Abstract
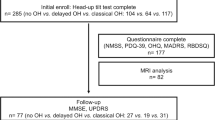
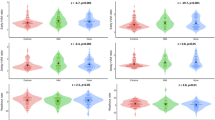
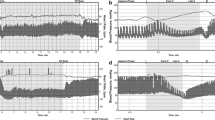
Patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) commonly have clinically significant orthostatic hypotension (OH). In such patients PD+OH might be confused with multiple system atrophy (MSA), in which OH is a frequent finding, or with pure autonomic failure (PAF), if OH preceded clinical manifestations of the movement disorder. This study addressed whether OH can occur as an early finding in PD+OH.Historical data were analyzed from 35 patients with PD+OH evaluated at the NIH. OH was considered early if the patient had OH before, concurrent with, or starting within 1 year after onset of a symptomatic movement disorder. MSA was excluded by myocardial 6-[18F]fluorodopamine-derived radioactivity more than 2 standard deviations below the normal mean. Among the 35 PD+OH patients, 21 (60 %) had documentation of OH as an early finding. In 4 such patients, OH had preceded parkinsonism, and in 4 others, OH had dominated the early clinical picture, even after cessation of levodopa treatment for the movement disorder. In PD, OH can occur early in the disease, occasionally preceding or overshadowing the movement disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akincioglu C, Unlu M, Tunc T (2003) Cardiac innervation and clinical correlates in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Nucl Med Commun 24:267–71
Allcock LM, Ullyart K, Kenny RA, Burn DJ (2004) Frequency of orthostatic hypotension in a community based cohort of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1470–471
Amino T, Orimo S, Takahashi A, Uchihara T, Mizusawa H (2005) Profound cardiac sympathetic denervation occurs in Parkinson disease. Brain Path 15:29–4
Arai K, Kato N, Kashiwado K, Hattori T (2000) Pure autonomic failure in association with human alpha-synucleinopathy. Neurosci Lett 296:171–73
Awerbuch GI, Sandyk R (1992) Autonomic functions in the early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Neurosci 64:7–4
Bellon AK, Jost WH, Schimrigk K, Konig J, Zeppezauer M (1996) Blood pressure adaptation and hormone regulation in Parkinson patients following orthostasis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 121:1077–083
Benarroch EE, Schmeichel AM, Parisi JE (2000) Involvement of the ventrolateral medulla in parkinsonism with autonomic failure. Neurology 54:963–68
Berding G, Schrader CH, Peschel T, Van Den Hoff J, Kolbe H, Meyer GJ, Dengler R, Knapp WH (2003) N-methyl (11)C]meta-Hydroxyephedrine positron emission tomography in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30:127–31
Bhattacharya KF, Nouri S, Olanow CW, Yahr MD, Kaufmann H (2003) Selegiline in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: its impact on orthostatic hypotension. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 9:221–24
Biaggioni I, Robertson RM (2002) Hypertension in orthostatic hypotension and autonomic dysfunction. Cardiol Clin 20:291–01
Bonuccelli U, Lucetti C, Del Dotto P, Ceravolo R, Gambaccini G, Bernardini S, Rossi G, Piaggesi A (2003) Orthostatic hypotension in de novo Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 60:1400–404
Bradbury S, Eggleston C (1927) Postural hypotension; an autopsy upon a case. Am Heart J 3:105–06
Braune S (2001) The role of cardiac metaiodobenzylguanidine uptake in the differential diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes. Clin Auton Res 11:351–55
Braune S, Reinhardt M, Bathmann J, Krause T, Lehmann M, Lucking CH (1998) Impaired cardiac uptake of meta-[123I]iodobenzylguanidine in Parkinson’s disease with autonomic failure. Acta Neurol Scand 97:307–14
Braune S, Reinhardt M, Schnitzer R, Riedel A, Lucking CH (1999) Cardiac uptake of [123I]MIBG separates Parkinson’s disease from multiple system atrophy. Neurology 53:1020–025
Briebach T, Baas H, Fischer PA (1990) Orthostatic dysregulation in Parkinson syndrome. Results of a study of 250 patients. Nervenarzt 61:491–94
Courbon F, Brefel-Courbon C, Thalamas C, Alibelli MJ, Berry I, Montastruc JL, Rascol O, Senard JM (2003) Cardiac MIBG scintigraphy is a sensitive tool for detecting cardiac sympathetic denervation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18:890–97
