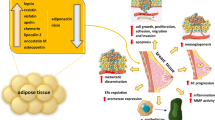
Abstract
Purpose of Review
In this review, we investigate the role of classic and novel adipocytokines in cancer pathogenesis synopsizing the mechanisms underlying the association between adipocytokines and malignancy. Special emphasis is given on novel adipocytokines as new evidence is emerging regarding their entanglement in neoplastic development.
Recent Findings
Recent data have emphasized the role of the triad of overweight/obesity, insulin resistance and adipocytokines in cancer. In the setting of obesity, classic and novel adipocytokines present independent and joint effects on activation of major intracellular signaling pathways implicated in cell proliferation, expansion, survival, adhesion, invasion, and metastasis. Until now, more than 15 adipocytokines have been associated with cancer, and this list continues to expand. While the plethora of circulating pro-inflammatory adipocytokines, such as leptin, resistin, extracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase, and chemerin are elevated in malignancies, some adipocytokines such as adiponectin and omentin-1 are generally decreased in cancers and are considered protective against carcinogenesis.
Summary
Elucidating the intertwining of inflammation, cellular bioenergetics, and adiposopathy is significant for the development of preventive, diagnostic, and therapeutic strategies against cancer. Novel more effective and safe adipocytokine-centered therapeutic interventions may pave the way for targeted oncotherapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AdipoR1/R2:
-
Adiponectin receptor 1/2
- Akt:
-
v-Akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog
- AMPK:
-
5’ AMP-activated protein kinase
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- ERK 1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
- GRP78:
-
Glucose-regulated protein 78
- GTP:
-
Guanosine-5′-triphosphate
- HIF-1a:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1a
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IGF:
-
Insulin-like growth factor
- IRS:
-
Insulin receptor substrate
- JAK:
-
Janus kinase
- JNK:
-
Jun N-terminal kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- LEPR:
-
Leptin receptor
- LIFRα:
-
Leukemia inhibitory receptor alpha
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NAD:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- Nampt:
-
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung carcinoma
- OSM:
-
Oncostatin M
- PBEF:
-
Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor
- PCOS:
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PPAR:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- RBP-4:
-
Retinol-binding protein
- ROCK:
-
Rho-associated coiled coil-containing protein kinase
- SNPs:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- STRA6:
-
Stimulated by retinoic acid 6
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- WHR:
-
Waist-to-hip ratio
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Jemal A, Miller KD, Ma J, Siegel RL, Fedewa SA, Islami F, et al. Higher lung cancer incidence in young women than young men in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1999–2009. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1715907.
Pischon T, Nimptsch K. Obesity and risk of cancer: an introductory overview. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2016;208:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42542-9_1.
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen C-S, Reynolds K, He J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes. 2008;32:1431–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.102.
Ackerman SE, Blackburn OA, Marchildon F, Cohen P. Insights into the link between obesity and cancer. Curr Obes Rep. 2017;6:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-017-0263-x.
Lauby-Secretan B, Scoccianti C, Loomis D, Grosse Y, Bianchini F, Straif K, et al. Body fatness and cancer—viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:794–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsr1606602.
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1625–38. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa021423.
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet. 2008;371:569–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60269-X.
Britton KA, Massaro JM, Murabito JM, Kreger BE, Hoffmann U, Fox CS. Body fat distribution, incident cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all-cause mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:921–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.06.027.
Lichtman MA. Obesity and neoplasms of lymphohematopoietic cells. Blood Adv. 2016;1:101–3. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2016001685.
Wallin A, Larsson SC. Body mass index and risk of multiple myeloma: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:1606–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.01.020.
Dalamaga M, Christodoulatos GS. Adiponectin as a biomarker linking obesity and adiposopathy to hematologic malignancies. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2015;23:5–20. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2015-0016.
Larsson SC, Wolk A. Overweight and obesity and incidence of leukemia: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int J Cancer. 2008;122:1418–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23176.
Larsson SC, Wolk A. Obesity and risk of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:1564–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.22762.
Park Y, Colditz GA. Diabetes and adiposity: a heavy load for cancer. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:82–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30396-0.
van Kruijsdijk RCM, van der Wall E, Visseren FLJ. Obesity and cancer: the role of dysfunctional adipose tissue. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2009;18:2569–78. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0372.
•• Dalamaga M, Christodoulatos GS, Mantzoros CS. The role of extracellular and intracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyl-transferase in cancer: diagnostic and therapeutic perspectives and challenges. Metabolism. 2018;82:72–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.01.001. This review explores the role of Nampt in cancer pathophysiology as well as synopsizes the mechanisms underlying the association between extracellular and intracellular Nampt and malignancy.
•• Dalamaga M, Diakopoulos KN, Mantzoros CS. The role of adiponectin in cancer: a review of current evidence. Endocr Rev. 2012;33:547–94. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2011-1015. This review investigates the role of adiponectin in cancer pathophysiology as well as synopsizes the mechanisms underlying the association between adiponectin and cancer.
Dalamaga M. Obesity, insulin resistance, adipocytokines and breast cancer: new biomarkers and attractive therapeutic targets. World J Exp Med. 2013;3:34–42. https://doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v3.i3.34.
Pickens CA, Sordillo LM, Zhang C, Fenton JI. Obesity is positively associated with arachidonic acid-derived 5- and 11-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE). Metabolism. 2017;70:177–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.01.034.
