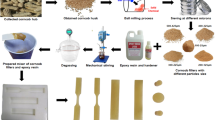
Abstract
This study addresses challenges of maize stalk wastes via conversion into nano-particles for producing epoxy composites at different levels of reinforcements. Mechanical tests were conducted on the produced epoxy composites. The result obtained reveals that development of epoxy polymer is synonymous with metallic crystal nucleation and growth. Epoxy composites have composite grains finer than those of the epoxy polymer. The hardness value increased from 2.2 HV of the pristine epoxy polymer to 10.35 and 17.83 HV at 2 wt% UCMSnp and CMSnp additions, respectively. The improvement in the hardness values is equal to about 370 and 710%, respectively; likewise, the tensile strengths. Better mechanical performance of the epoxy/carbonized maize stalk nano-composites than its counterpart containing uncarbonized maize stalk nano-particles is attributed to residual carbon in the carbonized maize stalk nano-particles known with high strength.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams, T.; Hosur, M.; Theodore, M.; Netravali, A.; Rangari, V.; Jeelani, S.: Time effects on morphology and bonding ability in mercerized natural fibers for composite reinforcement. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2011, 1–9 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/192865
Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T.: Sustainable bio-composites from renewable resources: opportunities and challenges in the green materials world. J. Polym. Environ. 10(1), 19–26 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021013921916
Adebisi, J.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Bello, S.A.; Ahmed, I.I.; Ojo, O.A.; Hassan, S.B.: Potential of producing solar grade silicon nano-particles from selected agro-wastes: a review. Sol. Energy 142, 68–86 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.12.001
Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Hassan, S.B.: Optimisation of charge ratios for ball milling synthesis: agglomeration and refinement of coconut shells. Eng. Appl. Sci. Res. (EASR) 42(4), 262–272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.14456/easr.2018.36
Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Kolawole, F.O.; Raji, N.K.; Hassan, S.B.: Quasi crystal Al (1xxx)/carbonised coconut shell nano-particles: synthesis and characterisation. MRS Adv. 3(42–43), 2559–2571 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.369
Joiner, A.: A silica toothpaste containing blue covarine: a new technological breakthrough in whitening. Int. Dent. J. 59(5), 284–288 (2009)
Joshi, H.H.; Gertz, R.E.; da Gloria Carvalho, M.; Beall, B.W.: Use of silica desiccant packets for specimen storage and transport to evaluate pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage among Nepalese children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46(9), 3175–3176 (2008)
Adebisi, J.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Bello, S.A.; Kolawole, F.O.; Ramakokovhu, M.M.; Daramola, M.O.; Hassan, S.B.: Extraction of silica from sugarcane bagasse, cassava periderm and maize stalk: proximate analysis and physico-chemical properties of wastes. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 10, 617–629 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0089-5
Adebisi, J.A., Agunsoye, J.O., Bello, S.A., Ramakokovhu, M.M., Daramola, M.O., Hassan, S.B.: Proximate analysis and physicochemical properties of sugarcane bagasse, cassava periderm and maize stalk. In: Paper Presented at the IWAN, India
Sri-Aprilia, N.A.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Bhat, A.H.; Dungani, R.; Hossain, M.S.: Exploring material properties of vinyl ester biocomposites filled carbonized Jatropha seed shell. BioResources 9(3), 4888–4898 (2014). https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.9.3.4888-4898
Bledzki, A.K.; Mamun, A.A.; Volk, J.: Barley husk and coconut shell reinforced polypropylene composites: the effect of fibre physical, chemical and surface properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(5), 840–846 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.01.022
Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Kolawole, F.O.; Suleiman, B.H.: Physical properties of coconut shell nano-particles. Kathmandu Univ. J. Sci., Eng. Technol. 12(1), 63–79 (2016)
Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Noriman, N.Z.; Ahmad, M.N.; Ratnam, M.M.; Fuaad, N.A.N.: Polyester composites filled carbon black and activated carbon from bamboo (Gigantochloa scortechinii): physical and mechanical properties. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 26(3), 305–320 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/0731684407065066
Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Firoozian, P.; Bakare, I.O.; Akil, H.M.; Noor, A.M.: Exploring biomass based carbon black as filler in epoxy composites: flexural and thermal properties. Mater. Des. 31(7), 3419–3425 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.01.044
Samantrai, S.P.; Raghavendra, G.; Acharya, S.K.: Effect of carbonization temperature and fibre content on the abrasive wear of rice husk char reinforced epoxy composite. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part J: J. Eng. Tribol. 228(4), 463–469 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650113516435
Ojha, S.; Acharya, S.K.; Raghavendra, G.: A novel approach to utilize waste carbon as reinforcement in thermoset composite. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part E: J. Process Mech. Eng. 230(4), 263–273 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408914547118
