Abstract
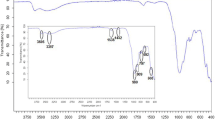
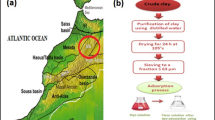
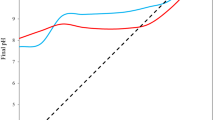
In this work the Removal of the basic blue 41 and crystal violet mixture was studied using Moroccan clay as an adsorbent. The morphology and structure of this local adsorbent were examined using different analysis techniques and physicochemical measures, including X-Ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), surface area (BET) and point of zero charge (pHpzc). The effects of three operating variables on removal efficiency of dye mixture were investigated and analyzed using Response surface methodology based on Box-Behnken design, namely: initial concentration of the dye mixture, adsorbent dose and solution pH. The proposed model (quadratic) was approved with high correlation coefficients (R2 = 0.9964), (R2adj = 0.9919), and a value of the percentage absolute error of deviation (AED) equal to 0.792. Furthermore, the p-value of the model was < 0.0001 and F-value of 217.37 implies the model is highly significant. The linear effects of dye mixture concentration and clay dose were the principal determining factors that affected the dye removal efficiency on local clay According to the analysis of variance (ANOVA). A significant dye removal rate (approximately 99% after only 50 min) was achieved under the following optimized conditions: dye concentration of 78.14 mg/L, adsorbent dose of 1.3 g/L and pH = 8.12. Practically, the removal rate was found to range from 55 to 99%. The isotherms and kinetics studies show that the adsorption process follows the Langmuir isotherm model (R2 = 0.98), and the adsorption is well described by the pseudo second order kinetic (R2 = 0.99), the calculated thermodynamic parameters revealed that the adsorption was endothermic. The present study showed that the tested local clay has significant adsorbing characteristics displaying high efficiency in removing basic blue 41 and crystal violet mixture. Thus, the germination test was initiated to confirm the low toxicity of the treated water after the adsorption process. The regeneration experiments were also carried out and it was found that the tested clay was regenerable.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desore A, Narula SA (2018) An overview on corporate response towards sustainability issues in textile industry. Environ Dev Sustain 20:1439–1459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-9949-1
Muthu SS (2017) Sustainability in the textile industry, Springer Singapore. Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2639-3
Lellis B, Fávaro-Polonio CZ, Pamphile JA, Polonio JC (2019) Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol Res Innov 3:275–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biori.2019.09.001
Wang S, Zhu ZH (2006) Characterisation and environmental application of an Australian natural zeolite for basic dye removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 136:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.038
Ai L, Zhang C, Liao F, Wang Y, Li M, Meng L, Jiang J (2011) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with magnetite loaded multi-wall carbon nanotube: Kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. J Hazard Mater 198:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.041
Sharma P, Das MR (2012) Removal of a cationic dye from aqueous solution using graphene oxide nanosheets: investigation of adsorption parameters. J Chem Eng Data 31:109–119
Abidi N, Errais E, Duplay J, Berez A, Jrad A, Schäfer G, Ghazi M, Semhi K, Trabelsi-Ayadi M (2015) Treatment of dye-containing effluent by natural clay. J Clean Prod 86:432–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.043
Cardoso NF, Lima EC, Royer B, Bach MV, Dotto GL, Pinto LAA, Calvete T (2012) Comparison of Spirulina platensis microalgae and commercial activated carbon as adsorbents for the removal of Reactive Red 120 dye from aqueous effluents. J Hazard Mater 241–242:146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.09.026
Parsaa JB, Abbasib M (2007) Decolorization of synthetic and real polluted water by indirect electrochemical oxidation process. Acta Chim Slov 54:792–796
Aguiar JE, de Oliveira JCA, Silvino PFG, Neto JA, Silva IJ, Lucena SMP (2016) Correlation between PSD and adsorption of anionic dyes with different molecular weigths on activated carbon. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 496:125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.09.054
