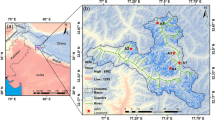
Abstract
Given extensive and rapid urbanization globally, assessing regional urban thermal effects (UTE) in both canopy and boundary layers under extreme weather/climate conditions is of significant interest. Rapid population and economic growth in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) have made it one of the largest city clusters in China. Here, we explore the three-dimensional (3D) UTE in the YRD using multi-source observations from high-resolution automatic weather stations, radiosondes, and eddy covariance sensors during the record-setting heat wave (HW) of July–August 2013. It is found that the regional canopy layer UTE is up to 0.6–1.2°C, and the nocturnal UTE (0.7–1.6°C) is larger than daytime UTE (0.2–0.5°C) during the HW. The regional canopy layer UTE is enhanced and expanded northwards, with some rural sites contaminated by the urban influences, especially at night. In the boundary layer, the strengthened regional UTE extends vertically to at least 925 hPa (∼750 m) during this HW. The strengthened 3D UTE in the YRD is associated with an enlarged Bowen ratio difference between urban and non-urban areas. These findings about the 3D UTE are beneficial for better understanding of the thermal environment of large city clusters under HW and for more appropriate adaption and mitigation strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao, X. Y., C. S. B. Grimmond, D. W. Liu, et al., 2016: Radiation fluxes in a business district of Shanghai, China. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 55, 2451–2468, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-16-0082.1.
Ao, X. Y., C. S. B. Grimmond, H. C. Ward, et al., 2018: Evaluation of the Surface Urban Energy and Water balance Scheme (SUEWS) at a dense urban site in Shanghai: Sensitivity to anthropogenic heat and irrigation. J. Hydrometeor., 19, 1983–2005, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-18-0057.1.
Ao, X. Y., J. G. Tan, X. Zhi, et al., 2019: Synergistic interaction between urban heat island and heat waves and its impact factors in Shanghai. Acta Geographica Sinica, 74, 1789–1802, doi: https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb201909007. (in Chinese)
Arnfield, A. J., 2003: Two decades of urban climate research: A review of turbulence, exchanges of energy and water, and the urban heat island. Int. J. Climatol., 23, 1–26, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.859.
Basara, J. B., P. K. Hall, Jr., A. J. Schroeder, et al., 2008: Diurnal cycle of the Oklahoma City urban heat island. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 113, D20109, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2008jd010311.
Chen, F., X. C. Yang, and W. P. Zhu, 2014: WRF simulations of urban heat island under hot-weather synoptic conditions: The case study of Hangzhou city, China. Atmos. Res., 138, 364–377, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.12.005.
CMA, 2018: Technical Specifications for Maintenance of Regional Automatic Weather Stations. QX/T 465–2018. (in Chinese). Available at http://cmastd.cmatc.cn/standardView.jspx?id=3076. Accessed on 5 May 2022.
Copernicus Climate Change Service, 2018: ERA5 hourly data on pressure levels from 1979 to present. doi: https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.bd0915c6
Cui, L. L., and J. Shi, 2012: Urbanization and its environmental effects in Shanghai, China. Urban Climate, 2, 1–15, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2012.10.008.
Dairaku, K., K. Kuraji, M. Suzuki, et al., 2000: The effect of rainfall duration and intensity on orographic rainfall enhancement in a mountainous area. J. Japan Soc. Hydrol. Water Resour., 13, 57–68, doi: https://doi.org/10.3178/jjshwr.13.57.
Du, Y., Z. Q. Xie, Y. Zeng, et al., 2007: Impact of urban expansion on regional temperature change in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Geogr. Sci., 17, 387–398, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-007-0387-0.
Estévez, J., P. Gavilán, and J. V. Giráldez, 2011: Guidelines on validation procedures for meteorological data from automatic weather stations. J. Hydrology, 402, 144–154, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.02.031.
Fischer, E. M., S. I. Seneviratne, P. L. Vidale, et al, 2007: Soil moisture—atmosphere interactions during the 2003 European summer heat wave. J. Climate, 20, 5081–5099, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI4288.1.
