Abstract
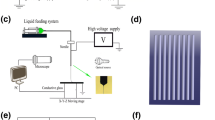
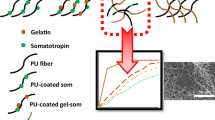
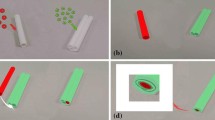
Nowadays, many studies focus on the preparation of small-diameter vascular scaffolds, but some issues still existed that need to be urgently solved, but there are still problems such as slow endothelialization and failure to keep the vessels open for a long time that need to be solved. In this paper, a composite process of preparing triple-layer vascular scaffolds with microchannel structure in the inner layer is proposed to guide cell growth and accelerate the endothelialization process. The PCL pattern was printed as the intermediate layer of the vascular scaffold by 3D printing method, and the width of the microchannel in the inner layer of the scaffold was controlled by the printing spacing. The inner and outer layers were prepared by electrospinning. Heparin is often used as an anticoagulant in vascular tissue engineering to improve the problem of thrombosis and blockage of vascular scaffold after transplantation into the body. Here, the inner layer carries heparin immobilized with silk fibroin by coaxial electrospinning, so that heparin can be released slowly. The addition of silk fibroin also improved the hydrophilicity of PCL electrospinning film by water contact angle test. The mechanical properties of vascular scaffolds with double intermediate layers (DIL) are better than those with single intermediate layers (SIL) and also better than pure electrospinning scaffolds. In vitro cell experiments showed that cells grow directionally on microchannel structures of inner layer and randomly on electrospinning film without microchannel structure. The results showed that the microchannels were more conducive to cell growth and proliferation at a diameter of 0.25 mm. The composite electrospinning films with silk fibroin and heparin facilitated cell adhesion and proliferation compared to the pure PCL films. All these results indicate that the vascular scaffolds have potential applications in clinic for vascular tissue regeneration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Jørgensen, S. Capewell, E. Prescott, S. Allender, S. Sans, T. Zdrojewski, D. DeBacquer, J. de Sutter, O.H. Franco, S. Løgstrup, M. Volpe, S. Malyutina, P. Marques-Vidal, G.S. Reiner, W.M.M. Tell, D.V. Verschuren, Population-level changes to promote cardiovascular health. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 20(3), 409–421 (2013)
Z. Zhang, B. Wang, D. Hui, J. Qiu, S. Wang, 3D bioprinting of soft materials-based regenerative vascular structures and tissues. Compos. B. Eng. 123, 279–291 (2017)
S. Esmaeili, M. Shahali, A. Kordjamshidi, Z. Torkpoor, F. Namdari, S.S. Samandari, M.G. Nejad, A. Khandan, An artificial blood vessel fabricated by 3D printing for pharmaceutical application. Nanomed 6(3), 183–194 (2019)
O.E. Teebken, A. Haverich, Tissue Engineering of Small Diameter Vascular Grafts. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 23, 475–485 (2002)
A.C. Thomas, G.R. Campbell, J.H. Campbell, Advances in vascular tissue engineering. J Cardiovasc. Pathol. 12(5), 271–276 (2003)
S. Park, J. Kim, M.K. Lee, C. Park, H.D. Jung, H.E. Kim, T.S. Jang, Fabrication of strong, bioactive vascular grafts with PCL/collagen and PCL/silica bilayers for small-diameter vascular applications. Mater. Des. 181(5), 108079 (2019)
H. Kuang, S. Yang, Y. Wang, Y. He, K. Ye, J. Hu, Electrospun Bilayer Composite Vascular Graft with an Inner Layer Modified by Polyethylene Glycol and Haparin to Regenerate the Blood Vessel. J Biomed Nanotechnol 15(1), 77–84 (2019)
X. Zhikai Tan, T. Gao, Y. Liu, J.Z. Yang, C. Tong, Electrospun vein grafts with high cell infiltration for vascular tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 81, 407–415 (2017)
H.Y. Mi, Y. Jiang, X. Jing, E. Enriquez, H. Li, Q. Li, L.S. Turng, Fabrication of triple layered vascular grafts composed of silk fibers, polyacrylamide hydrogel, and polyurethane nanofibers with biomimetic mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 98, 241–249 (2019)