Tanji K, Navio JA, Martín-Gómez AN, Hidalgo MC, Jaramillo-Páez C, Naja J, Hassoune H, Kherbeche A (2020) Role of Fe(III) in aqueous solution or deposited on ZnO surface in the photoassisted degradation of rhodamine B and caffeine. Chemosphere 241:125009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125009
Fahoul Y, Zouheir M, Tanji K, Kherbeche A (2022) Synthesis of a novel ZnAl2O4/CuS nanocomposite and its characterization for photocatalytic degradation of acid red 1 under UV illumination. J Alloys Compd 889:161708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161708
Vandevivere PC, Bianchi R, Verstraete W (1998) Review: Treatment and reuse of wastewater from the textile wet-processing industry: review of emerging technologies. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 72:289–302. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4660(199808)72:4%3c289::AID-JCTB905%3e3.3.CO;2-R
Zouheir M, Assila O, Tanji K, El Gaidoumi A, Araña J, Doña Rodríguez JM, Smått J-H, Huynh T-P, Kherbeche A (2021) Bandgap optimization of sol–gel-derived TiO2 and its effect on the photodegradation of formic acid. Nano Futur 5:025004. https://doi.org/10.1088/2399-1984/abfb7d
Hussein TK, Jasim NA (2021) A comparison study between chemical coagulation and electro-coagulation processes for the treatment of wastewater containing reactive blue dye. Mater Today Proc 42:1946–1950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.240
Dra A, Tanji K, Arrahli A, Iboustaten EM, El Gaidoumi A, Kherchafi A, Chaouni Benabdallah A, Kherbeche A (2020) Corrigendum to “Valorization of Oued Sebou Natural Sediments (Fez-Morocco Area) as Adsorbent of Methylene Blue Dye: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study.” Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2187129
Dra A, Tanji K, Arrahli A, Iboustaten EM, El Gaidoumi A, Kherchafi A, Benabdallah AC, Kherbeche A (2020) Valorization of Oued Sebou Natural Sediments (Fez-Morocco Area) as Adsorbent of Methylene Blue Dye : Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study. Sci World J 2020:2187129. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2187129
Gholami-Borujeni F, Mahvi AH, Naseri S, Faramarzi MA, Nabizadeh R, Alimohammadi M (2011) Application of immobilized horseradish peroxidase for removal and detoxification of azo dye from aqueous solution. Res J Chem Environ 15:217–222
Sadaf S, Bhatti HN, Nausheen S, Noreen S (2014) Potential use of low-cost lignocellulosic waste for the removal of direct violet 51 from aqueous solution: Equilibrium and breakthrough studies. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66:557–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9992-3
Mahmoud A (2017) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite of chitosan/SiO2/carbon nanotubes and its application for dyes removal. J Clean Prod 145:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.046
Khalilzadeh Shirazi E, Metzger JW, Fischer K, Hassani AH (2020) Removal of textile dyes from single and binary component systems by Persian bentonite and a mixed adsorbent of bentonite/charred dolomite. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 598:124807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124807
Chaari I, Medhioub M, Jamoussi F, Hamzaoui AH (2020) Acid-treated clay materials (Southwestern Tunisia) for removing sodium leuco-vat dye: Characterization, adsorption study and activation mechanism. J Mol Struct 1223:128944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128944
Dehmani Y, El Khalki O, Mezougane H, Abouarnadasse S (2021) Comparative study on adsorption of cationic dyes and phenol by natural clays. Chem Data Collect. 33:100674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdc.2021.100674
Saputra OA, Nauqinida M, Pujiasih S, Kusumaningsih T, Pramono E (2021) Improvement of anionic and cationic dyes removal in aqueous solution by Indonesian agro-waste oil palm empty fruit bunches through silylation approach. Groundw Sustain Dev 13:100570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2021.100570
Tatarchuk T, Paliychuk N, Bitra RB, Shyichuk A, Naushad MU, Mironyuk I, Ziółkowska D (2019) Adsorptive removal of toxic methylene blue and acid orange 7 dyes from aqueous medium using cobalt-zinc ferrite nanoadsorbents. Desalin Water Treat 150:374–385. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23751
Sarkar B, Rusmin R, Ugochukwu UC, Mukhopadhyay R, Manjaiah KM (2018) Modified clay minerals for environmental applications, Elsevier Inc., https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814617-0.00003-7.
