine norepinephrine levels (< 220 pg/mL) than in those with higher norepinephrine levels [121]. If confirmed in larger studies, this finding suggests that droxidopa is more effective for treating nOH in patients with peripheral autonomic pathology (e.g., PD and pure autonomic failure) than in those with central autonomic disorders (e.g., MSA).
In clinical trials, the most frequent adverse events associated with droxidopa treatment have included headache and dizziness [115, 116, 118]. Rates of supine hypertension have been reported to be low (< 8% of patients with supine systolic BP of > 180 mmHg) [117, 118], and a meta-analysis of clinical trial data found that droxidopa was not associated with significantly increased risk of supine hypertension (risk ratio [RR] 1.4; 95% credible interval [CrI] 0.71–2.7) [122]. The typical dosing of droxidopa is 100–600 mg three times during the waking day. The reported half-life is 2.5 h [113].
Midodrine is a peripheral alpha-1 agonist that increases vascular resistance and BP [9]. Midodrine improves standing systolic BP in patients with nOH in a dose-dependent manner, but its use may be limited by supine hypertension, piloerection, scalp tingling, and urinary retention [9, 108, 123, 124]. Midodrine increases standing and supine systolic BP, with a similar magnitude of effect on both (19.5- to 22.4-mmHg increase in standing systolic BP; 16.2- to 17.6-mmHg increase in supine systolic BP) [124]. The authors of a recent meta-analysis came to the conclusion, based on their results, that midodrine significantly increases standing systolic BP in patients with nOH (mean increase 17 mmHg), but it also significantly increases the risk of supine hypertension (RR 5.1; 95% CrI 1.6–24.0) [122]. Because only a limited number of studies were available for this meta-analysis, these conclusions should be interpreted with caution. The typical dosing of midodrine is 2.5–15 mg three times during the waking day. The reported half-life of the active metabolite (desglymidodrine) is 3–4 h [114].
Several medications are frequently used off label to treat nOH. Despite the longstanding and widespread use of off-label agents in clinical practice, the overall level of evidence supporting their use is limited by inconsistent findings of efficacy and small study sizes [125]. The most commonly used off-label agents are fludrocortisone (0.05–0.2 mg daily), which increases plasma volume, and pyridostigmine (60 mg three times per day), which amplifies ganglionic neurotransmission [9, 108]. Fludrocortisone may cause supine hypertension, hypokalemia, headache, and myocardial fibrosis [126], while the use of pyridostigmine may be limited by diarrhea, abdominal pain, and muscle twitches, but it does not cause supine hypertension [9, 127]. For post-prandial hypotension, octreotide, a somatostatin analog that decreases splanchnic blood pooling, or acarbose, an inhibitor of α-glucosidase in the small intestine, may be used [108, 128]. In addition to caveats because of the lack of large, well-conducted clinical studies, the safety profile of any agent used off label should be considered. For example, fludrocortisone may pose significant safety risks because of the risk of supine hypertension [125], and its use is contraindicated in patients with cardiovascular comorbidities, such as heart failure, kidney failure, and hypertension [129].
Supine Hypertension as a Treatment Consideration in Parkinson Disease
Because supine hypertension is another manifestation of the cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction that also causes nOH, it can occur in patients with nOH regardless of treatment. To complicate matters, the treatments that raise orthostatic BP may also increase BP when supine [9, 115, 124]. As described in the preceding text, the risk of supine hypertension associated with individual pressor agents used in the treatment of nOH may vary. In addition to the appropriate selection of nOH treatment based on the supine hypertension risk profile, 24-h ambulatory BP monitoring can provide the patient and clinician with information on when and under what circumstances the patient experiences nOH symptoms and supine hypertension, and this information should be considered when initiating or adjusting nOH pharmacotherapy [9, 48, 51].