Lee MK, Kim J-Y, Kim D-I, Kang D-W, Park J, Ahn K-Y, et al. Effect of home-based exercise intervention on fasting insulin and adipocytokines in colorectal cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Metabolism. 2017;76:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.07.005.
Mendonça FM, de Sousa FR, Barbosa AL, Martins SC, Araújo RL, Soares R, et al. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: which link? Metabolism. 2015;64:182–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.10.008.
Cabia B, Andrade S, Carreira MC, Casanueva FF, Crujeiras AB. A role for novel adipose tissue-secreted factors in obesity-related carcinogenesis. Obes Rev. 2016;17:361–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12377.
Sahin-Efe A, Katsikeris F, Mantzoros CS. Advances in adipokines. Metabolism. 2012;61:1659–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2012.09.001.
Reizes O, Berger NA. Adipocytokines, energy balance, and cancer. Springer International Publishing Switzerland; 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41677-9
Dalamaga M. Resistin as a biomarker linking obesity and inflammation to cancer: potential clinical perspectives. Biomark Med. 2014;8:107–18. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm.13.99.
Dalamaga M, Chou SH, Shields K, Papageorgiou P, Polyzos SA, Mantzoros CS. Leptin at the intersection of neuroendocrinology and metabolism: current evidence and therapeutic perspectives. Cell Metab. 2013;18:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.010.
Moon H-S, Dalamaga M, Kim S-Y, Polyzos SA, Hamnvik O-P, Magkos F, et al. Leptin’s role in lipodystrophic and nonlipodystrophic insulin-resistant and diabetic individuals. Endocr Rev. 2013;34:377–412. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2012-1053.
Lee CH, Woo YC, Wang Y, Yeung CY, Xu A, Lam KSL. Obesity, adipokines and cancer: an update. Clin Endocrinol. 2015;83:147–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.12667.
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr Rev. 2005;26:439–51. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2005-0005.
Brochu-Gaudreau K, Rehfeldt C, Blouin R, Bordignon V, Murphy BD, Palin M-F. Adiponectin action from head to toe. Endocrine. 2010;37:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-009-9278-8.
Wang Y, Lam KSL, Xu JY, Lu G, Xu LY, Cooper GJS, et al. Adiponectin inhibits cell proliferation by interacting with several growth factors in an oligomerization-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:18341–7. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M501149200.
Ziemke F, Mantzoros CS. Adiponectin in insulin resistance: lessons from translational research. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91:258S–61S. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.28449C.
Barb D, Williams CJ, Neuwirth AK, Mantzoros CS. Adiponectin in relation to malignancies: a review of existing basic research and clinical evidence. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:s858–66. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/86.3.858S.
Kelesidis I, Kelesidis T, Mantzoros CS. Adiponectin and cancer: a systematic review. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:1221–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6603051.
Hivert M-F, Sullivan LM, Fox CS, Nathan DM, D’Agostino RB, Wilson PWF, et al. Associations of adiponectin, resistin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:3165–72. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-0425.
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, et al. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:1930–5. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.86.5.7463.
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, et al. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1595–9.
Heidemann C, Sun Q, van Dam RM, Meigs JB, Zhang C, Tworoger SS, et al. Total and high-molecular-weight adiponectin and resistin in relation to the risk for type 2 diabetes in women. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:307–16.
Mazaki-Tovi S, Romero R, Vaisbuch E, Erez O, Mittal P, Chaiworapongsa T, et al. Maternal serum adiponectin multimers in gestational diabetes. J Perinat Med. 2009;37:637–50. https://doi.org/10.1515/JPM.2009.101.
Trujillo ME, Scherer PE. Adiponectin—journey from an adipocyte secretory protein to biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J Intern Med. 2005;257:167–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01426.x.
Durante-Mangoni E, Zampino R, Marrone A, Tripodi M-F, Rinaldi L, Restivo L, et al. Hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance are associated with serum imbalance of adiponectin/tumour necrosis factor-alpha in chronic hepatitis C patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:1349–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03114.x.
Lee DY, Rhee E-J, Chang Y, Sohn CIL, Shin H-C, Ryu S, et al. Impact of systemic inflammation on the relationship between insulin resistance and all-cause and cancer-related mortality. Metabolism. 2018;81:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.11.014.
Delporte ML, Brichard SM, Hermans MP, Beguin C, Lambert M. Hyperadiponectinaemia in anorexia nervosa. Clin Endocrinol. 2003;58:22–9.
Ebina K, Fukuhara A, Ando W, Hirao M, Koga T, Oshima K, et al. Serum adiponectin concentrations correlate with severity of rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by extent of joint destruction. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28:445–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1074-y.
Senolt L, Pavelka K, Housa D, Haluzík M. Increased adiponectin is negatively linked to the local inflammatory process in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine. 2006;35:247–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2006.09.002.
Zoccali C, Mallamaci F. Adiponectin and leptin in chronic kidney disease: causal factors or mere risk markers? J Ren Nutr. 2011;21:87–91. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2010.10.014.
Schulze MB, Shai I, Rimm EB, Li T, Rifai N, Hu FB. Adiponectin and future coronary heart disease events among men with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54:534–9.
Mantzoros CS, Li T, Manson JE, Meigs JB, Hu FB. Circulating adiponectin levels are associated with better glycemic control, more favorable lipid profile, and reduced inflammation in women with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:4542–8. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-0372.