Den Hartog Jager W, Bethlem J (1960) The distribution of Lewy bodies in the central and autonomic nervous system in idiopathic paralysis agitans. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:283–90
Druschky A, Hilz MJ, Platsch G, Radespiel-Troger M, Druschky K, Kuwert T, Neundorfer B (2000) Differentiation of Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy in early disease stages by means of I-123-MIBG-SPECT. J Neurol Sci 175:3–2
Evans DJ, Lewis PD, Malhotra O, Pallis C (1972) Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension. Report of an autopsied case with histochemical and ultrastructural studies of the neuronal inclusions. J Neurol Sci 17:209–18
Fichefet JP, Sternon JE, Franken L, Demanet JC, Vanderhaeghen JJ (1965) Anatomoclinical study of a case of “idiopathic” orthostatic hypotension, Pathogenic considerations. Acta Cardiol 20:332–48
Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S (1999) Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 56:33–9
Goldstein DS, Eisenhofer G, Dunn BB, Armando I, Lenders J, Grossman E, Holmes C, Kirk KL, Bacharach S, Adams R, Herscovitch P, Kopin IJ (1993) Positron emission tomographic imaging of cardiac sympathetic innervation using 6-[18F]fluorodopamine: initial findings in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol 22:1961–971
Goldstein DS, Holmes C, Cannon RO, III, Eisenhofer G, Kopin IJ (1997) Sympathetic cardioneuropathy in dysautonomias. N Engl J Med 336:696–02
Goldstein DS, Holmes C, Dendi R, Bruce S, Li S-T (2002) Orthostatic hypotension from sympathetic denervation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 58:1247–255
Goldstein DS, Holmes C, Li ST, Bruce S, Metman LV, Cannon RO (2000) Cardiac sympathetic denervation in Parkinson disease. Ann Intern Med 133:338–47
Goldstein DS, Pechnik S,Holmes C, Eldadah B, Sharabi Y (2003) Association between supine hypertension and orthostatic hypotension in autonomic failure. Hypertension 42:136–42
Goldstein DS, Polinsky RJ, Garty M, Robertson D, Brown RT, Biaggioni I, Stull R, Kopin IJ (1989) Patterns of plasma levels of catechols in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Ann Neurol 26:558–63
Graham JG, Oppenheimer DR (1969) Orthostatic hypotension and nicotine sensitivity in a case of multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 32:28–4
Hague K, Lento P, Morgello S, Caro S, Kaufmann H (1997) The distribution of Lewy bodies in pure autonomic failure: autopsy findings and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 94:192–96
Hamada K, Hirayama M, Watanabe H, Kobayashi R, Ito H, Ieda T, Koike Y, Sobue G (2003) Onset age and severity of motor impairment are associated with reduction of myocardial 123-I-MIBG uptake in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:423–26
Hillen ME, Wagner ML, Sage JI (1996) “Subclinical–orthostatic hypotension is associated with dizziness in elderly patients with Parkinson disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 77:710–12
Hoehn MM (1975) Levodopa-induced postural hypotension. Treatment with fludrocortisone. Arch Neurol 32:50–1
Holmberg B, Kallio M, Johnels B, Elam M (2001) Cardiovascular reflex testing contributes to clinical evaluation and differential diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndromes. Mov Disord 16:217–25
Hubble JP, Koller WC, Cutler NR, Sramek JJ, Friedman J, Goetz C, Ranhosky A, Korts D, Elvin A (1995) Pramipexole in patients with early Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 18:338–47
Iwanaga K, Wakabayashi K, Yoshimoto M, Tomita I, Satoh H, Takashima H, Satoh A, Seto M, Tsujihata M, Takahashi H (1999) Lewy body-type degeneration in cardiac plexus in Parkinson’s and incidental Lewy body diseases. Neurology 52:1269–271
Iwasa K, Nakajima K, Yoshikawa H, Tada A, Taki J, Takamori M (1998) Decreased myocardial 123I-MIBG uptake in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 97:303–06
Jimenez-Hoyuelaa JM, Rebollo AC, Campos V, Rius F (2003) 123I-MIBG myocardial sympathetic innervation scintigraphy and Parkinson’s disease. Preliminary results. Rev Esp Med Nucl 22:229–37
