Abstract
Symptomatic treatment options for Parkinson disease have steadily improved, and individualized therapeutic approaches are becoming established for every stage of the disease. However, disease-modifying therapy with a causal approach is still unavailable. The central causative role of alpha-synuclein pathology, including its progressive spread to most areas of the CNS, has been widely recognized, and a strong involvement of immune responses has recently been discovered. New immunologic technologies have been shown to effectively prevent the progression of alpha-synuclein pathology in animal models. These approaches have recently been translated into the first human clinical trials, representing a novel starting point for the causal therapy of Parkinson disease. In this review, the pathomechanistic role of alpha-synuclein and its influence on the surrounding cellular environment are analyzed with a strong focus on immune responses and neuroinflammation. The potential of novel immunotherapeutic approaches that reduce the burden of alpha-synuclein pathology in the CNS is critically evaluated, and currently ongoing human clinical trials are presented. The clinical development of these new immunotherapies is progressing rapidly and gives reason to hope that a causal therapy of Parkinson disease could be possible in the foreseeable future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Parkinson disease (PD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer disease (AD) and is neuropathologically characterized by nigrostriatal dopaminergic degeneration and the presence of aggregated and misfolded alpha-synuclein (aSyn). In clinical examination, PD patients show motor deficits such as bradykinesia, rigidity, tremor and postural instability, which reflect the degeneration of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and impairment of DA neurotransmission to basal ganglia motor circuits. The accompanying heavy burden of non-motor symptoms such as autonomic failure, daytime sleepiness, cognitive deficits, or even psychiatric alterations indicates the involvement of other CNS neurotransmitter systems [1].
As the main neuropathologic culprit, aSyn has been identified in humans and was found to be located in aSyn-immunopositive Lewy neurites and Lewy bodies. Several human postmortem studies have demonstrated that not only the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system is affected in PD but that—depending on the (prodromal) disease stage—also Lewy pathology can be early found in the peripheral autonomic nervous system, including neurons of the enteric plexus of the gastrointestinal tract, paravertebral autonomic ganglia and sympathetic nerve fibers in the adrenal gland and heart and in cutaneous nerves. In subsequent disease stages, the medulla, pons, midbrain, diencephalon, basal forebrain, amygdala, olfactory bulb, limbic cortex and finally higher order association cortices can be involved, too [1,2,3].
Thus, the extent of aSyn pathology is not a stable state but seems to progress in a prion-like cell-to-cell spreading to continuously involve further neuronal and non-neuronal cells—a disease propagation process that is also discussed for other neurodegenerative diseases in a similar way [4]. Importantly, aSyn-associated neurodegeneration is accompanied by neuroinflammatory features, which highlights the role of aSyn for the immune system and non-neuronal cells [5, 6]. As much as this spread of the disease in the CNS proves its aggressive character, there are also possibilities for new therapeutic approaches. A very obvious one is to interfere with disease dissemination and eliminate excess or toxic compounds of aSyn that are located extracellularly and therefore are readily accessible to therapeutic approaches.
In this review, we will describe the properties of aSyn and its pathophysiologic implications, in particular regarding its activation of cellular neuroinflammatory cascades. Thus, a clear rationale opens up to counteract this vicious circle by controlling the spread of disease with the help of immunologic, antibody-based technologies. The potential of these active and passive immunotherapies is presented from the fundamental scientific side as well as from recent human clinical data. Current knowledge is critically evaluated with the goal to provide a timely review on immunotherapies for PD for both the clinician and basic scientist. This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Alpha-Synuclein and its Role in the Pathogenesis of PD
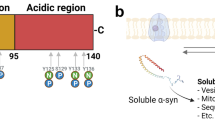
Alpha-synuclein is a soluble and cytoplasmic protein of 140-amino-acid (aa) length consisting of three domains: an amphipathic N-terminal region (1–65 aa), a non-amyloid-β component (NAC) region (66–95 aa) and a C-terminal domain (96–140 aa) [7]. In the CNS, aSyn is predominately expressed in neurons of the thalamus, basal ganglia and substantia nigra [8] but also in the peripheral nervous system in blood cells and in platelets [9, 10].
In human neuropathology, aggregated aSyn represents the main component of so-called Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites, which are intraneuronal filamentous inclusions and are located in perikarya or neurites, respectively, of degenerating DA neurons in PD patients [8, 11, 12]. In familial Parkinson disease, rare human genetic alterations occur mostly as point mutations in aSyn (A30P, E46 K, H50Q, G51D, A53E and A53T) or as gene duplications and triplications that cause autosomal-recessive or -dominant forms of PD [13].
The function of aSyn in neurons is only incompletely understood, but it is known to play an important role in neurotransmitter release, synaptic plasticity and synaptic vesicle recycling [7, 14, 15]. aSyn is stored in presynaptic nerve terminals and mediates synaptic vesicle fusion with soluble NSF attachment protein (SNARE) complex assemblies and via direct interaction with syntaxin-1, SNAP-25 and vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 (VAMP2)/synaptobrevin-2 [15,16,17]. This enables synaptic vesicle trafficking from the ready releasable pool to the presynaptic active zone where the content of the synaptic vesicles is secreted. In case of aSyn accumulation, the neurotransmitter release, vesicle trafficking, recycling and SNARE complex stability are all affected and thus severely impair synaptic function of dopaminergic neurons [16,17,18,19].
Under physiologic conditions, wild-type aSyn is a natively soluble unfolded monomer, which binds to curved membranes such as synaptic vesicles and regulates the above-mentioned SNARE-complex chaperoning function. Under pathologic circumstances with changes in pH level or oxidative stress, aSyn can convert to insoluble and aggregated forms that are enriched in β-sheets and assemble into oligomeric and fibrillar structures. These forms of aSyn have a strong pathogenic potential and may harm several physiologic functions of the cell [15, 20, 21].