Gorgui J, Gasbarrino K, Georgakis MK, Karalexi MA, Nauche B, Petridou ET, et al. Circulating adiponectin levels in relation to carotid atherosclerotic plaque presence, ischemic stroke risk, and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Metabolism. 2017;69:51–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.01.002.
Li S, Shin HJ, Ding EL, van Dam RM. Adiponectin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2009;302:179–88. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.976.
• Boutari C, Mantzoros CS. Inflammation: a key player linking obesity with malignancies. Metabolism. 2018;81:A3–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.12.015. This study reviews the relationship of obesity and cancer under the common theme of inflammation.
Diedrich J, Gusky HC, Podgorski I. Adipose tissue dysfunction and its effects on tumor metabolism. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2015;21:17–41. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2014-0045.
Pérez-Hernández AI, Catalán V, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Rodríguez A, Frühbeck G. Mechanisms linking excess adiposity and carcinogenesis promotion. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5:65. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2014.00065.
Wang Y, Lam KSL, Xu A. Adiponectin as a negative regulator in obesity-related mammary carcinogenesis. Cell Res. 2007;17:280–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2007.14.
Ma J-J, Shang J, Wang H, Sui J-R, Liu K, Du J-X. Serum adiponectin levels are inversely correlated with leukemia: a meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016;12:897–902. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1482.186695.
Wei T, Ye P, Peng X, Wu L-L, Yu G-Y. Circulating adiponectin levels in various malignancies: an updated meta-analysis of 107 studies. Oncotarget. 2016;7:48671–91. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8932.
Goktas S, Yilmaz MI, Caglar K, Sonmez A, Kilic S, Bedir S. Prostate cancer and adiponectin. Urology. 2005;65:1168–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2004.12.053.
Gialamas SP, Petridou ET, Tseleni-Balafouta S, Spyridopoulos TN, Matsoukis IL, Kondi-Pafiti A, et al. Serum adiponectin levels and tissue expression of adiponectin receptors are associated with risk, stage, and grade of colorectal cancer. Metabolism. 2011;60:1530–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2011.03.020.
Petridou E, Mantzoros C, Dessypris N, Koukoulomatis P, Addy C, Voulgaris Z, et al. Plasma adiponectin concentrations in relation to endometrial cancer: a case-control study in Greece. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:993–7. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2002-021209.
Mantzoros C, Petridou E, Alexe D-M, Skalkidou A, Dessypris N, Papathoma E, et al. Serum adiponectin concentrations in relation to maternal and perinatal characteristics in newborns. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151:741–6.
Miyoshi Y, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Matsuzawa Y, et al. Association of serum adiponectin levels with breast cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:5699–704.
Chen D-C, Chung Y-F, Yeh Y-T, Chaung H-C, Kuo F-C, Fu O-Y, et al. Serum adiponectin and leptin levels in Taiwanese breast cancer patients. Cancer Lett. 2006;237:109–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2005.05.047.
Jeong Y-J, Bong J-G, Park S-H, Choi J-H, Oh H-K. Expression of leptin, leptin receptor, adiponectin, and adiponectin receptor in ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2011;14:96–103. https://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2011.14.2.96.
•• Kim S, Lee Y, Kim JW, Son Y-J, Ma MJ, Um J-H, et al. Discovery of a novel potent peptide agonist to adiponectin receptor 1. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0199256. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199256. This study describes the discovery of an adiponectin agonist peptide that may provide insight in the development of malignancy therapeutics.
Friedman JM, Halaas JL. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 1998;395:763–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/27376.
Mantzoros CS, Magkos F, Brinkoetter M, Sienkiewicz E, Dardeno TA, Kim S-Y, et al. Leptin in human physiology and pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;301:E567–84. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00315.2011.
Booth A, Magnuson A, Fouts J, Foster M. Adipose tissue, obesity and adipokines: role in cancer promotion. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2015;21:57–74. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2014-0037.
Sharma D, Saxena NK, Vertino PM, Anania FA. Leptin promotes the proliferative response and invasiveness in human endometrial cancer cells by activating multiple signal-transduction pathways. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006;13:629–40. https://doi.org/10.1677/erc.1.01169.
Choi J-H, Park S-H, Leung PCK, Choi K-C. Expression of leptin receptors and potential effects of leptin on the cell growth and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in ovarian cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:207–10. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-0297.
Wang Y, Prywes R. Activation of the c-fos enhancer by the erk MAP kinase pathway through two sequence elements: the c-fos AP-1 and p62TCF sites. Oncogene. 2000;19:1379–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203443.
Frankenberry KA, Skinner H, Somasundar P, McFadden DW, Vona-Davis LC. Leptin receptor expression and cell signaling in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2006;28:985–93.
Harris HR, Tworoger SS, Hankinson SE, Rosner BA, Michels KB. Plasma leptin levels and risk of breast cancer in premenopausal women. Cancer Prev Res. 2011;4:1449–56. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0125.
Niu J, Jiang L, Guo W, Shao L, Liu Y, Wang L. The association between leptin level and breast cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e67349. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067349.
Andò S, Catalano S. The multifactorial role of leptin in driving the breast cancer microenvironment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;8:263–75. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.184.
García-Robles MJ, Segura-Ortega JE, Fafutis-Morris M. The biology of leptin and its implications in breast cancer: a general view. J Interf Cytokine Res. 2013;33:717–27. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2012.0168.
