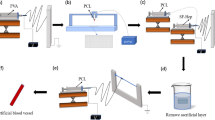
Abstract
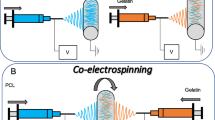
Vascular regeneration is strictly depended on the proliferation and spreading of the injured endothelial cell layer especially in the small diameter vessels. If a substrate is optimized for this application, there will be new hopes to control the vascular wall thickness. Herein, the various strategies including the surface modification, co-electrospinning and blend-electrospinning methods were employed to prepare the nanofibrous scaffolds from polyurethane (PU), gelatin and somatotropin. These protein biomolecules could support the endothelial cell attachment and also their proliferation, respectively. The assays including the scaffold fibers and cell morphologies, mechanical tensile behavior, surface wettability, the cell proliferation and the release kinetic profile confirmed the higher bioactivity of the scaffold which was fabricated by a blend of PU, gelatin and somatotropin agents. This group represented better cell spreading and cell attachment in spite of lower mechanical properties compared to the co-electrospun groups. Regarding this issue, the kinetic model for the release of somatotropin growth factor was an anomalous non-Fickian diffusion due to the impact of polymer relaxation and erosion on the somatotropin release. As a whole, by incorporation of somatotropin in the PU fibers, a sustained release pattern resulted. This controlled release manner of somatotropin enhanced the endothelial cell proliferation that is required for the therapeutic goal of the damaged vessels.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaziano TA (2005) Cardiovascular disease in the developing world and its cost-effective management. Circulation 112:3547–3553
Thomas JH, Pierce GE, Iliopoulos JI, Hermreck AS (1988) Vascular graft selection. Surg Clin N Am 68:865–874
Ercolani E, Del Gaudio C, Bianco A (2015) Vascular tissue engineering of small-diameter blood vessels: reviewing the electrospinning approach. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 9:861–888
Catto V, Farè S, Freddi G, Tanzi MC (2014) Vascular tissue engineering: recent advances in small diameter blood vessel regeneration. Int Sch Res Notices 2014:923030. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/923030
Táborská J, Riedelová Z, Brynda E, Májek P, Riedel T (2021) Endothelialization of an ePTFE vessel prosthesis modified with an antithrombogenic fibrin/heparin coating enriched with bound growth factors. RSC Adv 11:5903–5913
Chlupáč J, Filova E, Bačáková L (2009) Blood vessel replacement: 50 years of development and tissue engineering paradigms in vascular surgery. Physiol Res 58(Suppl 2):S119–S139
Chang WG, Niklason LE (2017) A short discourse on vascular tissue engineering. NPJ Regen Med 2:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41536-017-0011-6
Greco Song H-H, Rumma RT, Ozaki CK, Edelman ER, Chen CS (2018) Vascular tissue engineering: progress, challenges, and clinical promise. Cell Stem Cell 22:340–354
Dean EW, Udelsman B, Breuer CK (2012) Current advances in the translation of vascular tissue engineering to the treatment of pediatric congenital heart disease. Yale J Biol Med 85:229–238
Teebken OE, Haverich A (2002) Tissue engineering of small diameter vascular grafts. Eur J Vasc Endovas Surg 23:475–485
Furukawa KS, Ushida T, Toita K, Sakai Y, Tateishi T (2002) Hybrid of gel-cultured smooth muscle cells with PLLA sponge as a scaffold towards blood vessel regeneration. Cell Transplant 11:475–480
Badhe RV, Bijukumar D, Chejara DR, Mabrouk M, Choonara YE, Kumar P, du Toit LC, Kondiah PPD, Pillay V (2017) A composite chitosan-gelatin bi-layered, biomimetic macroporous scaffold for blood vessel tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym 157:1215–1225
