Abstract
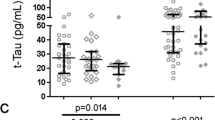
The long-term impact of chronic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection on brain status in injecting drug users (IDU) treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is unknown. Viral persistence in the brain with ongoing neuroinflammation may predispose to Alzheimer-like neurodegeneration. In this study, we investigated the brains of ten HAART-treated individuals (six IDU and four non-DU), compared with ten HIV negative controls (six IDU and four non-DU). HIV DNA levels in brain tissue were correlated with plasma and lymphoid tissue viral loads, cognitive status, microglial activation and Tau protein and amyloid deposition. Brain HIV proviral DNA levels were low in most cases but higher in HIV encephalitis (n = 2) and correlated significantly with levels in lymphoid tissue (p = 0.0075), but not with those in plasma. HIV positive subjects expressed more Tau protein and amyloid than HIV negative controls (highest in a 58 year old), as did IDU, but brain viral loads showed no relation to Tau and amyloid. Microglial activation linked significantly to HIV positivity (p = 0.001) and opiate abuse accentuated these microglial changes (p = 0.05). This study confirms that HIV DNA persists in brains despite HAART and that opiate abuse adds to the risk of brain damage in HIV positive subjects. Novel findings in this study show that (1) plasma levels are not a good surrogate indicator of brain status, (2) viral burden in brain and lymphoid tissues is related, and (3) while Tau and amyloid deposition is increased in HIV positive IDU, this is not specifically related to increased HIV burden within the brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andras IE, Toborek M (2013) Amyloid beta accumulation in HIV-1-infected brain: the role of the blood–brain barrier. IUBMB Life 65:43–49. doi:10.1002/iub.1106
Anthony IC, Ramage SN, Carnie FW, Simmonds P, Bell JE (2005) Does drug abuse alter microglial phenotype and cell turnover in the context of advancing HIV infection. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 31:325–338. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.00648.x
Anthony IC, Ramage SN, Carnie FW, Simmonds P, Bell JE (2006) Accelerated Tau deposition in the brains of individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus-1 before and after the advent of highly active anti-retroviral therapy. Acta Neuropathol 111:529–538. doi:10.1007/s00401-006-0037-0
Anthony IC, Norrby KE, Dingwall T, Carnie FW, Millar T, Arango JC, Robertson R, Bell JE (2010) Predisposition to accelerated Alzheimer-related changes in the brains of human immunodeficiency virus negative opiate abusers. Brain 133:3685–3698. doi:10.1093/brain/awq263
Bell JE, Donaldson YK, Lowrie S, McKenzie CA, Elton RA, Chiswick A, Brettle RP, Ironside JW, Simmonds P (1996) Influence of risk group and zidovudine therapy on the development of HIV encephalitis and cognitive impairment in AIDS patients. AIDS 10:493–499
Borjabad A, Morgello S, Chao W, Kim SY, Brooks AI, Murray J, Potash MJ, Volsky DJ (2011) Significant effects of antiretroviral therapy on global gene expression in brain tissues of patients with HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders. PLoS Pathog. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat. 1002213
Brew BJ, Crowe SM, Landay A, Cysique LA, Guillemin G (2009) Neurodegeneration and ageing in the HAART era. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 4:163–174. doi:10.1007/s11481-008-9143-1
Byrd D, Murray J, Safdieh G, Morgello S (2012) Impact of opiate addiction on neuroinflammation in HIV. J Neurovirol 18:364–373. doi:10.1007/s13365-012-0118-x
Clements JE, Gama L, Graham DR, Mankowski JL, Zink MC (2011) An SIV macaque model of HAART: viral latency in the periphery and the central nervous system. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 6:37–42. doi:10.1097/COH.0b03e3283412413
Cysique LA, Waters EK, Brew BJ (2011) Central nervous system antiretroviral efficacy in HIV infection: a qualitative and quantitative review and implications for future research. BMC Neurol 11:148. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-11-148
Dutta R, Roy S (2012) Mechanism(s) involved in opioid drug abuse modulation of HAND. Curr HIV Res 10:469–477. doi:10.2174/157016212802138805
Eisfeld C, Reichelt D, Evers S, Husstedt I (2013) CSF penetration by antiretroviral drugs. CNS Drugs 27:31–55. doi:10.1007/s40263-012-0018-x
Ersche KD, Clark L, London M, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2006) Profile of executive and memory function associated with amphetamine and opiate dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1036–1047. doi:10.1038/si.nnp.1300889
