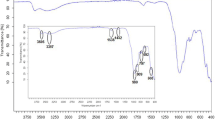
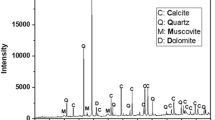
Abstract
In this study, a natural red clay, a low-cost and abundant adsorbent, was investigated for the removal of Basic Red 29 dye from aqueous solutions. The effects of key parameters such as pH, adsorbent dose, initial dye concentration, contact time, and ionic strength on the adsorption capacity of red clay were systematically studied and optimized using response surface methodology. The suggested model was approved with high correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.9994) and (Radj2 = 0.9985). Furthermore, the model's p value was found to be < 0.001 and an F-value of 1215.41 indicates the model's high significance. According to the analysis of variance (ANOVA), the linear effects of dye concentration and adsorbent dose were the determining factors that affect the dye removal efficiency. The adsorption capacity predicted by the model under optimum conditions (initial dye concentration of 129.25 mg/L, adsorbent dose of 1.07 g/L, and contact time of 41 min) was reached a value of 108.79 mg/g. The adsorption process followed the Langmuir isotherm model with a maximum adsorption capacity of 303.03 mg/g and was well described by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The effect of ionic strength revealed the importance of electrostatic interactions in the adsorption process, which was further supported by the proposed adsorption mechanism based on protonation/deprotonation and electrostatic attractions and repulsions between dye molecules and clay surface functional groups. Red clay demonstrated superior adsorption capacity for Basic Red 29 dye removal compared with other adsorbents reported in the literature. The regeneration experiments showed the effectiveness and reusability of red clay as an adsorbent. Additionally, a germination test was performed to confirm the low toxicity of the treated water after adsorption onto the red clay. The outcome of this research showed that red clay can be classified as a good and efficient adsorbent in dye removal.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Ben Mansour, O. Boughzala, D. Barillier, R. Mosrati, Les colorants textiles sources de contamination de l’eau : CRIBLAGE de la toxicité et des méthodes de traitement Textiles dyes as a source of wastewater contamination: screening of the toxicity and treatment methods. Rev. Des Sci. L’Eau 24, 31 (2011)
E. Rápó, S. Tonk, Factors affecting synthetic dye adsorption; desorption studies: a review of results from the last five years (2017–2021). Molecules (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175419
L.D. Ardila-Leal, R.A. Poutou-Piñales, A.M. Pedroza-Rodríguez, B.E. Quevedo-Hidalgo, A brief history of colour, the environmental impact of synthetic dyes and removal by using laccases. Molecules (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133813
A. Kausar et al., Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: a review. J. Mol. Liq. 256, 395–407 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
R. Al-Tohamy et al., A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 231, 113160 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113160
M.T. Yagub, T.K. Sen, S. Afroze, H.M. Ang, Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 209, 172–184 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002
E. Franciscon, A. Zille, F. Fantinatti-Garboggini, I.S. Silva, A. Cavaco-Paulo, L.R. Durrant, Microaerophilic-aerobic sequential decolourization/biodegradation of textile azo dyes by a facultative Klebsiella sp. strain VN-31. Process Biochem. 44(4), 446–452 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2008.12.009
Y. Anjaneyulu, N. Sreedhara Chary, N. Samuel Suman Raj, Decolourization of industrial effluents - available methods and emerging technologies - a review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 4(4), 245–273 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-005-1246-z
M. Berradi et al., Textile finishing dyes and their impact on aquatic environs. Heliyon (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02711
S. Benkhaya, S. M’rabet, A. Harfi, A review on classifications, recent synthesis and applications of textile dyes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 115, 107891 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2020.107891
A. Kesraoui, T. Selmi, M. Seffen, F. Brouers, Influence of alternating current on the adsorption of indigo carmine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24(11), 9940–9950 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7201-4
J. Sharma, S. Sharma, V. Soni, Classification and impact of synthetic textile dyes on Aquatic Flora: a review. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2021.101802
S.H. Javed, A. Zahir, A. Khan, S. Afzal, M. Mansha, Adsorption of Mordant Red 73 dye on acid activated bentonite: kinetics and thermodynamic study. J. Mol. Liq. 254, 398–405 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.01.100
M. Benjelloun, Y. Miyah, G. Akdemir Evrendilek, F. Zerrouq, S. Lairini, Recent advances in adsorption kinetic models: their application to dye types. Arab. J. Chem. 14(4), 103031 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103031
