Abstract
Background:
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have undergone extensive investigation for their potential therapeutic applications, primarily attributed to their paracrine activity. Recently, researchers have been exploring the therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by MSCs.
Methods:
MEDLINE/PubMed and Google scholar databases were used for the selection of literature. The keywords used were mesenchymal stem cells, extracellular vesicles, clinical application of EVs and challenges EVs production.
Results:
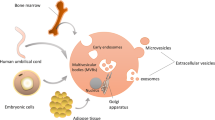
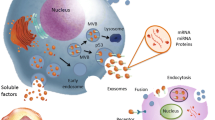
These EVs have demonstrated robust capabilities in transporting intracellular cargo, playing a critical role in facilitating cell-to-cell communication by carrying functional molecules, including proteins, RNA species, DNAs, and lipids. Utilizing EVs as an alternative to stem cells offers several benefits, such as improved safety, reduced immunogenicity, and the ability to traverse biological barriers. Consequently, EVs have emerged as an increasingly attractive option for clinical use.
Conclusion:
From this perspective, this review delves into the advantages and challenges associated with employing MSC–EVs in clinical settings, with a specific focus on their potential in treating conditions like lung diseases, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hass R, Kasper C, Böhm S, Jacobs R. Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): a comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell Commun Sign. 2011;9:12.
Squillaro T, Peluso G, Galderisi U. Clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells: an update. Cell Transplantat. 2016;25:829–48.
Williams LA, Davis-Dusenbery BN, Eggan KC. SnapShot: directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. Cell. 2012;149:1174-1174.e1.
Kimbrel EA, Lanza R. Next-generation stem cells: ushering in a new era of cell-based therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19:463–79.
Merkle FT, Ghosh S, Kamitaki N, Mitchell J, Avior Y, Mello C, et al. Human pluripotent stem cells recurrently acquire and expand dominant negative P53 mutations. Nature. 2017;545:229–33.
Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, Orr L, Turbide C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262:9412–20.
van der Pol E, Böing AN, Gool EL, Nieuwland R. Recent developments in the nomenclature, presence, isolation, detection and clinical impact of extracellular vesicles. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:48–56.
Kreimer S, Belov AM, Ghiran I, Murthy SK, Frank DA, Ivanov AR. Mass-spectrometry-based molecular characterization of extracellular vesicles: Lipidomics and proteomics. J Proteome Res. 2015;14:2367–84.
Elsharkasy OM, Nordin JZ, Hagey DW, de Jong OG, Schiffelers RM, el Andaloussi S, Vader P. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Why and how? Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;159:332–43.
Murphy DE, de Jong OG, Brouwer M, Wood MJ, Lavieu G, Schiffelers RM, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51:1–12.
Bruno S, Grange C, Collino F, Deregibus MC, Cantaluppi V, Biancone L, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33115.
Parekkadan B, van Poll D, Suganuma K, Carter EA, Berthiaume F, Tilles AW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules reverse fulminant hepatic failure. PLoS One. 2007;2:e941
de Jong OG, Kooijmans SAA, Murphy DE, Jiang L, Evers MJW, Sluijter JPG, et al. Drug delivery with extracellular vesicles: from imagination to innovation. Acc Chem Res. 2019;52:1761–70.
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C, Lakhal S, Wood MJA. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:341–5.
Yang J, Liu XX, Fan H, Tang Q, Shou ZX, Zuo DM, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against experimental colitis via attenuating colon inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0140551
Pant S, Hilton H, Burczynski ME. The multifaceted exosome: Biogenesis, role in normal and aberrant cellular function, and frontiers for pharmacological and biomarker opportunities. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1484–94.
Meng W, He C, Hao Y, Wang L, Li L, Zhu G. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020;27:585–98.
Turturici G, Tinnirello R, Sconzo G, Geraci F. Extracellular membrane vesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication: advantages and disadvantages. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;306:621–33.