Everall I, Vaida F, Khanlou N, Lazzaretto D, Achim C, Letendre S, Moore D, Ellis R, Cherner M, Gelman B, Morgello S, Singer E, Grant I, Masliah E, National NeuroAIDS Tissue Consortium (NNTC) (2009) Cliniconeuropathologic correlates of human immunodeficiency virus in the era of antiretroviral therapy. J Neurovirol 15:360–370. doi:10.3109/13550280903131915
Gelman BB, Chen T, Lisinicchia JG, Soukup VM, Carmical JR, Starkey JM, Masliah E, Commins DL, Brandt D, Grant I, Singer EJ, Levine AJ, Miller J, Winkler JM, Fox HS, Luxon BA, Morgello S, National NeuroAIDS Tissue Consortium (2012) The National NeuroAIDS Tissue Consortium brain gene array: two types of HIV-associated neurocognitive impairment. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal pone. 0046178
Gelman BB, Lisinicchia JG, Morgello S, Masliah E, Commins D, Achim CL, Fox HS, Kolson DL, Grant I, Singer E, Yiannoutsos CT, Sherman S, Gensler G, Moore DJ, Chen T, Soukup VM (2013) Neurovirological correlation with HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders and encephalitis in a HAART-era cohort. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 62:487–495. doi:10.1097/QAI.0b013e31827f1bdb
Gisslen M, Krut J, Andreasson U, Blennow K, Cinque P, Brew BJ, Spudich S, Hagberg L, Rosengren L, Price RW, Zetterberg H (2009) Amyloid and tau cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in HIV infection. BMC Neurol 9:63. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-9-63
Green DA, Masliah E, Vinters HV, Beizai P, Moore DJ, Achim CL (2005) Brain deposition of beta-amyloid is a common feature in HIV positive patients. AIDS 19:407–411
Gupta S, Knight AG, Losso BY, Ingram DK, Keller JN, Bruce-Keller AJ (2012) Brain injury caused by HIV protease inhibitors: role of lipodystrophy and insulin resistance. Antiviral Res 95:19–29. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.04.010
Harezlak J, Buchthal S, Taylor M, Schifitto G, Zhong J, Daar E, Alger J, Singer E, Campbell T, Yiannoutsos C, Cohen R, Navia B, HIV Neuroimaging Consortium (2011) Persistence of HIV-associated cognitive impairment, inflammation and neuronal injury in era of highly active antiretroviral treatment. AIDS 25:625–633. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283427da7
Hauser KF, Fitting S, Dever SM, Podhaizer EM, Knapp PE (2012) Opiate drug use and the pathophysiology of neuro-AIDS. Curr HIV Res 10:435–452. doi:10.2174/157016212802138779
Heaton RK, Franklin DR, Ellis RJ, McCutchan JA, Letendre SL, Leblanc S, Corkran SH, Duarte NA, Clifford DB, Woods SP, Collier AC, Marra CM, Morgello S, Mindt MR, Taylor MJ, Marcotte TD, Atkinson JH, Wolfson T, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, Simpson DM, Abramson I, Gamst A, Fennema-Notestine C, Jernigan TL, Wong J, Grant I, CHARTER Group, HNRC Group (2011) HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders before and during the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: differences in rates, nature and predictors. J Neurovirol 17:3–16. doi:10.1007/s13365-010-0006-1
Hughes ES, Bell JE, Simmonds P (1997) Investigation of the dynamics of the spread of human immunodeficiency virus to brain and other tissues by evolutionary analysis of sequences from the p17gag and env genes. J Virol 71:1272–1280
Kaul M (2009) HIV-1 associated dementia: update on pathological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Curr Opin Neurol 22:315–320. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e328329cf3c
Lamers SL, Salemi M, Galligan DC, Morris A, Gray R, Fogel G, Zhao L, McGrath MS (2010) Human immunodeficiency virus-1 evolutionary patterns associated with pathogenic processes in the brain. J Neurovirol 16:230–241. doi:10.3109/13550281003735709
Lamers SL, Gray RR, Salemi M, Huysentruyt LC, McGrath MS (2011) HIV-1 phylogenetic analysis shows HIV-1 transits through the meninges to brain and peripheral tissues. Infect Genet Evol 11:31–37. doi:10.1016/j.meegid. 2010.10.016
Langford D, Marquie-Beck J, de Almeida S, Lazzaretto D, Letendre S, Grant I, McCutchan JA, Masliah E, Ellis RJ, HIV Neurobehavioural Research Centre (HNRC) group (2006) Relationship of antiretroviral treatment to post mortem brain tissue viral load in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J Neurovirol 12:100–107. doi:10.1080/13550280600713932
Letendre SL, Ellis RJ, Everall I, Ances B, Bharti A, McCutchan JA (2009) Neurologic complications of HIV disease and their treatment. Top HIV Med 17:46–56