Importantly, aSyn can be released from intracellular compartments to the extracellular space. From there it may propagate to other neuronal or glial cells in which it elicits pathogenic cascades that impair their cellular function. Concerning these aSyn propagation mechanisms, three main principles are known. First, in healthy neurons a non-classical ER-/Golgi-independent protein export pathway can be used whereby aSyn can be directly integrated into secretory vesicles and subsequently released by exocytosis. Second, aSyn vesicles can be translocated into early endosomes and then be released to the extracellular space through recycling endosomes. As a third alternative, early endosomal aSyn can be incorporated to intraluminal vesicles that are part of the so-called multivesicular bodies (MVB). These can undergo a degradative process after fusion with lysosomes or directly secrete by fusion with the plasma membrane [22]. Several in vitro and in vivo animal studies have shown that especially oligomeric aSyn directly confers toxic effects to surrounding cells, whether they are neuronal or non-neuronal glial cells.
Concerning direct effects of aggregated aSyn onto neuronal cells, several in vitro studies have been performed. Primary hippocampal neuronal cells readily internalized exogenous preformed fibrils of artificial recombinant aSyn if provided in the cell culture medium. In the cytoplasm, these exogenous fibrils recruited endogenous aSyn and induced pathologic misfolded aSyn, which was phosphorylated, ubiquitinated and aggregated to insoluble fibrils. Similarly to human PD, a LN-like pathology developed, first located in axons, and was then propagated to form LB-like inclusions in the cell perikarya [23, 24]. The axonal protein accumulation was preceded by axonal transport alterations with an initial predominant anterograde direction of aSyn, being similar to the amyloid-beta1-42 form but different from the processing of huntingtin protein fragments [25]. Accumulating pathologic aSyn then led to selective decreases in synaptic proteins, progressive impairments in neuronal excitability and connectivity and finally neuronal death. Interestingly, endogenous aSyn was sufficient for the formation of these aggregates, and overexpression of wild-type or mutant aSyn was not necessarily required. A frequently observed uptake mechanism of aSyn could be attributed to absorptive-mediated endocytosis [23, 24]. More recent findings have shown that aSyn uptake is in part also cell surface receptor mediated utilizing the protein product of lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG3) [26], which is expressed not only by neuronal cells but also microglia [27]. The underlying mechanism here seems to be a temporary inhibition of the NMDA receptor making it obvious that aSyn-mediated impairment of cellular function is not only restricted to dopaminergic neurons [28].
To evaluate direct aSyn toxicity in vivo, a route of administration in animals has been the direct injection of various aggregated seeds into the substantia nigra of wild-type rats. This resulted in a progressive motor impairment and cell death with fibrils being the major toxic strain. Here, ribbons caused a histopathologic phenotype similar to human PD neuropathology [29]. These findings indicate that distinct aSyn strains display differential seeding capacities. Interestingly, aSyn assemblies also crossed the blood-brain barrier and distributed to the central nervous system after intravenous injection [29]. In another study, Luk et al. used wild-type mice that were unilaterally injected with recombinant aSyn into the dorsal striatum. At different time points, an increasing spread of Lewy bodies was observed, and although aSyn was only injected into one hemisphere, after several days Lewy bodies were also detected on the contralateral hemisphere and in diverse brain regions including the hippocampus [30]. Viral-mediated overexpression of wild-type and transgenic aSyn injected into the substantia nigra in mice severely damaged nigral dopaminergic cells and its axons. Importantly, also the intrinsic regenerative capacity of dopaminergic neurons is significantly impaired if dopamine neurons suffer from aSyn overload [31].
Extracellular aSyn has a strong impact on glial cells and there can elicit a variety of immunologic responses. Glial cells are by far the largest cell population, accounting for more than 50% of all cells in the brain, and thus comprise about 1000 billion cells [32]. They differentiate in the CNS, where they are collectively referred to as neuroglia, consisting of astroglia, microglia and oligodendroglia.
Astroglia account for by far the largest share of glial cells and perform many tasks essential to the survival of neurons. They ensure structural and metabolic cerebral homeostasis, regulate synaptic transmission, water transport and blood flow, and myelination and produce neurotrophic molecules such as GDNF [33]. Experiments with human ESC-derived astrocytes have demonstrated that these cells actively transferred aggregated aSyn to healthy astrocytes via direct contact and tunneling nanotubes in a propagating manner instead of degrading them [34]. The intracellularly accumulated aSyn affected the lysosomal machinery and induced mitochondrial damage. This elicited further internal proinflammatory responses and caused cellular death [22, 35]. The aSyn-induced impairments of astrocyte function could be alleviated by an application of oligomer-selective anti-aSyn antibodies [36].
Microglial cells represent the innate immune system of the CNS. Precursor cells migrate into the CNS already during the prenatal phase. Microglia account for approximately 10–20% of the total glia population [37]. The physiological function of CNS-resident microglia involves the maintenance of homeostasis through ongoing monitoring of the CNS environment and, if necessary, phagocytosis or pinocytosis of degradation products or cell debris [38]. Microglial cells have been shown to be able to directly engulf aSyn attempting to clear it from the extracellular space. This response was strongly dependent on its aggregation state [39]. Distinct oligomeric forms but not monomers or fibrils of aSyn interacted with microglial toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and activated the TLR2 signaling pathway [40] leading to increased production of neurotoxic ROS [41].