Jardé T, Perrier S, Vasson M-P, Caldefie-Chézet F. Molecular mechanisms of leptin and adiponectin in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2010.09.005.
Dubois V, Jardé T, Delort L, Billard H, Bernard-Gallon D, Berger E, et al. Leptin induces a proliferative response in breast cancer cells but not in normal breast cells. Nutr Cancer. 2014;66:645–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2014.894104.
Allott EH, Masko EM, Freedland SJ. Obesity and prostate cancer: weighing the evidence. Eur Urol. 2013;63:800–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.11.013.
Dong Z, Fu S, Xu X, Yang Y, Du L, Li W, et al. Leptin-mediated regulation of ICAM-1 is Rho/ROCK dependent and enhances gastric cancer cell migration. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:1801–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.70.
Koda M, Sulkowska M, Kanczuga-Koda L, Surmacz E, Sulkowski S. Overexpression of the obesity hormone leptin in human colorectal cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2006;60:902–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2006.041004.
Dalamaga M, Polyzos SA, Karmaniolas K, Chamberland J, Lekka A, Triantafilli M, et al. Fetuin-A levels and free leptin index are reduced in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a hospital-based case-control study. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016;57:577–84. https://doi.org/10.3109/10428194.2015.1075523.
Dalamaga M, Karmaniolas K, Panagiotou A, Hsi A, Chamberland J, Dimas C, et al. Low circulating adiponectin and resistin, but not leptin, levels are associated with multiple myeloma risk: a case–control study. Cancer Causes Control. 2009;20:193–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-008-9233-7.
Pan H, Deng L-L, Cui J-Q, Shi L, Yang Y-C, Luo J-H, et al. Association between serum leptin levels and breast cancer risk. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e11345. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000011345.
Wang P-P, He X-Y, Wang R, Wang Z, Wang Y-G. High leptin level is an independent risk factor of endometrial cancer: a meta-analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:1477–84. https://doi.org/10.1159/000366352.
• Tong X, Ma Y, Zhou Q, He J, Peng B, Liu S, et al. Serum and tissue leptin in lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:19699–711. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14963. This meta-analysis investigated the relation of leptin serum and tissue levels with lung cancer.
Dalamaga M, Migdalis I, Fargnoli JL, Papadavid E, Bloom E, Mitsiades N, et al. Pancreatic cancer expresses adiponectin receptors and is associated with hypoleptinemia and hyperadiponectinemia: a case–control study. Cancer Causes Control. 2009;20:625–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-008-9273-z.
Dalamaga M, Polyzos SA, Karmaniolas K, Chamberland J, Lekka A, Migdalis I, et al. Circulating fetuin-A in patients with pancreatic cancer: a hospital-based case-control study. Biomarkers. 2014;19:660–6. https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750X.2014.974071.
Dalamaga M, Crotty BH, Fargnoli J, Papadavid E, Lekka A, Triantafilli M, et al. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia risk in association with serum leptin and adiponectin: a case–control study in Greece. Cancer Causes Control. 2010;21:1451–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-010-9573-y.
Dalamaga M, Karmaniolas K, Chamberland J, Nikolaidou A, Lekka A, Dionyssiou-Asteriou A, et al. Higher fetuin-A, lower adiponectin and free leptin levels mediate effects of excess body weight on insulin resistance and risk for myelodysplastic syndrome. Metabolism. 2013;62:1830–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.007.
Dalamaga M, Karmaniolas K, Nikolaidou A, Chamberland J, Hsi A, Dionyssiou-Asteriou A, et al. Adiponectin and resistin are associated with risk for myelodysplastic syndrome, independently from the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) system. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:1744–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.04.015.
Dalamaga M, Nikolaidou A, Karmaniolas K, Hsi A, Chamberland J, Dionyssiou-Asteriou A, et al. Circulating adiponectin and leptin in relation to myelodysplastic syndrome: a case-control study. Oncology. 2007;73:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1159/000120995.
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 2001;409:307–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/35053000.
Krecki R, Drozdz J, Szcześniak P, Orszulak-Michalak D, Krzemińska-Pakuła M. Novel atherogenesis markers for identification of patients with a multivessel coronary artery disease. Kardiol Pol. 2008;66:1173-80-2.
Forrest OA, Chopyk DM, Gernez Y, Brown MR, Conrad CK, Moss RB, et al. Resistin is elevated in cystic fibrosis sputum and correlates negatively with lung function. J Cyst Fibros. 2018; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcf.2018.05.018.
Gong W-J, Zheng W, Xiao L, Tan L-M, Song J, Li X-P, et al. Circulating resistin levels and obesity-related cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2016;7:57694–704. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11034.
Samal B, Sun Y, Stearns G, Xie C, Suggs S, McNiece I. Cloning and characterization of the cDNA encoding a novel human pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:1431–7.
Rongvaux A, Shea RJ, Mulks MH, Gigot D, Urbain J, Leo O, et al. Pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor, whose expression is up-regulated in activated lymphocytes, is a nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, a cytosolic enzyme involved in NAD biosynthesis. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:3225–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4141(200211)32:11<3225::AID-IMMU3225>3.0.CO;2-L.
Ming G, Li X, Yin J, Ai Y, Xu D, Ma X, et al. JAZF1 regulates visfatin expression in adipocytes via PPARα and PPARβ/δ signaling. Metabolism. 2014;63:1012–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.05.006.