Gong, P., X. C. Li, and W. Zhang, 2019a: 40-year (1978–2017) human settlement changes in China reflected by impervious surfaces from satellite remote sensing. Sci. Bull., 64, 756–763, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2019.04.024.
Gong, P., H. Liu, M. N. Zhang, et al., 2019b: Stable classification with limited sample: Transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Sci. Bull., 64, 370–373, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2019.03.002.
Grimmond, C. S. B., and T. R. Oke, 1999: Heat storage in urban areas: Local-scale observations and evaluation of a simple model. J. Appl. Meteor., 38, 922–940, doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/511520-0450(1999)038<0922:HSIUAL>2.0.CO;2.
Grimmond, C. S. B., H. A. Cleugh, and T. R. Oke, 1991: An objective urban heat storage model and its comparison with other schemes. Atmos. Environ., 25, 311–326, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0957-1272(91)90003-W.
Grimmond, C. S. B., T. R. Oke, and H. A. Cleugh, 1993: The role of “rural” in comparisons of observed suburban-rural flux differences. Exchange processes at the land surface of a range of space and time scales. Proceedings International Symposium, Yokohama, Japan. IAHS Publ., 212, 165–174.
Guo, Y. J., and Y. H. Ding, 2009: Long-term free-atmosphere temperature trends in China derived from homogenized in-situ radiosonde temperature series. J. Climate, 22, 1037–1051, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2480.1.
Guo, Y. J., P. W. Thorne, M. P. McCarthy, et al., 2008: Radiosonde temperature trends and their uncertainties over eastern China. Int. J. Climatol., 28, 1269–1281, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1633.
Han, Y., Y. W. Zhou, J. P. Guo, et al., 2019: The characteristics of spatial and temporal variations in the PBL during the landfall of tropical cyclones across East China. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 58, 1557–1572, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-18-0131.1.
Hausfather, Z., M. J. Menne, C. N. Williams, et al., 2013: Quantifying the effect of urbanization on U.S. Historical Climatology Network temperature records. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 118, 481–494, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD018509.
Huang, B., G. H. Ni, and C. S. B. Grimmond, 2019: Impacts of urban expansion on relatively smaller surrounding cities during heat waves. Atmosphere, 10, 364, doi: https://doi.org/10.3900/atmos10070364.
Huang, Z., H. Chen, and H. Tian, 2011: Research on the heat wave index. Meteor. Mon., 37, 345–351. (in Chinese)
Ichinose, T., K. Shimodozono, and K. Hanaki, 1999: Impact of anthropogenic heat on urban climate in Tokyo. Atmos. Environ., 33, 3897–3909, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1352-2310(99)00132-6.
Jiang, S. J., X. Lee, J. K. Wang, et al., 2019: Amplified urban heat islands during heat wave periods. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 124, 7797–7812, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD030230.
Jiang, S. J., K. C. Wang, and Y. N. Mao, 2020: Rapid local urbanization around most meteorological stations explains the observed daily asymmetric warming rates across China from 1985 to 2017. J. Climate, 33, 9045–9061, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0118.1.
Jiang, X. L., D. H. Wang, J. J. Xu, et al., 2017: Characteristics of observed tropopause height derived from L-band sounder over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas. Asia-Pacific J. Atmos. Sci., 53, 1–10, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-016-0035-7.
Lau, N. C., and M. J. Nath, 2012: A model study of heat waves over North America: Meteorological aspects and projections for the twenty-first century. J. Climate, 25, 4761–4784, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00575.1.
Li, D., T. Sun, M. F. Liu, et al., 2015: Contrasting responses of urban and rural surface energy budgets to heat waves explain synergies between urban heat islands and heat waves. Environ. Res. Lett., 10, 054009, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/5/054009.
Liao, J. B., T. J. Wang, Z. Q. Jiang, et al., 2015: WRF/Chem modeling of the impacts of urban expansion on regional climate and air pollutants in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ., 106, 204–214, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.01.059.
Loridan, T., and C. S. B. Grimmond, 2012: Characterization of energy flux partitioning in urban environments: Links with surface seasonal properties. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 51, 219–241, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-11-038.1.