To reduce increased levels of harmfully aggregated extracellular but also endogenous aSyn, a clearing process of the protein has to be established. This can be achieved with immunotherapies using vaccination strategies or antibodies directed against aSyn [42]. If extracellular levels of aSyn decrease, the spread to other neuronal and non-neuronal cells such as astroglia or microglia will be reduced and ultimately prevent pathologic inflammatory activation [42, 43]. Other aSyn degradative processes are mediated through ubiquitination, lysosomal degradation by macroautophagy or chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) [7]. In the next section, we will present the current state of research in the first PD immunotherapies, which all have the goal of a causal disease modification in humans. Findings from animal studies and recent human clinical trials will be compared.
Alpha-synuclein as Target for Immunization Strategies
Immunotherapies against aSyn currently appear to be a very promising therapeutic approach for the modification of disease progression in the treatment of PD patients with early stage disease [44, 45]. The aim of these therapies is to reduce the load of extracellular aSyn and thereby halt the spread of aSyn in the brain. There are two principal forms of anti-aSyn immunotherapy: active immunization or vaccination, which employ the immune system to self-generate antibodies against aSyn, and passive immunization, which is achieved by the administration of antibodies directed against different domains of aSyn [46]. In the subsequent part we will discuss recent data from active and passive immunization therapies in animal models and human clinical trials.
Active Immunization Strategies
Animal Models
A seminal study in which an active immunization against aSyn was performed in animals in vivo was published already in 2005. Masliah et al. used transgenic mice overexpressing human aSyn under control of the platelet-derived growth factor-β promoter (PDGF-β promoter). In this animal model, mice have aSyn aggregations in neurons throughout various regions of the brain (the cortex, hippocampus and olfactory system), thus mimicking human Lewy body neuropathology [47]. Mice were immunized with purified recombinant human aSyn expressed in E. coli. The vaccination led to a production of antibodies with high affinity to aSyn. Immunized mice showed reduced aSyn aggregation in neuronal cell bodies and synapses with decreased neurodegeneration [48, 49]. The authors hypothesized an increased degradation of aggregated aSyn via lysosomal pathways, which was supported by colocalization of human aSyn and the lysosomal marker cathepsin D. Furthermore, they observed only a rather mild activation of micro- and astroglia in vaccinated mice [48, 49].
Ghochikyan et al. developed another vaccination approach. They used three different fragments of aSyn fused to the epitope P30 from tetanus toxin with the aim to generate antibodies against aSyn without eliciting a harmful TH cell response. Wild-type mice were immunized with the different vaccines in a 2-week interval over 6 weeks. This led to a strong humoral immune response whose aSyn antibodies recognized Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in brain tissue of DLB patients. In the mice, no TH cell response to aSyn was detected [50].
A third active immunization approach was the use of short aSyn peptide fragments. Mandler et al. immunized mice with a small peptide mimicking the C-terminal part of aSyn (110–130) (AFFITOPE vaccine AFF1) that induced a humoral response without eliciting a T cell autoimmune response. PDGF-aSyn and mThy1-aSyn mice were immunized with AFF1 twice a week to monthly over a 6-month period. Vaccinated mice showed an amelioration in motor function (body suspension test) and long-term memory (Water maze) as well as reduced neurodegeneration due to reduced accumulation of aSyn oligomers in axons and synapses. Furthermore, AFF1 treatment diminished astro- and microgliosis in PDGF-β aSyn mice and increased the production of antiinflammatory cytokines such as Il-1Ra, Il-2 and Il-27 [51]. In a follow-up study, AFF1 was applied to a mouse model of multiple system atrophy (MSA) in which aSyn is expressed specifically in oligodendrocytes under the control of the myelin basic protein promotor (MBP-aSyn mice). AFF 1-treated mice showed a decreased accumulation of aSyn and a reduced demyelination in the neocortex, striatum and corpus callosum. Overall, neurodegeneration and motor deficits were reduced as was disease spreading from oligodendrocytes to astrocytes. Microglia activation was stronger than in controls, which was supposed to be important for the effective clearance of aSyn [45].
A novel fourth vaccination strategy applied a combination of aSyn/Grp94 chaperone in a murine chronic MPTP model of PD. After direct immunization with aSyn/Grp94, an immune profile was observed in the peripheral system that consisted of a Th1-shifted aSyn-specific response accompanied by an immune-regulatory/Th2-skewed general phenotype. In the CNS, a strong suppression of microglial activation in the substantia nigra and striatum was observed [52]. This study indicates that remodeling even of peripheral immunity by vaccination could be a strong modifier of CNS neurodegenerative disease.
Human Clinical Trials
The active anti-aSyn vaccination strategies have so far only been studied in phase I human clinical trials. In the AFF008 study series, realized by the Austrian company AFFiRiS, a synthetic aSyn epitope called AFFITOPE® PD01A formulated with adjuvant was subcutaneously injected to patients with early PD. The study design was randomized, parallel group, single center, and the study goals were the tolerability and safety as well as immunogenicity of repeated subcutaneous (s.c.) administration of AFFITOPE® PD01A. In four consecutive studies, AFFiRiS008, 008E, 008A and 008AA, patients were randomized to receive four immunizations of either AFFITOPE® PD01A low dose (15 µg) or high dose (75 µg) (study AFF008). At screening, the average time of PD after the first diagnosis was 2.6 years. Of the 32 patients enrolled, 24 received active treatment, and 8 PD patients were left on standard of care medication serving as an observational comparison group. Twenty-one patients in the PD01A treatment groups and five in the observational group completed the entire series of studies. Patients were allowed to continue their standard of care PD medication. To extend the first observation period, an additional 12-month follow-up was added in the second study (AFF008E). In the third study (AFF008A), a booster immunization was applied after re-randomizing patients from study AFF008E into two different doses of boost agent (15 or 75 μg AFFITOPE® PD01A). In the fourth study (AFF008AA, “reboost study”), a second booster with a fixed dose of 75 μg AFFITOPE® PD01A was applied to patients who had previously been immunized altogether five times.