Zhang LQ, Heruth DP, Ye SQ. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in human diseases. J Bioanal Biomed. 2011;3:13–25. https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-593X.1000038.
Duarte-Pereira S, Silva SS, Azevedo L, Castro L, Amorim A, Silva RM. NAMPT and NAPRT1: novel polymorphisms and distribution of variants between normal tissues and tumor samples. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6311. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06311.
Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Owczarek A, Bożentowicz-Wikarek M, Brzozowska A, Mossakowska M, Zdrojewski T, et al. Relationship between circulating visfatin/NAMPT, nutritional status and insulin resistance in an elderly population—results from the PolSenior substudy. Metabolism. 2014;63:1409–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.07.013.
Galli M, Van Gool F, Rongvaux A, Andris F, Leo O. The nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase: a molecular link between metabolism, inflammation, and cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:8–11. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2465.
Moschen AR, Gerner RR, Tilg H. Pre-B cell colony enhancing factor/NAMPT/visfatin in inflammation and obesity-related disorders. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16:1913–20.
Park H-J, Kim S-R, Kim SS, Wee H-J, Bae M-K, Ryu MH, et al. Visfatin promotes cell and tumor growth by upregulating Notch1 in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2014;5:5087–99. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2086.
Moschen AR, Kaser A, Enrich B, Mosheimer B, Theurl M, Niederegger H, et al. Visfatin, an adipocytokine with proinflammatory and immunomodulating properties. J Immunol. 2007;178:1748–58.
Audrito V, Serra S, Brusa D, Mazzola F, Arruga F, Vaisitti T, et al. Extracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) promotes M2 macrophage polarization in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2015;125:111–23. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-07-589069.
Reddy PS, Umesh S, Thota B, Tandon A, Pandey P, Hegde AS, et al. PBEF1/NAmPRTase/Visfatin: a potential malignant astrocytoma/glioblastoma serum marker with prognostic value. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7:663–8.
Goralski KB, McCarthy TC, Hanniman EA, Zabel BA, Butcher EC, Parlee SD, et al. Chemerin, a novel adipokine that regulates adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:28175–88. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M700793200.
Wittamer V, Franssen J-D, Vulcano M, Mirjolet J-F, Le Poul E, Migeotte I, et al. Specific recruitment of antigen-presenting cells by chemerin, a novel processed ligand from human inflammatory fluids. J Exp Med. 2003;198:977–85. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20030382.
Bozaoglu K, Bolton K, McMillan J, Zimmet P, Jowett J, Collier G, et al. Chemerin is a novel adipokine associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology. 2007;148:4687–94. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-0175.
Chakaroun R, Raschpichler M, Klöting N, Oberbach A, Flehmig G, Kern M, et al. Effects of weight loss and exercise on chemerin serum concentrations and adipose tissue expression in human obesity. Metabolism. 2012;61:706–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2011.10.008.
Aronis KN, Sahin-Efe A, Chamberland JP, Spiro A, Vokonas P, Mantzoros CS. Chemerin levels as predictor of acute coronary events: a case–control study nested within the veterans affairs normative aging study. Metabolism. 2014;63:760–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.02.013.
Wang C, Wu WKK, Liu X, To K-F, Chen GG, Yu J, et al. Increased serum chemerin level promotes cellular invasiveness in gastric cancer: a clinical and experimental study. Peptides. 2014;51:131–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2013.10.009.
Erdogan S, Yilmaz FM, Yazici O, Yozgat A, Sezer S, Ozdemir N, et al. Inflammation and chemerin in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:6337–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4483-y.
Zhang J, Jin H-C, Zhu A-K, Ying R-C, Wei W, Zhang F-J. Prognostic significance of plasma chemerin levels in patients with gastric cancer. Peptides. 2014;61:7–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2014.08.007.
Kaur J, Adya R, Tan BK, Chen J, Randeva HS. Identification of chemerin receptor (ChemR23) in human endothelial cells: chemerin-induced endothelial angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;391:1762–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.150.
Tümmler C, Snapkov I, Wickström M, Moens U, Ljungblad L, Maria Elfman LH, et al. Inhibition of chemerin/CMKLR1 axis in neuroblastoma cells reduces clonogenicity and cell viability in vitro and impairs tumor growth in vivo. Oncotarget. 2017;8:95135–51. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19619.
• Lin Y, Yang X, Liu W, Li B, Yin W, Shi Y, et al. Chemerin has a protective role in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the expression of IL-6 and GM-CSF and MDSC accumulation. Oncogene. 2017;36:3599–608. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.516. This study displayed the tumor-suppressive effect of chemerin mediated by the inhibition of the tumor microenvironment inflammation.
Yang R-Z, Lee M-J, Hu H, Pray J, Wu H-B, Hansen BC, et al. Identification of omentin as a novel depot-specific adipokine in human adipose tissue: possible role in modulating insulin action. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006;290:E1253–61. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00572.2004.
Shibata R, Ouchi N, Takahashi R, Terakura Y, Ohashi K, Ikeda N, et al. Omentin as a novel biomarker of metabolic risk factors. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2012;4:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-5996-4-37.
Panagiotou G, Mu L, Na B, Mukamal KJ, Mantzoros CS. Circulating irisin, omentin-1, and lipoprotein subparticles in adults at higher cardiovascular risk. Metabolism. 2014;63:1265–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.06.001.
