Abstract
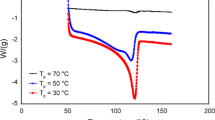
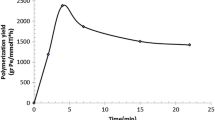
Fully entangled morphology which is usually expected for polyethylene produced using Ziegler–Natta (ZN) catalyst is due to the presence of active sites crowded on catalyst’s support surface as well as within its volume. In this research, the feasibility of producing disentangled, more precisely less entangled, polyethylene using a heterogeneous ZN catalyst supported on magnesium chloride, TiCl4/MgCl2, is introduced. Polymerization was carried out at rather low temperature and pressure, and the nascent polymer was characterized to investigate its entanglement state. The rheological measurements, at small amplitude oscillating in the time sweep mode, exhibited a rather good modulus build-up, demonstrating the nascent polymer in its dis(less)-entangled state. Tape and film samples were prepared from the synthesized polyethylene below its melting point to keep the morphology untapped. The solid-state drawability test was performed on the samples at 100 °C showing its improved drawability. Thus, it could be concluded that the polyethylene synthesized at rather low temperature of 0 °C and longer polymerization time was in disentangled state. Furthermore, a rheometrical analysis in frequency mode was used to estimate the molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the synthesized polyethylene qualitatively. From X-ray diffraction patterns the existence of a small amount of hexagonal phase in the nascent polymer could be detected, which may be due to the formation of extended chains during polymerization.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta S, Riyad MF (2016) Synthesis and tribological behavior of novel UHMWPE-Ti3SiC2 composites. Polym Compos 39:254–262
Vadivel HS, Golchin A, Emami N (2018) Tribological behaviour of carbon filled hybrid UHMWPE composites in water. Tribol Int 124:169–177
Wang Q, Wang H, Wang Y, Yan F (2016) Modification effects of short carbon fibers on mechanical properties and fretting wear behavior of UHMWPE composites. Surf Interface Anal 48:139–145
Ravanbakhsh S, Rezaei M, Sheikh N, Heidari A (2010) Irradiation grafting of methyl methacrylate monomer onto ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene: an experimental design approach for improving adhesion to bone cement. J Appl Polym Sci 116:886–894
SM Kurtz (2009) Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene in total joint replacement and medical devices, in: UHMWPE biomaterials handbook.8:98. Academic Press, USA
Rastogi S, Lippits DR, Peters GWM, Graf R, Yao Y, Spiess HW (2005) Heterogeneity in polymer melts from melting of polymer crystals. Nat Mater 4:635–641
Smith P, Lemstra PJ (1980) Ultra-drawing of high molecular weight polyethylene cast from solution. Colloid Polym Sci 258:891–894
Talebi S(2008) Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Kurelec L, Rastogi S, Meier RJ, Lemstra PJ (2000) Chain mobility in polymer systems: on the borderline between solid and melt. 3. Phase transformations in nascent ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene reactor powder at elevated pressure as revealed by in situ Raman spectroscopy. Macromolecules 33:5593–5601
Pandey A, Champouret Y, Rastogi S (2011) Heterogeneity in the distribution of entanglement density during polymerization in disentangled ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. Macromolecules 44:4952–4960
Rastogi S, Yao Y, Lippits DR, Hhne GWH, Graf R, Spiess HW, Lemstra PJ (2009) Segmental mobility in the non-crystalline regions of semicrystalline polymers and its implications on melting. Macromol Rapid Commun 30:826–839
Romano D, Ronca S, Rastogi S (2015) A hemi-metallocene chromium catalyst with trimethylaluminum-free methylaluminoxane for the synthesis of disentangled ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Macromol Rapid Commun 36:327–331
Talebi S, Duchateau R, Rastogi S, Kaschta J, Peters GWM, Lemstra PJ (2010) Molar mass and molecular weight distribution determination of UHMWPE synthesized using a living homogeneous catalyst. Macromolecules 43:2780–2788
Lippits DR, Rastogi S, Talebi S, Bailly C (2006) Formation of entanglements in initially disentangled polymer melts. Macromolecules 39:8882–8885
Ronca S, Forte G, Tjaden H, Yao Y, Rastogi S (2012) Tailoring molecular structure via nanoparticles for solvent-free processing of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composites. Polymer 53:2897–2907
Kaminsky W, Funck A, Klinke C (2008) In-situ polymerization of olefins on nanoparticles or fibers by metallocene catalysts. Top Catal 48:84
.Heidari A, Talebi S, Rezaei M, Keshavarz-Mirzamohamadi H, Jafariyeh-Yazdi E (2018) In situ synthesis of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/graphene oxide nanocomposite using the immobilized single-site catalyst. Polym Plast Technol Eng 17:1313–1324
