Abstract
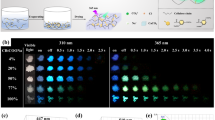
Polymer coloration technology has been receiving increasing attention in different fields including electronic packaging, artificial skin and 3D printing. Herein, we report a new strategy utilizing three primary nanocomposites (cellulose@Fe3O4, cellulose@FeOOH and cellulose@PB) as unique coloring components for scalable colored polymer-based composites. Taking the epoxy resin as polymer matrix for example, the as-made polymer-based composites present different colors, including red/yellow/blue colors and many spectral colors achieved by mixing the three primary nanocomposites. The nanocomposites act not only as the primary nanopigments, but also as the connected bridge to tightly stick polymer matrix through strong chemical bonding, respectively. In addition, the colored polymer-based composites show excellent opacity and UV protection. Our work offers a facile coloration approach for arbitrary colors over the whole visible spectra by mixing three primary nanocomposites at different ratios in the polymer field. With bright, uniform, and ratio-dependent color, we showcase three typical polymers to demonstrate the versatility of coloring strategy.
Graphical abstract
We have developed a simple strategy to fabricate cellulose in situ deposited three primary nanocomposites. Taking the polymer matrix for example, arbitrary color can be created by mixing them into polymer at different ratios over the whole visible spectra by dispersing three primary nanocomposites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rottger, M., Domenech, T., Van der Weegen, R., Nicolay, A.B.R., Leibler, L.: High-performance vitrimers from commodity thermoplastics through dioxaborolane metathesis. Science 356, 62–65 (2017)
Tran, P., Nguyen, Q.T., Lau, K.T.: Fire performance of polymer-based composites for maritime infrastructure. Compos. B Eng. 155, 31–48 (2018)
Cai, L., Peng, Y., Xu, J., Zhou, C., Wu, P., Lin, D., Fan, S., Cui, Y.: Temperature regulation in colored infrared transparent polyethylene textiles. Joule. 3, 1478–1486 (2019)
Meng, D.D., Zhang, C., Liang, Y., Qiu, W.Y., Kong, F.P., He, X., Chen, M., Liang, P., Zhang, Z.H.: Electrospun cobalt Prussian blue analogue-derived nanofibers for oxygen reduction reaction and lithium-ion batteries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 599, 280–290 (2021)
Wu, H.L., Qiu, Z.H.: Fe3O4@N-porous carbon nano rice/rGO sheet as positive electrode material for a high performance supercapattery. J. Alloy. Compd. 879, 11 (2021)
Zhou, Q.Q., Wu, W., Zhou, S.Q., Xing, T.L., Sun, G., Chen, G.Q.: Polydopamine-induced growth of mineralized gamma-FeOOH nanorods for construction of silk fabric with excellent superhydrophobicity, flame retardancy and UV resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 382, 12 (2020)
Gilbert, B., Frandsen, C., Maxey, E.R., Sherman, D.M.: Band-gap measurements of bulk and nanoscale hematite by soft x-ray spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 79, 7 (2009)
Rosseinsky, D.R., Lim, H., Jiang, H.J., Chai, J.W.: Optical charge-transfer in iron(III)hexacyanoferrate(II): electro-intercalated cations induce lattice-energy-dependent ground-state energies. Inorg. Chem. 42, 6015–6023 (2003)
Choi, J.W., Kim, J.Y., Lee, W., Lee, W.H., Jang, H.D., Lee, S.B.: UV protection characteristics and fabrication of modified TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 10, 428–434 (2004)
Sedighi, A., Montazer, M., Mazinani, S.: Fabrication of electrically conductive superparamagnetic fabric with microwave attenuation, antibacterial properties and UV protection using PEDOT/magnetite nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 160, 34–47 (2018)
Nilsson, H., Galland, S., Larsson, P.T., Gamstedt, E.K., Nishino, T., Berglund, L.A.: A non-solvent approach for high-stiffness all-cellulose biocomposites based on pure wood cellulose. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(12), 1704–1712 (2010)
Choi, H.Y., Lee, T.-W., Lee, S.-E., Lim, J., Jeong, Y.G.: Silver nanowire/carbon nanotube/cellulose hybrid papers for electrically conductive and electromagnetic interference shielding elements. Compos. Sci. Technol. 150, 45–53 (2017)