Hynes NRJ, Kumar JS, Kamyab H, Sujana JAJ, Al-Khashman OA, Kuslu Y, Ene A, Suresh Kumar B (2020) Modern enabling techniques and adsorbents based dye removal with sustainability concerns in textile industrial sector -A comprehensive review. J Clean Prod 272:122636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122636
Ismadji Suryadi ES, Felycia A (2015) Ayucitra, clay materials for environmental remediation. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16712-1_1
Zhou Y, Lu J, Zhou Y, Liu Y (2019) Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: a review. Environ Pollut 252:352–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.072
Santos SCR, Oliveira ÁFM, Boaventura RAR (2016) Bentonitic clay as adsorbent for the decolourisation of dyehouse effluents. J Clean Prod 126:667–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.03.092
Satlaoui Y, Trifi M, Fkih Romdhane D, Charef A, Azouzi R (2019) Removal properties, mechanisms, and performance of methyl green from aqueous solution using raw and purified sejnane clay type. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4121864
Barakan S, Aghazadeh V (2021) The advantages of clay mineral modification methods for enhancing adsorption efficiency in wastewater treatment: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:2572–2599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10985-9
Santos SCR, Boaventura RAR (2016) Adsorption of cationic and anionic azo dyes on sepiolite clay: Equilibrium and kinetic studies in batch mode. J Environ Chem Eng 4:1473–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.02.009
El-Khalfaouy R, Khallouk K, Elabed A, Addaou A, Laajeb A, Lahsini A (2022) Modeling and synthesis of carbon-coated LiMnPO4 cathode material: Experimental investigation and optimization using response surface methodology. J Electrochem Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.5599/jese.1191
Missana T, Alonso U, García-Gutiérrez M (2021) Evaluation of component additive modelling approach for europium adsorption on 2:1 clays: Experimental, thermodynamic databases, and models. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129877
Mosai AK, Tokwana BC, Tutu H (2022) Computer simulation modelling of the simultaneous adsorption of Cd, Cu and Cr from aqueous solutions by agricultural clay soil: A PHREEQC geochemical modelling code coupled to parameter estimation (PEST) study. Ecol Modell 465:109872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2022.109872
Sohrabi N, Mohammadi R, Ghassemzadeh HR, Heris SSS (2021) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study of diazinon adsorption from water by clay/GO/Fe3O4: Modeling and optimization based on response surface methodology and artificial neural network. J Mol Liq 328:115384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115384
Demirhan E (2020) Response surface methodology approach for adsorptive removal of Reactive Blue 19 onto green pea pod. Water Sci Technol 81:1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.199
Feddal I, Mimanne G, Dellani A, Taleb S (2020) Synthesis and characterization of an adsorbent material: Application to textile dye elimination. Mater Today Proc 49:981–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.105
Hamzezadeh A, Rashtbari Y, Afshin S, Morovati M, Vosoughi M (2022) Application of low-cost material for adsorption of dye from aqueous solution. Int J Environ Anal Chem 102:254–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1720011
Boulahbal M, Abderrahmane M, Canle M, Redouane-salah Z, Devanesan S, Alsalhi MS, Berkani M (2022) Chemosphere Removal of the industrial azo dye crystal violet using a natural clay : Characterization, kinetic modeling, and RSM optimization. Chemosphere 306:135516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135516
Wang C, Luo M, Xie C, Li K, Hang F, Shi C, Doherty WOS (2022) Effective adsorption of colorants from sugarcane juice by Bagasse-Based Biochar-Hydroxyapatite composite. Foods 11:2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142171
Trifi IM, Chaabane L, Dammak L, Baklouti L, Hamrouni B (2021) Response surface methodology for boron removal by donnan dialysis: Doehlert experimental design. Membranes (Basel) 11:731. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100731
Bentahar Y, Hurel C, Draoui K, Khairoun S, Marmier N (2016) Adsorptive properties of Moroccan clays for the removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous solution. Appl Clay Sci 119:385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.11.008
El Kassimi A, Boutouil A, El Himri M, Rachid Laamari M, El Haddad M (2020) Selective and competitive removal of three basic dyes from single, binary and ternary systems in aqueous solutions: A combined experimental and theoretical study. J Saudi Chem Soc 24:527–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSCS.2020.05.005
Thiam A, Tanji K, Assila O, Zouheir M, Haounati R, Arrahli A, Abeid A, Lairini S, Bouslamti R, Zerouq F, Kherbeche A (2020) Valorization of date pits as an effective biosorbent for remazol brilliant blue adsorption from aqueous solution. J Chem 2020:14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4173152
Farcas F, Touzé P (2001) La spectrométrie infrarouge à transformée de Fourier (IRTF) Une méthode intéressante pour la caractérisation des ciments
Boussaa SA, Kheloufi A, Boutarek NZ (2018) Caractérisation et valorisation du Quartz d’ Edough pour application photovoltaïque. Rev Des Energies Renouvelables 21 :391–396. https://doi.org/10.54966/jreen.v21i3.698.