Das CK, Jena BC, Banerjee I, Das S, Parekh A, Bhutia SK, et al. Exosome as a novel shuttle for delivery of therapeutics across biological barriers. Mol Pharm. 2019;16:24–40.
Pullan JE, Confeld MI, Osborn JK, Kim J, Sarkar K, Mallik S. Exosomes as drug carriers for cancer therapy. Mol Pharm. 2019;16:1789–98.
Khan AR, Yang X, Fu M, Zhai G. Recent progress of drug nanoformulations targeting to brain. J Controll Release. 2018;291:37–64.
Haraszti RA, Miller R, Stoppato M, Sere YY, Coles A, Didiot MC, et al. Exosomes produced from 3D cultures of MSCs by tangential flow filtration show higher yield and improved activity. Mol Ther. 2018;26:2838–47.
Kourembanas S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:13–27.
Munoz JL, Bliss SA, Greco SJ, Ramkissoon SH, Ligon KL, Rameshwar P. Delivery of functional anti-miR-9 by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes to glioblastoma multiforme cells conferred chemosensitivity. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013;2:e126
Phan J, Kumar P, Hao D, Gao K, Farmer D, Wang A. Engineering mesenchymal stem cells to improve their exosome efficacy and yield for cell-free therapy. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7:1522236.
Wang S, Qu X, Zhao RC. Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:9.
Frankel EB, Audhya A. ESCRT-dependent cargo sorting at multivesicular endosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;74:4–10.
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200:373–83.
Buschow SI, Nolte-’t Hoen EN, van Niel G, Pols MS, ten Broeke T, Lauwen M, et al. MHC II In dendritic cells is targeted to lysosomes or t cell-induced exosomes via distinct multivesicular body pathways. Traffic. 2009;10:1528–42.
Carney RP, Hazari S, Colquhoun M, Tran D, Hwang B, Mulligan MS, et al. Multispectral optical tweezers for biochemical fingerprinting of CD9-positive exosome subpopulations. Anal Chem. 2017;89:5357–63.
Chen J, Li P, Zhang T, Xu Z, Huang X, Wang R, et al. Review on strategies and technologies for exosome isolation and purification. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022:9:811971.
Whitford W, Guterstam P. Exosome manufacturing status. Fut Med Chem. 2019;11:1225–36.
Khalaj K, Figueira RL, Antounians L, Lauriti G, Zani A. Systematic review of extracellular vesicle-based treatments for lung injury: are EVs a potential therapy for COVID-19? J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9:1795365.
Krishnamachary B, Cook C, Kumar A, Spikes L, Chalise P, Dhillon NK. Extracellular vesicle-mediated endothelial apoptosis and EV-associated proteins correlate with COVID-19 disease severity. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10:e12117
Monsel A, Zhu YG, Gennai S, Hao Q, Hu S, Rouby JJ, et al. Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles in severe pneumonia in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192:324–36.
Morrison TJ, Jackson MV, Cunningham EK, Kissenpfennig A, McAuley DF, O’Kane CM, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells modulate macrophages in clinically relevant lung injury models by extracellular vesicle mitochondrial transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196:1275–86.
Chen J, Hu C, Pan P. Extracellular vesicle microRNA transfer in lung diseases. Front Physiol. 2017;8:1028.
Lee JH, Park J, Lee JW. Therapeutic use of mesenchymal stem cell–derived extracellular vesicles in acute lung injury. Transfusion. 2019;59:876–83.
Margaroli C, Madison MC, Viera L, Russell DW, Gaggar A, Genschmer KR, et al. A novel in vivo model for extracellular vesicle-induced emphysema. JCI Insight. 2022;7:e153560
Ridzuan N, Zakaria N, Widera D, Sheard J, Morimoto M, Kiyokawa H, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate airway inflammation in a rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:54.
Sundar IK, Li D, Rahman I. Small RNA-sequence analysis of plasma-derived extracellular vesicle miRNAs in smokers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as circulating biomarkers. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8:1684816.