Piltonen, P., Hildebrandt, N.C., Westerlind, B., Valkama, J.P., Tervahartiala, T., Illikainen, M.: Green and efficient method for preparing all-cellulose composites with NaOH/urea solvent. Compos. Sci. Technol. 135, 153–158 (2016)
Zhang, Y., Song, P.A., Liu, H.Z., Li, Q., Fu, S.Y.: Morphology, healing and mechanical performance of nanofibrillated cellulose reinforced poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 125, 62–70 (2016)
Shchipunov, Y., Postnova, I.: Cellulose mineralization as a route for novel functional materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 28 (2018)
Wicklein, B., Diem, A.M., Knoeller, A., Cavalcante, M.S., Bergstroem, L., Bill, J., Burghard, Z.: Dual-fiber approach toward flexible multifunctional hybrid materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1704274 (2018)
Shahzadi, K., Zhang, X., Mohsin, I., Ge, X., Jiang, Y., Peng, H., Liu, H., Li, H., Mu, X.: Reduced graphene oxide/alumina, a good accelerant for cellulose-based artificial nacre with excellent mechanical, barrier, and conductive properties. ACS Nano 11, 5717–5725 (2017)
Shojaeiarani, J., Bajwa, D.S., Hartman, K.: Esterified cellulose nanocrystals as reinforcement in poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites. Cellulose 26, 2349–2362 (2019)
de la Motte, H., Hasani, M., Brelid, H., Westman, G.: Molecular characterization of hydrolyzed cationized nanocrystalline cellulose, cotton cellulose and softwood kraft pulp using high resolution 1D and 2D NMR. Carbohydr. Polym. 85, 738–746 (2011)
Fraschini, C., Chauve, G., Bouchard, J.: TEMPO-mediated surface oxidation of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs). Cellulose 24, 2775–2790 (2017)
Hoeng, F., Denneulin, A., Neuman, C., Bras, J.: Charge density modification of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals for stable silver nanoparticles suspension preparation. J. Nanopart. Res. 17, 244 (2015)
Li, Y.L., Sun, H., Zhang, Y.Y., Xu, M., Shi, S.Q.: The three-dimensional heterostructure synthesis of ZnO/cellulosic fibers and its application for rubber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 177, 10–17 (2019)
Shi, Y.G., Jiang, R.M., Liu, M.Y., Fu, L.H., Zeng, G.J., Wan, Q., Mao, L.C., Deng, F.J., Zhang, X.Y., Wei, Y.: Facile synthesis of polymeric fluorescent organic nanoparticles based on the self-polymerization of dopamine for biological imaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 77, 972–977 (2017)
Zhang, X.Y., Huang, Q., Liu, M.Y., Tian, J.W., Zeng, G.J., Li, Z., Wang, K., Zhang, Q.S., Wan, Q., Deng, F.J., Wei, Y.: Preparation of amine functionalized carbon nanotubes via a bioinspired strategy and their application in Cu2+ removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 343, 19–27 (2015)
Liu, S.L., Zhang, L.N., Zhou, J.P., Xiang, J.F., Sun, J.T., Guan, J.G.: Fiberlike Fe2O3 macroporous nanomaterials fabricated by calcinating regenerate cellulose composite fibers. Chem. Mater. 20, 3623–3628 (2008)
Liu, Z., Wang, H.S., Li, B., Liu, C., Jiang, Y.J., Yu, G., Mu, X.D.: Biocompatible magnetic cellulose-chitosan hybrid gel microspheres reconstituted from ionic liquids for enzyme immobilization. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 15085–15091 (2012)
Sun, N., Swatloski, R.P., Maxim, M.L., Rahman, M., Harland, A.G., Haque, A., Spear, S.K., Daly, D.T., Rogers, R.D.: Magnetite-embedded cellulose fibers prepared from ionic liquid. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 283–290 (2008)
Zhang, M., Han, C., Cao, W.-Q., Cao, M.-S., Yang, H.-J., Yuan, J.: A nano-micro engineering nanofiber for electromagnetic absorber. Green shielding and sensor. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 27 (2020)
Xia, X.H., Chao, D.L., Zhang, Y.Q., Shen, Z.X., Fan, H.J.: Three-dimensional graphene and their integrated electrodes. Nano Today 9, 785–807 (2014)
Qiu, B., Xing, M., Zhang, J.: Recent advances in three-dimensional graphene based materials for catalysis applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 2165–2216 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Li, J., Ma, N., Meng, Z., Sui, G.: Processing cellulose@Fe3O4 into mechanical, magnetic and biodegradable synapse-like material. Compos. B Eng. 177, 1077432 (2019)