Non-pharmacologic management of supine hypertension can include avoidance of the supine position during rest and elevation of the head of the bed by 4–6 in. [130]. Steeper head-up tilt sleeping positions may be even more effective but are usually not tolerated by patients or their bed partners [9, 131, 132]. Patients should not lie flat for at least 3–4 h after any dose of midodrine or droxidopa [9, 113, 114]. When non-pharmacologic treatments are insufficient to control supine hypertension, clinicians can prescribe a short-acting antihypertensive medication to be taken before bedtime [9, 51]. Consensus panels of autonomic experts have suggested captopril, clonidine, hydralazine, losartan, or a nitroglycerin patch for this purpose [9, 133]; however, further research is required to better understand and determine optimal management strategies for supine hypertension in patients with nOH.
Given that both nOH and supine hypertension pose risks to patient safety, balanced management of the two conditions is often required. To determine the best treatment approach for the individual patient, healthcare providers should consider factors such as comorbidities, concomitant medications, and prognosis, as well as discuss the benefits and short- and long-term risks with each patient [9, 52, 54].
Conclusions
Neurogenic OH, defined by a sustained drop in BP upon standing and inadequate compensatory heart rate increase, is a common and potentially serious non-motor condition present in approximately 30% of patients with PD [25]. nOH results from degeneration of the autonomic nervous system and can impact patients’ activities of daily living. Screening for nOH with orthostatic symptom questionnaires, orthostatic BP measurements, and specialized autonomic testing (when necessary) in patients with PD will help identify symptomatic and asymptomatic cases and should prompt treatment. nOH symptoms can be treated with non-pharmacologic measures and with medications. Patients with nOH may also experience supine hypertension, which influences medical management decisions.
References
Goldman JG, Postuma R. Premotor and non-motor features of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 2014;27(4):434–41.
Lyons KE, Pahwa R. The impact and management of non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17[Suppl 12]:S308–14.
Wen MC, Chan LL, Tan LC, Tan EK. Depression, anxiety, and apathy in Parkinson’s disease: insights from neuroimaging studies. Eur J Neurol. 2016;23(6):1001–19.
Ziemssen T, Reichmann H. Non-motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson Relat Disord. 2007;13(6):323–32.
Goldstein DS. Dysautonomia in Parkinson disease. Compr Physiol. 2014;4(2):805–26.
Dickson DW. Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism: neuropathology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2(8):a009258.
Coon EA, Cutsforth-Gregory JK, Benarroch EE. Neuropathology of autonomic dysfunction in synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2018;33(3):349–58.
Kaufmann H, Goldstein DS. Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;117:259–78.
Gibbons CH, Schmidt P, Biaggioni I, et al. The recommendations of a consensus panel for the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension and associated supine hypertension. J Neurol. 2017;264(8):1567–82.
Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res. 2011;21(2):69–72.
Isaacson SH, Skettini J. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease: evaluation, management, and emerging role of droxidopa. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014;10:169–76.
Claassen DO, Adler CH, Hewitt LA, Gibbons C. Characterization of the symptoms of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension and their impact from a survey of patients and caregivers. BMC Neurol. 2018;18(1):125.
Goldstein DS, Sharabi Y. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a pathophysiological approach. Circulation. 2009;119(1):139–46.
Jones PK, Shaw BH, Raj SR. Orthostatic hypotension: managing a difficult problem. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2015;13(11):1263–76.
Brignole M, Moya A, de Lange FJ, et al. 2018 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(21):1883–948.
Wieling W, Krediet CT, van Dijk N, Linzer M, Tschakovsky ME. Initial orthostatic hypotension: review of a forgotten condition. Clin Sci (Lond). 2007;112(3):157–65.
Freeman R. Clinical practice. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(6):615–24.
Moya A, Sutton R, Ammirati F, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope (version 2009): the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Syncope of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2009;30(21):2631–71.
Stewart JM, Clarke D. “He’s dizzy when he stands up”: an introduction to initial orthostatic hypotension. J Pediatr. 2011;158(3):499–504.
Kaufmann H, Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Palma JA. Droxidopa in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2015;13(8):875–91.
Low PA, Singer W. Management of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: an update. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(5):451–8.
Low PA. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: pathophysiology and diagnosis. Am J Manag Care. 2015;21[13 Suppl]:s248–57.
Robertson D. The pathophysiology and diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension. Clin Auton Res. 2008;18[Suppl 1]:2–7.
