Abstract
Squarer-divider (SD) is a basic circuit that is used as a fundamental component in designing of various mathematical circuits. A high-performance SD circuit can be designed using MOS translinear loop (MTL) with transistors operating in strong inversion region. In this paper, a simple high-performance SD circuit operating at very low voltage of 0.7 V has been designed by MTL transistors biased using flipped voltage follower (FVF) cell. The FVF cell helps in reducing the voltage headroom consumption of stacked MOSFETs and thereby reduces overall supply voltage requirement of the circuit. It offers a bandwidth (BW) of 44.24 MHz and output resistance (rout) of 6.9KΩ when simulated in Cadence Virtuoso environment using 0.18 µm GPDK technology file. Further in the paper, another low voltage SD circuit (SD-II) has been proposed that offers higher BW and rout. These characteristics have been achieved by replacing floating-gate MOSFETs of original SD circuit with quasi-floating gate MOSFETs. Proposed SD-II shows an improvement in BW and rout by a factor of 1.2 and 1.31, respectively. Additional enhancement in BW is observed by the use of a compensating resistor between gate terminals of MOSFETs forming current mirror at output side (SD-III). To show the robustness of proposed SD-III in complete design space and with variations in temperature, corner and temperature analyses have been carried out. Application of proposed SD-III in implementing a low voltage RMS-to-DC converter operating at 0.7 V has been presented to show the practical usability of the proposed circuits.























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A I :
-
Current gain
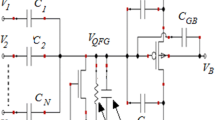
- C gb :
-
Parasitic capacitance present between bulk and gate terminal
- C gd :
-
Parasitic capacitance present between drain and gate terminal
- C gs :
-
Parasitic capacitance present between source and gate terminal
- C n :
-
Input capacitor of nth secondary gate of QFGMOS
- f 0 :
-
Cut-off frequency of QFGMOS
- gmi :
-
Small-signal transconductance of ith MOSFET
- I B :
-
Biasing current
- I D n :
-
Drain current of nth MOSFET
- I in :
-
Input current
- I out :
-
Output current
- I rms :
-
Output current of RMS-to-DC converter
- Ix :
-
Biasing current of FVF loop
- R g :
-
Resistance seen by capacitor Cg of Fig. 5 in SD-I
- R f :
-
Resistance seen by capacitor Cf of Fig. 5 in SD-I
- R large :
-
Resistance offered by transistor in cut-off mode, connected at gate terminal of QFGMOS
- r 0 i :
-
Small-signal output resistance of ith MOSFET
- r out :
-
Small-signal output resistance of proposed SD circuit
- Rx :
-
A resistor connected between gate-source capacitances of MOSFETs M7 and M8 of SD-III to increase bandwidth
- s ZP :
-
Location of poles
- τ LPF :
-
Time constant of low pass filter
- τ H :
-
High-frequency time constants
- V GSn :
-
Gate to source voltage of nth MOSFET
- V QFG :
-
Voltage at quasi-floating gate of QFGMOS
- V th :
-
Threshold voltage
References
Farshidi, E.; Ghanavati Nejad, T.: A new two-quadrant squarer/divider circuit for true RMS-to-DC converters in MOS technology. Measurement 45(4), 778–784 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2011.12.009.
Seevinck, E.; Wiegerink, R.: Generalized translinear circuit principle. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 26(8), 1098–1102 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1109/4.90062
Tangsrirat, W.; Pukkalanun, T.; Mongkolwai, P.; Surakampontorn, W.: Simple current-mode analog multiplier, divider, square-rooter and squarer based on CDTAs. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 65(3), 198–203 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2010.02.017
Farshidi, E.; Alaei-sheini, N,.:A micropower current-mode pattern-matching classifier circuit using FG-MOS transistors. IEEE Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, pp.860–863 (2009).
Fujisaka, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Ahn, C.; Kamio, T.; Haeiwa, K.: Sorter-based arithmetic circuits for sigma-delta domain signal processing—Part II: Multiplication and algebraic functions. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 59(9), 1966–1979 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2011.2180450
De La Cruz-Blas, C.; López-Martín, A.; Carlosena, A.: 1.5 V tunable Square-Root Domain filter. Electronics Lett. 40(4), 213 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20040171.