Overall, both doses of AFFITOPE® PD01A were well tolerated locally and systemically. No study drug-related serious adverse events (SAE) or suspected unexpected serious adverse reactions (SUSAR) occurred. The majority of adverse events (about 55%) consisted of local reactions mostly being only mild and without dose dependency. AFFITOPE® PD01A elicited a clear immune response against the peptide itself and cross-reactivity against the aSyn targeted epitope over time. The first boost immunization produced a significant effect on all analyzed titers, resulting in the maximum titers observed in all studies. An immune response was observed in 19 of 22 (86%) of the vaccinated patients. In 12 of the 19 (63%) responders, specific serum antibodies were generated. The second boost immunization had further stabilized the produced antibody titers. Altogether, a significant increase in titers against PD01A was observed over time, which translated into a humoral immune response against aSyn. Importantly, PD01-specific antibodies were also detectable in cerebrospinal fluid and were reported to bind to both oligomeric and fibrillar aSyn compared with its monomers. There was a trend in reduction of oligomeric aSyn levels in plasma as well as in cerebrospinal fluid upon treatment with PD01A at week 26. Clinical scores for PD were reported to be stable during the entire study period. However, because the study was not designed to evaluate clinical efficacy, no further data were provided. A limitation of this study series is the lack of a double-blind design. So far, no peer-reviewed publications are available [53,54,55].
In another vaccination study, a different synthetic aSyn epitope called AFFITOPE® PD03A was used. In the phase 1 AFFiRiS011 study with randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, blinded, bi-centered design, aims were to demonstrate safety, tolerability and immunogenicity in patients with early PD. At screening, the mean duration of PD after diagnosis was between 1.6 and 2.3 years. Thirty-six patients were randomized to a high dose of AFFITOPE® PD03A (75 μg), low dose (15 μg) or placebo group. Patients received fine injections, four for priming every 4 weeks and the fifth as boost immunization 9 months after the first immunization. Both doses of PD03A were locally and systemically well tolerated. Fifty-nine percent of adverse events consisted of only mild and dose-dependent local injection reactions. The immunogenicity profile in patients was judged as encouraging as patients efficiently rose one specific antibody response to aSyn [53, 54, 56].
In total, 98 patients have participated in studies investigating AFFITOPE® PD01A or PD03A and have been observed for up to 48 months (AFFITOPE® PD01A) and 12 months (AFFITOPE® PD03A), respectively. Regarding long-term safety, immunologic and clinical parameters, the results are promising. Now, the clinical efficacy has to be demonstrated in phase II studies.
Passive Immunization Strategies
Animal Models
The passive immunization approach basically consists of a transfer of anti-aSyn-directed antibodies to the CNS. In a pioneering study, a monoclonal antibody directed against the C-terminus of aSyn (9E4) was applied in transgenic mice overexpressing human wild-type aSyn under control of the PDGF-β promoter [57]. The antibody 9E4 was injected intravenously once a week over a 6-month period with a dose of 10 mg/kg bodyweight. An improved performance in the water maze as well as a reduced accumulation of calpain-cleaved aSyn in axons and synapses of cortical and hippocampal neurons was observed throughout the study [57].
The antibody 9E4 was directed against the C-terminal region of aSyn on purpose because there is evidence that the cleavage of aSyn at the C-terminal region is involved in the formation of the toxic aSyn oligomers. Cleavage of fibrillar aSyn at the C-terminus by calpain I produces fragments that match to C-terminally cleaved fragments as found in human LBs [58]. Furthermore, the expression of C-terminal truncated aSyn in mice facilitates its oligomerization and reduces dopamine levels in the striatum [59].
For this reason, another group applied a different C-terminal antibody (Ab274) in the same mouse model with weekly intraperitoneal injections. After 4 weeks of treatment, an amelioration of behavioral deficits and neurodegeneration was observed in the passively immunized group. Additionally, an increased localization of aSyn and AB274 in microglia was found. Here, the uptake of the Ab274/αSyn complex by microglia was demonstrated to be mediated via the Fcγ receptor and its transport to lysosomes in the microglial cell line (Bv2) [60].
In a third study, a transgenic Parkinson mouse model was used in which wild-type aSyn was overexpressed under control of the mThy1 promoter. This caused behavioral deficits and neuronal accumulation of aSyn in the thalamus, basal ganglia, substantia nigra and brainstem (Thy1 aSyn mice) [47, 61]. The immunization was performed with three C-terminally directed anti-aSyn antibodies, 1H7, 5C1 and 5D12, once a week over a 6-week period. The application of 1H7 and 5C1 led to a significant reduction of cleaved aSyn in the cortex and striatum resulting in an amelioration of axonal pathology and behavioral performance. Accompanying in vitro studies revealed a reduction of cell-to-cell transmission, and the antibodies inhibited the cleavage of aSyn by calpain-1. It was hypothesized that the stabilization of the C-terminal domain by 1H7 and 5C1 could protect against cleavage and thereby reduce the amount of toxic aSyn aggregation [44].
N-terminally directed anti-aSyn antibodies were also developed and have been applied in a rat model of PD. The model was generated by nigral injection of a recombinant adeno-associated viral vector expressing human wild-type aSyn under control of the CBA promoter. Intraperitoneal treatment with an anti-aSyn antibody (AB1) every 2 weeks for a total of 3 months resulted in a moderate but not significant amelioration of behavioral parameters and robust protection against the loss of nigral dopaminergic neurons. Overall, aSyn expression and microglial activation were decreased in the nigral region [62].