Buttafoco L, Boks NP, Engbers-Buijtenhuijs P, Grijpma DW, Poot AA, Dijkstra PJ, Vermes I, Feijen J (2006) Porous hybrid structures based on P(DLLA-co-TMC) and collagen for tissue engineering of small-diameter blood vessels. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 79B:425–434
Zamanlui S, Mahmoudifard M, Soleimani M, Bakhshandeh B, Vasei M, Faghihi S (2018) Enhanced chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on PCL/PLGA electrospun with different alignments and compositions. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 67:50–60
Zamanlui S, Mohammadi Amirabad L, Soleimani M, Faghihi S (2018) Influence of hydrodynamic pressure on chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cultured in perfusion system. Biologicals 56:1–8
Huang Z-M, Zhang Y-Z, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2003) A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 63:2223–2253
Luo J, Shi X, Lin Y, Yuan Y, Kural MH, Wang J, Ellis MW, Anderson CW, Zhang S-M, Riaz M, Niklason LE, Qyang Y (2021) Efficient differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into endothelial cells under xenogeneic-free conditions for vascular tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 119:184–196
Kim B-S, Baez CE, Atala A (2000) Biomaterials for tissue engineering. World J Urol 18:2–9
Sionkowska A (2011) Current research on the blends of natural and synthetic polymers as new biomaterials: review. Prog Polym Sci 36:1254–1276
Kielty CM, Stephan S, Sherratt MJ, Williamson M, Shuttleworth CA (2007) Applying elastic fibre biology in vascular tissue engineering. Philos Trans R Soc B 362:1293–1312
Mostafavi A, Daemi H, Rajabi S, Baharvand H (2021) Highly tough and ultrafast self-healable dual physically crosslinked sulfated alginate-based polyurethane elastomers for vascular tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym 257:117632
Piterina AV, Callanan A, Davis L, Meaney C, Walsh M, McGloughlin TM (2009) Extracellular matrices as advanced scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Biomed Mater Eng 19:333–348
Palmer RMJ, Ashton DS, Moncada S (1988) Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from l-arginine. Nature 333:664–666
Salehi-Nik N, Amoabediny G, Shokrgozar MA, Mottaghy K, Klein-Nulend J, Zandieh-Doulabi B (2015) Surface modification of silicone tubes by functional carboxyl and amine, but not peroxide groups followed by collagen immobilization improves endothelial cell stability and functionality. Biomed Mater 10:015024
Aldana AA, Abraham GA (2017) Current advances in electrospun gelatin-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Int J Pharm 523:441–453
Lincoln DT, Singal PK, Al-Banaw A (2007) Growth hormone in vascular pathology: neovascularization and expression of receptors is associated with cellular proliferation. Anticancer Res 27:4201–4218
Salehi-Nik N, Amoabediny G, Banikarimi SP, Pouran B, Malaie-Balasi Z, Zandieh-Doulabi B, Klein-Nulend J (2016) Nanoliposomal growth hormone and sodium nitrite release from silicone fibers reduces thrombus formation under flow. Ann Biomed Eng 44:2417–2430
Bastami F, Paknejad Z, Jafari M, Salehi M, Rezai Rad M, Khojasteh A (2017) Fabrication of a three-dimensional β-tricalcium-phosphate/gelatin containing chitosan-based nanoparticles for sustained release of bone morphogenetic protein-2: implication for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 72:481–491
Poormohammadian SJ, Darvishi P, Dezfuli AMG (2019) Enhancing natural gas dehydration performance using electrospun nanofibrous sol-gel coated mixed matrix membranes. Korean J Chem Eng 36:914–928
Hong JH, Jeong EH, Lee HS, Baik DH, Seo SW, Youk JH (2005) Electrospinning of polyurethane/organically modified montmorillonite nanocomposites. J Polym Sci Part B Polyms Phys 43:3171–3177