Freeman R, Abuzinadah AR, Gibbons C, Jones P, Miglis MG, Sinn DI. Orthostatic hypotension: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(11):1294–309.
Velseboer DC, de Haan RJ, Wieling W, Goldstein DS, de Bie RM. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinson Relat Disord. 2011;17(10):724–9.
Palma JA, Gomez-Esteban JC, Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, et al. Orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson disease: how much you fall or how low you go? Mov Disord. 2015;30(5):639–45.
Merola A, Romagnolo A, Rosso M, et al. Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: a prospective cohort study. Mov Disord. 2018;33(3):391–7.
Ha AD, Brown CH, York MK, Jankovic J. The prevalence of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension in patients with Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonism. Parkinson Relat Disord. 2011;17(8):625–8.
Senard JM, Rai S, Lapeyre-Mestre M, et al. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;63(5):584–9.
Merola A, Romagnolo A, Rosso M, et al. Orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease: does it matter if asymptomatic? Parkinson Relat Disord. 2016;33:65–71.
Palma JA, Kaufmann H. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2017;4(3):298–308.
Gibbons CH, Freeman R. Clinical implications of delayed orthostatic hypotension: a 10-year follow-up study. Neurology. 2015;85(16):1362–7.
Finucane C, O’Connell MD, Donoghue O, Richardson K, Savva GM, Kenny RA. Impaired orthostatic blood pressure recovery is associated with unexplained and injurious falls. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(3):474–82.
Verbaan D, Marinus J, Visser M, van Rooden SM, Stiggelbout AM, van Hilten JJ. Patient-reported autonomic symptoms in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2007;69(4):333–41.
Berg D, Postuma RB, Adler CH, et al. MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2015;30(12):1600–11.
Fereshtehnejad SM, Lokk J. Orthostatic hypotension in patients with Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonism. Parkinsons Dis. 2014;2014:475854.
Goldstein DS. Orthostatic hypotension as an early finding in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Auton Res. 2006;16(1):46–54.
Goldstein DS, Sharabi Y, Karp BI, et al. Cardiac sympathetic denervation preceding motor signs in Parkinson disease. Clin Auton Res. 2007;17(2):118–21.
Milazzo V, Di Stefano C, Servo S, Zibetti M, Lopiano L, Maule S. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension as the initial feature of Parkinson disease. Clin Auton Res. 2012;22(4):203–6.
Schrag A, Horsfall L, Walters K, Noyce A, Petersen I. Prediagnostic presentations of Parkinson’s disease in primary care: a case–control study. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(1):57–64.
Kaufmann H, Nahm K, Purohit D, Wolfe D. Autonomic failure as the initial presentation of Parkinson disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology. 2004;63(6):1093–5.
Nylin G, Levander M. Studies on the circulation with the aid of tagged erythrocytes in a case of orthostatic hypotension (asympathicotomic hypotension). Ann Intern Med. 1948;28(4):723–46.
Singer W, Berini SE, Sandroni P, et al. Pure autonomic failure: predictors of conversion to clinical CNS involvement. Neurology. 2017;88(12):1129–36.
Giannini G, Calandra-Buonaura G, Asioli GM, et al. The natural history of idiopathic autonomic failure: the IAF-BO cohort study. Neurology. 2018;91(13):e1245–54.
Kaufmann H, Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Palma JA, et al. Natural history of pure autonomic failure: a United States prospective cohort. Ann Neurol. 2017;81(2):287–97.
Fereshtehnejad SM, Romenets SR, Anang JB, Latreille V, Gagnon JF, Postuma RB. New clinical subtypes of Parkinson disease and their longitudinal progression: a prospective cohort comparison with other phenotypes. JAMA Neurol. 2015;72(8):863–73.
Goldstein DS, Holmes C, Sharabi Y, Wu T. Survival in synucleinopathies: a prospective cohort study. Neurology. 2015;85(18):1554–61.
Fanciulli A, Jordan J, Biaggioni I, et al. Consensus statement on the definition of neurogenic supine hypertension in cardiovascular autonomic failure by the American Autonomic Society (AAS) and the European Federation of Autonomic Societies (EFAS): endorsed by the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Clin Auton Res. 2018;28(4):355–62.