A second N-terminal anti-aSyn antibody (Syn303) was developed to specifically target misfolded aSyn in a mouse model with intrastriatal injections of synthetic preformed aSyn fibrils that spread in the brain and cause motor deficits and dopaminergic cell loss. The weekly intraperitoneal treatment with Syn303 up to 26 weeks inhibited the spreading of aSyn aggregates and improved behavioral deficits as well as dopaminergic cell loss [63].
Because aSyn exerts the strongest toxic effects in its aggregated conformational states, antibodies have been generated that specifically target oligomers and fibrils and avoid an impairment of physiologically needed aSyn. The Parkinson mouse model with expression of the human aSyn A30P mutant under the Thy-1 promoter leads to the formation of aSyn fibrils, which cause dopaminergic neurodegeneration and behavioral and motor deficits [64]. A weekly passive immunization of these mice with a monoclonal antibody specifically targeting the oligomeric/protofibrillar forms of aSyn (antibody mAb47) for a total of 14 weeks led to a significant decrease of pathogenic aSyn protofibrils in the spinal cord without changing the level of monomeric forms after 1 year. No differences in activation of microglia or astrocytes were found [65]. The rapid uptake of mAB47 is mediated by Fcγ receptors as was shown in H4 cells overexpressing aSyn [66].
In another approach, Thy1 aSyn mice were immunized weekly with specific antibodies (Syn-O1, Syn-O4 and Syn-F1) recognizing only oligomers and fibrils but not monomeric aSyn over 3 months. All three led to an amelioration of aSyn pathology and behavioral performance by preventing the accumulation of aSyn fibrils and related synaptic alterations. Furthermore, reduced astrogliosis and microglia activation in the hippocampus was observed [67].
Taken together, targeting aSyn by passive immunization is a very promising disease-modifying therapy in Parkinson models in vivo. An overview of animal studies with passive immunization is provided in Table 1. Consequently, this approach has been translated into human clinical trials.
Human Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have so far evaluated the safety and tolerability of ascending doses of an intravenous anti-aSyn antibody infusion in humans. The most advanced studies have already reached the clinical phase II study level and also involved PD patients.
The first aSyn-based therapeutic candidate for PD—named PRX002—was developed by Prothena and entered into clinical trials in 2015. It is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal version of the before-mentioned C-terminally directed murine monoclonal antibody 9E4. In a first single ascending-dose study in healthy volunteers, PRX002 demonstrated good safety and tolerability if intravenous infusions of 0.3, 1.0, 3.0, 10 or 30 mg/kg at maximum were applied. After a single intravenous infusion of 30 mg/kg, PRX002 antibody levels in serum rose to 578 μg/ml and, after a single intravenous infusion of 0.3 mg/kg, up to 7.6 μg/ml. The average terminal half-life across all doses was 18.2 days. Already within 1 h of PRX002 administration a significant dose-dependent reduction in free serum aSyn was observed. Total aSyn (free plus bound) increased dose dependently, presumably because of the expected change in kinetics following antibody binding [68].
Recently, the data of a multiple ascending-dose trial with PRX002 in patients with mild-to-moderate idiopathic PD (Hoehn and Yahr stages 1–3) were published. Here, participants were enrolled into six ascending-dose cohorts and were randomly assigned to receive PRX002 (0.3 mg/kg, 1.0 mg/kg, 3.0 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg or 60 mg/kg) or placebo. Three intravenous infusions of PRX002 or placebo were applied in 4-week intervals. Again, safety and tolerability data were favorable, and serum PRX002 levels increased in an approximately dose-proportional manner. Serum levels of free-to-total aSyn were significantly reduced. Mean terminal elimination half-life of the antibody was similar across all doses (10.2 days). In addition, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) data were demonstrated in this study. The mean cerebrospinal fluid PRX002 concentration increased with PRX002 dose and was approximately 0.3% relative to serum across all dose cohorts. However, no change in the level of CSF aSyn could be demonstrated, which was attributed to the relatively low affinity of the antibody for monomeric, as opposed to aggregated, forms of aSyn, which are much less abundant in CSF [69]. A phase 2, multinational study of PRX002/RO7046015 in recently diagnosed PD patients was initiated in summer 2017 in collaboration with Roche (PASADENA Study, ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03100149).
Another anti-aSyn-directed antibody that has been evaluated in a human clinical trial is the N-terminally directed BIIB054, realized by Biogen. It was developed by the Swiss biotech company Neurimmune and is a fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody. It has been isolated from B-cell lines derived from neurologically healthy individuals and is highly selective for the aggregated form of aSyn as has been shown in tissue sections and extracts from PD and DLB, but not in unaffected brains. Therefore, it binds much less of its monomeric form [70]. In a recently concluded phase 1, single ascending-dose study of BIIB054 in healthy volunteers, it was well tolerated at single doses up to 90 mg/kg and had a serum half-life of 28 days. The CSF concentrations achieved in healthy volunteers were 0.2% of those seen in plasma [71]. Single doses of BIIB054 up to 45 mg/kg were also well tolerated in PD patients, and the pharmacokinetic profile was comparable to what had been observed in healthy volunteers. In PD patients, the CSF:plasma ratio of BIIB054 was 0.4% [71]. Now, BIIB054 is being evaluated in a multinational phase 2 study with recently diagnosed PD patients (SPARK Study, ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03318523).
Two other anti-aSyn monoclonal antibodies are currently in the early stages of development. The monoclonal antibody MEDI1341 was developed by a collaboration between AstraZeneca and Takeda. It is supposed to have only a reduced immune effector function and is now entering phase 1 testing in healthy volunteers (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03272165). Another monoclonal antibody targeted at aSyn oligomers and protofibrils is BAN0805, which was developed in collaboration between Bioarctic and Abbvie. For now, there is no publicly available information regarding its development status [72]. An overview of human clinical trials with passive immunization is provided in Table 2.