R. B. Chavan, Environmentally friendly dyes, vol. 1. Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2011.
N.C. Dias, J.P. Bassin, G.L. Sant’Anna, M. Dezotti, Ozonation of the dye Reactive Red 239 and biodegradation of ozonation products in a moving-bed biofilm reactor: revealing reaction products and degradation pathways. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 144, 104742 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.104742
A. Alipour, M.M. Lakouarj, Photocatalytic degradation of RB dye by CdS-decorated nanocomposites based on polyaniline and hydrolyzed pectin: isotherm and kinetic. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7(1), 102837 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.102837
W. Przystas, E. Zablocka-Godlewska, E. Grabinska-Sota, Biological removal of azo and triphenylmethane dyes and toxicity of process by-products. Water Air Soil Pollut. 223(4), 1581–1592 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0966-7
A.A. Adeyemo, I.O. Adeoye, O.S. Bello, Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: a review. Appl Water Sci 7(2), 543–568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0322-y
Z. Yang, T.A. Asoh, H. Uyama, Removal of cationic or anionic dyes from water using ion exchange cellulose monoliths as adsorbents. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 92(9), 1453–1461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.20190111
A.Q. Alorabi, M.S. Hassan, M.M. Alam, S.A. Zabin, N.I. Alsenani, N.E. Baghdadi, Natural clay as a low-cost adsorbent for crystal violet dye removal and antimicrobial activity. Nanomaterials (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112789
A. Hamzezadeh, Y. Rashtbari, S. Afshin, M. Morovati, M. Vosoughi, Application of low-cost material for adsorption of dye from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 102(1), 254–269 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1720011
T. Ngulube, J.R. Gumbo, V. Masindi, A. Maity, An update on synthetic dyes adsorption onto clay based minerals: a state-of-art review. J. Environ. Manage. 191, 35–57 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.031
A. Dra, A. El Gaidoumi, K. Tanji, A. Chaouni Benabdallah, A. Taleb, A. Kherbeche, Characterization and quantification of heavy metals in Oued Sebou sediments. Sci. World J. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7496576
T. Zhang et al., Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: from natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 420, 127574 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127574
Y. Dehmani, O. El Khalki, H. Mezougane, S. Abouarnadasse, Comparative study on adsorption of cationic dyes and phenol by natural clays. Chem. Data Collect. 33, 100674 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdc.2021.100674
A. El Kassimi, A. Boutouil, M. El Himri, M. Rachid Laamari, M. El Haddad, Selective and competitive removal of three basic dyes from single, binary and ternary systems in aqueous solutions: a combined experimental and theoretical study. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 24(7), 527–544 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2020.05.005
A. Benhouria, M.A. Islam, H. Zaghouane-Boudiaf, M. Boutahala, B.H. Hameed, Calcium alginate-bentonite-activated carbon composite beads as highly effective adsorbent for methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 270, 621–630 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.030
J. Paul Guin, Y.K. Bhardwaj, L. Varshney, Radiation crosslinked swellable ionic gels: equilibrium and kinetic studies of basic dye adsorption. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(9), 4090–4099 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.988656
M.C. Avila, I.D. Lick, N.A. Comelli, M.L. Ruiz, Adsorption of an anionic dye from aqueous solution on a treated clay. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 15, 100688 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2021.100688
G. Annadurai, S. Rajesh Babu, G. Nagarajan, K. Ragu, Use of Box-Behnken design of experiments in the production of manganese peroxidase by Phanerochaete chrysosporium (MTCC 767) and decolorization of crystal violet. Bioprocess Eng. 23(6), 715–719 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004490000201
F. Marrakchi, M. Bouaziz, B.H. Hameed, Activated carbon–clay composite as an effective adsorbent from the spent bleaching sorbent of olive pomace oil: process optimization and adsorption of acid blue 29 and methylene blue. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 128, 221–230 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.10.015