Fanciulli A, Gobel G, Ndayisaba JP, et al. Supine hypertension in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Clin Auton Res. 2016;26(2):97–105.
Baker J, Kimpinski K. Management of supine hypertension complicating neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(8):653–63.
Sharabi Y, Goldstein DS. Mechanisms of orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension in Parkinson disease. J Neurol Sci. 2011;310(1–2):123–8.
Garland EM, Gamboa A, Okamoto L, et al. Renal impairment of pure autonomic failure. Hypertension. 2009;54(5):1057–61.
Maule S, Milan A, Grosso T, Veglio F. Left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with autonomic failure. Am J Hypertens. 2006;19(10):1049–54.
Vagaonescu TD, Saadia D, Tuhrim S, Phillips RA, Kaufmann H. Hypertensive cardiovascular damage in patients with primary autonomic failure. Lancet. 2000;355(9205):725–6.
Milazzo V, Maule S, Di Stefano C, et al. Cardiac organ damage and arterial stiffness in autonomic failure: comparison with essential hypertension. Hypertension. 2015;66(6):1168–75.
Palma JA, Redel-Traub G, Porciuncula A, et al. The impact of supine hypertension on target organ damage and mortality in patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Clin Auton Res. 2018;28:473.
Plaschke M, Trenkwalder P, Dahlheim H, Lechner C, Trenkwalder C. Twenty-four-hour blood pressure profile and blood pressure responses to head-up tilt tests in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. J Hypertens. 1998;16(10):1433–41.
Okamoto LE, Gamboa A, Shibao C, et al. Nocturnal blood pressure dipping in the hypertension of autonomic failure. Hypertension. 2009;53(2):363–9.
Kaufmann H, Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Hewitt LA, Rowse GJ, White WB. Effects of the novel norepinephrine prodrug, droxidopa, on ambulatory blood pressure in patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2016;10(10):819–26.
Milazzo V, Di Stefano C, Vallelonga F, et al. Reverse blood pressure dipping as marker of dysautonomia in Parkinson disease. Parkinson Relat Disord. 2018;56:82–7.
Routledge FS, McFetridge-Durdle JA, Dean CR. Night-time blood pressure patterns and target organ damage: a review. Can J Cardiol. 2007;23(2):132–8.
Tan LC, Tan AK, Tjia HT. The profile of hospitalised patients with Parkinson’s disease. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 1998;27(6):808–12.
Woodford H, Walker R. Emergency hospital admissions in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2005;20(9):1104–8.
Rudzinska M, Bukowczan S, Stozek J, et al. Causes and consequences of falls in Parkinson disease patients in a prospective study. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2013;47(5):423–30.
Francois C, Biaggioni I, Shibao C, et al. Fall-related healthcare use and costs in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension with Parkinson’s disease. J Med Econ. 2017;20(5):525–32.
Tinetti ME, Williams CS. Falls, injuries due to falls, and the risk of admission to a nursing home. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(18):1279–84.
Magerkurth C, Schnitzer R, Braune S. Symptoms of autonomic failure in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence and impact on daily life. Clin Auton Res. 2005;15(2):76–82.
McDonell KE, Shibao CA, Claassen DO. Clinical relevance of orthostatic hypotension in neurodegenerative disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2015;15(12):78.
Merola A, Sawyer RP, Artusi CA, et al. Orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson disease: impact on health care utilization. Parkinson Relat Disord. 2017;47:45–9.
McNicholas T, Tobin K, Carey D, O’Callaghan S, Kenny RA. Is baseline orthostatic hypotension associated with a decline in global cognitive performance at 4-year follow-up? Data from TILDA (The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing). J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(19):e008976.
Udow SJ, Robertson AD, MacIntosh BJ, et al. ‘Under pressure’: is there a link between orthostatic hypotension and cognitive impairment in alpha-synucleinopathies? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016;87(12):1311–21.
McDonald C, Newton JL, Burn DJ. Orthostatic hypotension and cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: causation or association? Mov Disord. 2016;31(7):937–46.