Zhang Y-Y, Zhou L-M. Omentin-1, a new adipokine, promotes apoptosis through regulating Sirt1-dependent p53 deacetylation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;698:137–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.11.016.
• Kawashima K, Maeda K, Saigo C, Kito Y, Yoshida K, Takeuchi T. Adiponectin and intelectin-1: important adipokine players in obesity-related colorectal carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2017;18. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040866. This review analyses the complex relation of the tumor suppresive adipokines, adiponectin and intelectin-1 with colorectal cancer.
Shen X-D, Zhang L, Che H, Zhang Y-Y, Yang C, Zhou J, et al. Circulating levels of adipocytokine omentin-1 in patients with renal cell cancer. Cytokine. 2016;77:50–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2015.09.004.
Aleksandrova K, di Giuseppe R, Isermann B, Biemann R, Schulze M, Wittenbecher C, et al. Circulating omentin as a novel biomarker for colorectal cancer risk: data from the EPIC-Potsdam Cohort Study. Cancer Res. 2016;76:3862–71. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3464.
Uyeturk U, Alcelik A, Aktas G, Tekce BK. Post-treatment plasma omentin levels in patients with stage III colon carcinoma. J BUON. 2014;19:681–5.
Karabulut S, Afsar CU, Karabulut M, Alis H, Bozkurt MA, Aydogan F, et al. Clinical significance of serum omentin-1 levels in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. BBA Clin. 2016;6:138–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.10.002.
Li D, Mei H, Pu J, Xiang X, Zhao X, Qu H, et al. Intelectin 1 suppresses the growth, invasion and metastasis of neuroblastoma cells through up-regulation of N-myc downstream regulated gene 2. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0320-6.
Carpéné C, Dray C, Attané C, Valet P, Portillo MP, Churruca I, et al. Expanding role for the apelin/APJ system in physiopathology. J Physiol Biochem. 2007;63:359–73.
Boucher J, Masri B, Daviaud D, Gesta S, Guigné C, Mazzucotelli A, et al. Apelin, a newly identified adipokine up-regulated by insulin and obesity. Endocrinology. 2005;146:1764–71. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2004-1427.
Castan-Laurell I, Dray C, Attané C, Duparc T, Knauf C, Valet P. Apelin, diabetes, and obesity. Endocrine. 2011;40:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9507-9.
Cavallo MG, Sentinelli F, Barchetta I, Costantino C, Incani M, Perra L, et al. Altered glucose homeostasis is associated with increased serum apelin levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS One. 2012;7:e51236. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051236.
Wysocka MB, Pietraszek-Gremplewicz K, Nowak D. The role of apelin in cardiovascular diseases, obesity and cancer. Front Physiol. 2018;9:557. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00557.
Lacquaniti A, Altavilla G, Picone A, Donato V, Chirico V, Mondello P, et al. Apelin beyond kidney failure and hyponatremia: a useful biomarker for cancer disease progression evaluation. Clin Exp Med. 2015;15:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-014-0272-y.
Noy N, Li L, Abola MV, Berger NA. Is retinol binding protein 4 a link between adiposity and cancer? Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2015;23:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2015-0019.
Kotnik P, Fischer-Posovszky P, Wabitsch M. RBP4: a controversial adipokine. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;165:703–11. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-11-0431.
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2005;436:356–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03711.
Cao H. Adipocytokines in obesity and metabolic disease. J Endocrinol. 2014;220:T47–59. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0339.
Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Z. Adipokine RBP4 drives ovarian cancer cell migration. J Ovarian Res. 2018;11:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-018-0397-9.
Jiao C, Cui L, Ma A, Li N, Si H. Elevated serum levels of retinol-binding protein 4 are associated with breast cancer risk: a case-control study. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0167498. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167498.
Fei W, Chen L, Chen J, Shi Q, Zhang L, Liu S, et al. RBP4 and THBS2 are serum biomarkers for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:92254–64. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21173.
Hida K, Wada J, Eguchi J, Zhang H, Baba M, Seida A, et al. Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor: a unique insulin-sensitizing adipocytokine in obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:10610–5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504703102.
Heiker JT. Vaspin (serpinA12) in obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation. J Pept Sci. 2014;20:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.2621.
Wada J. Vaspin: a novel serpin with insulin-sensitizing effects. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;17:327–33. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.17.3.327.
El-Mesallamy HO, Kassem DH, El-Demerdash E, Amin AI. Vaspin and visfatin/Nampt are interesting interrelated adipokines playing a role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2011;60:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2010.04.008.
Erdogan S, Sezer S, Baser E, Gun-Eryilmaz O, Gungor T, Uysal S, et al. Evaluating vaspin and adiponectin in postmenopausal women with endometrial cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20:669–75. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-13-0280.
Fazeli MS, Dashti H, Akbarzadeh S, Assadi M, Aminian A, Keramati MR, et al. Circulating levels of novel adipocytokines in patients with colorectal cancer. Cytokine. 2013;62:81–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2013.02.012.
Cymbaluk-Płoska A, Chudecka-Głaz A, Jagodzińska A, Pius-Sadowska E, Sompolska-Rzechuła A, Machaliński B, et al. Evaluation of biologically active substances promoting the development of or protecting against endometrial cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:1363–72. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S155942.
