Abstract
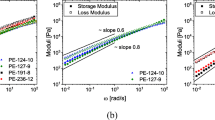
A correlation between molecular structure parameters and rheological behavior was determined for three different grades of high-density polyethylene (HDPE). The molecular structure parameters including number-average molecular weight (M n ), weight-average molecular weight (M w ), molecular weight distribution (MWD) and branching index were characterized by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). Moreover, a fast and easy method for investigating side chain branching using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was discussed. The rheological characterizations of both linear and non-linear viscoelastic regions were performed by a modular compact rheometer (MCR) in the dynamic mode. Zero shear viscosity (η 0), relaxation time, relaxation time distribution, stress relaxation modulus and damping function were obtained from the rheological characterization. Moreover, molecular weight distribution was calculated for each sample and compared with the GPC results. The GPC results confirmed broad molecular weight distribution for all three HDPE samples. The relationship between zero shear viscosity and molecular weight at 180 °C was found as \(\eta_{0} = 2.5 \times 10^{ - 14} M_{w}^{3.6}\) and for zero shear viscosity and MWD at 180 °C was found as \(\eta_{0} = 1.6 \times 10^{ - 15} M_{w}^{3.6} \left( {\frac{{M_{w} }}{{M_{n} }}} \right)\). By choosing the mixing parameter (β) value of 0.73, the values of molecular parameters obtained from the rheology and GPC tests were significantly accommodated. Furthermore, it was found that the damping function of type C was an appropriate type for the polyethylenes of selected broad MWD.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sugimoto M, Suzuki Y, Hyun K, Ahn KH, Ushioda T, Nishioka A, Taniguchi T, Koyama K (2006) Melt rheology of long-chain-branched polypropylenes. Rheol Acta 46:33–44
Lotti C, Isaac CS, Branciforti MC, Alves RMV, Liberman S, Bretas RES (2008) Rheological, mechanical and transport properties of blown films of high density polyethylene nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 44:1346–1357
Eskandari Jam J, Nekoomanesh M, Ahmadi M, Arabi H (2012) From molecular weight distribution to linear viscoelastic properties and back again: application to some commercial high-density polyethylenes. Iran Polym J 21:403–413
Kovács J, Pataki P, Orbán-Mester Á, Nagy G, Staniek P, Földes E, Pukánszky B (2011) Melt stabilisation of Phillips type polyethylene, Part III: correlation of film strength with the rheological characteristics of the polymer. Polym Degrad Stab 96:1771–1779
Mantia FPL, Scaffaro R, Carianni G, Mariani P (2005) Rheological properties of different film blowing polyethylene samples under shear and elongational flow. Macromol Mater Eng 290:159–164
Dealy JM, Larson RG (2006) Structure and rheology of molten polymers. Hanser, Munich
Steffl T (2004) Rheological and film blowing properties of various low density polyethylenes and their blends. Ph.D Thesis, University of Erlangen, Nurnberg
Gabriel C, Munstedt H (2002) Influence of long-chain branches in polyethylenes on linear viscoelastic flow properties in shear. Rheol Acta 41:232–244
Minoshima W, White JL, Spruiell JE (1980) Experimental investigation of the influence of molecular weight distribution on the rheological properties of polypropylene melts. Polym Eng Sci 20:1166–1176
Morrison FA (2001) Understanding rheology. Oxford University Press, Chicago
Piel C, Stadler FJ, Kaschta J, Rulhoff S, Mu¨nstedt H, Kaminsky W (2006) Structure–property relationships of linear and long-chain branched metallocene high-density polyethylenes characterized by shear rheology and SEC-MALLS. Macromol Chem Phys 207:26–38
Wasserman SH, Graessley WW (1992) Effects of polydispersity on linear viscoelasticity in entangled polymer melts. J Rheol 36:543–572
Meyer T, Keurentjes J (2005) Handbook of polymer reaction engineering. Wiley, New York
Maier D, Eckstein A, Friedrich C, Honerkamp J (1998) Evaluation of models combining rheological data with the molecular weight distribution. J Rheol 42:1153–1173
Thimm W, Friedrich C, Marth M, Honerkamp J (1999) An analytical relation between relaxation time spectrum and molecular weight distribution. J Rheol 43:1663–1672
