Abstract
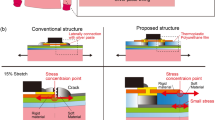
The distinguishing feature of a flexible electronic device is that it maintains its function even when the shape changes repeatedly. As the degree of integration of flexible devices increases, revealing failure mechanisms and extending the lifetime of the flexible devices are getting more difficult. One of the potential damage zones is the interface of heterogeneous material components, where strain can be localized due to the mismatch of mechanical properties. In this study, we investigate the mechanically reliable interconnect design of the flexible printed circuit board (FPCB) system in which the packaging chip is integrated. When the FPCB was bent, folding occurred at the edge of the packaging chip due to the high bending rigidity compared with the plastic substrate and resulted in high strain concentration. By introducing interconnect architecture that bypassed the strain concentration area around the packaging chip, mechanical damage of the interconnects was successfully reduced. Through finite element simulation, the strain applied to the interconnect crossing the strain-concentrated region was predicted to be 2 times larger than that bypassing the strain-concentrated region, from 8.32 to 4.64%. In addition, the strain gap of these two interconnects could be increased as the Young’s modulus mismatch between the packaging chip and the substrate increased. This study is expected to improve the design guidelines to mechanically reliable interconnects in highly integrated flexible electronics.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, B., Facchetti, A.: Mechanically flexible conductors for stretchable and wearable E-skin and E‐textile devices. Adv. Mater. 31, 1901408 (2019)
Zhou, L., Wanga, A., Wu, S.-C., Sun, J., Park, S., Jackson, T.N.: All-organic active matrix flexible display. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 083502 (2006)
Xu, S., Zhang, Y., Cho, J., Lee, J., Huang, X., Jia, L., Fan, J.A., Su, Y., Su, J., Zhang, H., Cheng, H., Lu, B., Yu, C., Chuang, C., Kim, T., Song, T., Shigeta, K., Kang, S., Dagdeviren, C., Petrov, I., Braun, P.V., Huang, Y., Paik, U., Rogers, J.A.: Stretchable batteries with self-similar serpentine interconnects and integrated wireless recharging systems. Nat. Commun. 4, 1543 (2013)
Kim, K., Lee, Y., Costa, A., Lee, Y., Jang, T., Lee, M., Joo, Y., Oh, K.H., Song, J., Choi, I.: Extremely versatile deformability beyond materiality: a new material platform through simple cutting for rugged batteries. Adv. Eng. Mater. 21, 1900206 (2019)
Lee, Y.-J., Lim, S.-M., Yi, S.-M., Lee, J.-H., Kang, S., Choi, G.-M., Han, H.N., Sun, J.-Y., Choi, I.-S., Joo, Y.-C.: Auxetic elastomers: mechanically programmable meta-elastomers with an unusual Poisson’s ratio overcome the Gauge limit of a capacitive type strain sensor. Extreme Mech. Lett. 31, 100516 (2019)
Choi, C., Choi, M.K., Liu, S., Kim, M.S., Park, O.K., Im, C., Kim, J., Qin, X., Lee, G.J., Cho, K.W., Kim, M., Joh, E., Lee, J., Son, D., Kwon, S.-H., Jeon, N.L., Song, Y.M., Lu, N., Kim, D.-H.: Human eye-inspired soft optoelectronic device using high-density MoS2-graphene curved image sensor array. Nat. Commun. 8, 1664 (2017)
Byun, J., Oh, E., Lee, B., Kim, S., Lee, S., Hong, Y.: A single droplet-printed double‐side universal soft electronic platform for highly integrated stretchable hybrid electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1701912 (2017)
Lee, Y.-J., Lee, U., Yeon, Y., Shin, H.-W., Evans, H.-A.-S., Joo, L.A.: Influences of semiconductor morphology on the mechanical fatigue behavior of flexible organic electronics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 241904 (2013)
Lee, Y.-Y., Lee, J.-H., Cho, J.-Y., Kim, N.-R., Nam, D.-H., Choi, I.-S., Nam, K.T., Joo, Y.-C.: Stretching-induced growth of PEDOT-rich cores: a new mechanism for strain-dependent resistivity change in PEDOT: PSS films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 4020–4027 (2013)
Lee, Y.-Y., Kang, H.-Y., Gwon, S.H., Choi, G.M., Lim, S.-M., Sun, J.-Y., Joo, Y.-C.: A strain-insensitive stretchable electronic conductor: PEDOT:PSS/acrylamide organogels. Adv. Mater. 28, 1636–1643 (2016)
Yoon, S.G., Koo, H.-J., Chang, S.T.: Highly stretchable and transparent microfluidic strain sensors for monitoring human body motions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 27562–27570 (2015)