Sluijter JPG, Davidson SM, Boulanger CM, Buzás EI, de Kleijn DPV, Engel FB, et al. Extracellular vesicles in diagnostics and therapy of the ischaemic heart: position paper from the working group on cellular biology of the heart of the European society of cardiology. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114:19–34.
Yun C, Lee S. Enhancement of functionality and therapeutic efficacy of cell-based therapy using mesenchymal stem cells for cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:982.
Scrimogeour L, Potz BA, Gheit A, Shi G, Stainley M, Zhang Z, et al. Extracelullar vesicles promote arteriogenesis in chronically ischemic myocardium in the setting of metabolic syndrome. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e012617
Huang J, Zhang Z, Guo J, Ni A, Deb A, Zhang L, et al. Genetic modification of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing ccr1 increases cell viability, migration, engraftment, and capillary density in the injured myocardium. Circ Res. 2010;106:1753–62.
Imanishi Y, Saito A, Komoda H, Kitagawa-Sakakida S, Miyagawa S, Kondoh H, et al. Allogenic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation has a therapeutic effect in acute myocardial infarction in rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44:662–71.
Guijarro D, Lebrin M, Lairez O, Bourin P, Piriou N, Pozzo J, et al. Intramyocardial transplantation of mesenchymal stromal cells for chronic myocardial ischemia and impaired left ventricular function: Results of the MESAMI 1 pilot trial. Int J Cardiol. 2016;209:258–65.
Lima CB, El Harane N, Desgres M, Perotto M, Alayrac P, Guillas C, et al. Extracellular vesicles fail to trigger the generation of new cardiomyocytes in chronically infarcted heart. Theranostics. 2021;11:10114–24.
Jansen F, Li Q. Exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers in cardiovascular diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;998:61–70.
Liu J, Jiang M, Deng S, Lu J, Huang H, Zhang Y, Gong P, Shen X, Ruan H, Jin M, Wang H. miR-93-5p-containing exosomes treatment attenuates acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage. Mol Therap: Nucleic Acids. 2018;11:103–15.
Yang Y, Li Y, Chen X, Cheng X, Liao Y, Yu X. Exosomal transfer of miR-30a between cardiomyocytes regulates autophagy after hypoxia. J Mol Med. 2016;94:711–24.
Jiang W, Tan Y, Cai M, Zhao T, Mao F, Zhang X, et al. Human umbilical cord MSC-derived exosomes suppress the development of CCl4-induced liver injury through antioxidant effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:6079642.
Watanabe Y, Tsuchiya A, Terai S. The development of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the present, and the perspective of cell-free therapy in the future. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020;27:70–80.
Borrelli DA, Yankson K, Shukla N, Ticer T, Wolfram J. Extracellular vesicle therapeutics for liver disease. J Control Release. 2018;273:86–98.
Haga H, Yan I, Takahashi K, Matsuda A, Patel T. Extracellular vesicles from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve survival from lethal hepatic failure in mice. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6:1262–72.
Lee Y, Tran B, Wang J, Liang I, You S, Zhu Y, et al. The role of extracellular vesicles in disease progression and detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2021.
Gutiérrez-Fernández M, de la Cuesta F, Tallón A, Cuesta I, Fernández-Fournier M, Laso-García F, et al. Potential roles of extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and a novel treatment approach in multiple sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:9011.
Manu MS, Hohjoh H, Yamamura T. Extracellular vesicles as pro-and anti-inflammatory mediators, biomarkers and potential therapeutic agents in multiple sclerosis. Aging Dis. 2021;12:1451–61.
Casado JG, Blazquez R, Vela FJ, Alvarez V, Tarazona R, Sanchez-Margallo FM. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: immunomodulatory evaluation in an antigen-induced synovitis porcine model. Front Veter Sci. 2017;4:99.