Ou, Y., Qiu, X., Xu, Z., Lin, J., Liao, D.: Synthesis of nanoscale Fe2O3 particles by homogenous precipitation method. J. Xiamen Univ. 43, 882–885 (2004)
Zhang, H.T., Huang, H., Sun, R., Huang, J.X.: Preparation of micron-size monodispersed PS/P(St/MAA) microspheres by seeded dispersion polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 99, 3586–3591 (2006)
Zhang, X., Si, Y.F., Mo, J.L., Guo, Z.G.: Robust micro-nanoscale flowerlike ZnO/epoxy resin superhydrophobic coating with rapid healing ability. Chem. Eng. J. 313, 1152–1159 (2017)
Chen, Y., Zhang, H.B., Wang, M., Qian, X.A., Dasari, Z.ZYu.: Phenolic resin-enhanced three-dimensional graphene aerogels and their epoxy nanocomposites with high mechanical and electromagnetic interference shielding performances. Compos. Sci. Technol. 152, 254–262 (2017)
Jiang, J.J., Deng, G.L., Chen, X., Gao, X.Y., Guo, Q., Xu, C.M., et al.: On the successful chemical recycling of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites under the mild condition. Compos. Sci. Technol. 151, 243–251 (2017)
Kontturi, E., Laaksonen, P., Linder, M.B., Nonappa, A.H., Groschel, O.J., Rojas, O.I.: Advanced materials through assembly of nanocelluloses. Adv. Mater. 30, 39 (2018)
Gui, Z., Zhu, H.L., Gillette, E., Han, X.G., Rubloff, G.W., Hu, L.B., Lee, S.B.: Natural cellulose fiber as substrate for supercapacitor. ACS Nano 7, 6037–6046 (2013)
Song, J.W., Chen, C.J., Yang, Z., Kuang, Y.D., Li, T., Li, Y.J., Huang, H., Kierzewski, I., Liu, B.Y., He, S.M., Gao, T.T., Yuruker, S.U., Gong, A., Yang, B., Hu, L.B.: Highly compressible, anisotropic aerogel with aligned cellulose nanofibers. ACS Nano 12, 140–147 (2018)
Chen, Y., Wang, H., Dang, B., Xiong, Y., Yao, Q., Wang, C., Sun, Q., Jin, C.: Bio-Inspired nacre-like nanolignocellulose-poly (vinyl alcohol)-TiO2 composite with superior mechanical and photocatalytic properties. Sci. Rep. 7, 1823 (2017)
Ren, P.-G., Wang, H., Yan, D.-X., Huang, H.-D., Wang, H.-B., Zhang, Z.-P., Xu, L., Li, Z.-M.: Ultrahigh gas barrier poly (vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite film filled with congregated and oriented Fe3O4@GO sheets induced by magnetic-field. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 97, 1–9 (2017)
Ishikawa, T., Kumagai, M., Yasukawa, A., Kandori, K., Nakayama, T., Yuse, F.: Influences of metal ions on the formation of gamma-FeOOH and magnetite rusts. Corros. Sci. 44, 1073–1086 (2002)
Cao, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, B., Lu, L.: In situ controllable growth of prussian blue nanocubes on reduced graphene oxide: facile synthesis and their application as enhanced nanoelectrocatalyst for H2O2 reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2, 2339–2346 (2010)
Tan, Y., Liu, Y.Z., Chen, W.S., Liu, Y.X., Wang, Q.W., Li, J., Yu, H.P.: Homogeneous dispersion of cellulose nanofibers in waterborne acrylic coatings with improved properties and unreduced transparency. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 3766–3772 (2016)
Wang, X., Chen, X., Cowling, S., Wang, L., Liu, X.: Polymer brushes tethered ZnO crystal on cotton fiber and the application on durable and washable UV protective clothing. Adv. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 1900564 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, J., Sui, G.: (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane grafted poly(dopamine)@Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their epoxy composites for functional application. Composites B 169, 148–156 (2019)
Wan, X., Zhan, Y., Long, Z., Zeng, G., Ren, Y., He, Y.: High-performance magnetic poly (arylene ether nitrile) nanocomposites: co-modification of Fe3O4 via mussel inspired poly(dopamine) and amino functionalized silane KH550. Appl. Surf. Sci. 425, 905–914 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences for the Joint Austrian-Chinese Cooperative R&D Projects FFG & CAS (No.GJHZ2045), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U20A20284).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Xu, Z., Meng, Z. et al. Cellulose in situ formation of three primary nanoparticles for polymer scalable colors. J Nanostruct Chem 13, 439–449 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-022-00469-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-022-00469-2