Abstract
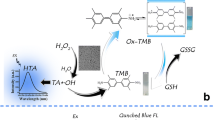
A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of captopril (CAP) on the basis of its radical restoration character was designed. In this system, carbon dots (CDs), having peroxidase mimetic activity, were applied as effective nanozymes. The blue-colored free cation radicals (λmax = 653 nm) were generated via oxidizing 3,3,5,5-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) by H2O2 in the presence of CDs as catalyst. The principal function of CDs was to improve the cation radical (TMB·+) production and consequently enhance the sensitivity of the method. Captopril was able to inhibit the formation of TMB·+. The UV–Vis spectroscopy was utilized to follow how concentration of CAP may impact on the absorption magnitude of the produced TMB·+. The linearity range of the calibration graph was from 0.50 to 9.0 µg mL−1 (2.3–41.4 µmol L−1), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9987, when the optimum experimental conditions were utilized. The LOD of the method was determined as 0.12 μg mL−1 (0.55 µmol L−1). The analysis of CAP in pharmaceutical preparation was successfully achieved in this method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Górska, A.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Szlósarczyk, M.; Piech, R.: Highly sensitive voltammetric determination of captopril on renewable amalgam film electrode. Talanta 237, 122937 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122937
Ramezani, A.M.; Absalan, G.; Ahmadi, R.: Green-modified micellar liquid chromatography for isocratic isolation of some cardiovascular drugs with different polarities through experimental design approach. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1010, 76–85 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.12.021
Wang, Z.X.; Gao, Y.F.; Yu, X.H.; Kong, F.Y.; Lv, W.X.; Wang, W.: Photoluminescent coral-like carbon-branched polymers as nanoprobe for fluorometric determination of captopril. Microchim. Acta. 185, 422 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2961-9
Hashemi, F.; Rastegarzadeh, S.; Pourreza, N.: Response surface methodology optimized dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles as colorimetric probe for determination of captopril. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 256, 251–260 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.178
Mukozhiwa, S.Y.; Khamanga, S.M.M.; Walker, R.B.: The use of experimental design for the development of a capillary zone electrophoresis method for the quantitation of captopril. Pharmazie. 72, 518–524 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2017.7071
Hadjmohammadi, M.R., Kamel, K., Khajooei nezhad, F.: Determination of captopril in human plasma with precolumn derivatization using solid phase extraction and HPLC. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 5, 324–327 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03246125
Sun, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X.: Determination of captopril by high-performance liquid chromatography with direct electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 105, 171–175 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.11.109
Rasool, M.F.; Qureshi, U.F.; Ranjha, N.M.; Imran, I.; Nisa, M.U.; Majeed, A.: Development and validation of reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) for quantification of captopril in rabbit plasma. Acta Chromatogr. 33, 315–321 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1556/1326.2020.00816
Silva, D.M.; Cunha Areias, M.C.: Rutin as an electrochemical mediator in the determination of captopril using a graphite paste electrode. Electroanalysis 32, 301–307 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201900145
Shahbakhsh, M.; Noroozifar, M.: 2D-Single-crystal hexagonal gold nanosheets for ultra-trace voltammetric determination of captopril. Microchim. Acta. 186, 195 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3260-9
Shahbakhsh, M.; Hashemzaei, Z.; Narouie, S.; Shahbakhsh, Y.; Noroozifar, M.: Gold nanoparticles/biphenol–biphenoquinone for ultra-trace voltammetric determination of captopril. Electroanalysis 33, 713–722 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060352
Dong, X., Wang, M., Tang, Y.: Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanospheres from chrysanthemum as a multifunctional sensor for permanganate, Hg(II), and captopril. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 271, 120886 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.120886
Wang, Q., Zhang, Z., Yang, T., Han, Y., Cheng, Y., Wu, J., Bai, J., Ma, C., Niu, Y., Shuang, S.: Multiple fluorescence quenching effects mediated fluorescent sensing of captopril based on amino acids-derivative carbon nanodots. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 269, 120742 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120742
Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Zeng, J.; Tan, J.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y.: Colorimetric captopril assay based on oxidative etching-directed morphology control of silver nanoprisms. Microchim. Acta. 187, 107 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4071-8
Rastegarzadeh, S., Hashemi, F.: A surface plasmon resonance sensing method for determining captopril based on in situ formation of silver nanoparticles using ascorbic acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 122, 536–541 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.11.074
Yuan, M.Y.; Xiao, S.J.; Wu, Y.N.; Qiu, A.T.; Guo, J.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.: Visual detection of captopril based on the light activated oxidase-mimic activity of covalent organic framework. Microchem. J. 175, 107080 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.107080