Pistoia V, Raffaghello L. Mesenchymal stromal cells and autoimmunity. Int Immunol. 2017;29:49–58.
Verderio C, Muzio L, Turola E, Bergami A, Novellino L, Ruffini F, et al. Myeloid microvesicles are a marker and therapeutic target for neuroinflammation. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:610–24.
Tian J, Casella G, Zhang Y, Rostami A, Li X. Potential roles of extracellular vesicles in the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of autoimmune diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16:620.
Cosenza S, Toupet K, Maumus M, Luz-Crawford P, Blanc-Brude O, Jorgensen C. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics. 2018;8:1399–410.
Zheng J, Zhu L, In II, Chen Y, Jia N, Zhu W. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells-secreted exosomal microRNA-192-5p delays inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;78:105985.
Wang Y, Zheng F, Gao G, Yan S, Zhang L, Wang L, et al. MiR-548a-3p regulates inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:1133–40.
Chen Z, Wang H, Xia Y. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal cell-derived miRNA-150-5p-expressing exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis mediated by the modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol. 2018;201:2472–82.
Meng HY, Chen LQ, Chen LH. The inhibition by human MSCs-derived miRNA-124a overexpression exosomes in the proliferation and migration of rheumatoid arthritis-related fibroblast-like synoviocyte cell. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21:150.
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Alivernini S, Ballantine LE, Asquith DL, Millar NL, Gilchrist DS, et al. MicroRNA-155 as a proinflammatory regulator in clinical and experimental arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;27:11193–8.
Wu H, Zhou X, Wang X, Cheng W, Hu X, Wang Y, et al. miR-34a in extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reduces rheumatoid arthritis inflammation via the cyclin I/ATM/ATR/p53 Axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:1896–910.
Bakirtzi K, Hatziapostolou M, Karagiannides I, Polytarchou C, Jaeger S, Iliopoulos D, et al. Neurotensin signaling activates microRNAs-21 and -155 and Akt, promotes tumor growth in mice, and is increased in human colon tumors. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1749–1761.e1.
Petit CSV, Barreau F, Besnier L, Gandille P, Riveau B, Chateau D, et al. Requirement of cellular prion protein for intestinal barrier function and mislocalization in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:122–32.e15.
Slater TW, Finkielsztein A, Mascarenhas LA, Mehl LC, Butin-Israeli V, Sumagin R. Neutrophil microparticles deliver active myeloperoxidase to injured mucosa to inhibit epithelial wound healing. J Immunol. 2017;198:2886–97.
Pouillon L, Bossuyt P, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Considerations, challenges and future of anti-tnf therapy in treating inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16:1277–90.
Ma ZJ, Wang YH, Li ZG, Wang Y, Li BY, Kang HY, et al. Immunosuppressive effect of exosomes from mesenchymal stromal cells in defined medium on experimental colitis. Int J Stem Cells. 2019;12:440–8.
Mao F, Wu Y, Tang X, Kang J, Zhang B, Yan Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells relieve inflammatory bowel disease in mice. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5356760.
Wu Y, Qiu W, Xu X, Kang J, Wang J, Wen Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate inflammatory bowel disease in mice through ubiquitination. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10:2026–36.
Valter M, Verstockt S, Finalte Ferreiro JA, Cleynen I. Extracellular vesicles in inflammatory bowel disease: small particles, big players. J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15:499–510.
Bakirtzi K, Man Law IK, Fang K, Iliopoulos D, Pothoulakis C. MiR-21 in Substance P-induced exosomes promotes cell proliferation and migration in human colonic epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019;317:G802–10.
Bebelman MP, Smit MJ, Pegtel DM, Baglio SR. Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;188:1–11.
Matsubara M, Bissell MJ. Inhibitors of Rho kinase (ROCK) signaling revert the malignant phenotype of breast cancer cells in 3D context. Oncotarget. 2016;7:31602–22.