Hassan, S.B.; Oghenevweta, E.J.; Aigbodion, V.S.: Potentials of maize stalk ash as reinforcement in polyster composites. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 11(4), 445 (2012)
Pokropivny, V.; Lohmus, R.; Hussainova, I.; Pokropivny, A.; Vlassov, S.: Introduction to nanomaterials and nanotechnology. Tartu University Press, Tartu (2007)
Bello, S.A.; Hassan, S.B.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Kana, M.G.Z.; Raheem, I.A.: Synthesis of uncarbonised coconut shell nano-particles: characterisation and particle size determination. Tribol. Ind. 37(2), 257–263 (2015)
Hassan, S.B.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Bello, S.A.: Ball milling synthesis of Al (1050) particles: morphological study and particle size determination. Ind. Eng. Lett. 5(11), 22–27 (2015)
Kolawole, F.O.; Kolawole, S.K.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Bello, S.A.; Adebisi, J.A.; Soboyejo, W.O.; Hassan, S.B.: Synthesis and characterization of cassava bark nano-particles. MRS Adv. 3(42–43), 2519–2526 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.412
Hanna, W.; Maung, K.; El-Danaf, E.A.; Almajid, A.A.; Soliman, M.S.; Mohamed, F.A.: Nanocrystalline 6061 Al powder fabricated by cryogenic milling and consolidated via high frequency induction heat sintering. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1–9 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/921017
Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Hassan, S.B.: Synthesis of coconut shell nano-particles via a top down approach: assessment of milling duration on the particle sizes and morphologies of coconut shell nano-particles. Mater. Lett. 159, 514–519 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.07.063
Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Anyanwu, J.E.; Bamigbaiye, A.A.; Hassan, S.B.: Potential of carbonised coconut shell as a ball-milling interface for synthesis of aluminium (1xxx) nano-particles. Ann. Fac. Eng. 15(2), 149–157 (2017)
Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Suleiman, B.H.: Effects of aluminium particles on mechanical and morphological properties of epoxy nano-composites. Acta Period. Technol. 48, 25–38 (2017)
Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Raji, N.K.; Adeyemo, R.G.; Alabi, A.G.F.; Hassan, S.B.: Flexural performances of epoxy aluminium particulate composites. Eng. J. 22(4), 97–107 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4186/ej.2018.22.4.97
Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Adeyemo, R.G.; Hassan, S.B.: Optimization of tensile properties of epoxy aluminum particulate composites using regression models. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. Press (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2018.06.002
Hassan, S.B., Agunsoye, J.O., Bello, S.A., Adebisi, J.A., Agboola, J.B.: Microstructure and mechanical properties of coconut shell reinforced epoxy composites In: Materials Science and Technology 2018 (MS&T18). Greater Columbus Convention Center, Columbus, pp. 1312–1318. Materials Science and Technology (2018)
Agunsoye, J.O.; Odumosu, A.K.; Dada, O.: Novel epoxy-carbonized coconut shell nano-particles composites for car bumper application. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102(1–4), 893–899 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3206-0
Fidelis, C.; Piwai, S.; Benias, C.N.; Guyo, U.; Mambo, M.: Maize stalk as reinforcement in natural rubber composites. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2(6), 263–271 (2013)
Hassan, S.B.; Oghenevweta, J.E.; Aigbodion, V.S.: Morphological and mechanical properties of carbonized waste maize stalk as reinforcement for eco-composites. Compos. B Eng. 43(5), 2230–2236 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.02.003
Saravana Bavan, D.; Mohan Kumar, G.C.: Morphological and thermal properties of maize fiber composites. Fibers Polym. 13(7), 887–893 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0887-0
Sarki, J.; Hassan, S.B.; Aigbodion, V.S.; Oghenevweta, J.E.: Potential of using coconut shell particle fillers in eco-composite materials. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(5), 2381–2385 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.11.025
Peters, S.T.: Handbook of Composites, 2nd edn. Springer, Dordrecht (1998)
Yang, F.; Yan, G.; Wang, Q.Y.; Xiong, X.M.; Li, S.Q.; Liu, G.Q.; Feng, J.Q.; Pang, Y.C.; Li, C.S.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, P.X.: The effect of high-energy ball milling on the microstructure and properties of Ti-doped MgB2 bulks and wires. Phys. Proc. 65, 157–160 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2015.05.090
Wolff, M.F.H.; Antonyuk, S.; Heinrich, S.; Schneider, G.A.: Attritor-milling of poly(amide imide) suspensions. Particuology 17, 92–96 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2013.11.005
Breitung-Faes, S.; Kwade, A.: Nano particle production in high-power-density mills. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 86(4), 390–394 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2007.11.006
Dewa, M.D.K.; Wiryolukito, S.; Suwarno, H.: Hydrogen absorption capacity of Fe–Ti–Al alloy prepared by high energy ball milling. Energy Proc. 68, 318–325 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.03.262
Liu, T.; Shen, H.; Wang, C.; Chou, W.: Structure evolution of Y2O3 nano-particle/Fe composite during mechanical milling and annealing. Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int. 23(4), 434–439 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2013.06.009