Lowry, W. P., 1977: Empirical estimation of urban effects on climate: A problem analysis. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 16, 129–135, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1977)016<0129:EEOUEO>2.0.CO;2.
Lu, H. M., M. L. Zhang, W. W. Sun, et al., 2018: Expansion analysis of Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration using DM-SP/OLS nighttime light imagery for 1993 to 2012. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf., 7, 52, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7020052.
Ma, S. M., T. J. Zhou, D. A. Stone, et al., 2017: Attribution of the July-August 2013 heat event in Central and Eastern China to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. Environ. Res. Lett., 12, 054020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa69d2.
Mardia, K. V., 1970: Measures of multivariate skewness and kurtosis with applications. Biometrika, 57, 519–530, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/57.3.519.
Miao, S. G., W. M. Jiang, P. Liang, et al., 2020: Advances in urban meteorological research in China. J. Meteor. Res., 36, 218–242, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-020-9858-3.
National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2014: China Statistical Yearbook: 2014. China Statistics Press, Beijing, 23–15. (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2018: China Statistical Yearbook: 2018. China Statistics Press, Beijing, 29–51. (in Chinese)
Oke, T. R., 1976: The distinction between canopy and boundary-layer urban heat islands. Atmosphere, 16, 268–277, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00046973.1976.9648422.
Oke, T. R., 1982: The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 108, 1–24, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49710845502.
Oke, T. R., G. Mills, A. Christen, et al., 2017: Urban Climates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 546 pp.
Peng, J. B., 2014: An investigation of the formation of the heat wave in southern china in summer 2013 and the relevant abnormal subtropical high activities. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 7, 286–290, doi: https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1674-2834.13.0097.
Piringer, M., C. S. B. Grimmond, S. M. Joffre, et al., 2002: Investigating the surface energy balance in urban areas—recent advances and future needs. Water Air Soil Poll. Focus, 2, 1–16, doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021302824331.
Ren, G. Y., Z. Y. Chu, Y. Q. Zhou, et al., 2005: Recent progresses in studies of regional temperature changes in China. Climatic Environ. Res., 10, 701–716, doi: https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.2005.04.01. (in Chinese)
Ren, Y. Y., and G. Y. Ren, 2011: A remote-sensing method of selecting reference stations for evaluating urbanization effect on surface air temperature trends. J. Climate, 24, 3179–3189, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3658.1.
Schatz, J., and C. J. Kucharik, 2015: Urban climate effects on extreme temperatures in Madison, Wisconsin, USA. Environ. Res. Lett., 10, 094024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/9/094024.
Schluenzen, K. H., C. S. B. Grimmond, and B. Alexande, 2021: Guidance to measuring, modelling and monitoring the canopy layer Urban Heat Island. EMS Annual Meeting Abstracts, Vol. 18, EMS2021-301, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/ems2021-301.
Shepherd, M., T. Andersen, C. Strother, et al., 2013: Urban Climate Archipelagos: A new Framework for urban impacts on Climate. Earthzine. Available online at https://earthzine.org/urban-climate-archipelagos-a-new-framework-for-urban-im-pacts-on-climate/. Accessed on 18 May 2022.
Stewart, I. D., 2011: A systematic review and scientific critique of methodology in modern urban heat island literature. Int. J. Climatol., 31, 200–217, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2141.
Stewart, I. D., and T. R. Oke, 2012: Local climate zones for urban temperature studies. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 93, 1879–1900, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/bams-d-11-00019.1.
Stone, B. Jr., 2012: The City and the Coming Climate: Climate Change in the Places We Live. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York, 198 pp.
Sun, J. Q., 2014: Record-breaking SST over mid-North Atlantic and extreme high temperature over the Jianghuai-Jiangnan region of China in 2013. Chinese Sci. Bull., 59, 3465–3470, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0425-0.
Sun, T., S. Kotthaus, D. Li, et al., 2017: Attribution and mitigation of heat wave-induced urban heat storage change. Environ. Res. Lett., 12, 114007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa922a.