Johnson RH, Lee Gde J, Oppenheimer DR, Spalding JM (1966) Autonomic failure with orthostatic hypotension due to intermediolateral column degeneration. A report of two cases with autopsies. Q J Med 35:276–92
Kato S, Oda M, Hayashi H, Shimizu T, Hayashi M, Kawata A, Tanabe H (1995) Decrease of medullary catecholaminergic neurons in multiple system atrophy and Parkinson’s disease and their preservation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 132:216–21
Kaufmann H (1996) Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure and multiple system atrophy. Clin Auton Res 6:125–26
Kaufmann H, Nahm K, Purohit D, Wolfe D (2004) Autonomic failure as the initial presentation of Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 63:1093–095
Kluyskens Y, Bossaert L, Snoeck J, Martin JJ (1977) Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension and the Shy and Drager syndrome; Physiological studies in four cases; pathological report of one case. Acta Cardiol 32:317–35
Kopin IJ, Polinsky RJ, Oliver JA, Oddershede IR, Ebert MH (1983) Urinary catecholamine metabolites distinguish different types of sympathetic neuronal dysfunction in patients with orthostatic hypotension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 57:632–37
Korchounov A, Kessler KR, Schipper HI (2004) Differential effects of various treatment combinations on cardiovascular dysfunction in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 109:45–1
Krygowska-Wajs A, Furgala A, Laskiewicz J, Szczudlik A, Thor PJ (2002) Early diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension in idopathic Parkinson’s disease. Folia Med Cracov 43:59–7
Kujawa K, Leurgans S, Raman R, Blasucci L, Goetz CG (2000) Acute orthostatic hypotension when starting dopamine agonists in Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 57:1461–463
Kuroiwa Y, Shimada Y, Toyokura Y (1983) Postural hypotension and low R-R interval variability in parkinsonism, spino-cerebellar degeneration, and Shy-Drager syndrome. Neurology 33:463–67
Linden D, Diehl RR, Berlit P (1997) Sympathetic cardiovascular dysfunction in long-standing idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Clin Auton Res 7:311–14
Litvan I, Goetz CG, Jankovic J, Wenning GK, Booth V, Bartko JJ, McKee A, Jellinger K, Lai EC, Brandel JP, Verny M, Chaudhuri KR, Pearce RK, Agid Y (1997) What is the accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of multiple system atrophy? A clinicopathologic study. Arch Neurol 54:937–44
Loew F, Gauthey L, Koerffy A, Herrmann FR, Estade M, Michel JP, Vallotton MB (1995) Postprandial hypotension and orthostatic blood pressure responses in elderly Parkinson’s disease patients. J Hypertens 13:1291–297
Magalhaes M, Wenning GK, Daniel SE, Quinn NP (1995) Autonomic dysfunction in pathologically confirmed multiple system atrophy and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease—a retrospective comparison. Acta Neurol Scand 91:98–02
Martignoni E, Pacchetti C, Godi L, Micieli G, Nappi G (1995) Autonomic disorders in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Suppl 45):11–9
Micieli G, Martignoni E, Cavallini A, Sandrini G, Nappi G (1987) Postprandial and orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 37:386–93
Miura H, Tsuchiya K, Kubodera T, Shimamura H, Matsuoka T (2001) An autopsy case of pure autonomic failure with pathological features of Parkinson’s disease. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 41:40–4
Nagayama H, Hamamoto M, Ueda M, Nagashima J, Katayama Y (2005) Reliability of MIBG myocardial scintigraphy in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:249–51
Nick J, Contamin F, Escourolle R, Guillard A, Marcantoni JP (1967) Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension with a complex neurological syndrome of extrapyramidal predominance. Rev Neurol (Paris) 116:213–27
Nishie M, Mori F, Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Yoshimoto M, Iwatsubo T, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2004) Accumulation of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein in the brain and peripheral ganglia of patients with multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 107:292–98
