Abstract
Black phosphorus quantum dots (BP QDs) with small size are synthesized using an easy to operate thermal method. It was found that BP QDs possess oxidase-mimicking activity. They can catalyze the oxidation of the substrate 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine to produce a blue-colored product even in the absence of hydrogen peroxide. Active oxygen species are proved to be involved in the reaction through the experiments of radical scavenging and electron spin resonance. Biothiols including reduced glutathione and cysteine inactivate the oxidase-mimicking activity of BP QDs, concomitant to the fading of the blue solution. This provides the base for a colorimetric method for the determination of glutathione and cysteine. The decreased absorbance at 652 nm displays linear response to the concentrations of glutathione ranging from 0.1 to 5.0 μmol L−1, and cysteine from 0.1 to 10.0 μmol L−1. The detection limits are 0.02 μmol L−1 and 0.03 μmol L−1 for glutathione and cysteine, respectively. Successive determinations of 1.0 μmol L−1 glutathione and 5.0 μmol L−1 cysteine solution give relative standard deviations of 0.8% and 1.7% (n = 11), respectively. As a preliminary application, the practicability of the method was evaluated by the determination of glutathione in pharmaceutical preparations. This work not only discovers a useful oxidase mimics but also sets up a reliable platform based on BP QDs in colorimetric detection.

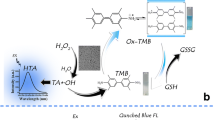
Schematic representation of colorimetric determination for biothiols through inactivating oxidase mimetic−like catalytic activity of black phosphorus quantum dots (BP QDs) on the oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) with dissolved oxygen to produce its blue oxidized product (oxTMB).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davids T, Schmidt M, Boettcher D, Bornscheuer UT (2013) Strategies for the discovery and engineering of enzymes for biocatalysis. Curr Opin Chem Biol 17:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.02.022
Kuah E, Toh S, Yee J, Ma Q, Gao ZQ (2016) Enzyme mimics: advances and applications. Chem Eur J 22:8404–8430. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201504394
Gao LZ, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang JB, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang TH, Feng J, Yang DL, Perrett S, Yan XY (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase–like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.260
Huang YY, Ren JS, Qu XG (2019) Nanozymes: classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation and applications. Chem Rev 119:4357–4412. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00672
Cui WW, Wang YY, Yang DD, Du JX (2017) Fluorometric determination of ascorbic acid by exploiting its deactivating effect on the oxidase–mimetic properties of cobalt oxyhydroxide nanosheets. Microchim Acta 184:4749–4755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2525-4
Hayat A, Haider W, Raza Y, Marty JL (2015) Colorimetric cholesterol sensor based on peroxidase like activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles incorporated carbon nanotubes. Talanta 143:157–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.051
Cheng HJ, Liu YF, Hu YH, Ding YB, Lin SC, Cao W, Wang Q, Wu JJX, Muhammad F, Zhao XZ, Zhao D, Li Z, Xing H, Wei H (2017) Monitoring of heparin activity in live rates using metal–organic framework nanosheets as peroxidase mimics. Anal Chem 89:11552–11559. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02895
Li JX, Gao ZQ, Ye HH, Wan SL, Pierce M, Tang DP, Xia XH (2017) A non–enzyme cascade amplification strategy for colorimetric assay of disease biomarkers. Chem Commun 53:9055–9058. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc04521b
Qu KG, Shi P, Ren JS, Qu XG (2014) Nanocomposite incorporating V2O5 nanowires and gold nanoparticles for mimicking an enzyme cascade reaction and its application in the determination of biomolecules. Chem Eur J 20:7501–7506. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201400309
Song HW, Li ZB, Peng YX, Li X, Xu XC, Pan JM, Niu XH (2019) Enzyme–triggered in situ formation of Ag nanoparticles with oxidase–mimicking activity for amplified determination of alkaline phosphatase activity. Analyst 144:2416–2422. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an00105k
Chen S, Quan Y, Yu YL, Wang JH (2017) Graphene quantum dot/silver nanoparticle hybrids with oxidase activities for antibacterial application. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00644
Gui RJ, Jin H, Wang ZH, Li JH (2018) Black phosphorus quantum dots: synthesis, properties, functionalized modification and applications. Chem Soc Rev 47:6795–6823. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cs00387d
Seo SJ, Kim YJ, Lee HU, Kim HR, Lee SY, Kim YS, Won JH, Kim YJ, Lee J (2018) Black phosphorus quantum dot–based field–effect transistors with ambipolar characteristics. Appl Surf Sci 448:576–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.158
Xu ZL, Lin SH, Onofrio N, Zhou LM, Shi FY, Lu W, Kang K, Zhang Q, Lau SP (2017) Exceptional catalytic effects of black phosphorus quantum dots in shuttling–free lithium sulfur batteries. Nat Commun 9:4164. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06629-9
Guo T, Wu Y, Lin Y, Xu X, Lian H, Huang GM, Liu JZ, Wu XP, Yang HH (2018) Black phosphorus quantum dots with renal clearance property for efficient photodynamic therapy. Small 14:1702815. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201702815
