Abstract
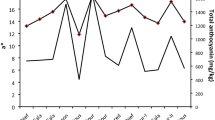
‘Goha’, ‘Gangha’, ‘Gwanha’, and ‘Yeolha’ are newly-developed Korean everbearing strawberry (Fragaria ananassa Duch.) cultivars. Bioactive phytochemicals play a crucial role in the prevention of cancer, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and metabolic diseases. We examined the free radical scavenging activity and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity in these four cultivars and a junebearing cultivar ‘Seolhyang’ for comparison. ‘Gwanha’ showed the strongest 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) free radical scavenging activities, and ‘Gwanha’ and ‘Goha’ had the most potent α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Total anthocyanin content (TAC) was the highest in ‘Gwanha’. The major anthocyanin components of everbearing strawberry were determined to be pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside (Pg3G), pelargonidin-3-O-rutinoside, and cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (C3G). A correlation study between activity and components revealed that TAC was highly correlated with antioxidant and antihyperglycemic activities, and in principal component analysis, C3G is highly correlated with antioxidant activity and Pg3G is highly correlated with the antihyperglycemic effect of everbearing strawberries. Among the four everbearing strawberry cultivars, ‘Gwanha’ and ‘Goha’ are rich sources of pelargonidin showing strong α-glucosidase inhibitory activity and are promising dietary sources to prevent diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaby K, Ekeberg D, Skrede G (2007) Characterization of phenolic compounds in strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa) fruits by different HPLC detectors and contribution of individual compounds to total antioxidant capacity. J Agric Food Chem 55:4395–4406. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0702592
Afrin S, Gasparrini M, Forbes-Hernandez TY, Reboredo-Rodriguez P, Mezzetti B, Varela-Lopez A, Giampieri F, Battino M (2016) Promising health benefits of the strawberry: a focus on clinical studies. J Agric Food Chem 64:4435–4449. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00857
Ali AM (2013) Anti-diabetic potential of phenolic compounds: a review. Int J Food Prop 16:91–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2011.595864
Alvarez-Suarez JM, Dekanski D, Ristic S, Radonjic NV, Petronijevic ND, Giampieri F, Astolfi P, González-Paramás AM, Santos-Bluelga C, Tulipani S, Quiles JL, Mezzetti B, Battino M (2011) Strawberry polyphenols attenuate ethanol-induced gastric lesions in rats by activation of antioxidant enzymes and attenuation of MDA increase. PLoS One 6:e25878. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025878
Arruda JE, Weiler MD, Valentino D, Willis WG, Rossi JS, Stern RA, Costa L (1996) A guide for applying principal-components analysis and confirmatory factor analysis to quantitative electroencephalogram data. Int J Psychophysiol 23:63–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8760(96)00032-3
Baby B, Antony P, Vijayan R (2018) Antioxidant and anticancer properties of berries. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:2491–2507. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1329198
Byrne CD, Wild SH (2011) Increased risk of glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes with statins. BMJ 343:d5004. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5004
Choi Y, Lee S, Chun J, Lee H, Lee J (2006) Influence of heat treatment on the antioxidant activities and polyphenolic compounds of Shiitake (Lentinus edodes) mushroom. Food Chem 99:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.08.004
da Silva FL, Escribano-Bailón MT, Alonso JJP, Rivas-Gonzalo JC, Santos-Buelga C (2007) Anthocyanin pigments in strawberry. LWT-Food Sci Technol 40:374–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2005.09.018
Daffertshofer A, Lamoth CJ, Meijer OG, Beek PJ (2004) PCA in studying coordination and variability: a tutorial. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 19:415–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2004.01.005
Einbond LS, Reynertson KA, Luo X-D, Basile MJ, Kennelly EJ (2004) Anthocyanin antioxidants from edible fruits. Food Chem 84:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00162-6
Gil-Izquierdo A, Zafrilla P, Tomas-Barberan FA (2002) An in vitro method to simulate phenolic compound release from the food matrix in the gastrointestinal tract. Eur Food Res Technol 214:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-001-0428-3
Gomes CA, Girão da Cruz T, Andrade JL, Milhazes N, Borges F, Marques MPM (2003) Anticancer activity of phenolic acids of natural or synthetic origin: a structure–activity study. J Med Chem 46:5395–5401. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm030956v
Jayaprakasam B, Vareed SK, Olson LK, Nair MG (2005) Insulin secretion by bioactive anthocyanins and anthocyanidins present in fruits. J Agric Food Chem 53:28–31. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf049018+
Kassim M, Achoui M, Mustafa MR, Mohd MA, Yusoff KM (2010) Ellagic acid, phenolic acids, and flavonoids in Malaysian honey extracts demonstrate in vitro anti-inflammatory activity. Nutr Res 30:650–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2010.08.008
Ko M, Jayaramaiah RH, Gupta R, Kim S, An J, Wang Z, Li M, Kang N, Hong K-P, Kang J-S, Kim S, Choi Y (2017) Evaluation of bioactive compounds in strawberry fruits by a targeted metabolomic approach. Hortic Sci Technol 35:805–819
Laube H (2002) Acarbose—an update of its therapeutic use in diabetes treatment. Clin Drug Investig 22:141–156. https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200222030-00001
Lee J, Durst RW, Wrolstad RE (2005) Determination of total monomeric anthocyanin pigment content of fruit juices, beverages, natural colorants, and wines by the pH differential method: collaborative study. J AOAC Int 88:1269–1278
Lee J, Lee E, Im J, Nam C, Yae B (2008) Breeding of new ever-bearing strawberry ‘Goha’ for summer culture. Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 26:413–416
