Abstract
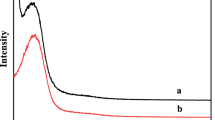
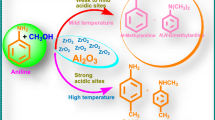
Tetragonal zirconia was synthesized through microwave modified method and screened for the model reaction (hydrogenation of octanal to octanol) in self-design microwave reactor in a solvent-free system. The catalyst shows microwave cooperative activity with high selectivity toward desire products. The same reaction was also performed under conventional heating system in Parr reactor. The microwave protocol was found more effective in term of conversion and selectivity under optimal reaction conditions. The enhance activity is due to enormous reducing sites production on the surface triggered by microwave irradiation. Here, the mechanism of acidic site population on the surface was comprehensively investigated and correlated with catalyst efficiency. The gas chromatographic studies revealed the formation of octanol as a major product while other small peaks reflect the formation of byproducts C16 aldol, C16 α, β-unsaturated aldehyde and C24 acetal. Thus, the tetragonal zirconia can be used for the conversion of aldehyde to alcohol under microwave irradiation efficiently.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scotti, N.; Bossola, F.; Zaccheria, F.; Ravasio, N.: Copper–Zirconia catalysts: powerful multifunctional catalytic tools to approach sustainable processes. Catalysts 10, 168 (2020)
Kauppi, E.I.; Honkala, K.; Krause, A.O.I.; Kanervo, J.M.; Lefferts, L.: ZrO2 Acting as a redox catalyst. Top. Catal. 59, 823–832 (2016)
Gole, B.J.L.; Prokes, S.M.; Stout, J.D.; Glembocki, O.J.; Yang, R.: Unique properties of selectively formed zirconia nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 5, 664–667 (2006)
Das, D.; Mishra, H.K.; Dalai, A.K.; Parida, K.M.: Iron, and manganese doped SO 42-/ZrO2-TiO2 mixed oxide catalysts: studies on acidity and benzene isopropylation activity. Catal. Lett. 93, 185–193 (2004)
Haikarainen, T.; Paturi, P.; Lindén, J.; Haataja, S.; Meyer, K.W.; Finne, J.; Papageorgiou, A.C.: Magnetic properties and structural characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles formed by Streptococcus suis Dpr and four mutants. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 16, 799–807 (2011)
He, D.; Ding, Y.; Luo, H.; Li, C.: Effects of zirconia phase on the synthesis of higher alcohols over zirconia and modified zirconia. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 208, 267–271 (2004)
Roy, S.: Nanocrystalline undoped tetragonal and cubic zirconia synthesized using poly-acrylamide as gel and matrix. J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 44, 227–233 (2007)
Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Tao, K.: A comparison of surface acidic features between tetragonal and monoclinic nanostructured zirconia. Catal. Commun. 3, 239–245 (2002)
Fernández-Morales, J.M.; Castillejos, E.; Asedegbega-Nieto, E.; Dongil, A.B.; Rodríguez-Ramos, I.; Guerrero-Ruiz, A.: Comparative study of different acidic surface structures in solid catalysts applied for the isobutene dimerization reaction. Nanomaterials 10, 1–16 (2020)
Fan, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, H.; Tian, J.; Xie, S.; Pei, Y.; Qiao, M.; Zong, B.: Pt–WOx on monoclinic or tetrahedral ZrO2: crystal phase effect of zirconia on glycerol hydrogenolysis to 1,3-propanediol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 217, 331–341 (2017)
Jung, K.T.; Bell, A.T.: Effects of catalyst phase structure on the elementary processes involved in the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from methanol and carbon dioxide over zirconia. Top. Catal. 20, 97–105 (2002)
Marlowe, J.; Acharya, S.; Zuber, A.; Tsilomelekis, G.: Characterization of sulfated SnO2–ZrO2 catalysts and their catalytic performance on the tert-butylation of phenol. Catalysts (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070726
Brei, V.V.: Superacids based on zirconium dioxide. Theor. Exp. Chem. 41, 165–175 (2005)
Thimmaraju, N.; Shamshuddin, S.Z.M.; Pratap, S.R.; Raja, K.: Efficient microwave synthesis of novel aromatic esters catalyzed by zirconia and its modified forms: a kinetic study. RSC. Adv. 5, 99517–99528 (2015)
Pratap, S.R.; Shamshuddin, S.Z.M.; Thimmaraju, N.; Shyamsundar, M.: Cordierite honeycomb monoliths coated with Al(III)/ZrO2 as an efficient and reusable catalyst for the Knoevenagel condensation: a faster kinetics. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 2734–2749 (2020)
Romano, P.N.; de Almeida, J.M.A.R.; Carvalho, Y.; Priecel, P.; Falabella, S.A.E.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.: Microwave-assisted selective hydrogenation of furfural to Furfuryl alcohol employing a green and noble metal-free copper catalyst. Chemsuschem 9, 3387–3392 (2016)