B. Kayan, B. Gözmen, Degradation of Acid Red 274 using H 2O 2 in subcritical water: application of response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 201–202, 100–106 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.045
A. Loqman, B. El Bali, A. El Gaidoumi, A. Boularbah, A. Kherbeche, J. Lützenkirchen, The first application of Moroccan perlite as industrial dyes removal. SILICON 14(6), 2813–2838 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01056-w
Y. Bentahar, Caractérisation physico-chimique des argiles marocaines : application à l’adsorption de l’arsenic et des colorants cationiques en solution aqueuse Thèse,” Sophia, p. 269, 2016, [Online]. Available: http://bib.rilk.com/5521/
A. Thiam et al., Valorization of date pits as an effective biosorbent for remazol brilliant blue adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4173152
F. Farcas, P. Touzé, La spectrométrie infrarouge à transformée de Fourier (IRTF). Bull. Des Lab. Des Ponts Chaussées 230(4350), 77–88 (2001)
S.A. Boussaa, A. Kheloufi, N.Z. Boutarek, Caractérisation et valorisation du Quartz d ’ Edough pour application photovoltaïque. Rev. des Energies Renouvelables 21(3), 391–396 (2018)
A. Dra et al., Erratum: valorization of oued sebou natural sediments (Fez-Morocco Area) as adsorbent of methylene blue dye: kinetic and thermodynamic study. Sci. World J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4815767
A. Ksakas, A. Loqman, B. El Bali, M. Taleb, A. Kherbeche, The adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by natural materials. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 6(7), 2003–2012 (2015)
A. Loqman, B. El Bali, J. Lützenkirchen, P.G. Weidler, A. Kherbeche, Adsorptive removal of crystal violet dye by a local clay and process optimization by response surface methodology. Appl Water Sci 7(7), 3649–3660 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0509-x
F. Allali, M. Monsif, N. Idrissi Kandri, A. Zerouale, Caractérisation physico-chimique des enduits anciens et de restauration de la muraille (Al Moahades) bab chaâfa de la médina de salé: Etude comparative. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 5, 1577–1586 (2014)
T.L. Silva et al., Mesoporous activated carbon from industrial laundry sewage sludge: adsorption studies of reactive dye Remazol Brilliant Blue R. Chem. Eng. J. 303, 467–476 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.009
I. Chaari, E. Fakhfakh, M. Medhioub, F. Jamoussi, Comparative study on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes by smectite rich natural clays. J. Mol. Struct. 1179, 672–677 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.11.039
I. Feddal, G. Mimanne, A. Dellani, S. Taleb, Synthesis and characterization of an adsorbent material: application to textile dye elimination. Mater. Today Proc. 49, 981–985 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.105
N. Nabbou, E. Benyagoub, M. Belhachemi, M. Boumelik, M. Benyahia, Removal performance for thermotolerant coliforms and fecal streptococci from dairy effluents by Kenadsa’s natural green clay (Bechar-Algeria) in a fixed-bed column. Appl Water Sci 11(6), 1–15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01441-1
A.A. Oladipo, M. Gazi, S. Saber-Samandari, Adsorption of anthraquinone dye onto eco-friendly semi-IPN biocomposite hydrogel: Equilibrium isotherms, kinetic studies and optimization. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45(2), 653–664 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.07.013
M. Alipour et al., Optimising the basic violet 16 adsorption from aqueous solutions by magnetic graphene oxide using the response surface model based on the Box-Behnken design. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 101(6), 758–777 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1671378
S. Niju, R. Rabia, K. Sumithra Devi, M. Naveen Kumar, M. Balajii, Modified Malleus malleus shells for biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: an optimization study using Box-Behnken design. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 11(3), 793–806 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0520-6
O. Assila, M. Zouheir, K. Tanji, R. Haounati, F. Zerrouq, A. Kherbeche, Copper nickel co-impregnation of Moroccan yellow clay as promising catalysts for the catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of caffeine. Heliyon 7(1), e06069 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06069
