Abstract
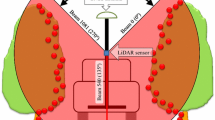
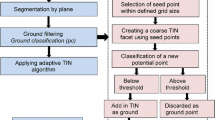
Preserving forests and their value to us is indispensable to human life. When making forest preservation plans and managing forests efficiently, it is necessary to use three dimensional (3D) models of the forest regions. Apart from the traditional and photogrammetric methods used for producing these maps, the LIght Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) measurement technique with its various advantages has been used in recent years. This paper explains the principle of the operation of the LIDAR measurement system and discusses the determination of digital elevation models (DEM) of forest areas and their usage in 3D models. This test study aims to convert the scattered distributed 3D datasets obtained from airborne LIDAR technology to a digital elevation model with a regular grid format. One of the most significant aspects of this process, the interpolation method, which affects the quality of the final product when generating the digital elevation model, is examined with respect to data density and distribution, grid size interval and terrain type.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aruga K., Sessions J., Akay A.E.: Application of an airborne laser scanner to forest road design with accurate earthwork volumes. J. For. Res 10(2), 113–123 (2005)
USGEO Support Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry and, Combat Land Degradation, Technical Reference Document. Public Engagement Workshop (2005). http://www.usgeo.gov/docs/review/Agriculture_Technical.pdf
Zawadzki J., Cieszewski C.J., Zasada M., Lowe R.C.: Applying geostatistics for investigations of forest ecosystems using remote sensing imagery. Silva Fennica 39, 599–617 (2005)
Akay A.E., Oguz H., Karas I.R., Aruga K.: Using LIDAR technology in forestry activities. Environ. Monitor. Assess 151(1–4), 117–125 (2009)
Hyde, P.; Dubayah, R.; Walker, W.; Blair, J.B.; Hofton, M.; Hunsaker, C.: Mapping forest structure for wildlife habitat analysis using multi-sensor. LIDAR, SAR/InSAR, ETM+, Quickbird, Synergy (2006)
Kini, A.U.; Popescu, S.C.: Treevaw: A Versatile Tool for Analyzing Forest Canopy Lidar Data—A Preview With an Eye Towards Future. ASPRS 2004 Fall Conference, Kansas City, Missouri (2004)
Chauve, A.; Mallet, C.; Bretar, F.; Durrieu, S.; Deseilligny, M.P.; Puech, W.: Processing Full-Waveform Lidar Data: Modelling Raw Signals. ISPRS Workshop on Laser Scanning and SilviLaser, Espoo, Finland, September (2007)
Hansen, J.; Jonas, D.: Airborne Laser Scanning or Aerial Photogrammetry for the Mine Surveyor. AAM Surveys Inc. (1999)
Konecny, G.: Laser scanning. Workshop Presentation (2007). http://www.cors-tr.iku.edu.tr
Sartori, M.; Starek, M.; Slatton, K.C.: ALSM Data Processing. GEM Center Report No. Rep_2004-06-001, Geosensing Engineering and Mapping (GEM) Civil and Coastal Engineering Department, University of Florida (2004)
Smith, S.L.; Holland, D.A.; Longley, P.A.: The effect of changing grid size in the creation of laser scanner digital surface models. In: Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Geocomputation, Southampton, UK, September (2003)
Rosso, P.; Ustin, S.; Hastings, A.: Use of Lidar to Produce High-Resolution Marsh Vegetation and Terrain Maps. ISPRS Workshop Three Dimensional Mapping from INSAR and LIDAR, Portland, OR (2003)
Aggett, G.: Airborne Laser Mapping with Lidar for Dummies. GIS for Local Government Conference (2005)
Reutebuch S.E., McGaughey R.J., Andersen H.E., Carson W.W.: Accuracy of a high-resolution LIDAR terrain model under a conifer forest canopy. Can. J. Remote Sens. 29, 527–535 (2003)
Kraus, K.; Pfeiffer, N.: Advanced DTM generation from Lidar data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 34, (2001)
Soycan, M.; Soycan, A.: Surface modeling for GPS-levelling geoid determination. Bulletin of International Geoid Service-Newton’s Bulletin. No 1., pp. 41–52 (2003)
Liu X., Zhang Z., Peterson J., Chandra S.: Lidar-derived high quality ground control information and DEM for image orthorectification. J. Geoinform 11, 37–53 (2007)
Wehr A., Lohr U.: Airborne laser scanning—an introduction and overview. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens 54(2), 68–82 (1999)
Shrestha R.L., Carter W.E., Lee M., Finer P., Sartori M.: Airborne laser swath mapping: accuracy assessment for surveying and mapping applications. J. Am. Cong. Survey. Mapp 59(2), 83–94 (1999)
Habib A.F.: Quality assurance and quality control of Lidar systems and derived data. University of Northern Iowa, Advanced Lidar Workshop (2007)
Stoker, J.: Introduction to Lidar technology. New Jersey Lidar Remote Sensing Workshop, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ (2007)
Hongson M.E., Bresnahan P.: Accuracy of airborne Lidar-derived elevation: empirical assessment and error budget. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens 70, 331–339 (2004)