Ramanjaneya M, Chen J, Brown JE, Tripathi G, Hallschmid M, Patel S, et al. Identification of nesfatin-1 in human and murine adipose tissue: a novel depot-specific adipokine with increased levels in obesity. Endocrinology. 2010;151:3169–80. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-1358.
Xu L, Wang H, Gong Y, Pang M, Sun X, Guo F, et al. Nesfatin-1 regulates the lateral hypothalamic area melanin-concentrating hormone-responsive gastric distension-sensitive neurons and gastric function via arcuate nucleus innervation. Metabolism. 2017;67:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2016.10.010.
Riva M, Nitert MD, Voss U, Sathanoori R, Lindqvist A, Ling C, et al. Nesfatin-1 stimulates glucagon and insulin secretion and beta cell NUCB2 is reduced in human type 2 diabetic subjects. Cell Tissue Res. 2011;346:393–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1268-5.
Xu Y, Pang X, Dong M, Wen F, Zhang Y. Nesfatin-1 inhibits ovarian epithelial carcinoma cell proliferation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;440:467–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.06.001.
Wang L, Ellis MJ, Gomez JA, Eisner W, Fennell W, Howell DN, et al. Mechanisms of the proteinuria induced by Rho GTPases. Kidney Int. 2012;81:1075–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2011.472.
Cetinkaya H, Karagöz B, Bilgi O, Ozgün A, Tunçel T, Emirzeoğlu L, et al. Nesfatin-1 in advanced lung cancer patients with weight loss. Regul Pept. 2013;181:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regpep.2012.11.005.
Franzén A, Heinegård D. Isolation and characterization of two sialoproteins present only in bone calcified matrix. Biochem J. 1985;232:715–24.
Kahles F, Findeisen HM, Bruemmer D. Osteopontin: a novel regulator at the cross roads of inflammation, obesity and diabetes. Mol Metab. 2014;3:384–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2014.03.004.
Lai C-F, Seshadri V, Huang K, Shao J-S, Cai J, Vattikuti R, et al. An osteopontin-NADPH oxidase signaling cascade promotes pro-matrix metalloproteinase 9 activation in aortic mesenchymal cells. Circ Res. 2006;98:1479–89. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000227550.00426.60.
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A, Kundu GC. Osteopontin: role in cell signaling and cancer progression. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2005.12.005.
Johnston NIF, Gunasekharan VK, Ravindranath A, O’Connell C, Johnston PG, El-Tanani MK. Osteopontin as a target for cancer therapy. Front Biosci. 2008;13:4361–72.
Rodrigues LR, Teixeira JA, Schmitt FL, Paulsson M, Lindmark-Mänsson H. The role of osteopontin in tumor progression and metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2007;16:1087–97. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-1008.
Bandopadhyay M, Bulbule A, Butti R, Chakraborty G, Ghorpade P, Ghosh P, et al. Osteopontin as a therapeutic target for cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014;18:883–95. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2014.925447.
Rittling SR, Chambers AF. Role of osteopontin in tumour progression. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:1877–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601839.
Zarling JM, Shoyab M, Marquardt H, Hanson MB, Lioubin MN, Todaro GJ. Oncostatin M: a growth regulator produced by differentiated histiocytic lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:9739–43.
Sanchez-Infantes D, White UA, Elks CM, Morrison RF, Gimble JM, Considine RV, et al. Oncostatin m is produced in adipose tissue and is regulated in conditions of obesity and type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:E217–25. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-3555.
Richards CD. The enigmatic cytokine oncostatin M and roles in disease. ISRN Inflamm. 2013;2013:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/512103.
Miles SA, Martínez-Maza O, Rezai A, Magpantay L, Kishimoto T, Nakamura S, et al. Oncostatin M as a potent mitogen for AIDS-Kaposi’s sarcoma-derived cells. Science. 1992;255:1432–4.
Amaral MC, Miles S, Kumar G, Nel AE. Oncostatin-M stimulates tyrosine protein phosphorylation in parallel with the activation of p42MAPK/ERK-2 in Kaposi’s cells. Evidence that this pathway is important in Kaposi cell growth. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:848–57. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI116659.
Lapeire L, Hendrix A, Lambein K, Van Bockstal M, Braems G, Van Den Broecke R, et al. Cancer-associated adipose tissue promotes breast cancer progression by paracrine oncostatin M and Jak/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res. 2014;74:6806–19. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0160.
Fossey SL, Bear MD, Kisseberth WC, Pennell M, London CA. Oncostatin M promotes STAT3 activation, VEGF production, and invasion in osteosarcoma cell lines. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:125. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-11-125.
Weiss TW, Simak R, Kaun C, Rega G, Pflüger H, Maurer G, et al. Oncostatin M and IL-6 induce u-PA and VEGF in prostate cancer cells and correlate in vivo. Anticancer Res. 2011;31:3273–8.
• Tawara K, Bolin C, Koncinsky J, Kadaba S, Covert H, Sutherland C, et al. OSM potentiates preintravasation events, increases CTC counts, and promotes breast cancer metastasis to the lung. Breast Cancer Res. 2018;20:–53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-018-0971-5. This study describes the ability of oncostatin-M to facilitate metastasis of breast cancer.
West NR, Murphy LC, Watson PH. Oncostatin M suppresses oestrogen receptor- expression and is associated with poor outcome in human breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2012;19:181–95. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-11-0326.
Vucenik I, Stains JP. Obesity and cancer risk: evidence, mechanisms, and recommendations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012;1271:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06750.x.