Liu Z, Zhao J-h, Liu P, He J-h (2016) Tunable surface morphology of electrospun PMMA fiber using binary solvent. Appl Surf Sci 364:516–521
Shakeel M, Matthews PC, Graham RS, Waters SL (2013) A continuum model of cell proliferation and nutrient transport in a perfusion bioreactor. Math Med Biol 30:21–44
Soliman S, Sant S, Nichol JW, Khabiry M, Traversa E, Khademhosseini A (2011) Controlling the porosity of fibrous scaffolds by modulating the fiber diameter and packing density. J Biomed Mater Res A 96:566–574
Kim SE, Heo DN, Lee JB, Kim JR, Park SH, Jeon SH, Kwon IK (2009) Electrospun gelatin/polyurethane blended nanofibers for wound healing. Biomed Mater 4:044106
Hosseinzadeh S, Nazari H, Sadegzadeh N, Babaie A, Kabiri M, Tasharrofi N, Soufi Zomorrod M, Soleimani M (2018) Polyethylenimine: a new differentiation factor to endothelial/cardiac tissue. J Cell Biochem 120:1511–1521
Liu M, Sun J, Sun Y, Bock C, Chen Q (2009) Thickness-dependent mechanical properties of polydimethylsiloxane membranes. J Micromech Microeng 19:035028
Khoramgah MS, Ranjbari J, Abbaszadeh H-A, Mirakabad FST, Hatami S, Hosseinzadeh S, Ghanbarian H (2020) Freeze-dried multiscale porous nanofibrous three dimensional scaffolds for bone regenerations. Bioimpacts 10:73–85
Hosseinzadeh S, Mahmoudifard M, Mohamadyar-Toupkanlou F, Dodel M, Hajarizadeh A, Adabi M, Soleimani M (2016) The nanofibrous PAN-PANi scaffold as an efficient substrate for skeletal muscle differentiation using satellite cells. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 39:1163–1172
Moon S-I, Jin F, Lee C-J, Tsutsumi S, Hyon S-H (2005) Novel carbon nanotube/poly (l-lactic acid) nanocomposites; their modulus, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity. Macromol Symp 224:287–296
Chen R, Huang C, Ke Q, He C, Wang H, Mo X (2010) Preparation and characterization of coaxial electrospun thermoplastic polyurethane/collagen compound nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 79:315–325
Huhtamäki T, Tian X, Korhonen JT, Ras RH (2018) Surface-wetting characterization using contact-angle measurements. Nat Protoc 13:1521–1538
Eddington DT, Puccinelli JP, Beebe DJ (2006) Thermal aging and reduced hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsiloxane. Sens Actuators B Chem 114:170–172
Zamiri C, Groves MJ (2005) Stabilization of somatropin by heparin. J Pharm Pharmacol 57:555–564
Sionkowska A, Wisniewski M, Skopinska J, Kennedy CJ, Wess TJ (2004) Molecular interactions in collagen and chitosan blends. Biomaterials 25:795–801
Nassar MA, El-Sakhawy M, Madkour HMF, El-ziaty AK, Mohamed SA (2014) Novel coating of bagasse paper sheets by gelatin and chitosan. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 29:741–746
Daffonchio D, Thaveesri J, Verstraete W (1995) Contact angle measurement and cell hydrophobicity of granular sludge from upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3676–3680
Vladkova TG (2010) Surface engineered polymeric biomaterials with improved biocontact properties. Int J Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/296094
Zhu M, Zuo W, Yu H, Yang W, Chen Y (2006) Superhydrophobic surface directly created by electrospinning based on hydrophilic material. J Mater Sci 41:3793–3797
Roura P, Fort J (2001) Equilibrium of drops on inclined hydrophilic surfaces. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 64:011601
Fletcher M, Marshall K (1982) Bubble contact angle method for evaluating substratum interfacial characteristics and its relevance to bacterial attachment. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:184–192
Zhang N, Halali MA, de Lannoy C-F (2020) Detection of fouling on electrically conductive membranes by electrical impedance spectroscopy. Sep Purif Technol 242:116823