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Mesoporous Iraqi red kaolin clay as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue dye: Adsorption kinetic, isotherm and mechanism study. Surfaces Interfaces 18:100422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.100422
Mondal NK, Kar S (2018) Potentiality of banana peel for removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution: isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0811-x
Mir M, Ghoreishi SM (2015) Response surface optimization of biodiesel production via catalytic transesterification of fatty acids. Chem Eng Technol 38:835–834. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201300328
Schmit F (2014) Catalyseurs à base d’oxyde de manganèse pour l’oxydation en voie humide catalytique de la méthylamine [Manganese-based oxides catalysts for the catalytic wet air oxidation of methylamine-containing aqueous effluent], HAL open science
Silva TL, Ronix A, Pezoti O, Souza LS, Leandro PKT, Bedin KC, Beltrame KK, Cazetta AL, Almeida VC (2016) Mesoporous activated carbon from industrial laundry sewage sludge: Adsorption studies of reactive dye Remazol Brilliant Blue R. Chem Eng J 303:467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.009
Zerhouni J, Filali FR, Bennani MN, Qabaqous O, Bouymajane A, Houssaini J, Allaoui S, Benhallam F (2021) Study of the effect of acid-base character of the lamellar double hydroxides “zn3al-co3” and of the “ghassoul” clay on their redox potential and antimicrobial activities, Iran. J Mater Sci Eng 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.22068/ijmse.2202.
Nabbou N, Benyagoub E, Belhachemi M, Boumelik M, Benyahia M (2021) Removal performance for thermotolerant coliforms and fecal streptococci from dairy effluents by Kenadsa’s natural green clay (Bechar-Algeria) in a fixed-bed column. Appl Water Sci 11:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01441-1
Khallouk K, Solhy A, Idrissi N, Flaud V, Kherbeche A, Barakat A (2020) Microwave-assisted selective oxidation of sugars to carboxylic acids derivatives in water over zinc-vanadium mixed oxide. Chem Eng J 385:123914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123914
Xu HY, Qi SY, Li Y, Zhao Y, Li JW (2013) Heterogeneous Fenton-like discoloration of Rhodamine B using natural schorl as catalyst: Optimization by response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5764–5772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1578-0
Almeida LC, Garcia-Segura S, Bocchi N, Brillas E (2011) Solar photoelectro-Fenton degradation of paracetamol using a flow plant with a Pt/air-diffusion cell coupled with a compound parabolic collector: Process optimization by response surface methodology. Appl Catal B Environ 103:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2011.01.003
Herney-Ramirez J, Lampinen M, Vicente MA, Costa CA, Madeira LM (2008) Experimental design to optimize the oxidation of orange II dye solution using a clay-based fenton-like catalyst. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:284–294. https://doi.org/10.1021/IE070990Y
Nahali L, Miyah Y, Mejbar F, Benjelloun M, Assila O, Fahoul Y, Nenov V, Zerrouq F (2022) Assessment of Brilliant green and Eriochrome Black T dyes adsorption onto fava bean peels: kinetics, isotherms and regeneration study. Deswater Com. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2022.27945
Rashtbari Y, Hazrati S, Azari A, Afshin S, Fazlzadeh M, Vosoughi M (2020) A novel, eco-friendly and green synthesis of PPAC-ZnO and PPAC-nZVI nanocomposite using pomegranate peel: Cephalexin adsorption experiments, mechanisms, isotherms and kinetics. Adv Powder Technol 31:1612–1623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.02.001
Mandal S, Alankar T, Hughes R, Marpu SB, Omary MA, Shi SQ (2022) Removal of hazardous dyes and waterborne pathogens using a nanoengineered bioadsorbent from hemp – Fabrication, characterization and performance investigation. Surfaces Interfaces 29:101797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101797
Yang J, Li M, Wang Y, Wu H, Ji N, Dai L, Li Y, Xiong L, Shi R, Sun Q (2019) High-strength physically multi-cross-linked chitosan hydrogels and aerogels for removing heavy-metal ions. J Agric Food Chem 67:13648–13657. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05063
You X, Wang R, Zhu Y, Sui W, Cheng D (2021) Comparison of adsorption properties of a cellulose-rich modified rice husk for the removal of methylene blue and aluminum (III) from their aqueous solution. Ind Crops Prod 170:113687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113687