Nylin G, Levander M (1948) Studies on the circulation with the aid of tagged erythrocytes in a case of orthostatic hypotension (asympathicotonic hypotension). Ann Intern Med 28:723–46
Ohmura M (2000) Loss of 123I-MIBG uptake by the heart in Parkinson’s disease: assessment of cardiac sympathetic denervation and diagnostic value. J Nucl Med 41:1594–595
Orimo S, Amino T, Itoh Y, Takahashi A, Kojo T, Uchihara T, Tsuchiya K, Mori F, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2005) Cardiac sympathetic denervation precedes neuronal loss in the sympathetic ganglia in Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl)
Orimo S, Oka T, Miura H, Tsuchiya K, Mori F, Wakabayashi K, Nagao T, Yokochi M (2002) Sympathetic cardiac denervation in Parkinson’s disease and pure autonomic failure but not in multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:776–77
Orimo S, Ozawa E,Nakade S, Sugimoto T, Mizusawa H (1999) (123)Imetaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:189–94
Orimo S, Ozawa E, Oka T, Nakade S, Tsuchiya K, Yoshimoto M, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2001) Different histopathology accounting for a decrease in myocardial MIBG uptake in PD and MSA. Neurology 57:1140–141
Papapetropoulos S, Paschalis C, Athanassiadou A, Papadimitriou A, Ellul J, Polymeropoulos MH, Papapetropoulos T (2001) Clinical phenotype in patients with alpha-synuclein Parkinson’s disease living in Greece in comparison with patients with sporadic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70:662–65
Polinsky RJ, Goldstein DS, Brown RT, Keiser HR, Kopin IJ (1985) Decreased sympathetic neuronal uptake in idiopathic orthostatic hypotension. Ann Neurol 18:48–3
Polinsky RJ, Jimerson DC, Kopin IJ (1984) Chronic autonomic failure: CSF and plasma 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol. Neurology 34:979–83
Polinsky RJ, Kopin IJ, Ebert MH, Weise V (1981) Pharmacologic distinction of different orthostatic hypotension syndromes. Neurology 31:1–
Rajput AH, Rozdilsky B (1976) Dysautonomia in Parkinsonism: a clinicopathological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 39:1092–100
Reinhardt MJ, Jungling FD, Krause TM, Braune S (2000) Scintigraphic differentiation between two forms of primary dysautonomia early after onset of autonomic dysfunction: value of cardiac and pulmonary iodine-123 MIBG uptake. Eur J Nucl Med 27:595–00
Roessmann U, Van den Noort S, McFarland DE (1971) Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension. Arch Neurol 24:503–10
Saiki S, Hirose G, Sakai K, Kataoka S, Hori A, Saiki M, Kaito M, Higashi K, Taki S, Kakeshita K, Fujino S, Miaki M (2004) Cardiac 123I-MIBG scintigraphy can assess the disease severity and phenotype of PD. J Neurol Sci 220:105–11
Saito F, Tsuchiya K, Kotera M (1992) An autopsied case of Parkinson’s disease manifesting Shy-Drager syndrome. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 32:1238–244
Sandyk R, Awerbuch GI (1992) Dysautonomia in Parkinson’s disease: relationship to motor disability. Int J Neurosci 64:23–1
Satoh A, Serita T, Seto M, Tomita I, Satoh H, Iwanaga K, Takashima H, Tsujihata M (1999) Loss of 123I-MIBG uptake by the heart in Parkinson’s disease: assessment of cardiac sympathetic denervation and diagnostic value. J Nucl Med 40:371–75
Satoh A, Serita T, Tsujihata M (1997) Total defect of metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) imaging on heart in Parkinson’s disease: assessment of cardiac sympathetic denervation. Nippon Rinsho 55:202–06
Schober R, Langston JW, Forno LS (1975) Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension. Biochemical and pathologic observations in 2 cases. Eur Neurol 13:177–88
Schwarz GA (1967) The orthostatic hypotension syndrome of Shy-Drager. A clinicopathologic report. Arch Neurol 16:123–39
Senard JM, Brefel-Courbon C, Rascol O, Montastruc JL (2001) Orthostatic hypotension in patients with Parkinson’s disease: pathophysiology and management. Drugs Aging 18:495–05
