Abstract
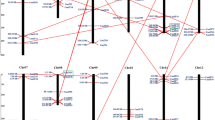
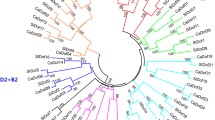
Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) is an economically important vegetable crop whose production and quality are severely reduced under adverse environmental stress conditions. The GATA transcription factors belonging to type IV zinc-finger proteins, play a significant role in regulating light morphogenesis, nitrate assimilation, and organ development in plants. However, the functional characteristics of GATA gene family during development and in response to environmental stresses have not yet been investigated in pepper. In this study, a total of 28 pepper GATA (CaGATA) genes were identified. To gain an overview of the CaGATAs, we analyzed their chromosomal distribution, gene structure, conservative domains, cis-elements, phylogeny, and evolutionary relationship. We divided 28 CaGATAs into four groups distributed on 10 chromosomes, and identified 7 paralogs in CaGATA family of pepper and 35 orthologous gene pairs between CaGATAs and Arabidopsis GATAs (AtGATAs). The results of promoter cis-element analysis and the quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis revealed that CaGATA genes were involved in regulating the plant growth and development and the responses to various abiotic stresses and hormone treatments in pepper. Tissue-specific expression analysis showed that most CaGATA genes were preferentially expressed in flower buds, flowers, and leaves. Several CaGATA genes, especially CaGATA14, were significantly regulated under multiple abiotic stresses, and CaGATA21 and CaGATA27 were highly responsive to phytohormone treatments. Taken together, our results lay a foundation for the biological function analysis of GATA gene family in pepper.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao T, Iwasaki T, Hosokawa D, Shinozaki K (1997) Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought- and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 9:1859–1868. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.9.10.1859
Agarwal M, Hao Y, Kapoor A, Dong CH, Fujii H, Zheng X, Zhu JK (2006) A R2R3 type MYB transcription factor is involved in the cold regulation of CBF genes and in acquired freezing tolerance. J Biol Chem 281:37636–37645. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605895200
An Y, Zhou Y, Han X et al (2020) The GATA transcription factor GNC plays an important role in photosynthesis and growth in poplar. J Exp Bot 71:1969–1984. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz564
Aravind L, Iyer LM (2012) The HARE-HTH and associated domains: novel modules in the coordination of epigenetic DNA and protein modifications. Cell Cycle 11:119–131. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.11.1.18475
Armstrong GA, Runge S, Frick G, Sperling U, Apel K (1995) Identification of NADPH:protochlorophyllide oxidoreductases A and B: a branched pathway for light-dependent chlorophyll biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 108:1505–1517. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.4.1505
Bai Y, Meng Y, Huang D, Qi Y, Chen M (2011) Origin and evolutionary analysis of the plant-specific TIFY transcription factor family. Genomics 98:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2011.05.002
Baskind HA, Na L, Ma Q, Patel MP, Geenen DL, Wang QT (2009) Functional conservation of Asxl2, a murine homolog for the drosophila enhancer of trithorax and polycomb group gene Asx. PLoS One 4:e4750. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004750
Bastakis E, Hedtke B, Klermund C, Grimm B, Schwechheimer C (2018) LLM-domain B-GATA transcription factors play multifaceted roles in controlling greening in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 30:582–599. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00947
Behringer C, Schwechheimer C (2015) B-GATA transcription factors-insights into their structure, regulation, and role in plant development. Front Plant Sci 6:90. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00090
Behringer C, Bastakis E, Ranftl QL, Mayer KF, Schwechheimer C (2014) Functional diversification within the family of B-GATA transcription factors through the leucine-leucine-methionine domain. Plant Physiol 166:293–305. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.246660
Bi YM, Zhang Y, Signorelli T, Zhao R, Zhu T, Rothstein S (2005) Genetic analysis of Arabidopsis GATA transcription factor gene family reveals a nitrate-inducible member important for chlorophyll synthesis and glucose sensitivity. Plant J 44:680–692. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02568.x
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-4-10
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R (2020) TBtools-an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chiang YH, Zubo YO et al (2012) Functional characterization of the GATA transcription factors GNC and CGA1 reveals their key role in chloroplast development, growth, and division in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 160:332–348. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.198705
