Abstract
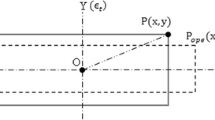
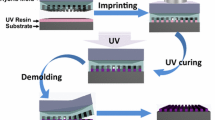
The duration and magnitude of imprinting pressure are very influential in the imprinting process, especially in window-open imprinting process. Resin flows spread over the imprinting area according to both the squeeze motion of the mold and the pressure gradient of the mold cavity-protrusion structure, which causes relatively large contact pressure concentrated in certain locations on the imprinting area. The concentrated contact pressure distorts the mold shape, which then results in pattern distortion. When the pattern density of the mold is unevenly distributed, especially across a large imprinting area, pattern distortion is easily influenced by the rigidity of the mold. To avoid pattern distortions, the imprinting period, and the magnitude and rate of the imprinting pressure must be optimized. In this study, variations in resin layer thickness and elastic deformation of mold materials are analyzed using elastohydrodynamic lubrication (EHL) theory. The film thicknesses of the resin layer are computed down to ∼nm and compared with the consideration of the elastic rigidity of the mold materials and without.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Lazzarino, C. Gourgon, P. Schiavone, and C. Perret, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 22, 3318 (2004).
N. Kehagias, V. Reboud, C. M. Sotomayor Torres, V. Sirotkin, A. Svintsov, and S. Zaitsev, Microelectronic Engineering 85, 846 (2008).
S. Jang, T. K. Lee, and J. G. Lee, Electron. Mater. Lett. 9, 621 (2013).
S. Jang, J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 12, 1 (2012).
S. Jang, J. G. Lee, and H. Lee, Electron. Mater. Lett. 9, 793 (2013).
B. Hamrock, S. Schmid, and B. Jacobson, Fundamentals of Fluid Film Lubrication, Marcel Dekker, ISBN 0-8247-5371-2 (2004).
S.-H. Hong, J.-Y. Hwanga, H. Lee, H.-C. Lee, and K.-W. Choi, Microelectron. Eng. 86, 295 (2009).
S. F. Wuister, J. H. Lammers, Y. W. Kruijt-Stegeman, L. van der Tempel, and F. Dijksman, Microelectron. Eng. 86, 681 (2009).
H. Lee and G.-Y. Jung, Microelectron. Eng. 77, 42 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, S. Study of mold elastic rigidity during UV imprinting process. Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 1051–1055 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-014-4085-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-014-4085-7