Potential risks associated with the use of immunotherapy in neurodegenerative diseases have to be differentiated between active or passive immunization (see overview for AD in [73]). Active immunization therapies perform a vaccination with antigenic material—a strategy that has so far mostly been used for the prevention of infectious diseases [74]. General side reactions may consist of a local (e.g., sore arm) or systemic inflammatory reaction (e.g., low-grade fever) that disappears in a few days and in part depends on the employed vaccination adjuvant [75]. In an early AD vaccination study, there were cases of aseptic meningoencephalitis that were probably of autoimmune origin being mediated by an overwhelming Th1 helper cell stimulation [76]. Newer therapies including aSyn now employ active vaccines that avoid Th1 helper cell stimulation [55]. In the current phase I aSyn studies, there were no relevant safety and tolerability issues.
Passive immunization approaches completely bypass these issues and administer specific antibodies. Here, systemic side reactions with low-grade fever are possible, and there is a risk of allergenic reactions. Anti-amyloid-beta trials in AD have shown mixed safety results. There has been no increased risk of any adverse event, serious adverse events or death with the exception of a nearly fivefold increase in so-called amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIAs) [77]. These can present both as vasogenic edema (ARIA-E) and cerebral microhemorrhages (ARIA-H) but are supposedly associated with amyloid-beta targeting and therefore are not expected in anti-aSyn therapies.
Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Through detailed studies on patients, but also in animal models of PD, key neurodegenerative pathomechanisms of this disease have been decrypted. In addition to the damage to neuronal cells, it is now obvious that also glial cells are affected and that a strong neuroimmunologic interaction takes place with aSyn being the central player. From today’s perspective, a modulation of this cross-cell disease propagation in PD appears possible by “targeting” of aSyn.
Very elegant neuroimmunologic tools have been developed to inhibit disease spread by extracellular aSyn. The elimination of aSyn by targeted antibody-based technologies with active or passive immunization therefore seems very pragmatic. Certainly, technologic challenges, such as overcoming the blood-brain barrier or the targeted elimination of only aggregated aSyn, still need to be optimized. However, we are well on the way to providing answers to these questions as several human clinical trials with ambitious expectations are currently underway. The simultaneous application of antibody-based therapies in atypical Parkinson’s syndromes such as PSP or also Alzheimer’s disease will in any case result in important basic insights. This will, it is our firm conviction, enable new technologic advances in the immunotherapy for PD and bring about new powerful options to modify disease progression.
References
Poewe W, Seppi K, Tanner CM, Halliday GM, Brundin P, Volkmann J, et al. Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17013.
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, De Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24(2):197–211.
Klingelhoefer L, Reichmann H. Pathogenesis of Parkinson disease—the gut-brain axis and environmental factorS. NAT REV NEUROL. 2015;11(11):625–36.
Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ. A critical appraisal of the pathogenic protein spread hypothesis of neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016;17(4):251–60.
Tönges L, Metzdorf J, Zella S. Parkinson's disease and neuroinflammation—Cellular pathology, mechanisms and therapeuticoptions. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2018;86(S 01):S10–20. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0044-101608.
Chitnis T, Weiner HL. CNS inflammation and neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(10):3577–87.
Bendor JT, Logan TP, Edwards RH. The function of alpha-synuclein. Neuron. 2013;79(6):1044–66.
Braak H, del Tredici K. Neuropathological staging of brain pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease: separating the wheat from the chaff. J Parkinsons Dis. 2017;7(S1):S71–85.
Barbour R, Kling K, Anderson JP, Banducci K, Cole T, Diep L, et al. Red blood cells are the major source of alpha-synuclein in blood. Neurodegener Dis. 2008;5(2):55–9.
Doppler K, Jentschke HM, Schulmeyer L, Vadasz D, Janzen A, Luster M, et al. Dermal phospho-alpha-synuclein deposits confirm rem sleep behaviour disorder as prodromal Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;133(4):535–45.
Dauer W, Przedborski S. Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron. 2003;39(6):889–909.
Baba M, Nakajo S, Tu PH, Tomita T, Nakaya K, Lee VM, et al. Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Am J Pathol. 1998;152(4):879–84.
Trinh J, Farrer M. Advances in the genetics of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013;9(8):445–54.
Burré J, Sharma M, Tsetsenis T, Buchman V, Etherton MR, Südhof TC. Alpha-synuclein promotes snare-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science. 2010;329(5999):1663–7.
Wong YC, Krainc D. Alpha-synuclein toxicity in neurodegeneration: mechanism and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 2017;23(2):1–13.
Bridi JC, Hirth F. Mechanisms, of alpha-synuclein induced synaptopathy in Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:80.
Sudhof TC. A molecular machine for neurotransmitter release: synaptotagmin and beyond. Nat Med. 2013;19(10):1227–31.
Lashuel HA, Overk CR, Oueslati A, Masliah E. The, many faces, of alpha-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14(1):38–48.
Sudhof TC. The presynaptic active zone. Neuron. 2012;75(1):11–25.
Bergstrom AL, Kallunki P, Fog K. Development, of passive immunotherapies for synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2016;31(2):203–13.
Burre J, Sharma M, Sudhof TC. Definition of a molecular pathway mediating alpha-synuclein neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 2015;35(13):5221–32.
Marques O, Outeiro TF. Alpha-synuclein: from secretion to dysfunction and death. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:E350.
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Patel TP, Tanik SA, Riddle DM, Stieber A, et al. Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils induce lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron. 2011;72(1):57–71.
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Lee VM. Addition, of exogenous alpha-synuclein preformed fibrils to primary neuronal cultures to seed recruitment of endogenous alpha-synuclein to lewy body and lewy neurite-like aggregates. Nat Protoc. 2014;9(9):2135–46.