Chini A, Fonseca S, Chico JM, Fernandez-Calvo P, Solano R (2009) The ZIM domain mediates homo- and heteromeric interactions between Arabidopsis JAZ proteins. Plant J 59:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03852.x
Ding L et al (2015a) HANABA TARANU regulates the shoot apical meristem and leaf development in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J Exp Bot 66:7075–7087. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv409
Ding L et al (2015b) HANABA TARANU (HAN) Bridges meristem and organ primordia boundaries through PINHEAD, JAGGED, BLADE-ON-PETIOLE2 and CYTOKININ OXIDASE 3 during flower development in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 11:e1005479. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005479
Fisher CL et al (2010) Additional sex combs-like 1 belongs to the enhancer of trithorax and polycomb group and genetically interacts with Cbx2 in mice. Dev Biol 337:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.10.004
Franco-Zorrilla JM, Lopez-Vidriero I, Carrasco JL, Godoy M, Vera P, Solano R (2014) DNA-binding specificities of plant transcription factors and their potential to define target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:2367–2372. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1316278111
Geng J, Liu JH (2018) The transcription factor CsbHLH18 of sweet orange functions in modulation of cold tolerance and homeostasis of reactive oxygen species by regulating the antioxidant gene. J Exp Bot 69:2677–2692. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery065
Gil KE et al (2017) Alternative splicing provides a proactive mechanism for the diurnal CONSTANS dynamics in Arabidopsis photoperiodic flowering. Plant J 89:128–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13351
Gillis WQ, St John J, Bowerman B, Schneider SQ (2009) Whole genome duplications and expansion of the vertebrate GATA transcription factor gene family. BMC Evol Biol 9:207. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-9-207
He X et al (2020) Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the TIFY gene family in the response to multiple stresses in Brassica napus L. BMC Genomics 21:736. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07128-2
Horton P, Park KJ, Obayashi T, Fujita N, Harada H, Adams-Collier CJ, Nakai K (2007) WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W585–W587. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm259
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31:1296–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Hudson D et al (2011) GNC and CGA1 Modulate chlorophyll biosynthesis and glutamate synthase (GLU1/Fd-GOGAT) expression in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 6:e26765. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026765
Iwasaki T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1995) Identification of a cis-regulatory region of a gene in Arabidopsis thaliana whose induction by dehydration is mediated by abscisic acid and requires protein synthesis. Mol Gen Genet 247:391–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293139
Jin J et al (2015) An Arabidopsis transcriptional regulatory map reveals distinct functional and evolutionary features of novel transcription factors. Mol Biol Evol 32:1767–1773. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msv058
Kiryushkin AS, Ilina EL, Puchkova VA, Guseva ED, Pawlowski K, Demchenko KN (2019) Lateral root initiation in the parental root meristem of cucurbits: old players in a new position. Front Plant Sci 10:365. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00365
Klermund C, Ranftl QL, Diener J, Bastakis E, Richter R, Schwechheimer C (2016) LLM-domain B-GATA transcription factors promote stomatal development downstream of light signaling pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana hypocotyls. Plant Cell 28:646–660. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00783
Kobayashi K, Masuda T (2016) Transcriptional regulation of tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 7:1811. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01811
Kobayashi K et al (2017) Shoot removal induces chloroplast development in roots via cytokinin signaling. Plant Physiol 173:2340–2355. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01368
Lescot M et al (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Li M et al (2019a) Leaf variegation and impaired chloroplast development caused by a truncated CCT domain gene in albostrians barley. Plant Cell 31:1430–1445. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00132
Li X, Guo C, Ahmad S, Wang Q, Yu J, Liu C, Guo Y (2019b) Systematic analysis of MYB family genes in potato and their multiple roles in development and stress responses. Biomolecules 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080317