N. Markandeya, S. Dhiman, P. Shukla, G.C. Kisku, Statistical optimization of process parameters for removal of dyes from wastewater on chitosan cenospheres nanocomposite using response surface methodology. J. Clean. Prod. 149, 597–606 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.078
O. Assila et al., Adsorption studies on the removal of textile effluent over two natural eco-friendly adsorbents. J. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6457825
M. Kousha, E. Daneshvar, M.S. Sohrabi, N. Koutahzadeh, A.R. Khataee, Optimization of C.I. Acid black 1 biosorption by Cystoseira indica and Gracilaria persica biomasses from aqueous solutions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 67, 56–63 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.10.007
M. Ahmadi, K. Rahmani, A. Rahmani, H. Rahmani, Removal of benzotriazole by Photo-Fenton like process using nano zero-valent iron: response surface methodology with a Box-Behnken design. Polish J. Chem. Technol. 19(1), 104–112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/pjct-2017-0015
R. Foroutan, S.J. Peighambardoust, S.H. Peighambardoust, M. Pateiro, J.M. Lorenzo, Adsorption of crystal violet dye using activated carbon of lemon wood and activated carbon/fe3 o4 magnetic nanocomposite from aqueous solutions: a kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Molecules 26(8), 1–19 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082241
M. Loutfi, R. Mariouch, I. Mariouch, M. Belfaquir, M.S. ElYoubi, Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions onto natural clay: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Mater. Today Proc. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.08.412
H. Haroon et al., Equilibrium kinetic and thermodynamic studies of Cr(VI) adsorption onto a novel adsorbent of Eucalyptus camaldulensis waste: batch and column reactors. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 33(10), 2898–2907 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0160-0
N. Le My Linh et al., Phenol red adsorption from aqueous solution on the modified bentonite. J. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1504805
B. Abdelkader, Application des Biomasses à la Récupération des Polluants des Eaux Usées. pp. 2017–2018, 2018
A.A. Oladipo, M. Gazi, Enhanced removal of crystal violet by low cost alginate/acid activated bentonite composite beads: optimization and modelling using non-linear regression technique. J. Water Process Eng. 2, 43–52 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.04.007
S.S. Mayakaduwa et al., Equilibrium and kinetic mechanisms of woody biochar on aqueous glyphosate removal. Chemosphere 144, 2516–2521 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.080
P. Pfeifer and K. Y. Liu, Multilayer adsorption as a tool to investigate the fractal nature of porous adsorbents,” in Equilibria and Dynamics of Gas Adsorption on Heterogeneous Solid Surfaces, vol. 104, W. Rudzinski, W. A. Steele, and G. Zgrablich, Eds. 1997, pp. 625–677
N. Loubna, Y. Miyah, A. Ouissal, E.B. Aziz, E.K. Bouchta, Z. Farid, Kinetic and thermodynamicstudy of the adsorption of twodyes: brilliant green and eriochrome black T using a natural adsorbent ‘sugarcane bagasse.’ Moroccan J. Chem. 7(4), 715–726 (2019)
W. Chai, Y. Huang, G. Han, J. Liu, S. Yang, Y. Cao, An Enhanced study on adsorption of Al(iii) onto Bentonite and Kaolin: kinetics, isotherms, and mechanisms. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 38(2), 106–115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2016.1262862
R. Mohadi, E. Normah, S. Fitri, N.R. Palapa, Unique adsorption properties of cationic dyes Malachite green and Rhodamine-B on Longan (Dimocarpus longan) Peel. Sci. Technol. Indones. 7(1), 115–125 (2022). https://doi.org/10.26554/sti.2022.7.1.115-125
H.A. Niaei, M. Rostamizadeh, F. Maasumi, M.J. Darabi, Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies of methylene blue adsorption over metal-doped Zeolite nano-adsorbent. Phys. Chem. Res. 9(1), 17–30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.22036/pcr.2020.233844.1781
D. Ewis, M.M. Ba-Abbad, A. Benamor, M.H. El-Naas, Adsorption of organic water pollutants by clays and clay minerals composites: a comprehensive review. Appl. Clay Sci. 229, 106686 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106686
E. Errais et al., Efficient anionic dye adsorption on natural untreated clay: kinetic study and thermodynamic parameters. Desalination 275(1–3), 74–81 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.02.031
E. Allahkarami, A. Dehghan Monfared, L.F.O. Silva, G.L. Dotto, Toward a mechanistic understanding of adsorption behavior of phenol onto a novel activated carbon composite. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-27507-5