Brahic M, Bousset L, Bieri G, Melki R, Gitler AD. Axonal transport and secretion of fibrillar forms of alpha-synuclein, ABETA42 peptide and httexon 1. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131(4):539–48.
Mao X, Ou MT, Karuppagounder SS, Kam TI, Yin X, Xiong Y, et al. Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiated by binding lymphocyte-activation gene 3. Science. 2016;353(6307):aah3374.
Zhang Y, Chen K, Sloan SA, Bennett ML, Scholze AR, O’Keeffe S, et al. An RNA-sequencing transcriptome and splicing database of glia, neurons, and vascular cells of the cerebral cortex. J Neurosci. 2014;34(36):11929–47.
Diogenes MJ, Dias RB, Rombo DM, Vicente Miranda H, Maiolino F, Guerreiro P, et al. Extracellular alpha-synuclein oligomers modulate synaptic transmission and impair LTP via NMDA-receptor activation. J Neurosci. 2012;32(34):11750–62.
Peelaerts W, Bousset L, van der Perren A, Moskalyuk A, Pulizzi R, Giugliano M, et al. Alpha-synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature. 2015;522(7556):340–4.
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, et al. Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science. 2012;338(6109):949–53.
Tonges L, Szego EM, Hause P, Saal KA, Tatenhorst L, Koch JC, et al. Alpha-synuclein mutations impair axonal regeneration in models of Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:239.
Herculano-Houzel S. The human brain in numbers: a linearly scaled-up primate brain. Front Hum Neurosci. 2009;3:31.
Sofroniew MV, Vinters HV. Astrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;119(1):7–35.
Rostami J, Holmqvist S, Lindstrom V, Sigvardson J, Westermark GT, Ingelsson M, et al. Human astrocytes transfer aggregated alpha-synuclein via tunneling nanotubes. J Neurosci. 2017;37(49):11835–53.
Dexter DT, Jenner P. Parkinson disease: from pathology to molecular disease mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;62:132–44.
Gustafsson G, Lindstrom V, Rostami J, Nordstrom E, Lannfelt L, Bergstrom J, et al. Alpha-synuclein oligomer-selective antibodies reduce intracellular accumulation and mitochondrial impairment in alpha-synuclein exposed astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):241.
Soulet D, Rivest S. Microglia. Curr Biol. 2008;18(12):R506–8.
Wolf SA, Boddeke HW, Kettenmann H. Microglia in physiology and diseaSE. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017;79:619–43.
Hoffmann A, Ettle B, Bruno A, Kulinich A, Hoffmann AC, Von Wittgenstein J, et al. Alpha-synuclein activates BV2 microglia dependent on its aggregation state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;479(4):881–6.
Kim C, Ho DH, Suk JE, You S, Michael S, Kang J, et al. Neuron-released oligomeric alpha-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1562.
Hoenen C, Gustin A, Birck C, Kirchmeyer M, Beaume N, Felten P, et al. Alpha-synuclein proteins promote pro-inflammatory cascades in microglia: stronger effects of the A53T mutant. PLoS One. 2016;11(9):E0162717.
Bergström AL, Kallunki P, Fog K. Development, of passive immunotherapies for synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2016;31(2):203–13.
Bruck D, Wenning GK, Stefanova N, Fellner L. Glia and alpha-synuclein in neurodegeneration: a complex interaction. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;85:262–74.
Games D, Valera E, Spencer B, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Adame A, et al. Reducing C-TERMINAL-truncated alpha-synuclein by immunotherapy attenuates neurodegeneration and propagation in Parkinson’s disease-like models. J Neurosci. 2014;34(28):9441–54.
Mandler M, Valera E, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Weninger H, Patrick C, et al. Active immunization against alpha-synuclein ameliorates the degenerative pathology and prevents demyelination in a model of multiple system atrophy. Mol Neurodegener. 2015;10:10.
Sardi SP, Cedarbaum JM, Brundin P. Targeted therapies for Parkinson’s disease: from genetics to the clinic. Mov Disord. 2018;33(5):684–96.
Rockenstein E, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Song D, Shults CW, Lang I, et al. Differential neuropathological alterations in transgenic mice expressing alpha-synuclein from the platelet-derived growth factor and Thy-1 promoters. J Neurosci Res. 2002;68(5):568–78.
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Alford M, Crews L, Hashimoto M, et al. Effects of alpha-synuclein immunization in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2005;46(6):857–68.
Lobello K, Ryan JM, Liu E, Rippon G, Black R. Targeting Beta amyloid: a clinical review of immunotherapeutic approaches in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;2012:628070. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/628070.
Ghochikyan A, Petrushina I, Davtyan H, Hovakimyan A, Saing T, Davtyan A, et al. Immunogenicity of epitope vaccines targeting differenT B cell antigenic determinants of human α-synuclein: feasibility study. Neurosci Lett. 2014;560:86–91.
Mandler M, Valera E, Rockenstein E, Weninger H, Patrick C, Adame A, et al. Next-generation active immunization approach for synucleinopathies: implications for parkinson’s disease clinical trials. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;127(6):861–79.
Villadiego J, Labrador-Garrido A, Franco JM, Leal-Lasarte M, De Genst EJ, Dobson CM, et al. Immunization with Α-Synuclein/Grp94 reshapes peripheral immunity and suppresses microgliosis in a chronic Parkinsonism model. GLIA. 2018;66(1):191–205.
Kingwell K. Zeroing in on neurodegenerative Α-synuclein. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(6):371–3.
Valera E, Masliah E. Immunotherapy for neurodegenerative diseases: focus on Α-synucleinopathies. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;138(3):311–22.
Affiris announces encouraging long-term data from a series of first-in-human studies using Affitope® PD01A targeting oligomeric alpha-synuclein in early Parkinson’s disease Patients [Press Release]. 2018.