Liu PP, Koizuka N, Martin RC, Nonogaki H (2005) The BME3 (Blue Micropylar End 3) GATA zinc finger transcription factor is a positive regulator of Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J 44:960–971. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02588.x
Liu J, Shen J, Xu Y, Li X, Xiao J, Xiong L (2016) Ghd2, a CONSTANS-like gene, confers drought sensitivity through regulation of senescence in rice. J Exp Bot 67:5785–5798. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw344
Liu Y et al (2019) A WRKY transcription factor PbrWRKY53 from Pyrus betulaefolia is involved in drought tolerance and AsA accumulation. Plant Biotechnol J 17:1770–1787. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13099
Liu X, Zhao C, Yang L, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Fang Z, Lv H (2020) Genome-wide identification, expression profile of the TIFY gene family in Brassica oleracea var. capitata, and their divergent response to various pathogen infections and phytohormone treatments. Genes (Basel) 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020127
Lowry JA, Atchley WR (2000) Molecular evolution of the GATA family of transcription factors: conservation within the DNA-binding domain. J Mol Evol 50:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002399910012
Luo XM et al (2010) Integration of light- and brassinosteroid-signaling pathways by a GATA transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 19:872–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.023
Manfield IW, Devlin PF, Jen CH, Westhead DR, Gilmartin PM (2007) Conservation, convergence, and divergence of light-responsive, circadian-regulated, and tissue-specific expression patterns during evolution of the arabidopsis GATA gene family. Plant Physiol 143:941–958. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.090761
Morita R, Sugino M, Hatanaka T, Misoo S, Fukayama H (2015) CO2-responsive CONSTANS, CONSTANS-like, and time of chlorophyll a/b binding protein expression1 protein is a positive regulator of starch synthesis in vegetative organs of rice. Plant Physiol 167:1321–1331. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00021
Neuhaus HE, Emes MJ (2000) Nonphotosynthetic metabolism in plastids. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:111–140. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.111
Onishi M, Tachi H, Kojima T, Shiraiwa M, Takahara H (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel salt-inducible gene encoding an acidic isoform of PR-5 protein in soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.). Plant Physiol Biochem 44:574–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2006.09.009
Patient RK, McGhee JD (2002) The GATA family (vertebrates and invertebrates). Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:416–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00319-2
Reyes JC, Muro-Pastor MI, Florencio FJ (2004) The GATA family of transcription factors in arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 134:1718–1732. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.037788
Richter R, Behringer C, Muller IK, Schwechheimer C (2010) The GATA-type transcription factors GNC and GNL/CGA1 repress gibberellin signaling downstream from DELLA proteins and PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTORS. Genes Dev 24:2093–2104. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.594910
Richter R, Bastakis E, Schwechheimer C (2013a) Cross-repressive interactions between SOC1 and the GATAs GNC and GNL/CGA1 in the control of greening, cold tolerance, and flowering time in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 162:1992–2004. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.219238
Richter R, Behringer C, Zourelidou M, Schwechheimer C (2013b) Convergence of auxin and gibberellin signaling on the regulation of the GATA transcription factors GNC and GNL in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:13192–13197. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304250110
Riechmann JL et al (2000) Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290:2105–2110. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5499.2105
Savojardo C, Martelli PL, Fariselli P, Profiti G, Casadio R (2018) BUSCA: an integrative web server to predict subcellular localization of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W459–W466. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky320
Scazzocchio C (2000) The fungal GATA factors. Curr Opin Microbiol 3:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00063-1
Scheible WR et al (2004) Genome-wide reprogramming of primary and secondary metabolism, protein synthesis, cellular growth processes, and the regulatory infrastructure of Arabidopsis in response to nitrogen. Plant Physiol 136:2483–2499. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.047019
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Seo DH, Seomun S, Choi YD, Jang G (2020) Root development and stress tolerance in rice: the key to improving stress tolerance without yield penalties. Int J Mol Sci 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051807
