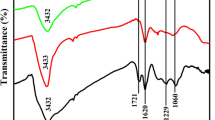
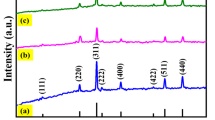
Abstract
In this paper, reduced graphene oxide–ZnO (RGO–ZnO) nanorods composite was prepared via a simple one-pot hydrothermal approach. The synthesized RGO–ZnO nanorods composite has been successfully applied for glassy carbon electrode (GCE) surface modification. The RGO–ZnO nanorods composite-modified GCE was applied for sensitive and selective determination of uric acid (UA). The biosensor exhibited a linear dependence on UA concentration ranging from 1 to 800 μM with a detection limit of 0.312 μM(S/N = 3). The proposed UA sensor also showed an excellent stability, reproducibility and anti-interference property.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bui L.V., Cooper C.: Reverse-phase liquid chromatographic determination of benzoic and sorbic acids in foods. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 70(5), 892–896 (1987)
Alderman M., Aiyer K.J.V.: Uric acid: role in cardiovascular disease and effects of losartan. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 20(3), 369–379 (2004). doi:10.1185/030079904125002982
Sun Z., Fu H., Deng L., Wang J.: Redox-active thionine-graphene oxide hybrid nanosheet: one-pot, rapid synthesis, and application as a sensing platform for uric acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 761, 84–91 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.aca.2012.11.057
Dai X., Fang X., Zhang C., Xu R., Xu B.: Determination of serum uric acid using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/isotope dilution mass spectrometry (ID-MS) as a candidate reference method. J. Chromatogr. B 857(2), 287–295 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.07.035
Zanon N.C.M., Oliveira O.N. Jr, Caseli L.: of uricase enzyme in Langmuir and Langmuir-Blodgett films of fatty acids: Possible use as a uric acid sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 373(1), 69–74 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.07.095
Georgakopoulos C.D., Lamari F.N., Karathanasopoulou I.N., Gartaganis V.S., Pharmakakis N.M., Karamanos N.K.: Tear analysis of ascorbic acid, uric acid and malondialdehyde with capillary electrophoresis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 24(8), 852–857 (2010)
Lebid M., Omari M.: Synthesis and electrochemical properties of LaFeO3 oxides prepared via Sol–Gel method. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(1), 147–152 (2014). doi:10.1007/s13369-013-0883-8
Fattah-alhosseini A.: Modified point defect model for the electrochemical behavior of the passive films formed on alloy C (UNS N10002) in Borax solutions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40(1), 63–67 (2015). doi:10.1007/s13369-014-1501-0
Zheng Y., Wang A., Lin H., Fu L., Cai W.: Sensitive electrochemical sensor for direct phoxim detection based on an electrodeposited reduced graphene oxide-gold nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 5(20), 15425–15430 (2015). doi:10.1039/C4RA15872E
Huang Y., Bu L., Wang W., Qin X., Li Z., Huang Z., Fu Y., Su X., Xie Q., Yao S.: One-pot preparation of uricase–poly(thiophene-3-boronic acid)–Ptnano composites for high-performance amperometric biosensing of uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 177, 116–123 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.snb.2012.10.101
Yang C.L., Liu H.Y., Xia Q.L., Li Z.H., Xiao Q.Z., Lei G.T.: Effects of SiO2 nanoparticles and diethyl carbonate on the electrochemical properties of a fibrous nanocomposite polymer electrolyte for rechargeable Lithium batteries. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(9), 6711–6720 (2014). doi:10.1007/s13369-014-1192-6
Fu L., Zheng Y., Wang A., Cai W., Fu Z., Peng F.: A novel nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide electrochemical sensor based on SnO2-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Sens. Lett. 13(1), 81–84 (2015). doi:10.1166/sl.2015.3414
Fu L., Zheng Y., Ren Q., Wang A., Deng B.: Green biosynthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles by plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract their photocatalytic activity toward rhodamine B degradation. J. Ovonic Res. 11(1), 21–26 (2015)
Fu L., Fu Z.: Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract—assisted biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int. 41(2, Part A), 2492–2496 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.10.069
Fu L., Cai W., Wang A., Zheng Y.: Photocatalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to aniline over tungsten oxide-silver nanowires. Mater. Lett. 142(0), 201–203 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2014.12.021
Cao G.S., Wang R., Wang P., Li X., Wang Y., Wang G., Li J.: Electrochemical Co3O4 nanoporous thin films sensor for hydrogen peroxide detection. Nano 09(04), 1450047 (2014). doi:10.1142/S1793292014500477
Erdem A., Karadeniz H., Caliskan A., Vaseashta A.: Electrochemical dna sensor technology for monitoring of drug–dna interactions. Nano 03(04), 229–232 (2008). doi:10.1142/S1793292008001064
Wang A., Ng H.P., Xu Y., Li Y., Zheng Y., Yu J., Han F., Peng F., Fu L.: Gold nanoparticles: synthesis, stability test, and application for the rice growth. J. Nanomater. 2014, 6 (2014)
Fu L., Wang A., Zheng Y., Cai W., Fu Z.: Electrodeposition of Ag dendrites/AgCl hybrid film as a novel photodetector. Mater. Lett. 142(0), 119–121 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2014.12.001
Ahmad A., Hussain F., Deen K.M., Ahmad R., Ali L., Kamran M., Azam M.: Corrosion behavior of X-70 pipe steel in crude oil environments depending upon surface characteristics. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(7), 5393–5404 (2014). doi:10.1007/s13369-014-1102-y
