Abstract
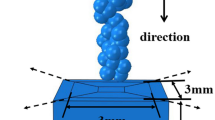
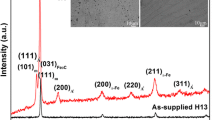
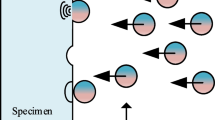
A significant amount of interstitial-free or IF steel is used to manufacture automotive body parts due to its high ductility, high formability, and low yield strength. But, the major drawback of this steel is the lower surface hardness. The current investigation intended to enhance the surface hardness by employing shot peening at different coverages. The work also studied the microstructural features intimated after the treatment and its effect on the surface hardness. The optical and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) results showed a prominent grain refinement and dislocation hardening, which improved the micro-hardness to 2.5 times. Tri-junctions, sub-grains, twins, nanocrystalline regions, and several dislocation-induced microstructural features, like dislocation bands, dislocation forests, dislocation walls, dislocation cell structure, etc., were detected in the samples after peening. These features bear a beneficial impact on the surface hardness of the substrate. A spatial filter (Sobel filter) was used to refine the image and detect the presence of NbC precipitates near the grain boundary. Using Gatan DigitalMicrograph software, the thermal imaging technique effectively identified thinner grain boundaries near the segregation zone.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data are included in the draft.
References
Y. Zhang, J. Wang, L. Wu, Z. Wang, L. Liu, V. Ji, S. Qu, Surface integrity and bending fatigue behavior of aeronautic gear steel under combined carburized treatment and shot peening. Int. J. Fatigue. 169, 107488 (2023)
S. Thielen, P. Breuninger, H. Hotz, C. Burkhart, T. Schollmayer, B. Sauer, S. Antonyuk, B. Kirsch, J.C. Aurich, Improving the tribological properties of radial shaft seal countersurfaces using experimental micro peening and classical shot peening processes. Tribol. Int. 155, 106764 (2021)
H.H. Xu, Y.C. Ye, G.F. Li, Experimental study on shot peening to improve diaphragm spring fatigue life of automobile clutch. Adv. Mater. Res. 941, 1497–1500 (2014)
M.N. James, D.G. Hattingh, L. Matthews, Embrittlement failure of 51CrV4 leaf springs. Eng. Fail. Anal. 139, 106517 (2022)
A. HeydariAstaraee, S. Bagherifard, E.A. Rajme Lopez, M. Guagliano, Adapting shot peening for surface texturing using customized additive manufactured shots. Adv. Eng. Mater. 25, 2201730 (2023)
Z. Ma, T. Chen, Z. Wang, X. Xing, X. Hou, C. Chang, Analysis of residual stress of gear tooth root after shot peening process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 125, 1–14 (2023)
L.B. Peral, P. Ebrahimzadeh, A. Gutiérrez, I. Fernández-Pariente, J. Wu, Effect of tempering temperature and grain refinement induced by severe shot peening on the corrosion behavior of a low alloy steel. J. Electroanal. Chem. 932, 117207 (2023)
U. Martin, I. Altenberger, B. Scholtes, K. Kremmer, H. Oettel, Cyclic deformation and near surface microstructures of normalized shot peened steel SAE 1045. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 246(1–2), 69–80 (1998)
H. Liu, P. Wei, C. Zhu, Q. Lin, Effect of shot peening coverage on hardness, residual stress and surface morphology of carburized rollers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 384, 125273 (2020)
H. Pan, W. Tao, B. Zhang, P. Jiang, Z. Wang, W. Wu, L. Liu, J. Li, Z. Wu, Z. Cai, Effect of shot peening strengths on microstructure and mechanical properties of 316L stainless steel prepared by 3D printing. Adv. Eng. Mater. 25, 2201675 (2023)
M. Ozturk, F. Husem, I. Karademir, E. Maleki, A. Amanov, O. Unal, Fatigue crack growth rate of AISI 4140 low alloy steel treated via shot peening and plasma nitriding. Vacuum. 207, 111552 (2023)
E. Maleki, O. Unal, M. Guagliano, S. Bagherifard, Analyzing the fatigue behavior and residual stress relaxation of gradient nano-structured 316L steel subjected to the shot peening via deep learning approach. Met. Mater. Int. 28, 112–131 (2022)