Centi J, Freeman R, Gibbons CH, Neargarder S, Canova AO, Cronin-Golomb A. Effects of orthostatic hypotension on cognition in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2017;88(1):17–24.
Schrezenmaier C, Gehrking JA, Hines SM, Low PA, Benrud-Larson LM, Sandroni P. Evaluation of orthostatic hypotension: relationship of a new self-report instrument to laboratory-based measures. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80(3):330–4.
Kaufmann H, Malamut R, Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Rosa K, Freeman R. The Orthostatic Hypotension Questionnaire (OHQ): validation of a novel symptom assessment scale. Clin Auton Res. 2012;22(2):79–90.
Shibao C, Lipsitz LA, Biaggioni I. ASH position paper: evaluation and treatment of orthostatic hypotension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013;15(3):147–53.
Shaw BH, Garland EM, Black BK, et al. Optimal diagnostic thresholds for diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension with a ‘sit-to-stand test’. J Hypertens. 2017;35(5):1019–25.
Loew F, Gauthey L, Koerffy A, et al. Postprandial hypotension and orthostatic blood pressure responses in elderly Parkinson’s disease patients. J Hypertens. 1995;13(11):1291–7.
Micieli G, Martignoni E, Cavallini A, Sandrini G, Nappi G. Postprandial and orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 1987;37(3):386–93.
van Twist DJL, Dinh T, Bouwmans EME, Kroon AA. Initial orthostatic hypotension among patients with unexplained syncope: an overlooked diagnosis? Int J Cardiol. 2018;271:269–73.
Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Kaufmann H, Palma JA, et al. Orthostatic heart rate changes in patients with autonomic failure caused by neurodegenerative synucleinopathies. Ann Neurol. 2018;83(3):522–31.
Balagny P, Wanono R, d’Ortho MP, Vidal-Petiot E. Reply to validation of the new diagnostic tests for neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Ann Neurol. 2018;84(6):957–8.
Metzler M, Duerr S, Granata R, Krismer F, Robertson D, Wenning GK. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. J Neurol. 2013;260(9):2212–9.
Low PA, Tomalia VA, Park KJ. Autonomic function tests: some clinical applications. J Clin Neurol. 2013;9(1):1–8.
Loavenbruck A, Sandroni P. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: roles of norepinephrine deficiency in its causes, its treatment, and future research directions. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015;31(11):2095–104.
Lipp A, Sandroni P, Ahlskog JE, et al. Prospective differentiation of multiple system atrophy from Parkinson disease, with and without autonomic failure. Arch Neurol. 2009;66(6):742–50.
Low PA. Composite autonomic scoring scale for laboratory quantification of generalized autonomic failure. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993;68(8):748–52.
Camerlingo M, Ferraro B, Gazzaniga GC, Casto L, Cesana BM, Mamoli A. Cardiovascular reflexes in Parkinson’s disease: long-term effects of levodopa treatment on de novo patients. Acta Neurol Scand. 1990;81(4):346–8.
Calne DB, Brennan J, Spiers AS, Stern GM. Hypotension caused by L-dopa. Br Med J. 1970;1(5694):474–5.
Jost WH, Bellon AK, Kaiser T, Schrank B. The impact of ropinirole on blood pressure and noradrenaline concentration after active orthostasis in Parkinsonian patients. Parkinson Relat Disord. 1998;4(2):61–3.
Bouhaddi M, Vuillier F, Fortrat JO, et al. Impaired cardiovascular autonomic control in newly and long-term-treated patients with Parkinson’s disease: involvement of L-dopa therapy. Auton Neurosci. 2004;116(1–2):30–8.
Barbeau A. L-dopa therapy in Parkinson’s disease: a critical review of nine years’ experience. Can Med Assoc J. 1969;101(13):59–68.
Haapaniemi TH, Kallio MA, Korpelainen JT, et al. Levodopa, bromocriptine and selegiline modify cardiovascular responses in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2000;247(11):868–74.
Churchyard A, Mathias CJ, Lees AJ. Selegiline-induced postural hypotension in Parkinson’s disease: a longitudinal study on the effects of drug withdrawal. Mov Disord. 1999;14(2):246–51.
