Abstract
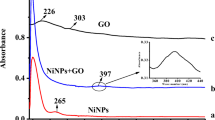
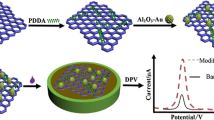
Reduced graphene oxide/polydiallyl dimethylammonium chloride/silver nanoparticles (rGO/PDDA/AgNPs) composite material was fabricated, and characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). A sensitive electrochemical sensor was constructed based on rGO /PDDA/AgNPs hybrid modified glassy carbon electrode for the determination of nicardipine (NP). The electrochemical behavior of NP on this sensor was investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV). The measurement conditions such as supporting electrolyte and scanning speed were also optimized. Under optimized conditions, this proposed sensor showed a good linear relationship between the peak current and the concentration of NP in the range of 1.0 × 10–7 ~ 1.2 × 10–4 M, and the detection limit was 3.3 × 10–8 M. The possible interference of different compounds on the determination of NP was investigated in detail. The recovery of NP was 98.0 ~ 104.1%, which indicated that the composite modified electrode had high accuracy. This electrochemical method is low cost, sensitive, and can be applied to the determination of NP in drugs or preparations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Zarei, L. Fatemi, K. Kor, J. Anal. Chem. 70, 615 (2015)
D.A. Stopher, A.P. Beresford, P.V. Macrae, M.J. Humphrey, J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 12, S55 (1988)
S.M. Al-Ghannam, A.M. Al-Olyan, Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 6, 222 (2008)
Z. Zhang, X. Zhang, F. Li, SCIENCE CHINA Chem. 53, 1183 (2010)
X. Wei, GengliangYanga. Li Qi, Yi Chen, Talanta 77, 1197 (2009)
S.M. Al-Ghannam, A.M. Al-Olayan, Arab. J. Chem. 12, 1983 (2019)
N. Yamane, T. TakamI, Z. Tozuka, Y. Sugiyama, A. Yamazaki, Y. Kumagai, Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 24, 389 (2009)
M. Qi, P. Wang, X. Jin, J. Chromatogr. B 830, 81 (2006)
J.A. Squella, Y. Borges, C. Celedon, P. Peredo, L.J. Nuñez-Vergara, Electroanalysis 3, 221 (1991)
Y. Zhi, J.B. Hu, Q.L. Li, Q.Q. Huang, Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 15, 128 (1999)
N. Rajabzadeh, A. Benvidi, M. Mazloum-Ardakani, Afsaneh Dehghani Firouzabadi, and Rasoul Vafazadeh. Electroanalysis 27, 2792 (2015)
D.F. Báez, S. Bollo, J. Solid State Electrochem. 20, 1059 (2016)
Y.L. Wei, A.T. Wang, Y.Y. Liu, Russ. J. Electrochem. 54, 1141 (2018)
A. Benvidi, Mohammad Taghi Nafar, Shahriar Jahanbani, Marzieh Dehghan Tezerjani, Masoud Rezaeinasab, Sudabeh Dalirnasab. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 75, 1435 (2017)
X.J. Zhu, J. Zhao, T.T. Jia, S.H. Li, N. Li, H.B. Hou, R.L. Zhong, Z. Fan, M.J. Guo, Carbohydr. Polym. 209, 258 (2019)
Y.-H. Li, Y. Ji, B.-B. Ren, L.-N. Jia, Q. Cai, X.-S. Liu, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 16, 1903 (2019)
Y. Lin, R. Chapman, M.M. Stevens, Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 3183 (2015)
R. Yang, X. Ding, Y. Zhou, Anal. Methods 7, 436 (2015)
G. Jie, L. Li, C. Chen, J. Xuan, J. Zhu, Biosens. Bioelectron. 24, 3352 (2009)
A. Benvidi, A. Dehghani-Firouzabadi, M. Mazloum-Ardakani, Bi-Bi Fatemeh Mirjalili, Reza Zare. J. Electroanal. Chem. 736, 22 (2015)
C.-L. Lee, H.-P. Chiou, C.-M. Syu, C.-C. Wu, Electrochem. Commun. 12, 1609 (2010)
J. Wang, Y. Li, D. Pan, H. Han, P. Zhang, Microchem. J. 164, 105965 (2021)
H.R. Zare, F. Jahangiri-Dehaghani, Z. Shekari, A. Benvidi, Appl. Surf. Sci. 375, 169 (2016)
A.T. Wang, Y.L. Wei, Y.G. Wang, D. Wang, X.R. Li, Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B Chemical Analysis) 55, 1055 (2019)
Y.L. Wei, A.T. Wang, L. Wang, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 15, 12599 (2020)
V.K. Gupta, B. Sethi, R.A. Sharma, S. Agarwal, A. Bharti, J. Mol. Liq. 177, 114 (2013)
R.S. Nicholson, I. Shain, Anal. Chem. 36, 706 (1964)
S. Karthikeyan, V.K. Gupta, R. Boopathy, A. Titus, G. Sekaran, J. Mol. Liq. 173, 153 (2012)
A.J. Bard, L.R. Faulkner, Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications (John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York, 2001), pp.236–237
F. Anson, Anal. Chem. 36, 932 (1964)
E. Laviron, J. Electroanal. Chem. 101, 19 (1979)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the Natural Science Key Foundation of Henan Province Universities of China (No. 17A150038), Henan Province Science and Technology Research Program Project, China (No. 232102320080), Henan Provincial Department of Education, China (23B150019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by AW and LW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YW and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Its publication has been approved by all co-authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This research has been finished by all the authors in the lab of our school. It was supported by the grants from the Natural Science Key Foundation of Henan Province Universitiesof China (No.17A150038), the Skeleton Teacher Foundation of Henan Province Universities, China (No. 2009GGJS_123)
Consent of publication
The work described here has not been published before. It is not under consideration for publication anywhere else.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Wang, A. & Wang, L. Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of nicardipine based on reduced graphene oxide/polydiallyl dimethylammonium chloride/nanosilver modified electrode. J IRAN CHEM SOC 20, 2679–2687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-023-02865-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-023-02865-z