M. Neslušan, L. Trško, P. Minárik, J. Čapek, J. Bronček, F. Pastorek, J. Cizek, J. Moravec, Non-destructive evaluation of steel surfaces after severe plastic deformation via the Barkhausen noise technique. Metals. 8(12), 1029 (2018)
O. Unal, R. Varol, Surface severe plastic deformation of AISI 304 via conventional shot peening, severe shot peening and repeening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 351, 289–295 (2015)
K. Fan, D. Liu, Y. Liu, J. Wu, H. Shi, X. Zhang, K. Zhou, J. Xiang, M.A. Wahab, Competitive effect of residual stress and surface roughness on the fatigue life of shot peened S42200 steel at room and elevated temperature. Tribol. Int. 183, 108422 (2023)
E. Maleki, O. Unal, K.R. Kashyzadeh, S. Bagherifard, M. Guagliano, A systematic study on the effects of shot peening on a mild carbon steel: Microstructure, mechanical properties, and axial fatigue strength of smooth and notched specimens. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 4, 100071 (2021)
T.B. Hilditch, T. De Souza, P.D. Hodgson, Properties and automotive applications of advanced high-strength steels (AHSS), in Welding and Joining of Advanced High Strength Steels (AHSS). (Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, 2015), pp.9–28
T.H. Wickenden, The properties and selection of automotive steels. SAE Trans. 27, 260–264 (1932)
I. Mohanty, D. Bhattacharjee, S. Datta, Designing cold rolled IF steel sheets with optimized tensile properties using ANN and GA. Comput. Mater. Sci. 50(8), 2331–2337 (2011)
S.I. Kim, Y. Lee, Influence of cooling rate and boron content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled high strength interstitial-free steels. Met. Mater. Int. 18, 735–744 (2012)
S. Hoile, Processing and properties of mild interstitial free steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 16(10), 1079–1093 (2000)
G.P. Singh, A.P. Moon, S. Sengupta, G. Deo, S. Sangal, K. Mondal, Corrosion behavior of IF steel in various media and its comparison with mild steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24, 1961–1974 (2015)
M. Oliaei, R. Jamaati, Improvement of the strength-ductility-toughness balance in interstitial-free steel by gradient microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 845, 143237 (2022)
G. Janardhan, G. Mukhopadhyay, K. Dutta, Failure behavior of Spot-welds on automotive steel sheets. Mater. Today Proc. 62, 6120–6124 (2022)
O. Saray, G. Purcek, I. Karaman, T. Neindorf, H.J. Maier, Equal-channel angular sheet extrusion of interstitial-free (IF) steel: microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528(21), 6573–6583 (2011)
Y. Shadangi, K. Chattopadhyay, V. Singh, Microstructural modification and tensile behavior of IF steel processed through surface mechanical attrition treatment. JOM. 72(12), 4330–4339 (2020)
P. Cai, X. Lian, Z. Tang, L. Zhang, T. Wang, L. Chai, and G. Wu, Effect of heterogeneous laser surface treatment on mechanical properties of interstitial free steel. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 580 (IOP Publishing, 2019), p. 012029
B.G. Slavin, D. Child, B. Moore, and W. Hennig, Evaluation of spherical conditioned cut wire in comparison to cast steel shot peening media applied to inconel 718. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Shot Peening (2017), p. 189-194
P. Byczkowska, J. Sawicki, B. Januszewicz, M. Stegliński, Influence of single-stage and duplex shot peening on surface roughness and residual stresses in Al Mg5 Mn1 Sc0, 8 Zr0, 4 alloy. Arch. Metall. Mater. 63(1), 505–511 (2018)
A.H. Astaraee, S. Bagherifard, E.A. RajmeLópez, M. Guagliano, Adapting shot peening for surface texturing using customized additive manufactured shots. Adv. Eng. Mater. 25, 2201730 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202201730