Noor E., Al-Moubaraki A.: Influence of soil moisture content on the corrosion behavior of X60 steel in different soils. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(7), 5421–5435 (2014). doi:10.1007/s13369-014-1135-2
Wang A., Fu L., Ng H.P., Cai W., Zheng Y., Han F., Wang Z., Peng F.: Monitoring fluorescence lifetime changes of CdTe QDs synthesized with different stabilizers by Photoluminscence and Zeta potential measurement. J. Non Oxide Glass. 7(1), 1–12 (2015)
Tang L., Wang Y., Li Y., Feng H., Lu J., Li J.: Preparation, structure, and electrochemical properties of reduced graphene sheet films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19(17), 2782–2789 (2009). doi:10.1002/adfm.200900377
He L., Fu L., Tang Y.: Catalytic performance of a novel Cr/ZnAlLaO catalyst for oxidative dehydrogenation of isobutane. Catal. Sci. Technol. 5(2), 1115–1125 (2015). doi:10.1039/C4CY00990H
Fu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, A.; Deng, B.; Peng, F.: Facile synthesis of Ag-AgCl/ZnO hybrid with high efficiency photocatalytic property under visible light. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 10(1), 117–124 (2015)
Nayak P., Santhosh P.N., Ramaprabhu S.: Electrochemical sensor for dopamine based on ZnO decorated graphene nanosheets as the transducer matrix. Graphene 1(1), 25–30 (2013). doi:10.1166/graph.2013.1009
Jiang L., Gu S., Ding Y., Jiang F., Zhang Z.: Facile and novel electrochemical preparation of a graphene-transition metal oxide nanocomposite for ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing of acetaminophen and phenacetin. Nanoscale 6(1), 207–214 (2014). doi:10.1039/c3nr03620k
Li B., Liu T., Wang Y., Wang Z.: ZnO/graphene-oxide nanocomposite with remarkably enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 377(1), 114–121 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2012.03.060
Zhang X., Zhang D., Chen Y., Sun X., Ma Y.: Electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide films: Preparation, characterization and their electrochemical properties. Chin. Sci. Bull. 57(23), 3045–3050 (2012). doi:10.1007/s11434-012-5256-2
Ahmad M., Ahmed E., Hong Z.L., Khalid N.R., Ahmed W., Elhissi A.: Graphene–Ag/ZnO nanocomposites as high performance photocatalysts under visible light irradiation. J. Alloy Compd. 577, 717–727 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.06.137
Oukil D., Benhaddad L., Aitout R., Makhloufi L., Pillier F., Saidani B.: Electrochemical synthesis of polypyrrole films doped by ferrocyanide ions onto iron substrate: Application in the electroanalytical determination of uric acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 204, 203–210 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.07.086
Wei Y., Li M., Jiao S., Huang Q., Wang G., Fang B.: Fabrication of CeO2 nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode and its application for electrochemical determination of UA and AA simultaneously. Electrochim. Acta 52(3), 766–772 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2006.06.006
Laviron E.: Adsorption autoinhibition and autocatalysis in polarography and linear potential sweep voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 52, 355–393 (1974)
Laviron E.: General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. 101, 19–28 (1979)
Cao X., Xu Y., Luo L., Ding Y., Zhang Y.: Simultaneous determination of uric acid and ascorbic acid at the film of chitosan incorporating cetylpyridine bromide modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 14(5), 829–834 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10008-009-0861-y
Manjunatha H., Nagaraju D.H., Suresh G.S., Venkatesha T.V.: Detection of uric acid in the presence of dopamine and high concentration of ascorbic acid using PDDA modified graphite electrode. Electroanalysis 21(20), 2198–2206 (2009). doi:10.1002/elan.200904662
Afrasiabi, M.; Kianipour, S.; Babaei, A.; Nasimi, A.A.; Shabanian, M.: A new sensor based on glassy carbon electrode modified with nanocomposite for simultaneous determination of acetaminophen, ascorbic acid and uric acid. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. (2013). doi: 10.1016/j.jscs.2013.02.002
Zhang H., Zhou Y., Zhang J., Gou L., Zheng J.: Highly selective and sensitive dopamine and uric acid electrochemical sensor fabricated with poly (orotic acid). J. Mol. Liq. 184, 43–50 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2013.04.020
Zhou Y., Zhang H., Xie H., Chen B., Zhang L., Zheng X., Jia P.: A novel sensor based on LaPO4 nanowires modified electrode for sensitive simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Electrochim. Acta 75(0), 360–365 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2012.05.023
Sun D., Zhao Q., Tan F., Wang X., Gao J.: Simultaneous detection of dopamine, uric acid, and ascorbic acid using SnO2 nanoparticles/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/carbon paste electrode. Anal. Methods 4(10), 3283 (2012). doi:10.1039/c2ay25401h
Cui R., Wang X., Zhang G., Wang C.: Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid, and uric acid using helical carbon nanotubes modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 161(1), 1139–1143 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.snb.2011.11.040
Liu X., Pan L., Lv T., Sun Z., Sun C.Q.: Visible light photocatalytic degradation of dyes by bismuth oxide-reduced graphene oxide composites prepared via microwave-assisted method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 408, 145–150 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2013.07.045
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L., Zheng, Y., Wang, A. et al. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide and ZnO Nanorods-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Uric Acid Detection. Arab J Sci Eng 41, 135–141 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1621-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1621-1