Senard JM, Rai S, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Brefel C, Rascol O, Rascol A, Montastruc JL (1997) Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:584–89
Shannon JR, Jordan J, Diedrich A, Pohar B, Black BK, Robertson D, Biaggioni I (2000) Sympathetically mediated hypertension in autonomic failure. Circulation 101:2710–715
Shy GM, Drager GA (1960) A neurological syndrome associated with orthostatic hypotension: a clinicalpathologic study. Arch Neurol 2:511–27
Takatsu H, Nagashima K, Murase M, Fujiwara H, Nishida H, Matsuo H, Watanabe S, Satomi K (2000) Differentiating Parkinson’s disease from multiple-system atrophy by measuring cardiac iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine accumulation. JAMA 284:44–5
Takatsu H, Nishida H, Matsuo H, Watanabe S, Nagashima K, Wada H, Noda T, Nishigaki K, Fujiwara H (2000) Cardiac sympathetic denervation from the early stage of Parkinson’s disease: clinical and experimental studies with radiolabeled MIBGJ Nucl Med 41:71–7
Takeda S, Yamazaki K, Miyakawa T, Arai H (1993) Parkinson’s disease with involvement of the parasympathetic ganglia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 86:397–98
Taki J, Nakajima K, Hwang EH, Matsunari I, Komai K, Yoshita M, Sakajiri K, Tonami N (2000) Peripheral sympathetic dysfunction in patients with Parkinson’s disease without autonomic failure is heart selective and disease specific. Eur J Nucl Med 27:566–73
Terao Y, Takeda K, Sakuta M, Nemoto T, Takemura T, Kawai M (1993) Pure progressive autonomic failure: a clinicopathological study. Eur Neurol 33:409–15
Thaisetthawatkul P, Boeve BF, Benarroch EE, Sandroni P, Ferman TJ, Petersen R, Low PA (2004) Autonomic dysfunction in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 62:1804–809
Thapedi IM, Ashenhurst EM, Rozdilsky B (1971) Shy-Drager syndrome. Report of an autopsied case. Neurology 21:26–2
Tranchant C, Guiraud-Chaumeil C, Echaniz-Laguna A, Warter JM (2000) Is clonidine growth hormone stimulation a good test to differentiate multiple system atrophy from idiopathic Parkinson’s disease? J Neurol 247:853–56
Turkka J, Suominen K, Tolonen U, Sotaniemi K, Myllyla VV (1997) Selegiline diminishes cardiovascular autonomic responses in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 48:662–67
van Dijk JG, Haan J, Zwinderman K, Kremer B, van Hilten BJ, Roos RA (1993) Autonomic nervous system dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: relationships with age, medication, duration, and severity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56:1090–095
van Ingelghem E, van Zandijcke M, Lammens M (1994) Pure autonomic failure: a new case with clinical, biochemical, and necropsy data. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:745–47
Vanderhaeghen JJ, Perier O, Sternon JE (1970) Pathological findings in idiopathic orthostatic hypotension. Its relationship with Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 22:207–14
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (1997) Neuropathology of autonomic nervous system in Parkinson’s disease. Eur Neurol 38(Suppl 2):2–
Wenning GK, Scherfler C, Granata R, Bosch S, Verny M, Chaudhuri KR, Jellinger K, Poewe W, Litvan I (1999) Time course of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension and urinary incontinence in patients with postmortem confirmed parkinsonian syndromes: a clinicopathological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:620–23
Yoshita M, Hayashi M, Hirai S (1998) Decreased myocardial accumulation of 123I-meta-iodobenzyl guanidine in Parkinson’s disease. Nucl Med Commun 19:137–42
Yoshita M, Hayashi M, Hirai S (1997) Iodine 123-labeled meta-iodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy in the cases of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease,multiple system atrophy, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 37:476–82
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldstein, D.S. Orthostatic hypotension as an early finding in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Auton Res 16, 46–54 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-006-0317-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-006-0317-8