Abstract
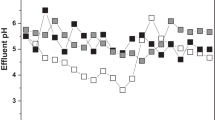
The focus of this report is directed towards the influence of transport properties of fermentation broth in degradation and decolorization of distillery spent wash using Cladosporium cladosporioides. Batch experiment was conducted in a bioreactor for 7 days with 250 rpm at 35 °C under optimum bioprocess conditions maintained using control system. Results of the morphological analysis revealed that C. cladosporioides has been observed to form mainly pellets during fermentation under mild agitation. The organism changed from filamentous form to pellet and then breaks, ending with filamentous form. All the models Power law, Bingham plastic, and Herschel–Bulkley fitted the general trend well with high R 2 values ranging from 0.9 to 0.98, indicating shear rate thinning nature of the broth. A maximum decolorization of 72.3 % was achieved with chemical oxygen demand reduction of 74.8 % due to the low viscous and pellet nature of the organism, leading to the transport properties of the fluid. Hence, transport phenomena channalyze the metabolic path way easily and leads to a novel approach for the industries to utilize the spent wash with minimum cost.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of waste and wastewater, 15th edn. American Public Health Associations, New York
Badino AC, Facciotti MCR, Schmidell W (2001) Volumetric oxygen transfer coefficients (kLa) in batchcultivations involving non-Newtonian broths. Biochem Eng J 8(2):111–119
Berovic M, Cimerman A, Steiner W, Koloni T (1991) Submerged citric acid fermentation: rheological properties of Aspergillus niger broth in a stirred tank reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34(5):579–581
Berovic M, Koloini T, Olsvik ES, Kristiansen B (1993) Rheological and morphological properties of submerge citric acid fermentation broth in stirred-tank and bubble column reactors. Chem Eng J 53(2):35–40
Blanch HW, Bhavaraju SM (1976) Non-Newtonian fermentation broths: rheology and mass transfer. Biotechnol Bioeng 18(6):745–790
Buchs J, Zoels B (2001) Evaluation of maximum to specific power consumption ratio in shaking bioreactor. J Chem Eng Jpn 34(5):647–653
Charles M (1978) Technical aspects of the rheological properties of microbial cultures. Adv Biochem Eng 8:1–62
Cho YJ, Hwang HJ, Kim SW, Song CH, Yun JW (2002) Effect of carbon source and aeration rate on broth rheology and fungal morphology during red pigment production by Paecilomyces sinclairii in a batch bioreactor. J Biotechnol 95:13–23
Daniel O, Schonholzer F, Zeyer J (1995) Quantification of fungal hyphae in leaves of deciduous trees by automated image analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(11):3910–3918
Fazenda ML, Harvey LM, McNeil B (2010) Effects of dissolved oxygen on fungal morphology and process rheology during fed batch processing of Ganoderma lucidum. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(4):844–851
Gehrig I, Bart HJ, Anke T, Germerdonk R (1998) Influence of morphology and rheology on the production characteristics of the basidiomycete Cyathus striatus. Biotechnol Bioeng 59(5):525–533
Goudar CT, Strevett KA, Shah SN (1999) Influence of microbial concentration on the rheology of non-Newtonia fermentation broths. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51(3):310–315
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Krishnan L, Mittal J (2006) Adsorption treatment and recovery of the hazardous dye, Brilliant Blue FCF, over bottom ash and de-oiled soya. J Colloid Interface Sci 293(1):16–26
Gupta VK, Jain R, Mittal A, Mathur M, Sikarwar S (2007a) Photochemical degradation of the hazardous dye Safranin-T using TiO2 catalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci 309(2):464–469
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007b) Removal of Reactofix goldenyellow 3 RFN from aqueous solution using wheat husk an agricultural waste. J Hazard Mater 142:443–448
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Malviya A, Mittal J (2009) Adsorption of carmoisine A from wastewater using waste materials—Bottom ash and deoiled soya. J Colloid Interface Sci 335(1):24–33
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Nayak A (2010) Biosorption of nickel onto treated alga (Oedogonium hatei): application of isotherm and kinetic models. J Colloid Interface Sci 342(1):533–539
Gupta VK, Agarwal S, Saleh TA (2011) Chromium removal by combining the magnetic properties of iron oxide with adsorption properties of carbon nanotubes. Water Res 45(6):2207–2212
Jaina K, Gupta VK, Bhatnagar A, Suhas (2003) A comparative study of adsorbents prepared from industrial wastes for removal of dyes. Sep Sci Technol 38(2):463–481
Ju L, Ho CS, Shanahan JF (1991) Effects of carbon dioxide on the rheological behavior and oxygen transfer in submerged penicillin fermentations. Biotechnol Bioeng 38(10):1223–1232
Kaur S, Kaler RSS (2008) Dextran and its effect on the flow behaviour of molasses and crystallization rate. J Food Eng 86:55–60
Kim JH, Lebeault JM, Reuss M (1983) Comparative study on rheological properties of mycelial broth in filamentous and pelleted forms. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 18:11–16
Lee BC, Bae JT, Pyo HB, Choe TB, Kim SW, Hwang HJ, Yun JW (2004) Submerged culture conditions for the production of mycelial biomass and exopolysaccharides by the edible Basidiomycete Grifola frondosa. Enzym Microb Technol 35(5):369–376