Shaikhali J et al (2012) The CRYPTOCHROME1-dependent response to excess light is mediated through the transcriptional activators ZINC FINGER PROTEIN EXPRESSED IN INFLORESCENCE MERISTEM LIKE1 and ZML2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:3009–3025. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.100099
Song X, Wang Y, Wang P, Pu G, Zou X (2020) GATA-type transcriptional factor Gat1 regulates nitrogen uptake and polymalic acid biosynthesis in polyextremotolerant fungus Aureobasidium pullulans. Environ Microbiol 22:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14841
Suarez-Lopez P, Wheatley K, Robson F, Onouchi H, Valverde F, Coupland G (2001) CONSTANS mediates between the circadian clock and the control of flowering in Arabidopsis. Nature 410:1116–1120. https://doi.org/10.1038/35074138
Sun H et al (2017) The JASMONATE ZIM-domain gene family mediates JA signaling and stress response in cotton. Plant Cell Physiol 58:2139–2154. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcx148
Teakle GR, Manfield IW, Graham JF, Gilmartin PM (2002) Arabidopsis thaliana GATA factors: organisation, expression and DNA-binding characteristics. Plant Mol Biol 50:43–57. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1016062325584
Urao T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao S, Shinozaki K (1993) An Arabidopsis myb homolog is induced by dehydration stress and its gene product binds to the conserved MYB recognition sequence. Plant Cell 5:1529–1539. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.5.11.1529
Vanholme B, Grunewald W, Bateman A, Kohchi T, Gheysen G (2007) The tify family previously known as ZIM. Trends Plant Sci 12:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.04.004
Wan H et al (2011) Identification of reference genes for reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR normalization in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 416:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.105
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1105-5
Wang Y, Pan F, Chen D, Chu W, Liu H, Xiang Y (2017) Genome-wide identification and analysis of the Populus trichocarpa TIFY gene family. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:360–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.04.015
Wray GA, Hahn MW, Abouheif E, Balhoff JP, Pizer M, Rockman MV, Romano LA (2003) The evolution of transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes. Mol Biol Evol 20:1377–1419. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msg140
Wu HM, Xie DJ, Tang ZS, Shi DQ, Yang WC (2020) PINOID regulates floral organ development by modulating auxin transport and interacts with MADS16 in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 18:1778–1795. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13340
Xia W, Yu H, Cao P, Luo J, Wang N (2017) Identification of TIFY family genes and analysis of their expression profiles in response to phytohormone treatments and Melampsora larici-populina Infection in Poplar. Front Plant Sci 8:493. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00493
Xin C, Yang J, Mao Y, Chen W, Wang Z, Song Z (2020) GATA-type transcription factor MrNsdD regulates dimorphic transition, conidiation, virulence and microsclerotium formation in the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium rileyi. Microb Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13581
Xu L, Yang L, Huang H (2007) Transcriptional, post-transcriptional and post-translational regulations of gene expression during leaf polarity formation. Cell Res 17:512–519. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2007.45
Yang X, Tuskan GA, Cheng MZ (2006) Divergence of the Dof gene families in poplar, Arabidopsis, and rice suggests multiple modes of gene evolution after duplication. Plant Physiol 142:820–830. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.083642
Yang S, Zhang X, Yue JX, Tian D, Chen JQ (2008) Recent duplications dominate NBS-encoding gene expansion in two woody species. Mol Gen Genomics 280:187–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-008-0355-0
Yang M et al (2018) Genome-wide association studies reveal the genetic basis of ionomic variation in rice. Plant Cell 30:2720–2740. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00375
Yang L et al (2020) Methylation of a CGATA element inhibits binding and regulation by GATA-1. Nat Commun 11:2560. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16388-1
Ye H, Du H, Tang N, Li X, Xiong L (2009) Identification and expression profiling analysis of TIFY family genes involved in stress and phytohormone responses in rice. Plant Mol Biol 71:291–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9524-8
Yu CS, Cheng CW, Su WC, Chang KC, Huang SW, Hwang JK, Lu CH (2014) CELLO2GO: a Web server for protein subCELlular LOcalization prediction with functional gene ontology annotation. PLoS One 9:e99368. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099368