Dyberg C, Fransson S, Andonova T, Sveinbjornsson B, Lannerholm-Palm J, Olsen TK, et al. Rho-associated kinase is a therapeutic target in neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114:E6603–12.
Matsuoka T, Yashiro M. Rho/ROCK signaling in motility and metastasis of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:13756–66.
Choi D, Montermini L, Meehan B, Lazaris A, Metrakos P, Rak J. et al. (2021) Oncogenic RAS drives the CRAF-dependent extracellular vesicle uptake mechanism coupled with metastasis. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10:e12091
Ruiz-Martinez M, Navarro A, Marrades RM, Vinolas N, Santasusagna S, Munoz C, et al. YKT6 expression, exosome release, and survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:51515–24.
Wang T, Gilkes DM, Takano N, Xiang L, Luo W, Bishop CJ, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors and RAB22A mediate formation of microvesicles that stimulate breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E3234–42.
Dong L, Pu Y, Zhang L, Qi Q, Xu L, Li W, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote lung adenocarcinoma growth by transferring miR-410. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:218.
Dai S, Wei D, Wu Z, Zhou X, Wei X, Huang H, et al. Phase I clinical trial of autologous ascites-derived exosomes combined with GM-CSF for colorectal cancer. Mol Ther. 2008;16:782–90.
Morse AM, Garst J, Osada T, Khan S, Hobeika A, Clay TM, et al. A phase I study of dexosome immunotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. 2005;3:9.
Giebel B, Kordelas L, Börger V. Clinical potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Investig. 2017;4:84.
Kordelas L, Rebmann V, Ludwig AK, Radtke S, Ruesing J, Doeppner TR, et al. MSC-derived exosomes: a novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia. 2014;28:970–3.
Gu ZW, He YF, Wang WJ, Tian Q, Di W. MiR-1180 from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induces glycolysis and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer cells by upregulating the Wnt signaling pathway. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019;20:219–37.
Qi J, Zhou Y, Jiao Z, Wang X, Zhao Y, Li Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor growth through hedgehog signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42:2242–54.
Zhou X, Li T, Chen Y, Zhang N, Wang P, Liang Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cellderived extracellular vesicles promote the in vitro proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through the activation of the ERK pathway. Int J Oncol. 2019;54:1843–52.
Ji R, Zhang B, Zhang X, Xue J, Yuan X, Yan Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells confer drug resistance in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle. 2015;14:2473–83.
Roccaro AM, Sacco A, Maiso P, Azab AK, Tai YT, Reagan M, et al. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:1542–55.
Li P, Xin H, Lu L. Extracellular vesicle-encapsulated microRNA-424 exerts inhibitory function in ovarian cancer by targeting MYB. J Transl Med. 2021;19:4.
Lopatina T, Grange C, Fonsato V, Tapparo M, Brossa A, Fallo S, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human liver stem cells inhibit tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 2019;144:322–33.
Brossa A, Fonsato V, Grange C, Tritta S, Tapparo M, Calvetti R, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human liver stem cells inhibit renal cancer stem cell-derived tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 2020;147:1694–706.
Izadpanah M, Seddigh A, Ebrahimi Barough S, Fazeli SAS, Ai J. Potential of extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative diseases: diagnostic and therapeutic indications. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;66:172–9.
Mathieu M, Martin-Jaular L, Lavieu G, Thery C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21:9–17.
Tian T, Zhang HX, He CP, Fan S, Zhu YL, Qi C, et al. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;150:137–49.
Zhang K, Zhao X, Chen X, Wei Y, Du W, Wang Y, et al. Enhanced therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes with an injectable hydrogel for hindlimb ischemia treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:30081–91.
Rufino-Ramos D, Albuquerque PR, Carmona V, Perfeito R, Nobre RJ, Pereira de Almeida L. Extracellular vesicles: novel promising delivery systems for therapy of brain diseases. J Controll Release. 2017;262:247–58.
