Abstract
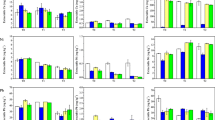
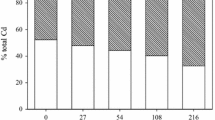
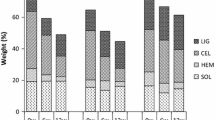
Organic amendments exert important effects on the migration and transformation of cadmium in soils. However, the adsorption capacities of different types of organic amendment and the stability of the adsorbed cadmium, especially during the decomposition process, are poorly understand. Here, using adsorption kinetics, isotherm analysis and functional group analysis methods we aim to investigate the adsorption behavior of cadmium on fresh and aged (six-month-old) commercial organic fertilizers produced from sheep manure, chicken manure and tobacco waste compost. Results showed chemical adsorption was the predominant cadmium adsorption process on the organic fertilizers, especially ion-exchanged Cd (59.7% to 78.0%) and hydrogen-bonded Cd (16.5% to 37.9%). The maximum cadmium adsorption capacity occurred on the tobacco waste compost (44.7 mg g−1) due to the high pH and surface organic functional groups, with values of 36.6 and 18.5 mg g−1, respectively, on the sheep and chicken manures. Similarly, increased contents of organic functional groups resulted in a higher adsorption cadmium capacity on the aged compost (50.3 mg g−1) than on the fresh tobacco compost (44.7 mg g−1), indicating that the decomposition process increased the cadmium adsorption capacity of the compost within six months. Our results suggest that aging of tobacco compost could improve its capacity for the adsorption of cadmium. Thus, application of organic fertilizer derived from tobacco waste compost would be feasible as a stable technique for the remediation of cadmium contaminated soil due to its high and persistent cadmium adsorption capacity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Andreas R, Zhang J (2014) Characteristics of adsorption interactions of cadmium (II) onto humin from peat soil in freshwater and seawater media. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92:352–357
Chang R, Sohi SP, Jing F, Li Y, Chen J (2019) A comparative study on biochar properties and Cd adsorption behavior under effects of ageing processes of leaching, acidification and oxidation. Environ Pollut 254:113123
Cheng Q, Huang Q, Khan S, Liu Y, Liao Z, Li G, Ok SY (2016) Adsorption of Cd by peanut husks and peanut husk biochar from aqueous solutions. Ecol Eng 87:240–245
Deng Y, Huang S, Dong C, Meng Z, Wang X (2020) Competitive adsorption behavior and mechanisms of cadmium, nickel and ammonium from aqueous solution by fresh and ageing rice straw biochars. Bioresour Technol 303:122853
Ellerbrock RH, Gerke HH, Bohm C (2009) In situ DRIFT characterization of organic matter composition on soil structural surfaces. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:531–540
Hamid Y, Tang L, Hussain B, Usman M, Liu L, Sher A, Yang X (2020) Adsorption of Cd and Pb in contaminated gleysol by composite treatment of sepiolite, organic manure and lime in field and batch experiments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 196:110539
Hossain MS, Hossain A, Sarkar MAR, Jahiruddin M, Sila JAT, Hossain MI (2016) Productivity and soil fertility of the rice-wheat system in the high Ganges River floodplain of Bangladesh is influenced by the inclusion of legumes and manure. Agric Ecosyst Environ 218:40–52
Huang X, Zemlyanov DY, Diaz-Amaya S, Salehi M, Stanciu L, Whelton AJ (2020) Competitive heavy metal adsorption onto new and aged polyethylene under various drinking water conditions. J Hazard Mater 385:121585
Li Y, Ma J, Shafi M, Sun Y, Li Y, Chen Z, Xiang Z, Jin G, Zhong B, Ye Z, Liu D (2020) Effects of adsorption characteristics of different amendments on heavy metals (Pb, Zn and Cd). J Soils Sediments 20:2868–2876
Lin S, Zhang J, Li J, Wu W (2018) Adsorption and desorption of Pb (II) and Cu (II) by six commercial organic fertilizers from Hainan province. J Fujian Agric for Univ 47:97–103 (in Chinese)
Liu L, Guo X, Zhang C, Luo C, Xiao C, Li R (2019) Adsorption behaviors and mechanisms of heavy metal ions on municipal waste composts with different degree of maturity. Environ Technol 40:2862–2976
Ministry of Environment Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEPRC) (2014) Bulletin of national soil pollution survey (in Chinese)
Mu H, Zhuang Z, Li Y, Qiao Y, Chen Q, Xiong J, Guo L, Jiang R, Li H (2020) Heavy metal contents in animal manure in China and the related soil accumulation risks. Environ Sci 41:986–996
Muhammad Q, Liu Y, Huang J, Liu K, Muhammad M, Lv Z, Hou H, Lan X, Ji J, Waqas A, Li D, Zhang H (2020) Soil nutrients and heavy metal availability under long-term combined application of swine manure and synthetic fertilizers in acidic paddy soil. J Soils Sediments 20:2093–2106
Palansooriya KN, Shaheen SM, Chen SS, Tsang DCW, Hashimoto Y, Hou D, Bolan NS, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2020) Soil amendments for immobilization for potentially toxic elements in contaminated soil: a critical review. Environ Int 134:105064
Peng H, Gao P, Chu G, Pan B, Peng J, Xing B (2017) Enhanced adsorption of Cu (II) and Cd (II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars. Environ Pollut 229:846–853
Qi Y, Zhu J, Fu Q, Hu H, Rong X, Huang Q (2017) Characterization and Cu sorption properties of humic acid from the decomposition of rice straw. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:23744–23752
Rechberger MV, Kloss S, Wang SL, Lehmann J, Rennhofer H, Ottner F, Wriessning K, Daudin G, Lichtenegger H, Soja G, Zehetner F (2019) Enhanced Cu and Cd sorption after soil aging of woodchip-derived biochar: what were the driving factors? Chemosphere 216:463–471