Shaterian, M.; Twigg, C.; Azhari, J.: An MTL-based configurable block for current-mode nonlinear analog computation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 60(9), 587–591 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2013.2268660
De La Cruz-Blas, C.; Lopez-Martin, A.; Carlosena, A.: 1.5-V MOS translinear loops with improved dynamic range and their applications to current-mode signal processing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digital Signal Process.g 50(12), 918–927 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2003.820230
Carvajal, R., et al.: The flipped voltage follower: a useful cell for low-voltage low-power circuit design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 52(7), 1276–1291 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2005.851387
Gupta, R.; Sharma, S.: Quasi-floating gate MOSFET based low voltage current mirror. Microelectron. J. 43(7), 439–443 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2012.04.006
Voo, T.; Toumazou, C.: High-speed current mirror resistive compensation technique. Electron. Lett. 31(4), 248–250 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:19950207
Yin, L.; Embabi, S. H. K.; Sánchez-Sinencio, E.: A floating-gate MOSFET D/A converter. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS’97), vol. 1, pp. 409–412 (1997).
Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Urquidi, C.; Gonzalez-Carvajal, R.; Torralba, A.; Lopez-Martin, A.: A new family of very low-voltage analog circuits based on quasi-floating-gate transistors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Analog Digital Signal Process. 50(5), 214–220 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2003.811434
Kircay, A.; Keserlioglu, M; Cam, U.: A new current-mode square-root-domain general notch filter. J. Circuits Syst. Comp. 22(1) 1250072 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218126612500727.
Martincorena-Arraiza, M.; De La Cruz Blas, C.; Algueta-Miguel, J.; Lopez-Martin, A.: A 1.2-V Current-Mode RMS-to-DC Converter Based on a Novel Two-Quadrant Electronically Simulated MOS Translinear Loop. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs. 67(3), 420–424 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2019.2920729.
Srivastava, R.; Gupta, M.; Singh, U.: Low-voltage FGMOS squarer/divider-based analog building blocks. Int. J. Electron. 102(4), 563–581 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207217.2014.905996
Kaewdang, K.; Kumwachara, K.; Surakampontorn*, W.: A simple wide-band CMOS based true rms-to-dc converter. Int. J. Electron. 91(7), 407–420 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207210412331294621.
Seevinck, E.; Vittoz, E.; Plessis, M.D.; Joubert, T.H.; Beetge, W.: CMOS translinear circuits for minimum supplyvoltage. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II, Analog Digit. Signal Process. 47(12), 1560–1564 (2000).
Sedra, A.S.; Smith, K.C.: Microelectronic Circuits, 4th edn. Oxford University Press, New York (1998)
Aggarwal, B.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, A.: A comparative study of various current mirror configurations: Topologies and characteristics. Microelectron. J. 53, 134–155 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2016.04.015
Maryan, M.; Ghanaatian, A.; Azhari, S.; Abrishamifar, A.: Low-power high-speed analog multiplier/divider based on a new current squarer circuit. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43(6), 2909–2918 (2017)
Maryan, M.; Azhari, S.: A MOS translinear cell-based configurable block for current- mode analog signal processing. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 92(1), 1–13 (2017)
Farshidi, E.; Sayedi, S.: A 1.2V current-mode true RMS–DC converter based on the floating gate MOS translinear principle. Microelectron. J. 39(2), 293–298 (2008)
Naderi, A.; Khoei, A.; Hadidi, K.; Ghasemzadeh, H.: A new high speed and low power four-quadrant CMOS analog multiplier in current mode. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 63(9), 769–775 (2009)
Maryan, M.; Sajadinia, H.; Azhari, S.: A high precision low distortion current squarer/divider circuit based on FGMOS translinear principle. In: 2019 5th Conference on Knowledge Based Engineering and Innovation (KBEI), (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/kbei.2019.8734938.
Maryan, M.; Azhari, S.; Ayatollahi, A.; Sajadinia, H.: 0.8-V 1.4-nW multi-decade frequency range true RMS to DC converter based on two-quadrant current squarer circuit. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 14(1), 17–25 (2020)
Aghaei, T.; Naderi Saatlo, A.: A new strategy to design low power translinear based CMOS analog multiplier. Integration 69, 180–188 (2019).
Maryan, M.; Azhari, S.: CMOS design of computational current-mode static and dynamic functions based on analog translinear cell. Comput. Electr. Eng. 68, 629–645 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aggarwal, B., Chhabra, A. & Yadav, S. A New FVF and QFGMOS Based High-Performance Low Voltage Analog Squarer-Divider Circuit. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 14435–14453 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06752-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06752-2