C.A. Wilkens, C.J. Rivet, T.L. Akentjew, J. Alverio, M. Khoury, J.P. Acevedo, Layer-by-layer approach for a uniformed fabrication of a cell patterned vessel-like construct. Biofabrication 9(1), 015001 (2016)
P. Wang, Y. Sun, X. Shi, H. Shen, H. Ning, H. Liu, 3D printing of tissue engineering scaffolds: a focus on vascular regeneration. Bio-des. Manuf. 4, 344–378 (2021)
Q. Saad, Z. Muhammad, N. Shariq, K. Zohaib, S. Altaf, H. Shehriar, R. Ihtesham, Electrospinning of Chitosan-Based Solutions for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(2), 407 (2018)
Z.H. Wang, C.G. Liu, D. Zhu, X. Gu, Y. Xu, Q.H. Qin, N.G. Dong, S.M. Zhang, J.L. Wang, Untangling the co-effects of oriented nanotopography and sustained anticoagulation in a biomimetic intima on neovessel remodeling. Biomaterials 231, 119654 (2020)
J. Yoon, H.S. Yang, B.S. Lee, W.R. Yu, Recent Progress in Coaxial Electrospinning: New Parameters, Various Structures, and Wide Applications. Adv. Mater. 30(42), 1704765 (2018)
J. Wang, M. Windbergs, Controlled dual drug release by coaxial electrospun fibers-Impact of the core fluid on drug encapsulation and release-ScienceDirect. Int. J. Pharm. 556, 363–371 (2019)
B. Pant, M. Park, S.J. Park, Drug delivery applications of core-sheath nanofibers prepared by coaxial electrospinning: a review. Pharmaceutics 11(7), 305 (2019)
H.J. Li, W.G. Fan, X. Zhu, Three-dimensional printing: The potential technology widely used in medical fields. J Biomed Mater Res A 108(11), 2217–2229 (2020)
J.L. Sang, N.H. Dong, S.P. Ji, S.K. Kwon, H.L. Jin, J.H. Lee, D.K. Wan, K.I. Keun, A.P. Su, Characterization and preparation of bio-tubular scaffolds for fabricating artificial vascular grafts by combining electrospinning and a 3D printing system. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(5), 2996–2999 (2015)
S. Sarkar, G.Y. Lee, J.Y. Wong, T.A. Desai, Development and characterization of a porous micro-patterned scaffold for vascular tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 27(27), 4775–4782 (2006)
Z. Zhang, B. Wang, D. Hui, J. Qiu, S. Wang, 3D bioprinting of soft materials-based regenerative vascular structures and tissues-ScienceDirect. Compos. B. Eng. 123, 279–291 (2017)
L. Bao, F.F. Hong, G. Li, G. Hu, L. Chen, Improved Performance of Bacterial Nanocellulose Conduits by the Introduction of Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles and Heparin for Small-Caliber Vascular Graft Applications. Biomacromol 22(2), 353–364 (2021)
T. Tanaka, Y. Abe, C.J. Cheng, R. Tanaka, T. Asakura, Development of Small-Diameter Elastin-Silk Fibroin Vascular Grafts. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 622220 (2021)
L. Liu, S. Zhang, J. Huang, Progress in modification of silk fibroin fiber. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62(6), 919–930 (2019)
M.K. Debari, C.I. King, T.A. Altgold, R.D. Abbott, Silk Fibroin as a Green Material. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 7(8), 3530–3544 (2021)
W.H. Park, W.S. Ha, H. Ito, T. Miyamoto, H. Inagaki, Y. Noishiki, Relationships between antithrombogenicity and surface free energy of regenerated silk fibroin films. Fibers Polym. 2, 58–63 (2001)
Y. Yao, J. Wang, Y. Cui, R. Xu, Z. Wang, J. Zhang, K. Wang, Y. Li, Q. Zhao, D. Kong, Effect of sustained heparin release from PCL/chitosan hybrid small-diameter vascular grafts on anti-thrombogenic property and endothelialization. Acta Biomater. 10(6), 2739 (2014)
M.A. Woodruff, D.W. Hutmacher, The return of a forgotten polymer-Polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35(10), 1217–1256 (2010)
H.L. Khor, K.W. Ng, J.T. Schantz, T.T. Phan, T.C. Lim, S.H. Teoh, D.W. Hutmacher, Poly(ε-caprolactone) films as a potential substrate for tissue engineering an epidermal equivalent. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 20(1), 71–75 (2002)
S.J. Lee, M.E. Kim, H. Nah, J.M. Seok, M.H. Jeong, K. Park, K. Kwon, J.S. Lee, S.A. Park, Vascular endothelial growth factor immobilized on mussel-inspired three-dimensional bilayered scaffold for artificial vascular graft application: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 537, 333–344 (2019)