Ruthven DM (2003) Adsorption (Chemical Engineering). In: Meyers RA (ed) Encyclopedia of physical science and technology, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 251–271
Rwiza MJ, Oh SY, Kim KW, Kim SD (2018) Comparative sorption isotherms and removal studies for Pb (II) by physical and thermochemical modification of low-cost agro-wastes from Tanzania. Chemosphere 195:135–145
Satarug S, Garrett SH, Sens MA (2010) Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environ Health Perspect 118:183–190
Sim JT, Maguire RO (2005) Manure management. In: Daniel H (ed) Encyclopedia of soils in the environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 402–410
Su YF, Wen YJ, Yang WJ, Zhang Xia M, Zhou N, Xiong YF, Zhou Z (2021) The mechanism transformation of ramie biochar’s cadmium adsorption by aging. Bioresour Technol 330:124947
Tang J, Zhang L, Zhang J, Ren L, Zhou Y, Zheng Y, Luo L, Yang Y, Huang H, Chen A (2020) Physicochemical features, metal availability and enzyme activity in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by biochar and compost. Sci Total Environ 701:134751
Tauqeer HM, Karczewska A, Lewinska K, Fatma M, Khan SA, Farhan M, Turan V, Ramzani PMA, Iqbal M (2021) Environmental concerns associated with explosives (HMX, TNT, and RDX), heavy metals and metalloids from shooting rangesoils: prevailing issues, leading management practices, and future perspectives. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Prasad MNV (eds) Handbook of Bioremediation. Academic Press, pp 569–590
Turan V, Khan SA, Ur-Rahman M, Iqbal M, Ramzani PMA, Fatima M (2018) Promoting the productivity and quality of brinjal aligned with heavy metals immobilization in a wastewater irrigated heavy metal polluted soil with biochar and chitosan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:409–419
Uçar S, Erdem M, Tay T, Karagoz S (2015) Removal of lead (II) and nickel (II) ions from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared from rapeseed oil cake by Na2CO3 activation. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:747–756
Wang H, Feng M, Zhou F, Huang X, Tsang DCW, Zhang W (2017) Effects of atmospheric ageing under different temperatures on surface properties of sludge-derived biochar and metal/metalloid stabilization. Chemosphere 184:176–184
Wang L, Chen L, Tsang DCW, Li JS, Baek K, Hou D, Ding S, Poon CS (2018a) Recycling dredged sediment into fill materials, partition blocks, and paving blocks: technical and economic assessment. J Clean Prod 199:69–76
Wang RZ, Huang DL, Liu GY, Zhang C, Lai C, Zeng GM, Cheng M, Gong XM, Wan J, Luo H (2018b) Investigating the adsorption behavior and the relative distribution of Cd2+ sorption mechanisms on biochars by different feedstock. Bioresour Technol 261:265–271
Yang L, Fan L, Huang B, Xin J (2020) Efficiency and mechanisms of fermented horse manure, vermicompost, bamboo biochar, and fly ash on Cd accumulation in rice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:27859–27869
Yu Y, Wan Y, Camara AY, Li H (2018) Effects of the addition and aging of humic acid-base amendments on the solubility of Cd in soil solution and its accumulation in rice. Chemosphere 196:303–310
Zhang X, Meng HB, Shen YJ, Li J, Wang JR, Zhou HB, Ding JT, Wang J, Song LQ (2018) Survey on heavy metal concentrations and maturity indices of organic fertilizer in China. Int J Agric Bio Eng 11:172–179
Zhou L, Liu Y, Liu S, Yin Y, Zeng G, Tian X, Hu X, Jiang L, Ding Y, Liu S, Huang X (2016) Investigation of the adsorption-reduction mechanisms of hexavalent chromium by ramie biochars of different pyrolytic temperatures. Bioresour Technol 218:351–359
Zhou N, Chen H, Xi J, Yao D, Zhou Z, Tian Y, Lu X (2017) Biochars with excellent Pb (II) adsorption property produced from fresh and dehydrated banana peels via hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour Technol 232:204–210
Zhou T, Wu LH, Luo YM, Christie P (2018) Effects of organic matter fraction and compositional changes on distribution of cadmium and zinc in long-term polluted paddy soils. Environ Pollut 232:514–522
Zhu W, Du W, Shen X, Zhang H, Ding Y (2017) Comparative adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ by cow manure and its vermicompost. Environ Pollut 227:89–97
Zubair M, Ramzani PMA, Rasool B, Khan MA, Ur-Rahman M, Akhtar I, Turan V, Tauqeer HM, Farhad M, Khan SA, Iqbal J, Iqbal M (2021) Efficacy of chitosan-coated textile waste biochar applied to Cd-polluted soil for reducing Cd mobility in soil and its distribution in Moringa (Moringa oleifera L.). J Environ Manage 284:112047
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation for High-level Talents from Basic and Applied Basic Research Progress of Hainan Province (Grant No. 2019RC022) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21866013).
Funding
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation for High-level Talents from Basic and Applied Basic Research Progress of Hainan Province (Grant No. 2019RC022) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21866013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YW, QZ and ZW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YW, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Hari Pant.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhao, Q., Wei, Z. et al. Effects of aging on the persistence of cadmium adsorption on organic fertilizers. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 1951–1960 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04097-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04097-9