Banik, B.K.; Barakat, K.J.; Dilip, R.W.; Manhas, M.S.; Bose, A.K.: Microwave-assisted rapid and simplified hydrogenation. J. Org. Chem. 64, 5746–5753 (2010)
Zhang, X.; Hayward, D.O.; Lee, C.; Mingos, D.M.P.: Microwave assisted catalytic reduction of sulfur dioxide with methane over MoS2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B. 33, 137–148 (2001)
Teng, W.K.; Yusoff, R.; Aroua, M.K.; Ngoh, G.C.: Process optimization and kinetics of microwave assisted transesterification of crude glycerol for the production of glycerol carbonate. Sustain. Energy Fuels 5, 274–282 (2021)
Xu, W.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Yang, P.; You, Z.; Luo, Y.: Microwave-assisted catalytic reduction of NO into N2 by activated carbon supported Mn2O3 at low temperature under O2 excess. Fuel Process. Technol. 127, 1–6 (2014)
Pratap, S.R.; Shamshuddin, S.Z.M.; Shyamprasad, K.: Microwave assisted synthesis of propyl esters over modified versions of zirconia: kinetic study. Chem. Data Collect. 30, 100579 (2020)
Gawande, M.B.; Shelke, S.N.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S.: Microwave-assisted chemistry: synthetic applications for rapid assembly of nanomaterials and organics. Acc. Chem. Res. 47, 1338–1348 (2014)
Barthos, R.; Lónyi, F.; Onyestyák, G.Y.; Valyon, J.: An NH3-TPD and-FR study on the acidity of sulfated zirconia. Solid State Ion. 141, 253–258 (2001)
Akinnawo, C.A.; Bingwa, N.; Meijboom, R.: Surface properties vs activity of meso-ZrO2 catalyst in chemoselective Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction of citral: effect of calcination temperature. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 311, 110693 (2021)
Heshmatpour, F.; Aghakhanpour, R.B.: Synthesis and characterization of superfine pure tetragonal nanocrystalline sulfated zirconia powder by a non-alkoxide sol–gel route. Adv. Powder Technol. 23, 80–87 (2012)
Faro, A.C., Jr.; Souza, K.R.; Camorim, V.L.; Cardoso, M.B.: Zirconia–alumina mixing in alumina-supported zirconia prepared by impregnation with solutions of zirconium acetylacetonate. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 5, 1932–1940 (2003)
Morterra, C.; Cerrato, G.: Titrating surface acidity of sulfated zirconia catalysts: is the adsorption of pyridine a suitable probe? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1, 2825–2831 (1999)
Sigwadi, R.; Dhlamini, M.; Mokrani, T.; Nemavhola, F.: Preparation of a high surface area zirconium oxide for fuel cell application. IJMME 14, 1–11 (2019)
García-Pérez, D.; Alvarez-Galvan, M.C.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G.: Influence of the reduction temperature and the nature of the support on the performance of zirconia and alumina-supported pt catalysts for n-dodecane hydroisomerization. Catalysts 11, 1–16 (2021)
Chetty, T.; Dasireddy, V.D.; Callanan, L.H.; Friedrich, H.B.: Continuous flow preferential hydrogenation of an octanal/octene mixture using Cu/Al2O3 catalysts. ACS Omega 3, 7911–7924 (2018)
Pentsak, E.O.; Cherepanova, V.A.; Sinayskiy, M.A.; Samokhin, A.V.; Ananikov, V.P.: Systematic study of the behavior of different metal and metal-containing particles under the microwave irradiation and transformation of nanoscale and microscale morphology. Nanomaterials 9, 55 (2019)
Jacob, K.H.; Knözinger, E.; Benier, S.: Adsorption sites on polymorphic zirconia. J. Mater. Chem. 3, 651–657 (1993)
Shao, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Hu, G.; Hu, X.: Competition between acidic sites and hydrogenation sites in Cu/ZrO2 catalysts with different crystal phases for conversion of biomass-derived organics. Green Energy Environ. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2020.05.007
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Higher Education Commission of Pakistan under Project No. 20-1897/HEC/NRPU/R&D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zaffar Iqbal was involved in investigation. Saima Sadiq was involved in writing—original draft. Muhammad Sadiq was involved in supervision. Idrees Khan was involved in writing—review & editing. Khalid Saeed was involved in conceptualization.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, Z., Sadiq, S., Sadiq, M. et al. Effect of Microwave Irradiation on the Catalytic Activity of Tetragonal Zirconia: Selective Hydrogenation of Aldehyde. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 5841–5848 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05712-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05712-6