Lim JS, Kim JH, Kim C, Kim SW (2002) Morphological and rheological properties of culture broth of Cephalosporium acremonium M25. Korea–Aust Rheol J 14:11–116
Metz B, Kossen F, Van Suijdam JC (1979) The rheology of mold suspensions. Adv Biochem Eng 11:104–156
Mittal A, Gupta VK, Malviya A, Mittal J (2008) Process development for the batch and bulk removal and recovery of a hazardous, water-soluble azo dye (Metanil Yellow) by adsorption over waste materials (Bottom Ash and De-Oiled Soya). J Hazard Mater 151(2–3):821–832
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Kaur D, Gupta VK (2010) Adsorption of hazardous dye crystal violet from wastewater by waste materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 343(2):463–473
Packer HL, Thomas CR (1990) Morphological measurement on filamentous micro organisms by fully automatic image analysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:870–881
Park EY, Koike Y, Higashiyama K, Fujikawa S, Okabe M (1999) Effect of nitrogen source on mycelial morphology and arachidonic acid production in cultures of Mortierella alpina. J Biosci Bioeng 88:61–67
Pazouki M, Panda T (2000) Understanding the morphology of fungi. Bioprocess Eng 22:127–143
Raghukumar C, Rivonkar G (2001) Decolorization of molasses spent wash by white-rot fungus Flavodon flavus, isolated from a marine habitat. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:510–514
Ravikumar R, Monash P, Derek Chan JC, Saravanan K (2010) Microbial decolorization of biomethanate distillery spentwash using Aspergillus nidulans. Asian J Microbiol Biotech Enviro Sci 12:337–342
Ravikumar R, Vasanthi NS, Saravanan K (2011) Single factorial experimental design for decolorizing anaerobically treated distillery spent wash using Cladosporium cladosporioides. Int J Environ Sci Tech 8:97–106
Ravikumar R, Vasanthi NS, Saravanan K (2013a) Biodegradation and decolorization of distillery spent wash with product release by a novel strain Cladosporium cladosporioides: optimization and biokinetics. Chem Biochem J Q 27(3):373–383
Ravikumar R, Renuka K, Sindhu V, Malarmathi KB (2013b) Response surface methodology and artificial neural network for modeling and optimization of distillery spent wash treatment using Phormidium valderianum BDU 140441. Pol J Env Stud 22(4):20–28
Rodríguez Porcel EM, Casas López JL, Sánchez Pérez JA, Fernández Sevilla JM, García Sánchez JL, Chisti Y (2006) Aspergillus terreus broth rheology, oxygen transfer, and lovastatin production in a gas-agitated slurry reactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:4837–4843
Sanghavi BJ, Mobina SM, Mathurb P, Lahirib GK, Srivastavaa AK (2013a) Biomimetic sensor for certain catecholamines employing copper(II) complex and silver nanoparticle modified glassy carbon paste electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 39(2):124–132
Sanghavi BJ, Sitaula S, Griep MH, Karna SP, Ali MF, Swami NS (2013b) Real-time electrochemical monitoring of adenosine triphosphate in the picomolar to micromolar range using graphene-modified electrodes. Anal Chem 85(17):8158–8165
Sinha J, Bae JT, Park JP, Song CH, Yun JW (2001) Effect of substrate concentration on broth rheology and fungal morphology during exo-biopolymer production by Paecilomyces japonica in a batch bioreactor. Enzym Microb Technol 29(6):392–399
Smith JJ, Lilly MD, Fox RI (1990) The effect of agitation on the morphology and penicillin production of Penicillium chrysogenum. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:1011–1023
Tucker KG, Thomas CR (1993) Effect of biomass concentration and morphology on the rheological parameters of Penicillium chrysogenum fermentation broths. Trans Chem Eng 71:111–117
Vahabzadeh F, Mehranian M, Saatari AR (2004) Color removal ability of Phanerochaete chrysosporium in relation to lignin peroxides and manganese peroxides produced in molasses wastewater. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:859–864
Van Suijdam JC, Metz B (1981) Influence of engineering variables upon themorphology of filamentous molds. Biotechnol Bioeng 23:111–148
Acknowledgments
This work is the result of Ph.D. work of the first author. The author wishes to express their gratitude for the support extended by management of Bannari Amman Distillery Division, Periyapuliyur, Erode District, and Tamilnadu, India for providing us the spent wash and also soil sample. We wish to express our thanks to the management of Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, India in carrying out the research in Bioprocess Laboratory, Department of Biotechnology. All the authors are cordially wish to express their thanks to the reviews for their valuable suggestions in improving this research work and manuscript. We also thank Foundation for Revitalization of Local Health Traditions (FRLHT), Bangalore, India for the image analysis and Agharkar Research Institute, Pune, Maharashtra, India (ARI)-National Fungal Culture Collection of India (NFCCI) for DNA sequencing report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravikumar, R. Effect of transport phenomena of Cladosporium cladosporioides on decolorization and chemical oxygen demand of distillery spent wash. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 1581–1590 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0520-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0520-4