Abstract
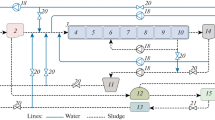
Three different schemes of wastewater treatment consisting of anaerobic, anoxic, and aerobic reactors are evaluated. A2O process (anaerobic, anoxic, and aerobic reactors with internal and external recycles), reverse R-A2O process (anoxic, anaerobic, and aerobic reactors with external recycle), and inverted I-A2O process (anoxic, anaerobic, and aerobic with internal and external recycles) are considered. Dissolved oxygen (DO) is maintained in the respective aerobic reactors using a proportional–integral controller. Activated sludge model no. 2 (ASM2d) is used for the A2O process and is modified to represent R-A2O and I-A2O processes. On comparison, the R-A2O process reduces the operational cost index (OCI) by 4.2% in comparison with the A2O process with improved TP removal of 32.2%. Metal addition is carried out in the last aerobic reactor and carbon addition is carried out in the first anaerobic reactor in each process. It is observed that with an increase in dosage there is a trade-off between effluent quality index (EQI) and OCI. In the R-A2O process, it is observed that if dissolved oxygen (DO) increases, the phosphorus violations also increase. The combination of DO control with metal and carbon additions resulted in optimized results. Further, evaluation is carried out at different temperatures (10, 15, and 20 °C) by changing the kinetic parameters.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alisawi HAO (2020) Performance of wastewater treatment during variable temperature. Appl Water Sci 10(4):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-1171-x
Amand L, Olsson G, Carlsson B (2013) Aeration control–a review. Water Sci Technol 67(11):2374–98.https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.139.
Bo BXZ (2006) The principle and full-scale application of reversed a~ 2/o process for removing nitrogen and phosphorus. J Environ Eng 2006:3. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBBE.2009.5163643
Chen HB, Tang XC, He QB, Qu JN, Gao TY (2007) Phosphorus uptaking behavior of phosphorus accumulating organisms in reversed AAO Process. China Environ Sci 27(1):49–53
Chen HB, Tang XC, Dong B, Gao TY, Wagner M (2008) Study on full-scale application of reversed AAO process. Fresen Environ Bull 17–652:657
Chen Z, Chang Z, Zhang L, Wang J, Qiao L, Song X, Li J (2020) Effects of carbon source addition on microbial community and water quality in recirculating aquaculture systems for Litopenaeus vannamei. Fisheries Sci 1:1–1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-020-01423-3
Copp J (2002) The COST simulation benchmark: description and simulator manual. Office for official publications of the European Community, Luxembourg
Eckenfelder WW, Grau P (1998) Activated Sludge: Process Design and Control, 2nd edn. Technomic Publishing Company, Pennsylvania, pp 1–20
Ersu CB, Ong SK, Arslankaya E, Lee YW (2010) Impact of solids residence time on biological nutrient removal performance of membrane bioreactor. Water Res 44(10):3192–3202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.036
Fang F, Ni B, Li W, Sheng G, Yu H (2011) A simulation-based integrated approach to optimize the biological nutrient removal process in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Chem Eng J 174(2–3):635–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.09.079
Fang F, Qiao LL, Cao JS, Li Y, Xie WM, Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2016) Quantitative evaluation of A2O and reversed A2O processes for biological municipal wastewater treatment using a projection pursuit method. Sep Purif Technol 166:164–170
Gernaey KV, Jørgensen SB (2004) Benchmarking combined biological phosphorus and nitrogen removal wastewater treatment processes. Control Eng Pract 12(3):357–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0661(03)00080-7
Gernaey K, Mussati M, Yuan Z, Nielsen MK, Jørgensen SB (2002) Control strategy evaluation for combined N and P removal using a benchmark wastewater treatment plant. IFAC Proc 35(1):381–386. https://doi.org/10.3182/20020721-6-ES-1901.01456
Gernaey KV, Jeppsson U (2014) Benchmarking of control strategies for wastewater treatment plants. IWA publishing, North America
Guerrero J, Flores-Alsina X, Guisasola A, Baeza JA, Gernaey KV (2013) Effect of nitrite, limited reactive settler and plant design configuration on the predicted performance of simultaneous C/N/P removal WWTPs. Bioresour Technol 136:680–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.021
Guerrero J, Guisasola A, Baeza JA (2014) A novel control strategy for efficient biological phosphorus removal with carbon-limited wastewaters. Water Sci Technol 70(4):691–697. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.280
Gujer W (2010) Nitrification and me - a subjective review. Water Res 44(2010):1–19
Henze M, Gujer W, Mino T, van Loosdrecht MC (2000) Activated sludge models ASM1, ASM2, ASM2d and ASM3. IWA publishing, London, UK. https://doi.org/10.2166/9781780402369
Hongyang X, Pedret C, Santin I, Vilanova R (2018) Decentralized model predictive control for N and P removal in wastewater treatment plants. 22nd International Conference on System Theory Control and Computing (ICSTCC), IEEE: pp 224–230
Hu X, Wisniewski K, Czerwionka K, Zhou Q, Xie L, Makinia J (2016) Modeling the effect of external carbon source addition under different electron acceptor conditions in biological nutrient removal activated sludge systems. Environ Sci Technol 50(4):1887–1896. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04849
Kang XS, Liu CQ, Zhang B, Bi XJ, Zhang F, Cheng LH (2011) Application of reversed A2/O process on removing nitrogen and phosphorus from municipal wastewater in China. Water Sci Technol 63(10):2138–2142. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.340
Kerrn-Jespersen JP, Henze M (1993) Biological phosphorus uptake under anoxic and aerobic conditions. Water Res 27(4):617–624
Klein K, Mandel A, Lilleoja H, Salmar S, Tenno T (2020) Assessment of enhanced biological phosphorus removal process inhibition. SN Appl Sci 2(9):1–10