Tuminello WH (1999) Determination molecular weight distribution from the rheological properties of polymer melts. In: Presented at the society of rheology meeting
Thimm W, Friedrich C, Marth M, Honerkamp J (2000) On the Rouse spectrum and the determination of the molecular weight distribution from rheological data. J Rheol 44:429–438
Doi M, Edwards SF (1986) The theory of polymer dynamics. Oxford University Press, New York
Des Cloizeaux J (1988) Double reptation vs simple reptation in polymer melts. Europhys Lett 5:437–442
Anderssen RS, Mead DW (1998) Theoretical deviation of molecular weight scaling for rheological parameters. J Non-Newton Fluid 76:299–306
Ferry JD (1980) Viscoelastic properties of polymers, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Samurkas T, Larson RG, Dealy JM (1989) Strong extensional and shearing flows of a branched polyethylene. J Rheol 33:559–578
Vega JF, Santamaria A, Munoz-Escalona A, Lafuente P (1998) Small-amplitude oscillatory shear flow measurements as a tool to detect very low amounts of long chain branching in polyethylenes. Macromolecules 31:3639–3647
Osaki K (1993) On the damping function of shear relaxation modulus for entangled polymers. Rheol Acta 32:429–437
Osaki K, Watanabe H, Inoue T (1996) Damping function of the shear relaxation modulus and the chain retraction process of entangled polymers. Macromolecules 29:3611–3614
Hatzikiriakos SG, Migler HB (2005) Polymer processing instabilities control and understanding. CRC Press, New York
Sun T, Brant P, Chance RR, Graessley WW (2001) Effect of short chain branching on the coil dimensions of polyolefins in dilute solution. Macromolecules 34:6812–6820
Zimm BH, Stockmayer WH (1949) The dimensions of chain molecules containing branches and rings. J Chem Phys 17:1301–1314
Fan Y, Xue Y, Nie W, Xiangling JI, Bo S (2009) Characterization of the microstructure of bimodal HDPE resin. Polym J 41:622–628
Brandrup J, Immergut EH, Grulke EA (1999) Polymer handbook, 4th edn. Wiley, New York
Sandler SR, Karo W, Bonesteel J, Pearce EM (1998) Polymer synthesis and characterization. Academic, California
Mark JE (1999) Polymer data handbook. Oxford University Press, New York
Saunders G, MacCreath B (2011) Biodegradable polymers—analysis of engineering polymers by GPC/SEC. Application compendium. Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara
Bird RB, Armstrong RC, Hassager O (1987) Dynamics of polymeric liquids, vol 1. Wiley, New York
Wasserman SH, Graessley WW (1996) Prediction of linear viscoelastic response for entangled polyolefin melts from molecular weight distribution. Polym Eng Sci 36(6):852–861
Osman MA, Atallah A (2006) Effect of the particle size on the viscoelastic properties of filled polyethylene. Polymer 47:2357–2368
Khan SA, Prudhomme RK, Larson RG (1987) Comparison of the rheology of polymer melts in shear, and biaxial and uniaxial extensions. Rheol Acta 26:144–151
Yoshikawa K, Toneaki N, Moteki Y, Takahashi M, Masuda T (1991) Dynamic viscoelasticity, stress relaxation and elongational flow behavior of high density polyethylene melts. J Rheol 35:701
Mahendrasingam A, Blundell DJ, Martin C, Fuller W, MacKerron DH, Harvie JL, Oldman RJ, Riekel C (2000) Influence of temperature and chain orientation on the crystallization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) during fast drawing. Polymer 41:7803–7814
Marrucci G, Grizzuti N (1983) The free energy function of the Doi–Edwards theory: analysis of the instabilities in stress relaxation. J Rheol 27:433–450
Rolon-Garrido VH, Wagner MH (2009) The damping function in rheology. Rheol Acta 48:245–284
Hummell DO, Scholl F (1988) Atlas of polymer and plastics analysis. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinhein
Blitz JP, McFaddin DC (1994) The characterization of short chain branching in polyethylene using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J Appl Polym Sci 51:13–20
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge R and D Department of Jam Petrochemical Co. for supplying materials and providing a fund for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirkavand, M.J., Azizi, H., Ghasemi, I. et al. A correlation between microstructure and rheological properties of broad MWD high-density polyethylene. Iran Polym J 24, 953–963 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-015-0383-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-015-0383-7