Tan, J. G., L. M. Yang, C. S. B. Grimmond, et al., 2015: Urban integrated meteorological observations: Practice and experience in Shanghai, China. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 96, 85–102, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-13-00216.1.
Tao, S. Y., and L. X. Chen, 1987: A Review of Recent Research on the East Asian Summer Monsoon in China. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 60–92.
United Nations, 2018: 2018 Revision of World Urbanization Prospects. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, 1–126. Available online at https://www.un.org/devel-opment/desa/publications/2018-revision-of-world-urbanization-prospects.html. Accessed on 12 May 2022.
Wang, J., Z. W. Yan, X. W. Quan, et al., 2017: Urban warming in the 2013 summer heat wave in eastern China. Climate Dyn., 48, 3015–3033, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3248-7.
Wang, J., Y. Chen, W. L. Liao, et al., 2021: Anthropogenic emissions and urbanization increase risk of compound hot extremes in cities. Nat. Clim. Chang, 11, 1084–1089, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-021-01196-2.
Ward, H. C., and C. S. B. Grimmond, 2017: Assessing the impact of changes in surface cover, human behaviour and climate on energy partitioning across Greater London. Landsc. Urban Plan., 165, 142–161, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.04.001.
Wu, K., and X. Q. Yang, 2013: Urbanization and heterogeneous surface warming in eastern China. Chinese Sci. Bull., 58, 1363–1373, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5627-8.
Xia, J. J., K. Tu, Z. W. Yan, et al., 2016: The super-heat wave in eastern China during July–August 2013: A perspective of climate change. Int. J. Climatol., 36, 1291–1298, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4424.
Yang, P., G. Y. Ren, and W. D. Liu, 2013: Spatial and temporal characteristics of Beijing urban heat island intensity. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 52, 1803–1816, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-12-0125.1.
Zeng, Y., X. F. Qiu, L. H. Gu, et al., 2009: The urban heat island in Nanjing. Quatern. Int., 208, 38–43, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2009.02.018.
Zhai, P. M., and X. H. Pan, 2003: Trends in temperature extremes during 1951–1999 in China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, 1913, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2003gl018004.
Zhang, H. S., X. Y. Zhang, Q. H. Li, et al., 2020: Research progress on estimation of the atmospheric boundary layer height. J. Meteor. Res., 34, 482–498, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-020-9910-3.
Zhang, K. X., R. Wang, C. C. Shen, et al., 2010: Temporal and spatial characteristics of the urban heat island during rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China. Environ. Monit. Assess., 169, 101–112, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1154-8.
Zhang, L. S., J. J. Xue, W. G. Wang, et al., 2014: Comparative analysis of extreme high temperature weather in the summers of 2013 and 2003. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 7, 132–136, doi: https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1674-2834.13.0073.
Zhang, N., Z. Q. Gao, X. M. Wang, et al., 2010: Modeling the impact of urbanization on the local and regional climate in Yangtze River Delta, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 102, 331–342, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-010-0263-1.
Zhang, P. F., G. Y. Ren, Y. Qin, et al., 2021: Urbanization effects on estimates of global trends in mean and extreme air temperature. J. Climate, 34, 1923–1945, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0389.1.
Zhong, S., Y. Qian, C. Zhao, et al., 2017: Urbanization-induced urban heat island and aerosol effects on climate extremes in the Yangtze River Delta region of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 17, 5439–5457, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-5439-2017.
Zittis, G., Hadjinicolaou, P., Fnais, M., et al., 2015: Projected changes in heat wave characteristics in the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East. Reg. Environ. Change, 16, 1863–1876, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-014-0753-2.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the reviewers and editors for their helpful suggestions to improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research (2020B0301030004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (42175056, 41790471), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (21ZR1457600), China Meteorological Administration Innovation and Development Project (CXFZ2022J009), and UK—China Research and Innovation Partnership Fund through the Met Office Climate Science for Service Partnership (CSSP) China as part of the Newton Fund.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Liang, P., Grimmond, S. et al. Three-Dimensional Urban Thermal Effect across a Large City Cluster during an Extreme Heat Wave: Observational Analysis. J Meteorol Res 36, 387–400 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-022-1171-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-022-1171-x