Schindler C, Collinson A, Matthews C, Pointon A, Jenkinson L, Minter RR, et al. Exosomal delivery of doxorubicin enables rapid cell entry and enhanced in vitro potency. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0214545
Millard M, Yakavets I, Piffoux M, Brun A, Gazeau F, Guigner JM, et al. mTHPC-loaded extracellular vesicles outperform liposomal and free mTHPC formulations by an increased stability, drug delivery efficiency and cytotoxic effect in tridimensional model of tumors. Drug Deliv. 2018;25:1790–801.
Prada I, Amin L, Furlan R, Legname G, Verderio C, Cojoc D. A new approach to follow a single extracellular vesicle: cell interaction using optical tweezers. Biotechniques. 2016;60:35.
Gao X, Ran N, Dong X, Zuo B, Yang R, Zhou Q, et al. Anchor peptide captures, targets, and loads exosomes of diverse origins for diagnostics and therapy. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10:eaat0195.
Aqil F, Jeyabalan J, Agrawal AK, Kyakulaga A-H, Munagala R, Parker L, et al. Exosomal delivery of berry anthocyanidins for the management of ovarian cancer. Food Funct. 2017;8:4100–7.
Melnik BC, John S, Schmitz G. Milk: an exosomal microRNA transmitter promoting thymic regulatory T cell maturation preventing the development of atopy? J Transl Med. 2014;12:43.
Munagala R, Aqil F, Jeyabalan J, Gupta RC. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016;371:48–61.
Del Pozo-Acebo L, Hazas MLL, Tomé-Carneiro J, Gil-Cabrerizo P, San-Cristobal R, Busto R, et al. Bovine milk-derived exosomes as a drug delivery vehicle for miRNA-based therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:1105.
Sedykh S, Kuleshova A, Nevinsky G. Milk exosomes: perspective agents for anticancer drug delivery. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6646.
Meng W, He C, Hao Y, Wang L, Li L, Zhu G. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020;27:585–98.
Hong Y, Nam GH, Koh E, Jeon S, Kim GB, Jeong C, et al. Exosome as a vehicle for delivery of membrane protein therapeutics, PH20, for enhanced tumor penetration and antitumor efficacy. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1703074.
Zolnik BS, González-Fernández Á, Sadrieh N, Dobrovolskaia MA. Minireview: nanoparticles and the immune system. Endocrinology. 2010;151:458–65.
Fernandez-Fernandez A, Manchanda R, McGoron AJ. Theranostic applications of nanomaterials in cancer: drug delivery, image-guided therapy, and multifunctional platforms. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2011;165:1628–51.
Armstrong JPK, Stevens MM. Strategic design of extracellular vesicle drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;130:12–6.
van der Meel R, Fens MHAM, Vader P, van Solinge WW, Eniola-Adefeso O, Schiffelers RM. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Lessons from the liposome field. J Controll Release. 2014;195:72–85.
Yang B, Chen Y, Shi J. exosome biochemistry and advanced nanotechnology for next-generation theranostic platforms. Adv Mater. 2019;31:1802896.
Liu C, Feng Q, Sun J. Lipid nanovesicles by microfluidics: manipulation, synthesis, and drug delivery. Adv Mater. 2019;31:1804788.
Monopoli MP, Åberg C, Salvati A, Dawson KA. Biomolecular coronas provide the biological identity of nanosized materials. Nat Nanotechnol. 2012;7:779–86.
Owensiii D, Peppas N. Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2006;307:93–102.
Szebeni J. Complement activation-related pseudoallergy: a stress reaction in blood triggered by nanomedicines and biologicals. Mol Immunol. 2014;61:163–73.
Sahay G, Querbes W, Alabi C, Eltoukhy A, Sarkar S, Zurenko C, et al. Efficiency of siRNA delivery by lipid nanoparticles is limited by endocytic recycling. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:653–8.