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Miraprex® (pramipexole dihydrochloride). Full prescribing information. Ridgefield: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2007.
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Miraprex ER® (pramipexole dihydrochloride). Full prescribing information. Ridgefield: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2014.
Novartis International AG. Parlodel® (Bromocriptine mesylate). Full prescribing information. Suffern: Novartis International AG; 2011.
Teva Pharmaceuticals. Rasagiline (rasagiline). Full prescribing information. Parsippany: Teva Pharmaceuticals; 2019.
GlaxoSmithKline. REQUIP (ropinirole). Full prescribing information. Research Triangle Park: GlaxoSmithKline; 2018.
Merck & Co., Inc. Sinemet® (carbidopa levodopa). Full prescribing information. Whitehouse Station: Merck & Co., Inc.; 2018. https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/s/sinemet/sinemet_pi.pdf
Valeant Pharmaceuticals. ZELAPAR® (selegiline hydrochloride). Full prescribing information. Aliso Viejo: Valeant Pharmaceuticals; 2008.
Adamas Pharma, LLC. GOCOVRI™ (amantadine). Full prescribing information. Emeryville: Adamas Pharma, LLC; 2017.
Pahwa R, Tanner CM, Hauser RA, et al. ADS-5102 (amantadine) extended-release capsules for levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson disease (EASE LID Study): a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2017;74(8):941–9.
Oertel W, Eggert K, Pahwa R, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of ADS-5102 (amantadine) extended-release capsules for levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease (EASE LID 3). Mov Disord. 2017;32(12):1701–9.
Goldstein DS, Eldadah BA, Holmes C, et al. Neurocirculatory abnormalities in Parkinson disease with orthostatic hypotension: independence from levodopa treatment. Hypertension. 2005;46(6):1333–9.
Kim JS, Lee SH, Oh YS, et al. Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in mild and advanced Parkinson’s disease. J Mov Disord. 2016;9(2):97–103.
Korchounov A, Kessler KR, Schipper HI. Differential effects of various treatment combinations on cardiovascular dysfunction in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 2004;109(1):45–51.
Shen WK, Sheldon RS, Benditt DG, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the evaluation and management of patients with syncope: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(5):e39–110.
Craig GM. Clinical presentation of orthostatic hypotension in the elderly. Postgrad Med J. 1994;70(827):638–42.
Perez-Lloret S, Rey MV, Fabre N, et al. Factors related to orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson Relat Disord. 2012;18(5):501–5.
Newton JL, Frith J. The efficacy of non-pharmacologic intervention for orthostatic hypotension associated with aging. Neurology. 2018;91(7):e652–6.
Mills PB, Fung CK, Travlos A, Krassioukov A. Nonpharmacologic management of orthostatic hypotension: a systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;96(2):366–75.
Lundbeck NA Ltd. NORTHERA® (droxidopa). Deerfield: Lundbeck NA Ltd; 2017.
Shire US Inc. ProAmatine® (midodrine hydrochloride). Full prescribing information. Lexington: Shire US Inc.; 2017.
Hauser RA, Isaacson S, Lisk JP, Hewitt LA, Rowse G. Droxidopa for the short-term treatment of symptomatic neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease (nOH306B). Mov Disord. 2015;30(5):646–54.
Kaufmann H, Freeman R, Biaggioni I, et al. Droxidopa for neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Neurology. 2014;83(4):328–35.
Biaggioni I, Arthur Hewitt L, Rowse GJ, Kaufmann H. Integrated analysis of droxidopa trials for neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. BMC Neurol. 2017;17(1):90.
Hauser RA, Biaggioni I, Hewitt LA, Vernino S. Integrated analysis of droxidopa for the treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in patients with Parkinson disease. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2018;5(6):627–34.
François C, Shibao CA, Biaggioni I, et al. Six-month use of droxidopa for neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2019;6(3):235–42.
Hauser RA, Heritier S, Rowse GJ, Hewitt LA, Isaacson SH. Droxidopa and reduced falls in a trial of Parkinson patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2016;39(5):220–6.