A.R. Park, Y.H. Park, H.J. Kim, M.K. Kim, S.G. Kim, H. Kweon, S.C. Kundu, Tri-layered silk fibroin and poly-ɛ -caprolactone small diameter vascular grafts tested in vitro and in vivo. Macromol Res 23(10), 924–936 (2015)
R. Singh, D. Eitler, R. Morelle, R.P. Friedrich, I. Cicha, Optimization of cell seeding on the electrospun PCL-silk fibroin scaffolds. Eur. Polym. J. 134, 109838 (2020)
S. Khazaei, S.A. Mozaffari, F. Ebrahimi, Polyvinyl alcohol as a crucial omissible polymer to fabricate an impedimetric glucose biosensor based on hierarchical 3D-NPZnO/chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 266, 118105 (2021)
S.K. Norouzi, A. Shamloo, Bilayered heparinized vascular graft fabricated by combining electrospinning and freeze-drying methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 94, 1067–1076 (2019)
S. Akbari, D. Mohebbi-Kalhori, A. Samimi, Effect of corrugated structure on the collapsing of the small-diameter vascular scaffolds. J Biomater Appl 34(10), 1355–1367 (2020)
C. Liu, Research progress in electrospinning process. Synthetic Fiber Ind 35(2), 53–56 (2012)
B. Zxa, A. Hl, A. Qz, A. Yn, Z.A. Di, Silk Fibroin/Polydopamine Modified Nanocapsules for High-Performance Adhesion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 646, 128951 (2022)
B. Gefa, A. Hh, A. Xm, A. Hw, Fabrication of scaffold based on gelatin and polycaprolactone (PCL) for wound dressing application. J Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 42, 3321 (2021)
M. Fallah, S.H. Bahrami, M. Ranjbar-Mohammadi, Fabrication and characterization of PCL/gelatin/curcumin nanofibers and their antibacterial properties. J Ind. Text. 42, 533–535 (2015)
S. Singh, B.M. Wu, J.C. Dunn, The enhancement of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis by polycaprolactone scaffolds with surface cross-linked heparin. Biomaterials 32(8), 2059–2069 (2011)
E. Pektok, B. Nottelet, J.C. Tille, R. Gurny, A. Kalangos, M. Moeller, B.H. Walpoth, Degradation and healing characteristics of small-diameter poly(epsilon-caprolactone) vascular grafts in the rat systemic arterial circulation. Circulation 118(24), 2563–2570 (2008)
D. Jin, J. Hu, D. Xia, H. Kuang, J. Du, X. Mo, M. Yin, Evaluation of a simple off-the-shelf bi-layered vascular scaffold based on poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone)/silk fibroin in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed 14, 4261 (2019)
R.S. More, M.J. Brack, A.H. Gershlick, Heparin after angioplasty: an unresolved issue? Eur. Heart J. 14, 1543–1547 (1993)
S. Jia, Q. Chen, Y. Yan, Application of heparin in surface modification of small-caliber artificial blood vessels. Chin J Med Phys 35(10), 1236–1240 (2018)
L.E. Niklason, J. Gao, W.M. Abbott, Functional Arteries Grown in Vitro. Science 284(5413), 489–493 (1999)
T. Eufrásio-da-Silva, E. Ruiz-Hernandez, J. O’Dwyer, D. Picazo-Frutos, G.P. Duffy, B.P. Murphy, Enhancing medial layer recellularization of tissue-engineered blood vessels using radial microchannels. Regen. Med. 14(11), 1014 (2019)
H. Onoe, T. Okitsu, A. Itou, M. Kato-Negishi, R. Gojo, D. Kiriya, K. Sato, S. Miura, S. Iwanaga, K. Kuribayashi-Shigetomi, Metre-long cell-laden microfibres exhibit tissue morphologies and functions. Nat. Mater. 12(6), 584–590 (2013)
X. Lin, D. Tang, H. Lyu, Q. Zhang, Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/polyurethane core-sheath nanofibers by coaxial electrospinning for drug controlled release. Micro Nano Lett. 11(5), 260–263 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge funding support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 52175474).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Wang, Q., Liu, S. et al. Fabrication Process of Triple-Layer Small-Diameter Vascular Scaffold with Microchannel Structure in the Inner Layer for Accelerated Endothelialization. Fibers Polym 24, 469–482 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-023-00094-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-023-00094-y