Abstract
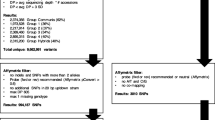
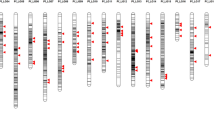
Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) is a representative root crop of the Brassicaceae family and is important to the vegetable seed industry in East Asia. Due to its agronomic importance, various molecular markers, genetic maps, genomic resources, and genome assemblies of radish have been developed during the past decade. Marker integration and comparative mapping using these resources will accelerate genetic improvements in radish cultivars. With the goal of establishing a marker-based high-throughput genetic analysis tool, we integrated 3765 nonredundant genetic markers into the Rs1.0 reference genome and converted them into 1182 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers via whole-genome resequencing data of the mapping parents ‘WK10039’ and ‘WK10024’. A genetic map covering 721.3 cM with 768 framework loci was constructed by analyzing these SNP conversion markers in the F2 mapping population, which was composed of 93 individuals. Comparison of this map with the Rs1.0 reference genome and other linkage maps showed the physical and genetic correlations of the markers. To develop a high-throughput genotyping system for large accessions or populations with smaller numbers of SNPs, 674 Fluidigm and 68 kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) markers were validated. Application of the 68 KASP assays to 127 commercial cultivars enabled successful identification and classification of genotypes; 11 KASP markers constituted the minimum marker set. The SNP markers used to construct the genetic maps will be a useful resource in research on radish and should lead to low-cost, accurate, and high-throughput genotyping platforms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asamizu E, Ichihara H, Nakaya A, Nakamura Y, Hirakawa H, Ishii T, Tamura T, Fukami-Kobayashi K, Nakajima Y et al (2014) Plant genome database Japan (PGDBj): a portal website for the integration of plant genome-related databases. Plant Cell Physiol 55:e8
Cheon K-S, Baek J, Cho Y-i, Jeong Y-M, Lee Y-Y, Oh J, Won Y, Kang D-Y, Oh H et al (2018) Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery and Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR (KASP) marker development with Korean Japonica rice varieties. Plant Breed Biotechnol 6:391–403
Cheon K-S, Jeong Y-M, Lee Y-Y, Oh J, Kang D-Y, Oh H, Kim S, Kim N, Lee E et al (2019) Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR marker eevelopment and quantitative trait locus mapping for Bakanae disease resistance in Korean Japonica rice varieties. Plant Breed Biotechnol 7:208–219
Jeong Y-M, Chung W-H, Chung H, Kim N, Park B-S, Lim K-B, Yu H-J, Mun J-H (2014a) Comparative analysis of the radish genome based on a conserved ortholog set (COS) of Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 127:1975–1989
Jeong Y-M, Chung W-H, Mun J-H, Kim N, Yu H-J (2014b) De novo assembly and characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Gene 551:39–48
Jeong Y-M, Chung W-H, Choi A, Mun J-H, Kim N, Yu H-J (2016a) The complete mitochondrial genome of cultivated radish WK10039 (Raphanus sativus L.). Mitochondrial DNA 27:941–942
Jeong Y-M, Kim N, Ahn B, Oh M, Chung W-H, Chung H, Jeong S, Lim K-B, Hwang Y-J et al (2016b) Elucidating the triplicated ancestral genome structure of radish based on chromosome-level comparison with the Brassica genomes. Theor Appl Genet 129:1357–1372
Jo J, Purushotham P, Han K, Lee H, Nah G, Kang B (2017) Development of a genetic map for onion (Allium cepa L.) using reference-free genotyping-by-sequencing and SNP assays. Front Plant Sci 8:1606
Kim K, Chung H, Cho G, Ma K, Chandrabalan D, Gwag J, Kim T, Cho E, Park Y (2007) PowerCore: a program applying the advanced M strategy with a heuristic search for establishing core sets. Bioinformatics 23:2155–2162
Kim N, Jeong Y-M, Jeong S, Kim G-B, Baek S, Kwon Y-E, Cho A, Choi S-B, Kim J et al (2016) Identification of candidate domestication regions in the radish genome based on high-depth resequencing analysis of 17 genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 129:1797–1814
Kitashiba H, Li F, Hirakawa H, Kawanabe T, Zou ZW, Hasegawa Y, Tonosaki K, Shirasawa S, Fukushima A et al (2014) Draft sequences of the radish (Raphanus sativus L.) genome. DNA Res 21:481–490
Lee Y-J, Mun J-H, Jeong Y-M, Joo S-H, Yu H-J (2018) Assembly of a radish core collection for evaluation and preservation of genetic diversity. Hort Environ Biotechnol 59:711–721
Li F, Hasegawa Y, Saito M, Shirasawa S, Fukushima A, Ito T, Fujii H, Kishitani S, Kitashiba H et al (2011) Extensive chromosome homoeology among Brassiceae species were revealed by comparative genetic mapping with high-density EST-based SNP markers in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). DNA Res 18:401–411