Loh, Z.H.; Samanta, A.K.; Sia Heng, P.W.: Overview of milling techniques for improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 10(4), 255–274 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2014.12.006
Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, P.: Optimization of FeSe superconductors with the high-energy ball milling aided sintering process. J. Mater. 1(2), 118–123 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2015.04.004
Zhang, X.; Mu, H.; Huang, X.; Fu, Z.; Zhu, D.; Ding, H.: Cryogenic milling of aluminium-lithium alloys: thermo-mechanical modelling towards fine-tuning of part surface residual stress. Proc. CIRP 31, 160–165 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.03.055
Wan, Y.-J.; Tang, L.-C.; Yan, D.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.-B.; Wu, L.-B.; Jiang, J.-X.; Lai, G.-Q.: Improved dispersion and interface in the graphene/epoxy composites via a facile surfactant-assisted process. Compos. Sci. Technol. 82, 60–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.04.009
Wan, Y.-J.; Gong, L.-X.; Tang, L.-C.; Wu, L.-B.; Jiang, J.-X.: Mechanical properties of epoxy composites filled with silane-functionalized graphene oxide. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 64, 79–89 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.04.023
Tang, L.-C.; Wan, Y.-J.; Peng, K.; Pei, Y.-B.; Wu, L.-B.; Chen, L.-M.; Shu, L.-J.; Jiang, J.-X.; Lai, G.-Q.: Fracture toughness and electrical conductivity of epoxy composites filled with carbon nanotubes and spherical particles. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 45, 95–101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.09.012
Tang, L.-C.; Wan, Y.-J.; Yan, D.; Pei, Y.-B.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.-B.; Wu, L.-B.; Jiang, J.-X.; Lai, G.-Q.: The effect of graphene dispersion on the mechanical properties of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 60, 16–27 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.03.050
Bello, S.A.: Development and Characterisation of Epoxy-Aluminium-Coconut Shell Particulate Hybrid Nano-composites for Automobile Applications. University of Lagos, Lagos (2017)
William Jr., D.C.: Materials Science and Engineering an Introduction, 7th edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2007)
Dotan, A.: Biobased Thermosets, pp. 577–622 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-1-4557-3107-7.00015-4
Agunsoye, J.O.; Aigbodion, V.S.: Bagasse filled recycled polyethylene bio-composites: morphological and mechanical properties study. Results Phys. 3, 187–194 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2013.09.003
Asuke, F.; Aigbodion, V.S.; Abdulwahab, M.; Fayomi, O.S.I.; Popoola, A.P.I.; Nwoyi, C.I.; Garba, B.: Effects of bone particle on the properties and microstructure of polypropylene/bone ash particulate composites. Results Phys. 2, 135–141 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2012.09.001
Abiko, H.; Furuse, M.; Takano, T.: Reduction of adsorption capacity of coconut shell activated carbon for organic vapors due to moisture contents. Ind. Health 48, 427–437 (2010)
Akram, M.; Taha, I.; Ghobashy, M.M.: Potential of carbon particle reinforced polypropylene formed in situ through the pyrolysis of carboxymethylcellulose. Compos. Commun. 1, 6–14 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2016.07.005
Bello, S.A.; Raheem, I.A.; Raji, N.K.: Study of tensile properties, fractography and morphology of aluminium (1xxx)/coconut shell micro particle composites. J. King Saud. Univ. Eng. Sci. 29, 269–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2015.10.001
Aigbodion, V.S.; Hassan, S.B.; Oghenevweta, J.E.: Microstructural analysis and properties of Al–Cu–Mg/bagasse ash particulate composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 497(1–2), 188–194 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.02.190
Mohammad, S., Laurentiu, N., Anwarul, H.: Development of High-Strength and Highly Ductile Hypo-Eutectic Al–Si Alloys by Nano-refining the Constituent Phases. In: Paper Presented at the TMS. The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society
Srivastava, V.K.; Verma, A.: Mechanical behaviour of copper and aluminium particles reinforced epoxy resin composites. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 5(4), 84–89 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5923/j.materials.20150504.02
Pargi, M.N.F.; Teh, P.L.; Hussiensyah, S.; Yeoh, C.K.; Abd Ghani, S.: Recycled-copper-filled epoxy composites: the effect of mixed particle size. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 10(1), 3 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40712-015-0030-2
Ozsoy, N.; Ozsoy, M.; Mimaroglu, A.: Comparison of mechanical chracteristics of chopped bamboo and chopped coconut shell reinforced epoxy matrix composite materials. Eur. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 3(8), 15–20 (2014)
Funding
No funding was received on this work. It is self-sponsored.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest on this work.
Ethical Approval
Authors declare that all third parties’ rights in line with ethical standards are respected.
Informed Consent
This research does not involve human participant nor animal.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agunsoye, J.O., Bamigbaiye, A.A., Bello, S.A. et al. Mechanical Properties of Maize Stalk Nano-particle Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 5087–5097 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04345-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04345-5