Affiris announces top line results of first-in-human clinical study using AFFITOPE®PD03A, Confirming immunogenicity and safety profile In Parkinson’s disease patients [Press Release]. 2017. http://www.affiris.com/news/affiris-announces-top-line-results-of-first-in-human-clinical-study-using-affitope/.
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Crews L, Spencer B, Adame A, et al. Passive immunization reduces behavioral and neuropathological deficits in an alpha-synuclein transgenic model of lewy body disease. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):E19338.
Mishizen-Eberz AJ, Norris EH, Giasson BI, Hodara R, Ischiropoulos H, Lee VM, et al. Cleavage of alpha-synuclein by calpain: potential role in degradation of fibrillized and nitrated species of alpha-synuclein. Biochemistry. 2005;44(21):7818–29.
Tofaris GK, Garcia Reitböck P, Humby T, Lambourne SL, O’Connell M, Ghetti B, et al. Pathological changes in dopaminergic nerve cells of the substantia nigra and olfactory bulb in mice transgenic for truncated human alpha-synuclein(1-120): implications for lewy body disorders. J Neurosci. 2006;26(15):3942–50.
Bae EJ, Lee HJ, Rockenstein E, Ho DH, Park EB, Yang NY, et al. Antibody-aided clearance of extracellular Α-synuclein prevents cell-to-cell aggregate transmission. J Neurosci. 2012;32(39):13454–69.
Fleming SM, Salcedo J, Fernagut PO, Rockenstein E, Masliah E, Levine MS, et al. Early and progressive sensorimotor anomalies in mice overexpressing wild-type human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci. 2004;24(42):9434–40.
Shahaduzzaman M, Nash K, Hudson C, Sharif M, Grimmig B, Lin X, et al. anti-human Α-synuclein N-terminal peptide antibody protects against dopaminergic cell death and ameliorates behavioral deficits in an aav-α-synuclein rat model of Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):E0116841.
Tran HT, Chung CH, Iba M, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Luk KC, et al. Α-synuclein immunotherapy blocks uptake and templated propagation of misfolded α-synuclein and neurodegeneration. Cell Rep. 2014;7(6):2054–65.
Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L, Muller V, Jacobsen H, Schindzielorz A, et al. Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson’s disease-associated mutant alpha-synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J Neurosci. 2000;20(17):6365–73.
Lindström V, Fagerqvist T, Nordström E, Eriksson F, Lord A, Tucker S, et al. Immunotherapy targeting α-synuclein protofibrils reduced pathology iN (THY-1)-H[A30P] α-synuclein mice. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;69:134–43.
Gustafsson G, Eriksson F, Möller C, Da Fonseca TL, Outeiro TF, LannfelT L, et al. Cellular uptake of α-synuclein oligomer-selective antibodies is enhanced by the extracellular presence of α-synuclein and mediated via Fcγ ReceptorS. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017;37(1):121–31.
El-Agnaf O, Overk C, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Florio J, Adame A, et al. Differential effects of immunotherapy with antibodies targeting α-synuclein oligomers and fibrils in a transgenic model of synucleinopathy. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;104:85–96.
Schenk DB, Koller M, Ness DK, Griffith SG, Grundman M, Zago W, et al. First-in-human assessment of PRX002, an anti-alpha-synuclein monoclonal antibody, in healthy volunteers. Mov Disord. 2017;32(2):211–8.
Jankovic J, Goodman I, Safirstein B, Marmon TK, Schenk DB, Koller M et al. Safety and tolerability of multiple ascending doses of PRX002/RG7935, an anti-α-synuclein monoclonal antibody, in patients with parkinson disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018;75(10):1206–14. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.1487.
Weihofen A, Patel H, Huy C, Liu C, Combaluzier I, Mueller-Steiner S, et al. Binding and functional characterization of human-derived anti-alpha-synuclein antibody BIIB054. Neurodeg Dis. 2017;17 (SUPPL 1)(8):59.
Brys M, Hung S, Fanning L, Penner N, Yang M, Welch M, et al. Randomized, double- blind, placebo-controlled, single ascending dose study of antialpha-synuclein antibody biib054 in patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2018;90(15 15 SUPPLEMENT):S26.001.
Bioarctic enters into collaboration with abbvie for parkinson disease research [Press Release]. 2018. https://www.bioarctic.se/en/section/media/press-releases/
Wisniewski T, Goni F. Immunotherapeutic approaches for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2015;85(6):1162–76.
Zepp F. Principles of vaccination. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1403:57–84.
Guy B. The perfect mix: recent progress in adjuvant research. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5(7):505–17.
Tabira T. Immunization therapy for alzheimer disease: a comprehensive review of active immunization strategies. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010;220(2):95–106.
Penninkilampi R, Brothers HM, Eslick GD. Safety and efficacy of anti-amyloid-beta immunotherapy in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017;12(1):194–203.
Brys I, Halje P, Scheffer-Teixeira R, Varney M, Newman-Tancredi A, Petersson P. Neurophysiological effects in cortico-basal ganglia-thalamic circuits of antidyskinetic treatment with 5-HT1A receptor biased agonists. Exp Neurol. 2018;302:155–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.01.010.
Acknowledgements
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Disclosures
Samis M.A. Zella, Judith Metzdorf, Emine Ciftci, Friederike Ostendorf, Siegfried Muhlack, Ralf Gold and Lars Tönges have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. I declare that the submitted work is entirely our own and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced digital features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.7378277.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Zella, S.M.A., Metzdorf, J., Ciftci, E. et al. Emerging Immunotherapies for Parkinson Disease. Neurol Ther 8, 29–44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-018-0122-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-018-0122-z