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Ding L, Wu Z, Liu R, Meyerowitz EM (2013) Transcription repressor HANABA TARANU controls flower development by integrating the actions of multiple hormones, floral organ specification genes, and GATA3 family genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:83–101. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.107854
Zhang J et al (2015) Combinations of the Ghd7, Ghd8 and Hd1 genes largely define the ecogeographical adaptation and yield potential of cultivated rice. New Phytol 208:1056–1066. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13538
Zhang Y et al (2016a) An A20/AN1-type zinc finger protein modulates gibberellins and abscisic acid contents and increases sensitivity to abiotic stress in rice (Oryza sativa). J Exp Bot 67:315–326. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv464
Zhang Y et al (2016b) MYC cis-elements in PsMPT promoter is involved in chilling response of Paeonia suffruticosa. PLoS One 11:e0155780. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155780
Zhang Z et al (2018) The genetic architecture of nodal root number in maize. Plant J 93:1032–1044. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13828
Zhang L, Song Z, Li F, Li X, Ji H, Yang S (2019) The specific MYB binding sites bound by TaMYB in the GAPCp2/3 promoters are involved in the drought stress response in wheat. BMC Plant Biol 19:366. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1948-y
Zhang C et al (2020a) A GATA transcription factor from soybean (Glycine max) regulates chlorophyll biosynthesis and suppresses growth in the transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants (Basel) 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9081036
Zhang X et al (2020b) Genome-wide identification of the Tify gene family and their expression profiles in response to biotic and abiotic stresses in tea plants (Camellia sinensis). Int J Mol Sci 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218316
Zhao Y, Medrano L, Ohashi K, Fletcher JC, Yu H, Sakai H, Meyerowitz EM (2004) HANABA TARANU is a GATA transcription factor that regulates shoot apical meristem and flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2586–2600. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.024869
Zhao G et al (2016) Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the TIFY gene family in response to drought in cotton. Mol Gen Genomics 291:2173–2187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1248-2
Zhu XG, Long SP, Ort DR (2010) Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:235–261. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112206
Zhu D, Bai X, Luo X, Chen Q, Cai H, Ji W, Zhu Y (2013) Identification of wild soybean (Glycine soja) TIFY family genes and their expression profiling analysis under bicarbonate stress. Plant Cell Rep 32:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1360-7
Acknowledgements
Great gratitude goes to linguistics professor Ping Liu from Foreign Language College, Huazhong Agriculture University, Wuhan, China, for her work on English editing and language polishing.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key R&D Program of China, grant numbers 2016YFE0205500 and 2017YFD0101903; Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, grant number 2019CFB577; and China Agriculture Research System, grant number CARS-23-G28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Y. and M.Y.; methodology, C.Y. and N.L.; software, C.Y., N.L. and S.G.; formal analysis, C.Y. and S.G.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Y. and N.L.; investigation, F.W.; resources, C.J. and Y.Y.; data curation, C.Y. and N.L.; writing—review and editing, C.Y., N.L., M.Y., and Y.Y.; project administration, C.J.; funding acquisition, M.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: Izabela Pawłowicz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Fig. S1:
The conservative domain analysis of CaGATA genes (PNG 271 kb)
Fig. S2:
Paralogous relationship analysis of CaGATA genes (PNG 416 kb)
Fig. S3:
The number of various cis-elements on the promoters of each CaGATA gene. Promoter sequences (-2000 bp) of 28 CaGATA genes were analyzed (PNG 387 kb)
Fig. S4:
Relative expression levels of CaGATA genes significantly induced by (a) MV, (b) Salt, (c) HT (Heat), (d) Cold, (e) Dr (Drought) (PNG 493 kb)
Fig. S5:
Relative expression levels of CaGATA genes significantly induced by (a) ABA, (b) GA, (c) ET, (d) SA, (e) IAA, (f) JA (PNG 441 kb)
ESM 1
(DOCX 30 kb)
ESM 2
(XLSX 77 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, C., Li, N., Yin, Y. et al. Genome-wide identification and function characterization of GATA transcription factors during development and in response to abiotic stresses and hormone treatments in pepper. J Appl Genetics 62, 265–280 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-021-00618-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-021-00618-3