Nazifi, M.; Ahmadi, R.; Ramezani, A.M.; Absalan, G.: Introducing hierarchical hollow MnO2 microspheres as nanozymes for colorimetric determination of captopril. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 413, 7063–7072 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03672-2
Safavi, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Mohammadpour, Z.: Colorimetric sensing of silver ion based on anti aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 242, 609–615 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.043
Tan, J.; Wu, S.; Cai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.: Reversible regulation of enzyme-like activity of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots for colorimetric pharmaceutical analysis. J. Pharm. Anal. 12, 113–121 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2021.03.010
Gao, L.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Perrett, S.; Yan, X.: Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 577–583 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.260
Nazifi, M.; Ramezani, A.M.; Absalan, G.; Ahmadi, R.: Colorimetric determination of D-penicillamine based on the peroxidase mimetic activity of hierarchical hollow MoS2 nanotubes. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 332, 129459 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129459
Tang, G.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Yan, X.; Fan, K.: Nanozyme for tumor therapy: Surface modification matters. Exploration. 1, 75–89 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/EXP.20210005
Zandieh, M.; Liu, J.: Nanozyme catalytic turnover and self-limited reactions. ACS Nano 15, 15645–15655 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c07520
Wei, H.; Gao, L.; Fan, K.; Liu, J.; He, J.; Qu, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, E.; Yan, X.: Nanozymes: A clear definition with fuzzy edges. Nano Today 40, 101269 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101269
Shi, W.; Wang, Q.; Long, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, S.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.: Carbon nanodots as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to glucose detection. Chem. Commun. 47, 6695 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc11943e
Shamsipur, M.; Safavi, A.; Mohammadpour, Z.: Indirect colorimetric detection of glutathione based on its radical restoration ability using carbon nanodots as nanozymes. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 199, 463–469 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.04.006
Mohammadpour, Z.; Safavi, A.; Shamsipur, M.: A new label free colorimetric chemosensor for detection of mercury ion with tunable dynamic range using carbon nanodots as enzyme mimics. Chem. Eng. J. 255, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.012
Zhao, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Lu, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Cui, J.; Lu, G.: High-activity Mo, S co-doped carbon quantum dot nanozyme-based cascade colorimetric biosensor for sensitive detection of cholesterol. J. Mater. Chem. B. 7, 7042–7051 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TB01731C
Yousefinejad, S.; Rasti, H.; Hajebi, M.; Kowsari, M.; Sadravi, S.; Honarasa, F.: Design of C-dots/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite as an efficient new nanozyme and its application for determination of H2O2 in nanomolar level. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 247, 691–696 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.02.145
Zhuo, S.; Fang, J.; Zhu, C.; Du, J.: Preparation of palladium/carbon dot composites as efficient peroxidase mimics for H2O2 and glucose assay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 412, 963–972 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02320-0
Zhou, L.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X.: Carbon nanodots as fluorescence probes for rapid, sensitive, and label-free detection of Hg2+ and biothiols in complex matrices. Chem. Commun. 48, 1147–1149 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC16791C
Josephy, P.D., Eling, T., Mason, R.P.: The horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of 3,5,3’,5’-tetramethylbenzidine. Free radical and charge-transfer complex intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 3669–3675 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)34832-4
Wu, M., Lv, Y., Lin, Z.: Dual-mode colorimetric and fluorescence sensing system for the detection of captopril based on Fe/NC nanozymes and carbon dots. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 282, 121683 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.121683
Nugroho Prasetyo, E.; Kudanga, T.; Steiner, W.; Murkovic, M.; Nyanhongo, G.S.; Guebitz, G.M.: Laccase-generated tetramethoxy azobismethylene quinone (TMAMQ) as a tool for antioxidant activity measurement. Food Chem. 118, 437–444 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.102
Tamba, M.; Torreggiani, A.: Free radical scavenging and copper chelation: A potentially beneficial action of captopril. Free Radic. Res. 32, 199–211 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760000300211
Acknowledgements
The authors of this article gratefully express their most appreciation to Shiraz University Research Council, Iran, for the financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malaei, R., Ramezani, A.M., Ahmadi, R. et al. Colorimetric Analysis of Captopril on the Basis of Its Free Radical Scavenger Character with Carbon Nanozymes as Catalyst. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 7437–7444 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07489-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07489-8