Palma JA, Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Martinez J, Kaufmann H. Supine plasma NE predicts the pressor response to droxidopa in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Neurology. 2018;91(16):e1539–44.
Chen JJ, Han Y, Tang J, Portillo I, Hauser RA, Dashtipour K. Standing and supine blood pressure outcomes associated with droxidopa and midodrine in patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a Bayesian meta-analysis and mixed treatment comparison of randomized trials. Ann Pharmacother. 2018;52(12):1182–94.
Wright RA, Kaufmann HC, Perera R, et al. A double-blind, dose-response study of midodrine in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Neurology. 1998;51(1):120–4.
Low PA, Gilden JL, Freeman R, Sheng KN, McElligott MA. Efficacy of midodrine vs placebo in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. A randomized, double-blind multicenter study. Midodrine Study Group. JAMA. 1997;277(13):1046–51.
Eschlbock S, Wenning G, Fanciulli A. Evidence-based treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension and related symptoms. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017;124(12):1567–605.
AvKARE, Inc. AvPAK (fludrocortisone acetate). Full prescribing information. Pulaski: AvKARE, Inc.; 2018.
Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC. Mestinon (pyridostigmine). Prescribing information, Bridgewater: Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC; 2013.
Shibao C, Gamboa A, Diedrich A, et al. Acarbose, an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, attenuates postprandial hypotension in autonomic failure. Hypertension. 2007;50(1):54–61.
Ricci F, De Caterina R, Fedorowski A. Orthostatic hypotension: epidemiology, prognosis, and treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66(7):848–60.
Ten Harkel AD, Van Lieshout JJ, Wieling W. Treatment of orthostatic hypotension with sleeping in the head-up tilt position, alone and in combination with fludrocortisone. J Intern Med. 1992;232(2):139–45.
Espay AJ, LeWitt PA, Hauser RA, Merola A, Masellis M, Lang AE. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension in Parkinson’s disease and related synucleinopathies: prioritisation of treatment targets. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(9):954–66.
Wieling W, Raj SR, Thijs RD. Are small observational studies sufficient evidence for a recommendation of head-up sleeping in all patients with debilitating orthostatic hypotension? MacLean and Allen revisited after 70 years. Clin Auton Res. 2009;19(1):8–12.
Jordan J, Fanciulli A, Tank J, et al. Management of supine hypertension in patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: scientific statement of the American Autonomic Society, European Federation of Autonomic Societies, and the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2019;37(8):1541–6.
Acknowledgements
Funding
Lundbeck (Deerfield, IL) provided funding for editorial support for manuscript preparation and for the Rapid Service Fee. This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health (NS 32352 Autonomic Disorders Program Project NS 44233 Pathogenesis and Diagnosis of Multiple System Atrophy, NS 92625 Multiple System Atrophy—Novel Targets in Early Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutic Approach, U54 NS065736 Autonomic Rare Disease Clinical Consortium), Mayo CTSA (UL1 TR000135), and Mayo Funds.
Medical Writing, Editorial, and Other Assistance
Medical writing and editorial assistance in the preparation of this article was provided by Lauren Stutzbach, PhD, and Lisa Havran, PhD, of the CHC Group (North Wales, PA, USA). Support for this assistance was funded by Lundbeck.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published. JK Cutsforth-Gregory and PA Low contributed to all aspects of development for this review manuscript, including conception, organization, execution, drafting, review, and critique. Both authors provided final approval of the manuscript for submission.
Disclosures
Dr. Cutsforth-Gregory receives royalties for the textbook Mayo Clinic Medical Neurosciences. Dr. Low receives research support from the National Institutes of Health (P01 NS44233, U54 NS065736, R01 NS092625, and UL1 TR000135), US FDA (R01 FD004789), Cure MSA Foundation, and Mayo Funds; has served as a clinical editor of Autonomic Neuroscience; and has received honoraria from Lundbeck for serving as a consultant or on advisory boards.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced Digital Features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.9255536.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Cutsforth-Gregory, J.K., Low, P.A. Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension in Parkinson Disease: A Primer. Neurol Ther 8, 307–324 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-019-00152-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-019-00152-9