Gilleron J, Querbes W, Zeigerer A, Borodovsky A, Marsico G, Schubert U, et al. Image-based analysis of lipid nanoparticle–mediated siRNA delivery, intracellular trafficking and endosomal escape. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:638–46.
Hoen E, Cremer T, Gallo R, Margolis L. Extracellular vesicles and viruses: are they close relatives? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:9155–61.
Mali S. Delivery systems for gene therapy. Indian J Hum Genet. 2013;19:3.
Fitzner D, Schnaars M, van Rossum D, Krishnamoorthy G, Dibaj P, Bakhti M, et al. Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:447–58.
Luan X, Sansanaphongpricha K, Myers I, Chen H, Yuan H, Sun D. Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017;38:754–63.
Vader P, Mol EA, Pasterkamp G, Schiffelers RM. Extracellular vesicles for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;106:148–56.
Fuhrmann G, Serio A, Mazo M, Nair R, Stevens MM. Active loading into extracellular vesicles significantly improves the cellular uptake and photodynamic effect of porphyrins. J Controll Release. 2015;205:35–44.
Lamparski HG, Metha-Damani A, Yao JY, Patel S, Hsu DH, Ruegg C, et al. Production and characterization of clinical grade exosomes derived from dendritic cells. J Immunol Methods. 2002;270:211–26.
Trounson A, McDonald C. Stem cell therapies in clinical trials: progress and challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17:11–22. .
Cai J, Wu J, Wang J, Li Y, Hu X, Luo S, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from different sources of mesenchymal stem cells: therapeutic effects and translational potential. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:69.
Labusca L, Herea DD, Mashayekhi K. Stem cells as delivery vehicles for regenerative medicine-challenges and perspectives. World J Stem Cells. 2018;10:43–56.
Momen-Heravi F, Balaj L, Alian S, Mantel PY, Halleck AE, Trachtenberg AJ, et al. Current methods for the isolation of extracellular vesicles. Biol Chem. 2013;394:1253–62.
Veettil MV, Kumar B, Ansari MA, Dutta D, Iqbal J, Gjyshi O, et al. ESCRT-0 component hrs promotes macropinocytosis of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. J Virol. 2016;90:3860–72.
Merchant ML, Rood IM, Deegens JKJ, Klein JB. Isolation and characterization of urinary extracellular vesicles: implications for biomarker discovery. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13:731–49.
Street JM, Koritzinsky EH, Glispie DM, Star RA, Yuen PST. Urine exosomes. Adv Clin Chem. 2017;78:103–22.
Pachler K, Lener T, Streif D, Dunai ZA, Desgeorges A, Feichtner M, et al. A Good Manufacturing Practice–grade standard protocol for exclusively human mesenchymal stromal cell–derived extracellular vesicles. Cytotherapy. 2017;19:458–72.
Bahr MM, Amer MS, Abo-El-Sooud K, Abdallah AN, El-Tookhy OS. Preservation techniques of stem cells extracellular vesicles: a gate for manufacturing of clinical grade therapeutic extracellular vesicles and long-term clinical trials. Int J Vet Sci Med. 2020;8:1–8.
Piffoux M, Nicolás-Boluda A, Mulens-Arias V, Richard S, Rahmi G, Gazeau F, et al. Extracellular vesicles for personalized medicine: the input of physically triggered production, loading and theranostic properties. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;138:247–58.
Liao W, Du Y, Zhang C, Pan F, Yao Y, Zhang T, et al. Exosomes: the next generation of endogenous nanomaterials for advanced drug delivery and therapy. Acta Biomater. 2019;86:1–14.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia for the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) with Project Code FRGS/1/2019/STG03/USM/02/2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical statement
There are no animal experiments carried out for this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Che Shaffi, S., Hairuddin, O.N., Mansor, S.F. et al. Unlocking the Potential of Extracellular Vesicles as the Next Generation Therapy: Challenges and Opportunities. Tissue Eng Regen Med (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-024-00634-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-024-00634-4