Li P, Bi XJ, Wang J (2017) Ru SG (2017) Microbial diversity in activated sludges of conventional and reversed A2/O processes. China Environ Sci 37:1137–1145
Liu CQ, Zhang F, Bi XJ, Zhang B (2008) Contrast between Inverted A2/O process and Improved A2/O process in full-scale test. Technol Water Treatm 34(5):53–56
López-Vázquez CM, Hooijmans CM, Brdjanovic D, Gijzen DH, van Loosdrecht M (2008) Factors affecting the microbial populations at full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) wastewater treatment plants in The Netherlands. Water Res 42(10):2349–2360
Machado VC, Gabriel D, Lafuente J, Baeza JA (2009) Cost and effluent quality controllers design based on the relative gain array for a nutrient removal WWTP. Water Res 43(20):5129–5141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.08.011
Massara TM, Solís B, Guisasola A, Katsou E, Baeza JA (2018) Development of an ASM2d-N2O model to describe nitrous oxide emissions in municipal WWTPs under dynamic conditions. Chem Eng J 335:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.119
Metcalf L, Eddy HPG (1991) Wastewater engineering: treatment, disposal, and reuse, vol 4. McGraw-Hill, New York
Mulkerrins D, Jordan C, McMahon S, Colleran E (2000) Evaluation of the parameters affecting nitrogen and phosphorus removal in anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A/A/O) biological nutrient removal systems. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 75:261–268
Nopens I, Benedetti L, Jeppsson U, Pons MN, Alex J, Copp JB, Gernaey KV, Rosen C, Steyer JP, Vanrolleghem PA (2010) Benchmark simulation model no 2: finalisation of plant layout and default control strategy. Water Sci Technol 62(9):1967–1974
Oehmen A, Lopez-Vazquez CM, Carvalho G, Reis MA, Van Loosdrecht MC (2010) Modelling the population dynamics and metabolic diversity of organisms relevant in anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic enhanced biological phosphorus removal processes. Water Res 44(15):4473–4486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.017
Ostace GS, Baeza JA, Guerrero J, Guisasola A, Cristea VM, Agachi PŞ, Lafuente J (2013) Development and economic assessment of different WWTP control strategies for optimal simultaneous removal of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Comput Chem Engg 53:164–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2013.03.007
Ramin E, Flores-Alsina X, Gaszynski C, Harding T, Ikumi D, Brouckaert C, Gernaey KV (2022) Plant-wide assessment of alternative activated sludge configurations for biological nutrient removal under uncertain influent characteristics. Sci Total Environ 822:153678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153678
Ramphao M, Wentzel MC, Merritt R, Ekama GA, Young T, Buckley CA (2005) Impact of membrane solid–liquid separation on design of biological nutrient removal activated sludge systems. Bio Technol Bio Engg 89(6):630–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20311
Sheik AG, Seepana MM, Ambati SR (2021) Supervisory control configurations design for nitrogen and phosphorus removal in wastewater treatment plants. Water Environ Res 93(8):1289–1302
Sheik AG, Machavolu VRK, Seepana MM, Ambati SR (2022) Integrated supervisory and override control strategies for effective biological phosphorus removal and reduced operational costs in wastewater treatment processes. Chemosphere 287:132346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132346
Shiek AG, Machavolu VR, Seepana MM, Ambati SR (2020) Design of control strategies for nutrient removal in a biological wastewater treatment process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 6:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09347-2
Takács I, Patry GG, Nolasco D (1991) A dynamic model of the clarification-thickening process. Water Res 25(10):1263–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(91)90066-Y
Wang Q, Chen Q, Chen J (2017) Optimizing external carbon source addition in domestics wastewater treatment based on online sensor data and a numerical model. Water Sci Technol 75(11):2716–2725. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.128
Xie WM, Zeng RJ, Li WW, Wang G, Zhang LM (2018) A modeling understanding on the phosphorous removal performances of A 2 O and reversed A 2 O processes in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(23):22810–22817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2317-3
Xu SN, Bernards M, Hu Z (2014) Evaluation of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2/O) and reverse A2/O processes in biological nutrient removal. Water Environ Res 86(11):2186–2193. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143014X14062131178394
Zhang B, Gao T (2000) An anoxic/anaerobic/aerobic process for the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater. J Environ Sci Health 35(10):1797–1801. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520009377075
Zhang M, Peng Y, Wang C, Wang C, Zhao W, Zeng W (2016) Optimization denitrifying phosphorus removal at different hydraulic retention times in a novel anaerobic anoxic oxic-biological contact oxidation process. Biochem Eng J 106:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.10.027
Zhou Z, Wu Z, Wang Z, Tang S, Gu G, Wang L, Wang Y, Xin Z (2011) Simulation and performance evaluation of the anoxic/anaerobic/aerobic process for biological nutrient removal. Korean J Chem Eng 28(5):1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0502-2
Zhou Z, Shen X, Jiang LM, Wu Z, Wang Z, Ren W, Hu D (2015) Modeling of multimode anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic wastewater treatment process at low temperature for process optimization. Chem Eng J 281:644–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.07.017
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Senthil Kumar Ponnusamy.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheik, A.G., Seepana, M.M. & Ambati, S.R. Model-based evaluation of three different A2O processes in the presence of carbon and metal dosages. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 6575–6588 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04306-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04306-5