H. Li, L. Liu, J. Cui, J. Cui, F. Wang, F. Zhang, High-efficiency adsorption and regeneration of methylene blue and aniline onto activated carbon from waste edible fungus residue and its possible mechanism. RSC Adv. 10(24), 14262–14273 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra01245a
A.H. Jawad, A.S. Abdulhameed, Mesoporous Iraqi red kaolin clay as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue dye: adsorption kinetic, isotherm and mechanism study. Surf. Interfaces 18, 100422 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.100422
S. Bentahar, A. Dbik, M. El Khomri, N. El Messaoudi, A. Lacherai, Removal of a cationic dye from aqueous solution by natural clay. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 6, 255–262 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.02.002
A. El Kassimi, Y. Achour, M. El Himri, R. Laamari, M. El Haddad, Removal of two cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto local clay: experimental and theoretical study using DFT method. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 00(00), 1–22 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1873306
M. Onay, Ç. Sarici Özdemir, Equilibrium studies for dye adsorption onto red clay. Naturengs Mtu J. Eng. Nat. Sci. Mal. Turgut Ozal Univ. 2, 36–45 (2022). https://doi.org/10.46572/naturengs.1120218
M. Bergaoui et al., Novel insights into the adsorption mechanism of methylene blue onto organo-bentonite: adsorption isotherms modeling and molecular simulation. J. Mol. Liq. 272, 697–707 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.001
M. Momina, M. Shahadat, S. Isamil, Regeneration performance of clay-based adsorbents for the removal of industrial dyes: a review. RSC Adv. 8(43), 24571–24587 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra04290j
T. Alsawy, E. Rashad, M. El-Qelish, R.H. Mohammed, A comprehensive review on the chemical regeneration of biochar adsorbent for sustainable wastewater treatment. npj Clean Water 5(1), 29 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00172-3
T. Garoma, L. Skidmore, Modeling the influence of ethanol on the adsorption and desorption of selected BTEX compounds on bentonite and kaolin. J. Environ. Sci. 23(11), 1865–1872 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60653-5
M. Bouzid, L. Sellaoui, M. Khalfaoui, H. Belmabrouk, A. Ben Lamine, Adsorption of ethanol onto activated carbon: modeling and consequent interpretations based on statistical physics treatment. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 444, 853–869 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2015.09.097
M.I. Khan, Adsorption of methylene blue onto natural Saudi Red Clay: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Mater. Res. Express (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab903c
E.D.C. Analytique, L. De Biochimie, L.D.C. Organique, C. Ayyad, Adsorptive removal of a cationic dye - basic red 46 - from aqueous solutions using animal bone meal. J. Eng. Stud. Res. 18(3), 43–52 (2012)
T. Jóźwiak, U. Filipkowska, P. Marciniak, Use of hen feathers to remove reactive black 5 and basic red 46 from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 232, 129–139 (2021). https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27513
N. Sivarajasekar, R. Baskar, Adsorption of basic red 9 onto activated carbon derived from immature cotton seeds: isotherm studies and error analysis. Desalin. Water Treat. 52(40–42), 7743–7765 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.834518
P. Sivakumar, P.N. Palanisamy, Adsorption studies of Basic Red 29 by a non-conventional activated carbon prepared from Euphorbia antiquorum L. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 1(3), 502–510 (2009)
A. Geetha, N. Palanisamy, Equilibrium and kinetic studies for the adsorption of Basic Red 29 from aqueous solutions using activated carbon and conducting polymer composite. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(18), 8406–8419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1020510
H.C. Chu, L.H. Lin, H.J. Liu, K.M. Chen, Utilization of dried activated sludge for the removal of basic dye from aqueous solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 51(37–39), 7074–7080 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.772540
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Souhassou, H., Fahoul, Y., El Mrabet, I. et al. Optimization of basic red 29 dye removal onto a natural red clay using response surface methodology. J IRAN CHEM SOC 21, 275–291 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-023-02924-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-023-02924-5