Abstract
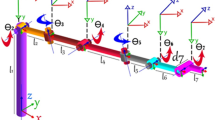
In this study, a hardware design that runs the PSO algorithm at the micro level is carried out using FPGA technology, which facilitates prototyping and testing of integrated circuit systems. In this way, a high rate of acceleration has been achieved for swarm algorithms that perform stochastic search and whose calculation time is not suitable for real-time systems. For this, the inverse kinematics problem, which is used in the robotics field and which forms the basis of the robot control system, is solved for a 7-joint serial robot manipulator. Since the study aims to compare software-based calculations and hardware-based calculations, the results are presented in a comparative way with the results obtained with Matlab software. The tests have been performed in the study revealed two important situations. Firstly, the biggest handicap of algorithms such as PSO that reach a result by searching in a certain solution space is that the solution times are not suitable for real-time applications. The other is that FPGA can be used as a prototyping device for real-time applications due to its speed and hardware-based running. Because according to the test results, FPGA has accelerated the calculations up to 1000 times.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dörfler, K.; Dielemans, G.; Lachmayer, L.; Recker, T.; Raatz, A.; Lowke, D.; Gerke, M.: Additive Manufacturing using mobile robots: opportunities and challenges for building construction. Cem. Concr. Res. 158, 1–13 (2022)
Brahmia, B.; Maarouf, S.; Jacqueline, T.; Cristobal, O.; Philippe, S.; Mohammad, H.: Adaptive control of a 7-DOF exoskeleton robot with uncertainties on kinematics and dynamics. Eur. J. Control. 42, 77–87 (2018)
Iliukhin, V.; Mitkovskii, K.; Bizyanova, D.: The modeling of inverse kinematics for 5 DOF manipulator. Proc. Eng. 176, 498–505 (2017)
Kucuk, S.; Bingul, Z.: Inverse kinematics solutions for industrial robot manipulators with offset wrists. Appl. Math. Model 38, 1983–1999 (2015)
El-Sherbiny, A.; El-Hosseini, M.; Haikal, A.: A new ABC variant for solving inverse kinematics problem in 5 DOF robot arm. Appl. Soft Comput. 73, 24–38 (2018)
Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, G.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, B.: A Curve Approximation approach using bio-inspired polar coordinate bald eagle search algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 15, 1–25 (2022)
Köker, R.: A genetic algorithm approach to a neural-network-based inverse kinematics solution of robotic manipulators based on error minimization. Inf. Sci. 222, 528–543 (2013)
Ayyıldız, M.; Çetinkaya, K.: Comparison of four different heuristic optimization algorithms for the inverse kinematics solution of a real 4-DOF serial robot manipulator. Neural Comput. Appl. 36, 825–836 (2016)
Abainiave, K.; Ali, Y.: Bio-inspired approach for inverse kinematics of 6-DOF robot manipulator with obstacle avoidance. In: International conference on pattern analysis and intelligent systems, 2018
Dereli, S.; Köker, R.: A meta-heuristic proposal for inverse kinematics solution of 7-DOF serial robotic manipulator: quantum behaved particle swarm algorithm. Artif. Intell. Rev. 53, 949–964 (2020)
Dereli, S.; Köker, R.: Iw-PSO approach to the inverse kinematics problem solution of a 7-DOF serial robot manipulator. Sigma 36, 77–85 (2018)
Sancaktar, I.; Tuna, B.; Ulutas, M.: Inverse kinematics application on medical robot using adapted PSO method. Eng. Sci. Technolo. An Int. J. 21, 1006–1010 (2018)
Zhang, L.; Xiao, N.: A novel artificial bee colony algorithm for inverse kinematics calculation of 7-DOF serial manipulators. Soft. Comput. 23, 3269–3277 (2019)
Rokbani, N.; Casals, A.; Alimi, A.: IK-FA, a new heuristic inverse kinematics solver using firefly algorithm. In: Computational Intelligence Applications in Modeling and Control, pp. 369–395, 2015.