Lopes-da-Silva F, de Pascual-Teresa S, Rivas-Gonzalo J, Santos-Buelga C (2002) Identification of anthocyanin pigments in strawberry (cv Camarosa) by LC using DAD and ESI-MS detection. Eur Food Res Technol 214:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-001-0434-5
Lopez A, Montano A, Garcia P, Garrido A (2006) Fatty acid profile of table olives and its multivariate characterization using unsupervised (PCA) and supervised (DA) chemometrics. J Agric Food Chem 54:6747–6753. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0612474
Mcdougall GJ, Stewart D (2005) The inhibitory effects of berry polyphenols on digestive enzymes. BioFactors 23:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.5520230403
Moazen S, Amani R, Rad AH, Shahbazian H, Ahmadi K, Jalali MT (2013) Effects of freeze-dried strawberry supplementation on metabolic biomarkers of atherosclerosis in subjects with type 2 diabetes: a randomized double-blind controlled trial. Ann Nutr Metab 63:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1159/000356053
Mudnic I, Modun D, Brizic I, Vukovic J, Generalic I, Katalinic V, Bilusic T, Ljubenkov I, Boban M (2009) Cardiovascular effects in vitro of aqueous extract of wild strawberry (Fragaria vesca, L) leaves. Phytomed 16:462–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2008.11.004
Nile SH, Park S (2014) Edible berries: bioactive components and their effect on human health. Nutrition 30:134–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2013.04.007
Nishioka T, Kawabata J, Aoyama Y (1998) Baicalein, an α-glucosidase inhibitor from Scutellaria baicalensis. J Nat Product 61:1413–1415. https://doi.org/10.1021/np980163p
Oki T, Matsui T, Osajima Y (1999) Inhibitory effect of α-glucosidase inhibitors varies according to its origin. J Agric Food Chem 47:550–553. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf980788t
Pantelidis GE, Vasilakakis M, Manganaris GA, Diamantidis G (2007) Antioxidant capacity, phenol, anthocyanin and ascorbic acid contents in raspberries, blackberries, red currants, gooseberries and Cornelian cherries. Food Chem 102:777–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.06.021
Prakash D, Suri S, Upadhyay G, Singh BN (2007) Total phenol, antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of some medicinal plants. Int J Food Sci Nutr 58:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/09637480601093269
Rajalahti T, Kvalheim OM (2011) Multivariate data analysis in pharmaceutics: a tutorial review. Int J Pharm 417:280–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.02.019
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Bio Med 26:1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
Scherrer H, Risken H, Leiber T (1988) Eigenvalues of the Schrodinger equation with rational potentials. Phys Rev A Gen Phys 38:3949–3959. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.38.3949
Schneider H, Simmering R, Hartmann L, Pforte H, Blaut M (2000) Degradation of quercetin-3-glucoside in gnotobiotic rats associated with human intestinal bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 89:1027–1037. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.01209.x
Seeram NP (2010) Recent trends and advances in berry health benefits research. J Agric Food Chem 58:3869–3870. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf902806j
Seeram NP, Adams LS, Zhang Y, Lee R, Sand D, Scheuller HS, Herber D (2006) Blackberry, black raspberry, blueberry, cranberry, red raspberry, and strawberry extracts inhibit growth and stimulate apoptosis of human cancer cells in vitro. J Agric Food Chem 54:9329–9339. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf061750g
Shim Y, Doo H, Ahn S, Kim Y, Seong J, Park I, Min B (2003) Inhibitory effect of aqueous extract from the gall of Rhus chinensis on alpha-glucosidase activity and postprandial blood glucose. J Ethnopharmacol 85:283–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(02)00370-7
Singh N, Rajini P (2004) Free radical scavenging activity of an aqueous extract of potato peel. Food Chem 85:611–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.07.003
Skrede G, Wrolstad R, Durst R (2000) Changes in anthocyanins and polyphenolics during juice processing of highbush blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum L). J Food Sci 65:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2000.tb16007.x
Tadera K, Minami Y, Takamatsu K, Matsuoka T (2006) Inhibition of alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase by flavonoids. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 52:149–153. https://doi.org/10.3177/Jnsv.52.14
Tulipani S, Alvarez-Suarez JM, Busco F, Bompadre S, Quiles JL, Mezzetti B, Battino M (2011) Strawberry consumption improves plasma antioxidant status and erythrocyte resistance to oxidative haemolysis in humans. Food Chem 128:180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.025
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001
Winardiantika V, Lee Y, Park N, Yeoung Y-R (2015) Effects of cultivar and harvest time on the contents of antioxidant phytochemicals in strawberry fruits. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 56:732–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-0052-y
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) [Grant Number. NRF-2015R1D1A3A01020708] and Research Fund of Kyungpook National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MJP performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; DHR performed the experiments and analyzed the data; JYC and DGL performed the experiments; JNL contributed the four cultivars of everbearing strawberries; YHK contributed reagents, materials, and analysis tools, and guided the experiment and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sanghyun Lee.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, M.J., Ryu, D.H., Cho, J.Y. et al. Potential for antioxidant and antihyperglycemic activities of four everbearing strawberry cultivars. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 61, 615–623 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00240-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00240-y