W. Li, M. Vittorietti, G. Jongbloed, J. Sietsma, The combined influence of grain size distribution and dislocation density on hardness of interstitial free steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 45, 35–43 (2020)
M.A. Lopez-Sanchez, S. Llana-Fúnez, An evaluation of different measures of dynamically recrystallized grain size for paleopiezometry or paleowattometry studies. Solid Earth. 6(2), 475–495 (2015)
K. Bhansali, A.J. Keche, C.L. Gogte, S. Chopra, Effect of grain size on Hall-Petch relationship during rolling process of reinforcement bar. Mater. Today Proc. 26, 3173–3178 (2020)
D.S. Rao, K. Muraleedharan, C. Humphreys, TEM specimen preparation techniques. Microsc. Sci. Technol. Appl. Educ. 2, 1232 (2010)
T. Zhou, R.P. Babu, Z. Hou, P. Hedström, On the role of transmission electron microscopy for precipitation analysis in metallic materials. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 47(3), 388–414 (2022)
Y. Ji, and A. Xu, A new method for automatically measurement of vickers hardness using thick line hough transform and least square method. 2009 (October) 2nd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing (IEEE, 2009), p. 1-4. https://doi.org/10.1109/CISP.2009.5305653
F. Hanning, A.K. Khan, J. Andersson, O. Ojo, Advanced microstructural characterization of cast ATI 718Plus®—effect of homogenisation heat treatments on secondary phases and repair welding behavior. Weld. World. 64, 523–533 (2020)
C. Zhang, T. Fu, H. Chen, Y. Gao, Microstructure evolution of surface gradient nanocrystalline by shot peening of TA17 titanium alloy. Metall. and Mater. Trans. A. 52, 1790–1798 (2021)
M. Umemoto, Y. Todaka, K. Tsuchiya, Formation of nanocrystalline structure in steels by air blast shot peening. Mater. Trans. 44(7), 1488–1493 (2003)
Y. Chen, J. Du, S. Deng, L. Tian, K. Hu, Effect of ultrasonic shot peening duration on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 934, 168023 (2023)
L.B. Peral, A. Quintero, A.T. Vielma, M.F. Barbés, I. Fernández-Pariente, TEM evaluation of steel nanocrystalline surfaces obtained by severe shot peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 418, 127238 (2021)
S. Bagheri, M. Guagliano, Review of shot peening processes to obtain nanocrystalline surfaces in metal alloys. Surf. Eng. 25(1), 3–14 (2009)
J.F.C. Lins, H.R.Z. Sandim, H.J. Kestenbach, D. Raabe, K.S. Vecchio, A microstructural investigation of adiabatic shear bands in an interstitial free steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 457(1–2), 205–218 (2007)
H.S. Lee, D.S. Kim, J.S. Jung, Y.S. Pyoun, K. Shin, Influence of peening on the corrosion properties of AISI 304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 51(12), 2826–2830 (2009)
Y. Liu, Y. Cao, W. Liu, Q. Mao, H. Zhou, Y. Zhao, Y. Zhu, Adiabatic shear localization induced by rotationally accelerated shot peening. J. Mater. Sci. 58, 1–10 (2023)
J.S. Robach, I.M. Robertson, B.D. Wirth, A. Arsenlis, In-situ transmission electron microscopy observations and molecular dynamics simulations of dislocation-defect interactions in ion-irradiated copper. Philos. Mag. 83(8), 955–967 (2003)
X.D. Ren, X.Q. Yang, W.F. Zhou, J.J. Huang, Y.P. Ren, C.C. Wang, L. Li, Thermal stability of surface nano-crystallization layer in AZ91D magnesium alloy induced by laser shock peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 334, 182–188 (2018)
F.F. Lavrentev, The type of dislocation interaction as the factor determining work hardening. Mater. Sci. Eng. 46(2), 191–208 (1980)
O.M.D.M. Messé, S. Stekovic, M.C. Hardy, C.M.F. Rae, Characterization of plastic deformation induced by shot-peening in a Ni-base superalloy. JOM. 66, 2502–2515 (2014)
L.E. Murr, Strain-induced dislocation emission from grain boundaries in stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 51(1), 71–79 (1981)
J. Polák, R. Petráš, M. Heczko, I. Kuběna, T. Kruml, G. Chai, Low cycle fatigue behavior of Sanicro25 steel at room and at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 615, 175–182 (2014)