Li W, Yang H, Zhang J, Mu J, Gong D, Wang X (2016) Immobilization of isolated FI catalyst on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-functionalized silica for the synthesis of weakly entangled polyethylene. Chem Commun 52:11092–11095
Entezami A, Najafi Moghadam P (2005) Supported zirconocene catalyst for preventing reactor fouling in ethylene polymerization. Polym Int 54:1326–1329
Alexandre M, Martin E, Dubois P, Marti MG, Jerome R (2000) Use of metallocenes in the polymerization-filling technique with production of polyolefin-based composites. Macromol Rapid Commun 21:931–936
Redzic E, Garoff T, Mardare CC, List M, Hesser G, Mayrhofer L, Hassel AW, Paulik C (2016) Heterogeneous Ziegler–Natta catalysts with various sizes of MgCl2 crystallites: synthesis and characterization. Iran Polym J 25:321–337
Kissin YV, Mink R, Nowlin T (1999) Ethylene polymerization reactions with Ziegler–Natta catalysts. I. Ethylene polymerization kinetics and kinetic mechanism. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 37:4255–4272
Kissin YV, Mirabella FM, Meverden CC (2005) Multi-center nature of heterogeneous Ziegler–Natta catalysts: TREF confirmation. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 43:4351–4362
Ferry JD (1980) Viscoelastic properties of polymers 10:243. Wiley, USA
Dealy JM, Larson RG (2006) Structure and rheology of molten polymers, 5. Hanser, Munich, p 152
Li W, Guan C, Xu J, Mu J, Gong D, Chen Z, Zhou Q (2014) Disentangled UHMWPE/POSS nanocomposites prepared by ethylene in situ polymerization. Polymer 55:1792–1798
Suzuki Y, Terao H, Fujita T (2003) Recent advances in phenoxy-based catalysts for olefin polymerization. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 76:1493–1517
Furuyama R, Saito J, Ishii S, Makio H, Mitani M, Tanaka H, Fujita T (2005) Fluorinated bis (phenoxy-imine) Ti complexes with MAO: remarkable catalysts for living ethylene and syndioselective living propylene polymerization. J Organomet Chem 690:4398–4413
Shirkavand MJ, Azizi H, Ghasemi I, Karrabi M, Rashedi R (2015) A correlation between microstructure and rheological properties of broad MWD high-density polyethylene. Iran Polym J 24:953–963
Men Y, Rieger J, Endeler HF, Lilge D (2003) Mechanical α-process in polyethylene. Macromolecules 36:4689–4691
Ward IM, Hadley DW (1993) An introduction to the mechanical properties of solid polymers.10:280. Wiley, USA
Hu WG, Schmidt-Rohr K (1999) Polymer ultradrawability: the crucial role of α-relaxation chain mobility in the crystallites. Acta Polym 50:271–285
Ronca S, Romano D, Forte G, Andabloâ Reyes E, Rastogi S (2012) Improving the performance of a catalytic system for the synthesis of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene with a reduced number of entanglements. Adv Polym Tech 31:193–204
Capaccio G, Ward I (1974) Preparation of ultra-high modulus linear polyethylenes; effect of molecular weight and molecular weight distribution on drawing behaviour and mechanical properties. Polymer 15:233–238
Yamamoto T, Miyaji H, Asai K (1977) Structure and properties of high pressure phase of polyethylene. Jpn J Appl Phys 16:1891
Kakiage M, Yamanobe T, Komoto T, Murakami S, Uehara H (2006) Transient crystallization during drawing from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene melts having different entanglement characteristics. Polymer 47:8053–8060
Uehara H, Kanamoto T, Kawaguchi A, Murakami S (1996) Real-time X-ray diffraction study on two-stage drawing of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene reactor powder above the static melting temperature. Macromolecules 29:1540–1547
Hosseinnezhad R, Talebi S, Rezaei M (2016) The unique effect of chain entanglements and particle morphology on the sintering of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. J Elastomers Plast 49:609–629
Pereira RA, Dias ML, Mano EB (2000) Orthorhombic-hexagonal phase transition in high density polyethylene crystals. Intern J Polym Mater 45:69–78
Rastogi S, Odell JA (1993) Stress stabilization of the orthorhombic and hexagonal phases of UHM PE gel-spun fibres. Polymer 34:1523–1527
Gedde ULF (2013) Polymer physics. Springer, Germany
Zachariades AE, Kanamoto T (1986) The effect of initial morphology on the mechanical properties of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Polym Eng Sci 26:658–661
Ivan’kova EM, Myasnikova LP, Marikhin VA, Baulin AA, Volchek BZ (2001) On the memory effect in UHMWPE nascent powders. J Macromol Sci Ph 40:813–832
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heidari, A., Zarghami, H., Talebi, S. et al. A disentangled state using TiCl4/MgCl2 catalyst: a case study of polyethylene. Iran Polym J 27, 701–708 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-018-0648-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-018-0648-z