Marra CM, Zhao Y, Clifford DB, Letendre S, Evans S, Henry K, Ellis RJ, Rodriguez B, Coombs RW, Schifitto G, McArthur JC, Robertson K, AIDS Clinical Trials Group 736 Study Team (2009) Impact of combination antiretroviral therapy on cerebrospinal fluid HIV RNA and neurocognitive performance. AIDS 23:1359–1366. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832c4152
Patrick C, Crews L, Desplats P, Dumaop W, Rockenstein E, Achim CL, Everall I, Masliah E (2011) Increased CDK5 expression in HIV encephalitis contributes to neurodegeneration via Tau phosphorylation and is reversed with Roscovitine. Am J Pathol 178:1646–1661. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.12.033
Paulino AD, Ubhi K, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Crews L, Letendre S, Ellis R, Everall IP, Grant I, Masliah E (2011) Neurotoxic effects of the HCV core protein are mediated by sustained activation of ERK via TLR2 signalling. J Neurovirol 17:327–340. doi:10.1007/s13365-011-0039-0
Ramage SN, Anthony IC, Carnie FW, Busuttil A, Robertson R, Bell JE (2005) Hyperphosphorylated tau and amyloid precursor protein deposition is increased in the brains of young drug abusers. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 31:439–448. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2005.007670.x
Reddy PV, Pilakka-Kanthikeel S, Saxena SK, Saiyed Z, Nair MP (2012) Interactive effects of morphine on HIV infection: role in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder. AIDS Res Treat. doi:10.1155/2012/953678
Robbins TW, Ersche KD, Everitt BJ (2008) Drug addiction and the memory systems of the brain. Ann NY Acad Sci 1141:1–21. doi:10.1196/annals.1441.020
Schouten J, Cinque P, Gisslen M, Reiss P, Portegies P (2011) HIV-1 infection and cognitive impairment in the cART era: a review. AIDS 25:561–575. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283437f9a
Tomlinson GS, Simmonds P, Busuttil A, Chiswick A, Bell JE (1999) Upregulation of microglia in drug users with and without pre-symptomatic HIV infection. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 25:369–379. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2990.1999.00197.x
Wang TH, Donaldson YK, Brettle RP, Bell JE, Simmonds P (2001) Identification of shared populations of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infecting microglia and tissue macrophages outside the central nervous system. J Virol 75:11686–11699. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.23.11686-11699.2001
Weed M, Adams RJ, Hienz RD, Meulendyke KA, Linde ME, Clements JE, Mankowski JL, Zink MC (2012) SIV/macaque model of HIV infection in cocaine users: minimal effects of cocaine on behaviour, virus replication and CNS inflammation. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7:401–411
Xu J, Ikezu T (2009) The comorbidity of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders and Alzheimer's disease: a foreseeable medical challenge in post-HAART era. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 4:200–212. doi:10.1007/s11481-008-9136-0
Zhao L, Galligan DC, Lamers SL, Yu S, Shagrun L, Salemi M, McGrath MS (2009) High level of HIV-1 DNA concentrations in brain tissues differentiate patients with post-HAART AIDS dementia complex or cardiovascular disease from those with AIDS. Sci China C Life Sci 52:651–656. doi:10.1007/s11427-009-0085-5
Zink MC, Brice AK, Kelly KM, Queen SE, Gama L, Li M, Adams RJ, Bartizal C, Varrone J, Rahi A, Graham DR, Tarwater PM, Mankowski JL, Clements JE (2010) Simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy have reduced central nervous system viral replication and inflammation but persistence of viral DNA. J Inf Dis 202:161–170. doi:10.1086/653213
Acknowledgments
The Edinburgh HIV Brain Bank is funded by the UK Medical Research Council. We thank the clinicians who looked after these subjects including Drs R Brettle and R Robertson and Professor C Leen, the clinical database manager Alan Wilson, and staff members who have assisted with the investigation of the tissue samples including Frances Carnie and Dr I Anthony. Lastly, this study would not have been possible without the generous trust and support of the donors and their families.
Conflict of interest
All three authors, Dr Donald Smith and Professors Peter Simmonds and Jeanne Bell, declare that they have no conflict of interest with the UK Medical Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, D.B., Simmonds, P. & Bell, J.E. Brain viral burden, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in HAART-treated HIV positive injecting drug users. J. Neurovirol. 20, 28–38 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-013-0225-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-013-0225-3