Misra PK, Mishra BK, Somasundaran P (2005) Organization of amphiphiles: Part IV. Characterization of the microstructure of the adsorbed layer of decylethoxylene nonyl phenol. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 252:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2004.08.076
Ezzati R (2020) Derivation of pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order and modified pseudo-first-order rate equations from Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms for adsorption. Chem Eng J 392:123705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123705
Alorabi AQ, Hassan MS, Alam MM, Zabin SA, Alsenani NI, Baghdadi NE (2021) Natural clay as a low-cost adsorbent for crystal violet dye removal and antimicrobial activity. Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112789
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Peighambardoust SH, Pateiro M, Lorenzo JM (2021) Adsorption of crystal violet dye using activated carbon of lemon wood and activated carbon/fe3 o4 magnetic nanocomposite from aqueous solutions: A kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Molecules 26:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082241
Avila MC, Lick ID, Comelli NA, Ruiz ML (2021) Adsorption of an anionic dye from aqueous solution on a treated clay. Groundw Sustain Dev 15:100688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2021.100688
Aragaw TA, Alene AN (2022) A comparative study of acidic, basic, and reactive dyes adsorption from aqueous solution onto kaolin adsorbent: Effect of operating parameters, isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Emerg Contam 8:59–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2022.01.002
El Kassimi A, Achour Y, El Himri M, Laamari R, El Haddad M (2021) Removal of two cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto local clay: experimental and theoretical study using DFT method. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1873306
Loqman A, El Bali B, El Gaidoumi A, Boularbah A, Kherbeche A, Lützenkirchen J (2021) The first application of moroccan perlite as industrial dyes removal. Silicon 14:2813–2838. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12633-021-01056-W
Zhang T, Wang W, Zhao Y, Bai H, Wen T, Kang S, Song G, Song S, Komarneni S (2021) Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem Eng J 420:127574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127574
Ashrafi SD, Kamani H, Soheil Arezomand H, Yousefi N, Mahvi AH (2016) Optimization and modeling of process variables for adsorption of Basic Blue 41 on NaOH-modified rice husk using response surface methodology. Desalin Water Treat 57:14051–14059. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1060903
Humelnicu I, Băiceanu A, Ignat ME, Dulman V (2017) The removal of Basic Blue 41 textile dye from aqueous solution by adsorption onto natural zeolitic tuff: Kinetics and thermodynamics. Proc Saf Environ Prot 105:274–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.11.016
Pavlović MD, Buntić AV, Mihajlovski KR, Šiler-Marinković SS, Antonović DG, Radovanović Ž, Dimitrijević-Branković SI (2014) Rapid cationic dye adsorption on polyphenol-extracted coffee grounds-A response surface methodology approach. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:1691–1699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.12.018
Loqman A, El Bali B, Lützenkirchen J, Weidler PG, Kherbeche A (2017) Adsorptive removal of crystal violet dye by a local clay and process optimization by response surface methodology. Appl Water Sci 7:3649–3660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0509-x
Oladipo AA, Gazi M (2014) Enhanced removal of crystal violet by low cost alginate/acid activated bentonite composite beads: Optimization and modelling using non-linear regression technique. J Water Process Eng 2:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.04.007
Funding
This work had not received any funding from any Organization or Institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors certify that they have no conflicts of interests associated with this publication and no funding was received for this study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Souhassou, H., Khallouk, K., El Khalfaouy, R. et al. Optimization of a Binary Dye Mixture Adsorption by Moroccan Clay Using the Box-Behnken Experimental Design. Chemistry Africa 6, 2011–2027 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00608-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00608-4