Ligibel JA, Alfano CM, Courneya KS, Demark-Wahnefried W, Burger RA, Chlebowski RT, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology position statement on obesity and cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3568–74. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.58.4680.
Moschen AR, Molnar C, Wolf AM, Weiss H, Graziadei I, Kaser S, et al. Effects of weight loss induced by bariatric surgery on hepatic adipocytokine expression. J Hepatol. 2009;51:765–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2009.06.016.
Venojärvi M, Wasenius N, Manderoos S, Heinonen OJ, Hernelahti M, Lindholm H, et al. Nordic walking decreased circulating chemerin and leptin concentrations in middle-aged men with impaired glucose regulation. Ann Med. 2013;45:162–70. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2012.727020.
Tee MC, Cao Y, Warnock GL, Hu FB, Chavarro JE. Effect of bariatric surgery on oncologic outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:4449–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3127-9.
Ashrafian H, Ahmed K, Rowland SP, Patel VM, Gooderham NJ, Holmes E, et al. Metabolic surgery and cancer: protective effects of bariatric procedures. Cancer. 2011;117:1788–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25738.
Haider DG, Schindler K, Schaller G, Prager G, Wolzt M, Ludvik B. Increased plasma visfatin concentrations in morbidly obese subjects are reduced after gastric banding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1578–81. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-2248.
Terra X, Auguet T, Guiu-Jurado E, Berlanga A, Orellana-Gavaldà JM, Hernández M, et al. Long-term changes in leptin, chemerin and ghrelin levels following different bariatric surgery procedures: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2013;23:1790–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-013-1033-9.
Zhu J, Schott M, Liu R, Liu C, Shen B, Wang Q, et al. Intensive glycemic control lowers plasma visfatin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Horm Metab Res. 2008;40:801–5. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1082040.
Mallik R, Chowdhury TA. Metformin in cancer. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.05.023.
Hajavi J, Momtazi AA, Johnston TP, Banach M, Majeed M, Sahebkar A. Curcumin: a naturally occurring modulator of adipokines in diabetes. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118:4170–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26121.
Rene Gonzalez R, Watters A, Xu Y, Singh UP, Mann DR, Rueda BR, et al. Leptin-signaling inhibition results in efficient anti-tumor activity in estrogen receptor positive or negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11:R36. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr2321.
Lanier V, Gillespie C, Leffers M, Daley-Brown D, Milner J, Lipsey C, et al. Leptin-induced transphosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor increases Notch and stimulates endothelial cell angiogenic transformation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;79:139–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2016.08.023.
Khan S, Shukla S, Sinha S, Meeran SM. Role of adipokines and cytokines in obesity-associated breast cancer: therapeutic targets. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013;24:503–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.10.001.
Otvos L, Kovalszky I, Olah J, Coroniti R, Knappe D, Nollmann FI, et al. Optimization of adiponectin-derived peptides for inhibition of cancer cell growth and signaling. Biopolymers. 2015;104:156–66. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.22627.
Tworoger SS, Eliassen AH, Kelesidis T, Colditz GA, Willett WC, Mantzoros CS, et al. Plasma adiponectin concentrations and risk of incident breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1510–6. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-1975.
Chong DQ, Mehta RS, Song M, Kedrin D, Meyerhardt JA, Ng K, et al. Prediagnostic plasma adiponectin and survival among patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2015;8:1138–45. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0175.
Dalamaga M, Sotiropoulos G, Karmaniolas K, Pelekanos N, Papadavid E, Lekka A. Serum resistin: a biomarker of breast cancer in postmenopausal women? Association with clinicopathological characteristics, tumor markers, inflammatory and metabolic parameters. Clin Biochem. 2013;46:584–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.01.001.
Dalamaga M, Archondakis S, Sotiropoulos G, Karmaniolas K, Pelekanos N, Papadavid E, et al. Could serum visfatin be a potential biomarker for postmenopausal breast cancer? Maturitas. 2012;71:301–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2011.12.013.
Zhang K, Zhou B, Zhang P, Zhang Z, Chen P, Pu Y, et al. Genetic variants in NAMPT predict bladder cancer risk and prognosis in individuals from southwest Chinese Han group. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:4031–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1527-z.
Kalia M. Biomarkers for personalized oncology: recent advances and future challenges. Metabolism. 2015;64:S16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.10.027.
Burgess S, Timpson NJ, Ebrahim S, Davey Smith G. Mendelian randomization: where are we now and where are we going? Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44:379–88. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv108.
Ebrahim S, Davey SG. Mendelian randomization: can genetic epidemiology help redress the failures of observational epidemiology? Hum Genet. 2008;123:15–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0448-6.
Nimptsch K, Song M, Aleksandrova K, Katsoulis M, Freisling H, Jenab M, et al. Genetic variation in the ADIPOQ gene, adiponectin concentrations and risk of colorectal cancer: a Mendelian randomization analysis using data from three large cohort studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32:419–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-017-0262-y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Nikolaos Spyrou, Konstantinos I. Avgerinos, Christos S Mantzoros, and Maria Dalamaga declare they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Metabolism
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spyrou, N., Avgerinos, K.I., Mantzoros, C.S. et al. Classic and Novel Adipocytokines at the Intersection of Obesity and Cancer: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies. Curr Obes Rep 7, 260–275 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-018-0318-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-018-0318-7