Aguilar F., Aguilar M.A., Aguera F., Sanchez J.: The accuracy of grid digital elevation models linearly constructed from scattered sample data. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci 20, 169–192 (2006)
Algarni D.A., Hassan M.E.I.: Comparison of thin plate spline, polynomial, CI-function and Shepard’s interpolation techniques with GPS-derived DEM. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf 3, 155–161 (2001)
Surfer®getting started guide. Contouring and 3D Surface Mapping for Scientists and Engineers. Golden Software Reference Guide, Golden Software, Inc. (2009)
Shi W.Z., Tian Y.: A hybrid interpolation method for the refinement of a regular grid digital elevation model. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci 20, 53–67 (2006)
Zimmerman D., Pavlik C., Ruggles A., Armstrong M.P.: An experimental comparison of ordinary and universal Kriging and inverse distance weighting. Math. Geol 31(4), 375–390 (1999)
Ali, T.: On the selection of appropriate interpolation method for creating coastal terrain models from LIDAR data. In: Proceedings of the American Congress on Surveying and Mapping (ACSM) Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, April 16–21 (2004)
Blaschke T., Tiede D., Heurich M.: 3D landscape metrics to modelling forest structure and diversity based on laser scanning data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inform. Sci 36(8/W2), 129–132 (2004)
Mardikis M.G., Kalivas D.P., Kollias V.J.: Comparison of interpolation methods for the prediction of reference evapotranspiration—an application in Greece. Water Resour. Manage 19(3), 251–278 (2005)
Chaplot V., Darboux F., Bourennane H., Leguédois S., Silvera N., Phachomphon K.: Accuracy of interpolation techniques for the derivation of digital elevation models in relation to landform types and data density. Geomorphology 77(1–2), 126–141 (2006)
Kyriakidis P.C., Goodchild M.F.: On the prediction error variance of three common spatial interpolation schemes. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci 20(8), 823–855 (2006)
Lloyd C.D., Atkinson P.M.: Deriving ground surface digital elevation models from LIDAR data with geostatistics. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci 20(5), 535–563 (2006)
Alsaaran, N.A.: Experimental performance of spatial interpolators for groundwater salinity. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 30(1A) 3–15 (2005)
Hofierka, J.; Cebecauer, T.; Šúri, M.: Optimisation of interpolation parameters using a cross-validation. Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography, Digital Terrain Modelling. pp. 67–82 (2007)
Soycan, A.; Soycan, M.: Digital elevation model production from scanned topographic contour maps via thin plate spline interpolation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 34(1A) 121–134 (2009)
Gonçalves, G.: Analysis of interpolation errors in urban digital surface models created from Lidar data. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Spatial Accuracy Assessment in Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences, Lisbon, Portugal (2006)
Meneses, A.S.; Ramírez, F.; García, B.; Cabrejas, J.; González-Audícana, M.: Quality control in digital terrain models. J. Survey. Eng. 131, 118–124 (2005)
Oksanen, J.: Digital Elevation Model Error in Terrain Analysis. Ed., p. 51. Helsinki University Press, Helsinki (2006)
Weng Q.: Quantifying uncertainty of digital elevation models derived from topographic maps. In: Richardson, D., Oosterom, P. (eds) Advances in Spatial Data Handling., pp. 403–418. Springer, New York (2002)
Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.: Lidar data reduction for efficient and high quality dem generation. In: The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Science, XXXVII (B3b), Beijing (2008)
McCullagh M.J.: Terrain and surface modelling systems: theory and practice. Photogramm. Rec 72(12), 747–779 (1988)
Behan, A.: On the matching accuracy of rasterised scanning laser altimeter data. In: The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Science, pp. 548–555. Amsterdam, The Netherlands, XXXIII (3A) (2000)
Hu, Y.: Automated extraction of digital terrain models, roads and buildings using airborne Lidar data (2003). http://www.geomatics.ucalgary.ca/links/GradTheses.html (Accessed 30 April 2008)
Gruen A., Wang X.: CC-Modeler: a topology generator for 3-D city models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens 53(5), 286–295 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soycan, M., Tunalıoğlu, N., Öcalan, T. et al. Three Dimensional Modeling of a Forested Area Using an Airborne Light Detection and Ranging Method. Arab J Sci Eng 36, 581–595 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-011-0054-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-011-0054-8