Zeng, K.; Ma, Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Shen, T.; Yan, C.: FPGA-based accelerator for object detection: a comprehensive survey. The J. Supercomput. 78, 14096–14136 (2022)
Naru, E.; Saini, H.; Sharma, M.: A recent review on lightweight cryptography in IoT. In: International Conference on I-SMAC, 2017
Tuncer, A.; Yıldırım, M.: Design and implementation of a genetic algorithm IP core on an FPGA for path planning of mobile robots. Turk. J. Elec. Eng. Comp. Sci. 24, 5055–5067 (2016)
Allaire, F.; Tarbouchi, M.; Labonté, G.; Fusina, G.: FPGA implementation of genetic algorithm for UAV real-time path planning. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 54, 495–510 (2009)
Alabdo, A.; Garcia, J.P.; Pomares, J.; Torres, F.: FPGA-based architecture for direct visual control robotic systems. Mechatronics 39, 204–216 (2016)
Irgens, P.; Bader, C.; Lé, T.; Saxena, D.; Ababei, C.: An efficient and cost effective FPGA based implementation of the Viola-Jones face detection algorithm. HardwareX 1, 68–75 (2017)
Dereli, S.: Micro-sized parallel system design proposal for the solution of robotics based engineering problem. Microsyst. Technol. 27, 4217–4226 (2021)
Simas, H.; Di Gregorio, R.: Collision avoidance for redundant 7-DOF robots using a critically damped dynamic approach. Robotics 11, 1–19 (2022)
Chen, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Gao, X.: Control of a 7-DOF robotic arm system with an SSVEP-based BCI. Int. J. Neural Syst. 28, 1–15 (2018)
Kucuk, S.; Bingul, Z.: Comparative study of performance indices for fundamental robot manipulators. Robot. Autonom. Syst. 54, 567–573 (2006)
Toshani, M.: Real-time inverse kinematics of redundant manipulators using neural networks and quadratic programming: a Lyapunov-based approach. Robot. Auton. Syst. 62, 766–781 (2014)
Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R.: Particle Swarm optimization. In: International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 1995.
Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Yu, L.: Review of advanced FPGA architectures and technologies. J. Electr. (China) 31, 371–393 (2014)
Petrica, L.: FPGA optimized cellular automaton random number generator. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 111, 251–259 (2018)
Li, J.; Fang, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, Y.: Study of CORDIC algorithm based on FPGA. In: Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), 2016
Harrison, K.; Engelbrecht, A.; Ombuki-Berman, B.: Inertia weight control strategies for particle swarm optimization. Swarm Intell. 10, 267–305 (2016)
Jiao, B.; Lian, Z.; Gu, X.: A dynamic inertia weight particle swarm optimization algorithm. Chaos Solit. Fract. 37, 698–705 (2008)
Gupta, V.; Chittawadigi, R.; Saha, S.: RoboAnalyzer: robot visualization software for robot technicians. In: Advances in Robotics, 2017
Monmasson, E.; Idkhajine, L.; Cirstea, M.; Bahri, I.; Tisan, A.; Naouar, M.W.: FPGAs in industrial control applications. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 28, 224–243 (2011)
El-Sherbiny, A.; Elhosseini, M.A.; Haikal, A.Y.: A comparative study of soft computing methods to solve inverse kinematics problem. Ain Shams Eng. J. 9, 2535–2548 (2017)
Kucuk, S.; Bingül, Z.: Inverse kinematics solutions for industrial robot manipulators with offset wrists. Appl. Math. Model. 38, 1983–1999 (2014)
Momani, S.M.; Hammour, Z.; Alsmadi, O.: Solution of inverse kinematics problem using genetic algorithms. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci 10, 1–9 (2016)
Wichapong, K.; Bureerat, S.; Pholdee, N.: Solving inverse kinematics of robot manipulators by means of meta-heuristic optimisation. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/370/1/012056
Lopez-Franco, C.; Hernandez-Barragan, J.; Alanis, A.Y.; Arana-DanieL, N.: A soft computing approach for inverse kinematics of robot manipulator. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 74, 104–120 (2018)
Collinsm, T.J.; Shen, W.M.: Particle swarm optimization for high-DOF inverse kinematics. In: IEEE International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics, 2017
Dalmedico, J.F.; Mendonça,M.; Souza, L.B.; Barros, R.V.P.D.; Chrun, I.R.: Artificial neural networks applied in the solution of the inverse kinematics problem of a 3D manipulator arm. In: International joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN) (pp. 1–6). IEEE, 2018
Dereli, S.: A new modified grey wolf optimization algorithm proposal for a fundamental engineering problem in robotics. Neural Comput. Appl. 33, 14119–14131 (2021)
Dereli, S.: A Novel approach based on average swarm intelligence to improve the whale optimization algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47, 1763–1776 (2022)
Lee, H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, Y.; Hong, E.: Real-time particle swarm optimization on FPGA for the optimal message-chain structure. Electronics (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7110274
Li, Y.; Liu, Z.;Xu, K.; Yu, H.; Ren, F.: A 7.663-TOPS 8.2-W energy-efficient FPGA accelerator for binary convolutional neural networks. In: FPGA, pp. 290–291, 2017
Karakuzu, C.; Karakaya, F.; Çavuşlu, M.A.: FPGA implementation of neuro-fuzzy system with improved PSO learning. Neural Netw. 79, 128–140 (2016)
Li, R.; Huang, X.; Tian, S.; Hu, R.; He, D.; Gu, Q.: FPGA-based design and implementation of real-time robot motion planning. In International Conference on Information Science and Technology (ICIST), IEEE
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dereli, S., Köker, R. Hardware Design of FPGA-Based Embedded Heuristic Optimization Technique for Solving a Robotic Problem: IC-PSO. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 10441–10455 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07655-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07655-6