Yin F, Hu K, Chen S, Wang DY, Zhang JN, Xie MS, Yang D, Qiu M, Zhang H, Li ZG (2017) Black phosphorus quantum dot based novel siRNA delivery systems in human pluripotent teratoma PA–1 cells. J Mater Chem B 5:5433–5440. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb01068k
Zhu CY, Xu F, Zhang L, Li ML, Chen J, Xu SH, Huang GG, Chen WH, Sun LT (2016) Ultrafast preparation of black phosphorus quantum dots for efficient humidity sensing. Chem Eur J 22:7357–7362. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201600719
Gu W, Pei XY, Cheng YX, Zhang CL, Zhang JD, Yan YH, Ding CP, Xian YZ (2017) Black phosphorus quantum dots as the ratiometric fluorescence probe for trace mercury ion determination based on inner filter effect. ACS Sens 2:576–582. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00102
Li Y, Liu ZM, Hou YQ, Yang GC, Fei XX, Zhao HN, Guo YX, Su CK, Wang Z, Zhong HQ, Zhuang ZF, Guo ZY (2017) Multifunctional nanoplatform based on black phosphorus quantum dots for bioimaging and photodynamic/photothermal synergistic cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:25098–25106. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b05824
Liu HJ, Sun MX, Su YY, Deng DY, Hu JY, Lv Y (2018) Chemiluminescence of black phosphorus quantum dots induced by hypochlorite and peroxide. Chem Commun 54:7987–7990. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc04513e
Poole LB (2015) The basics of thiols and cysteines in redox biology and chemistry. Free Radical Bio Med 80:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.11.013
Turell L, Radi R, Alvarez B (2013) The thiol pool in human plasma: the central contribution of albumin to redox processes. Free Radical Bio Med 65:244–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.050
Ghasemi F, Hormozi-Nezhad MR, Mahmoudi M (2015) A colorimetric sensor array for determination and discrimination of biothiols based on aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 882:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.04.011
Kappi FA, Tsogas GZ, Routsi AM, Christodouleas DC, Giokas DL (2018) Paper–based devices for biothiols sensing using the photochemical reduction of silver halides. Anal Chim Acta 1036:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.062
Zheng W, Shen DJ, Pan YD, Yi DY, Long YJ, Zheng HZ (2019) Enhancing the peroxidase–like activity of ficin by rational blocking thiol groups for colorimetric determination of biothiols. Talanta 204:833–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.073
Guo Y, Yang LL, Li WW, Wang XF, Shang YH, Li BX (2016) Carbon dots doped with nitrogen and sulfur and loaded with copper (II) as a “turn–on” fluorescent probe for cysteine, glutathione and homocysteine. Microchim Acta 183:1409–1416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1779-6
Elgawish MS, Kishikawa N, Kuroda N (2015) Quinones as novel chemiluminescent probes for the sensitive and selective determination of biothiols in biological fluids. Analyst 140:8148–8156. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an01604e
Feng LY, Wu L, Xing FF, Hu LZ, Ren JS, Qu XG (2017) Novel electrochemiluminescence of silver nanoclusters fabricated on triplex DNA scaffolds for label–free determination of biothiols. Biosens Bioelectron 98:378–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.016
Wu GZ, Zhou JQ, Jiang XY, Guo XY, Gao F (2013) Electrochemical determination of low–molecular–mass biothiols in biological fluids at carbon spheres–modified glassy carbon electrodes. Electroanalysis 4:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-012-0107-0
Isokawa M, Funatsu T, Tsunoda M (2013) Fast and simultaneous analysis of biothiols by high–performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence determination under hydrophilic interaction chromatography conditions. Analyst 138:3802–3808. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an00527e
Xu YH, Wang ZT, Guo ZN, Huang H, Xiao QL, Zhang H, Yu XF (2016) Solvothermal synthesis and ultrafast photonics of black phosphorus quantum dots. Adv Opt Mater 4:1223–1229. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201600214
Asati A, Santra S, Kaittanis C, Nath S, Perez JM (2009) Oxidase–like activity of polymer–coated cerium oxide nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:2308–2312. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200805279
Zhou Y, Du JX, Wang Z (2019) Fluorescein and its derivatives: new coreactants for luminol chemiluminescence reaction and its application for sensitive determination of cobalt ion. Talanta 191:422–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.09.007
National Pharmacopoeia Commission (2015) Chinese pharmacopoeia (part II). China Medical Science and Technology Press, Beijing, p 512
Sun JJ, Wang Q, Yang JJ, Zhang JJ, Li Z, Li H, Yang XF (2019) 2,4−Dinitrobenzenesulfonate−functionalized carbon dots as a turn−on fluorescent probe for imaging of biothiols in living cells. Microchim Acta 186:402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3503-9
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21675107) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. GK201801006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 454 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., Li, H. & Du, J. Black phosphorus quantum dots are useful oxidase mimics for colorimetric determination of biothiols. Microchim Acta 187, 229 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4222-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4222-y