Liu D, Abdullah CAC, Sear RP, Keddie JL (2010) Cell adhesion on nanopatterned fibronectin substrates. Soft Matter 6:5408–5416
Wang W, Caetano G, Ambler WS, Blaker JJ, Frade MA, Mandal P, Diver C, Bártolo P (2016) Enhancing the hydrophilicity and cell attachment of 3D printed PCL/graphene scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Materials (Basel) 9:992
Mirakabad FST, Hosseinzadeh S, Abbaszadeh HA, Khoramgah MS, Ghanbarian H, Ranjbari J, Kazemi B (2019) The comparison between the osteogenic differentiation potential of clay-polyacrylonitrile nanocomposite scaffold and graphene-polyacrylonitrile scaffold in human mesenchymal stem cells. Nano Biomed Eng 11:238–253
Wan X, Bovornchutichai P, Cui Z, O’Neill E, Ye H (2017) Morphological analysis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells co-cultured with ovarian cancer cells in 3D: an oncogenic angiogenesis assay. PLoS One 12:e0180296
Mulder PPMFA, Molema G, Koster S, van der Linden HJ, Verpoorte E (2006) Behaviour of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) cultivated in microfluidic channels. International Conference Microtechnology Med Biology, Okinawa, Japan, 9–12 May. https://doi.org/10.1109/MMB.2006.251515
Xu K, Shuai Q, Li X, Zhang Y, Gao C, Cao L, Hu F, Akaike T, Wang J-X, Gu Z, Yang J (2016) Human VE-cadherin fusion protein as an artificial extracellular matrix enhancing the proliferation and differentiation functions of endothelial cell. Biomacromol 17:756–766
Cao Y, Lee BH, Peled HB, Venkatraman SS (2016) Synthesis of stiffness-tunable and cell-responsive gelatin–poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogel for three-dimensional cell encapsulation. J Biomed Mater Res A 104:2401–2411
Bak T-Y, Kook M-S, Jung S-C, Kim B-H (2014) Biological effect of gas plasma treatment on CO2 gas foaming/salt leaching fabricated porous polycaprolactone scaffolds in bone tissue engineering. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/657542
Yang G, Lin H, Rothrauff BB, Yu S, Tuan RS (2016) Multilayered polycaprolactone/gelatin fiber-hydrogel composite for tendon tissue engineering. Acta biomater 35:68–76
Ma Z, He W, Yong T, Ramakrishna S (2005) Grafting of gelatin on electrospun poly (caprolactone) nanofibers to improve endothelial cell spreading and proliferation and to control cell orientation. Tissue Eng 11:1149–1158
Yang F, Miao Y, Wang Y, Zhang L-M, Lin X (2017) Electrospun zein/gelatin scaffold-enhanced cell attachment and growth of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Materials (Basel) 10:1168
Li Y-H, Huang Y-D (2007) The study of collagen immobilization on polyurethane by oxygen plasma treatment to enhance cell adhesion and growth. Surf Coat Technol 201:5124–5127
Hosseinzadeh S, Soleimani M, Rezayat SM, Ai J, Vasei M (2014) The activation of satellite cells by nanofibrous poly ɛ-caprolacton constructs. J Biomater Appl 28:801–812
Skotak M, Ragusa J, Gonzalez D, Subramanian A (2011) Improved cellular infiltration into nanofibrous electrospun cross-linked gelatin scaffolds templated with micrometer-sized polyethylene glycol fibers. Biomed Mater 6:055012
Gong Y, Ma Z, Zhou Q, Li J, Gao C, Shen J (2008) Poly(lactic acid) scaffold fabricated by gelatin particle leaching has good biocompatibility for chondrogenesis. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 19:207–221
Gao H, Gu Y, Ping Q (2007) The implantable 5-fluorouracil-loaded poly (l-lactic acid) fibers prepared by wet-spinning from suspension. J Control Release 118:325–332
Kim K, Luu YK, Chang C, Fang D, Hsiao BS, Chu B, Hadjiargyrou M (2004) Incorporation and controlled release of a hydrophilic antibiotic using poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-based electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds. J Control Release 98:47–56