P. Tadge, P.K. Gupta, C. Sasikumar, Surface nano-crystallizationof AISI 304 stainless steel through shot peening technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2(4–5), 3245–3250 (2015)
I.S. Yasnikov, Y. Kaneko, M. Uchida, A. Vinogradov, The grain size effect on strain hardening and necking instability revisited from the dislocation density evolution approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 831, 142330 (2022)
I. Gutierrez-Urrutia, D. Raabe, Grain size effect on strain hardening in twinning-induced plasticity steels. Scripta Mater. 66(12), 992–996 (2012)
H. Fan, Q. Wang, J.A. El-Awady, D. Raabe, M. Zaiser, Strain rate dependency of dislocation plasticity. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1845 (2021)
N. Shigematsu, D.J. Prior, J. Wheeler, First combined electron backscatter diffraction and transmission electron microscopy study of grain boundary structure of deformed quartzite. J. Microsc. 224(3), 306–321 (2006)
P.R. Howell, A.R. Jones, B. Ralph, Techniques for the observation of grain boundaries in an austenitic stainless steel. J. Microsc. 102(3), 323–330 (1974)
L. Liu, J. Wang, J. Zhou, Effects of laser shock peening on mechanical behaviors and microstructural evolution of brass. Vacuum. 148, 178–183 (2018)
A. Moshkovich, V. Perfilyev, T. Bendikov, I. Lapsker, H. Cohen, L. Rapoport, Structural evolution in copper layers during sliding under different lubricant conditions. Acta Mater. 58(14), 4685–4692 (2010)
M.S. Chen, W.Q. Yuan, Y.C. Lin, H.B. Li, Z.H. Zou, Modeling and simulation of dynamic recrystallization behavior for 42CrMo steel by an extended cellular automaton method. Vacuum. 146, 142–151 (2017)
J. Sheng, S. Huang, J.Z. Zhou, Z.W. Wang, Effects of warm laser peening on the elevated temperature tensile properties and fracture behavior of IN718 nickel-based superalloy. Eng. Fract. Mech. 169, 99–108 (2017)
M. Cabibbo, E. Evangelista, M. Vedani, Influence of severe plastic deformations on secondary phase precipitation in a 6082 Al–Mg–Si alloy. Metall. and Mater. Trans. A. 36, 1353–1364 (2005)
A. Shibata, G. Miyamoto, S. Morito, A. Nakamura, T. Moronaga, H. Kitano, K. Tsuzaki, Substructure and crystallography of lath martensite in as-quenched interstitial-free steel and low-carbon steel. Acta Mater. 246, 118675 (2023)
U. Trdan, M. Skarba, J. Grum, Laser shock peening effect on the dislocation transitions and grain refinement of Al–Mg–Si alloy. Mater Charact. 97, 57–68 (2014)
Y.G. Liu, M.Q. Li, Structure response characteristics and surface nanocrystallization mechanism of alpha phase in Ti–6Al–4V subjected to high energy shot peening. J. Alloys Compd. 773, 860–871 (2019)
P. Liu, S. Sun, J. Hu, Effect of laser shock peening on the microstructure and corrosion resistance in the surface of weld nugget zone and heat-affected zone of FSW joints of 7050 Al alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 112, 1–7 (2019)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Department of MME, NIT, Karnataka, for providing the research facilities for the current work.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from public, commercial, or not-for-profit funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BS- Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing- original draft. UBK- Writing- review and editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Special issue credit line: This invited article is part of a special topical focus in the journal Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis on Quantitative Metallography and Microstructure Modeling.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, B., Udaya Bhat, K. Microstructural Features Intimated in Automotive Grade IF Steel Subjected to Conventional and Severe Shot Peening. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-024-01069-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-024-01069-y