Liu C, Wang S, Xu W, Liu X (2017) Genome-wide transcriptome profiling of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) in response to vernalization. PLoS ONE 12:e0177594
Mitsui Y, Shimomura M, Komatsu K, Namiki N, Shibata-Hatta M, Imai M, Katayose Y, Mukai Y, Kanamori H et al (2015) The radish genome and comprehensive gene expression profile of tuberous root formation and development. Sci Rep 5:10835
Moghe G, Hufnagel D, Tang H, Xiao Y, Dworkin I, Town C, Conner J, Shiu S (2014) Consequences of whole-genome triplication as revealed by comparative genomic analyses of the wild radish Raphanus raphanistrum and three other Brassicaceae species. Plant Cell 26:1925–1937
Mun J-H, Chung H, Chung W-H, Oh M, Jeong Y-M, Kim N, Ahn B-O, Park B-S, Park S et al (2015) Construction of a reference genetic map of Raphanus sativus based on genotyping by whole-genome resequencing. Theor Appl Genet 128:259–272
Nadeem M, Nawaz M, Shahid M, Doğan Y, Comertpay G, Yıldız M, Hatipoğlu R, Ahmad F, Alsaleh A et al (2018) DNA molecular markers in plant breeding: current status and recent advancements in genomic selection and genome editing. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32:261–285
Nie S, Li C, Xu L, Wang Y, Huang D, Muleke E, Sun X, Xie Y, Liu L (2016) De novo transcriptome analysis in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) and identification of critical genes involved in bolting and flowering. BMC Genom 17:389
Semagn K, Babu R, Hearne S, Olsen M (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP): overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol Breed 33:1–14
Shen D, Sun H, Huang M, Zheng Y, Li X, Fei Z (2013) RadishBase: a database for genomics and genetics of radish. Plant Cell Physiol 54:e3
Shirasawa K, Oyama M, Hirakawa H, Sato S, Tabata S, Fujioka T, Kimizuka-Takagi C, Sasamoto S, Watanabe A et al (2011) An EST-SSR linkage map of Raphanus sativus and comparative genomics of the Brassicaceae. DNA Res 18:221–232
Singh P, Tripathi S, Somani K (2001) Hybrid seed production of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). J New Seeds 3:51–58
Thomson M (2014) High-throughput SNP genotyping to accelerate crop improvement. Plant Breed Biotechnol 2:195–212
van Ooijen J (2006) JoinMap® 4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma B V, Wageningen
Voorrips R (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Heredity 93:77–78
Wang S, Wang X, He Q, Liu X, Xu W, Li L, Gao J, Wang F (2012) Transcriptome analysis of the roots at early and late seedling stages using Illumina paired-end sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers in radish. Plant Cell Rep 31:1437–1447
Wang Y, Pan Y, Liu Z, Zhu X, Zhai L, Xu L, Yu R, Gong Y, Liu L (2013) De novo transcriptome sequencing of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) and analysis of major genes involved in glucosinolate metabolism. BMC Genom 14:836
Xiaohui Z, Zhen Y, Shiyoung M, Yang Q, Xinhua Y, Xiaohua C, Feng C, Zhangyan W, Yuyan S et al (2015) A de novo genome of a Chinses radish cultivar. Hort Plant J 1:155–164
Xie Y, Ye S, Wang Y, Xu L, Zhu X, Yang J, Feng H, Yu R, Karanja B et al (2015) Transcriptome-based gene profiling provides novel insights into the characteristics of radish root response to Cr stress with next-generation sequencing. Front Plant Sci 6:202
Xu Y (2010) Molecular plant breeding. CABI International, Wallingford
Yu R, Xu L, Zhang W, Wang Y, Luo X, Wang R, Zhu X, Xie Y, Karanja B et al (2016) De novo taproot transcriptome sequencing and analysis of major genes involved in sucrose metabolism in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Front Plant Sci 7:585
Yu H-J, Baek S, Lee Y-J, Cho A, Mun J-H (2019) The radish genome database (RadishGD): An integrated information resource for radish genomics. Database 2019:baz009
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Next-Generation Biogreen21 program (Grant No. PJ013194), the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No. NRF-2017R1D1A1B06029741), and the Catholic University of Korea (Grant No. M-2019-B0014-003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JHM and HJY planned the project, designed the research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. YMJ performed the experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. YJL, BY, and AC performed the experiments and analyzed data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sung-Chur Sim.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, HJ., Jeong, YM., Lee, YJ. et al. Marker integration and development of Fluidigm/KASP assays for high-throughput genotyping of radish. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 61, 767–777 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00253-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00253-7