Zhou, R., Guo, W., Yu, R., Pan, C.: Highly flexible, conductive and catalytic Pt networks as transparent counter electrodes for wearable dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 23028–23034 (2015)
Hwang, B., Shin, H.-A.-S., Kim, T., Joo, Y.-C., Han, S.M.: Highly reliable Ag nanowire flexible transparent electrode with mechanically welded junctions. Small 10, 3397–3404 (2014)
Kim, D.-H., Ahn, J.-H., Choi, W.M., Kim, H.-S., Kim, T.-H., Song, J., Huang, Y.Y., Liu, Z., Lu, C., Rogers, J.A.: Stretchable and foldable silicon integrated circuits. Science 320, 507–511 (2008)
Hsu, Y.-Y., Gonzalez, M., Bossuyt, F., Vanfleteren, J., De Wolf, I.: Polyimide-enhanced stretchable interconnects: design, fabrication, and characterization. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 58, 2680–2688 (2011)
Kim, B.-J., Cho, Y., Jung, M.-S., Shin, H.-A.-S., Moon, M.-W., Han, H.N., Nam, K.T., Joo, Y.-C., Choi, I.-S.: Fatigue-free, electrically reliable copper electrode with nanohole array. Small 8, 3300–3306 (2012)
Naserifar, N., LeDuc, P.R., Fedder, G.K.: Material gradients in stretchable substrates toward integrated electronic functionality. Adv. Mater. 28, 3584–3591 (2016)
Yi, S.-M., Choi, I.-S., Kim, B.-J., Joo, Y.-C.: Reliability issues and solutions in flexible electronics under mechanical fatigue. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14, 387–404 (2018)
Gan, L., Ben-Nissan, B., Ben-David, A.: Modelling and finite element analysis of ultra-microhardness indentation of thin films. Thin Solid Films 290–291, 362–366 (1996)
Yu, D.Y.W., Spaepen, F.: The yield strength of thin copper films on kapton. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 2991–2997 (2004)
Kim, J.-H., Lee, T.-I., Kim, T.-S., Paik, K.-W.: Effects of ACFs adhesion on the bending reliability of chip-in-flex packages for wearable electronics applications. In: 2016 IEEE 66th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), IEEE: Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 2461–2467 (2016)
Ko, C.-T., Yang, H., Lau, J.H., Li, M., Lin, C., Chang, C.-L., Pan, J.-Y., Wu, H.-H., Xu, I., Chen, T., Li, Z., Tan, K.H., Lo, P., So, R., Chen, Y.H., Fan, N., Kuah, E., Lin, M., Cheung, Y.M., Ng, E., Xi, C., Beica, R., Lim, S.P., Lee, N.C., Tao, M., Lo, J., Lee, R.: Feasibility study of fan-out panel-level packaging for heterogeneous integrations. In :2019 IEEE 69th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE: Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 14–20 (2019)
Lu, N., Suo, Z., Vlassak, J.: The effect of film thickness on the failure strain of polymer-supported metal films. Acta Mater. 58, 1679–1687 (2010)
Kraft, O., Schwaiger, R., Wellner, P.: Fatigue in thin films: lifetime and damage formation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 319–321, 919–923 (2001)
Sun, X.J., Wang, C.C., Zhang, J., Liu, G., Zhang, G.J., Ding, X.D., Zhang, G.P., Sun, J.: Thickness dependent fatigue life at microcrack nucleation for metal thin films on flexible substrates. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 195404 (2008)
Schwaiger, R., Dehm, G., Kraft, O.: Cyclic deformation of polycrystalline Cu films. Philos. Mag. 83, 693–710 (2003)
Kim, B.-J., Shin, H.-A.-S., Jung, S.-Y., Cho, Y., Kraft, O., Choi, I.-S., Joo, Y.-C.: Crack nucleation during mechanical fatigue in thin metal films on flexible substrates. Acta Mater. 61, 3473–3481 (2013)
Deng, G., Nakanishi, T.: Advances in Ceramics-Characterization, Raw Materials, Processing, Properties, Degradation and Healing. IntechOpen, London (2011)
Lacour, S.P., Wagner, S., Huang, Z., Suo, Z.: Stretchable gold conductors on elastomeric substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2404–2406 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (No. 2022R1A5A7000765), MOTIE(Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (20019469) and KSRC(Korea Semiconductor Research Consortium) (852) support program for the development of the future semiconductor device, and Technology Innovation Program (20011119) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JS., Lee, YJ., Seol, J. et al. Vertical Pattern of Interconnects to Bypass High Strain Near a Hard Die on a Flexible Substrate Under Mechanical Bending. Electron. Mater. Lett. 20, 122–130 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-023-00444-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-023-00444-1