Xu X, Zhong W, Zhou S, Trajtman A, Alfa M (2010) Electrospun PEG–PLA nanofibrous membrane for sustained release of hydrophilic antibiotics. J Appl Polym Sci 118:588–595
Salehi-Nik N, Malaie-Balasi Z, Amoabediny G, Banikarimi SP, Zandieh-Doulabi B, Klein-Nulend J (2017) Sustained release of growth hormone and sodium nitrite from biomimetic collagen coating immobilized on silicone tubes improves endothelialization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 77:1204–1215
da Silveira GA, Machado DC, Rodrigo Marinovic D, Pagnoncelli RM (2017) Assessment of adhesion and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in polymer matrices with rhGH. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 32:e183–e189
Barthes J, Özçelik H, Hindié M, Ndreu-Halili A, Hasan A, Vrana NE (2014) Cell microenvironment engineering and monitoring for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: the recent advances. BioMed Res Int 2014:921905
Gagandeep GT, Malik B, Rath G, Goyal AK (2014) Development and characterization of nano-fiber patch for the treatment of glaucoma. Eur J Pharm Sci 53:10–16
Liang K, Li XC, Tay BK (2013) Study of bone morphogenetic protein-2 delivery with different TiO2 nanotube structures. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 5:162–166
Buijs J, Britt DW, Hlady V (1998) Human growth hormone adsorption kinetics and conformation on self-assembled monolayers. Langmuir 14:335–341
Meghdadi M, Atyabi S-M, Pezeshki-Modaress M, Irani S, Noormohammadi Z, Zandi M (2019) Cold atmospheric plasma as a promising approach for gelatin immobilization on poly (ε-caprolactone) electrospun scaffolds. Prog Biomater 8:65–75
Lee J, Yoo JJ, Atala A, Lee SJ (2012) Controlled heparin conjugation on electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone)/gelatin fibers for morphology-dependent protein delivery and enhanced cellular affinity. Acta Biomater 8:2549–2558
Solomon KD, Ong JL (2013) Vascular endothelial growth factor attachment to hydroxyapatite via self-assembled monolayers promotes angiogenic activity of endothelial cells. Thin Solid Films 537:256–262
Bose PSC, Reddy PS, Ravi V, Sarita D, Kumar TMP (2011) Formulation and evaluation of sustained release of floating tablets of diltiazem HCl using xanthan gum. Res J Pharm Bio Chem Sci 2:319–328
Nguyen TTT, Ghosh C, Hwang S-G, Chanunpanich N, Park JS (2012) Porous core/sheath composite nanofibers fabricated by coaxial electrospinning as a potential mat for drug release system. Int J Pharm 439:296–306
Shi M, Kretlow JD, Spicer PP, Tabata Y, Demian N, Wong ME, Kasper FK, Mikos AG (2011) Antibiotic-releasing porous polymethylmethacrylate/gelatin/antibiotic constructs for craniofacial tissue engineering. J Control Release 152:196–205
Hosseinzadeh S, Esnaashari S, Sadeghpour O, Hamedi S (2016) Predictive modeling of phenolic compound release from nanofibers of electrospun networks for application in periodontal disease. J Polym Eng 36:457–464
Conti S, Maggi L, Segale L, Machiste EO, Conte U, Grenier P, Vergnault G (2007) Matrices containing NaCMC and HPMC: 1. Dissolution performance characterization. Int J Pharm 333:136–142
Dash S, Murthy PN, Nath L, Chowdhury P (2010) Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol Pharm 67:217–223
Acknowledgements
This work was benefitted from a grant of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences with the ethical number of IR.SBMU.RETECH.REC.1395.53 and ID number of 9190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinzadeh, S., Zarei-Behjani, Z., Bohlouli, M. et al. Fabrication and optimization of bioactive cylindrical scaffold prepared by electrospinning for vascular tissue engineering. Iran Polym J 31, 127–141 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-021-00983-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-021-00983-0