Abstract
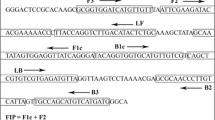
Association of 16SrVI group phytoplasmas in symptomatic sweet cherry samples was confirmed in our previous study by amplifying the 16 S rRNA gene in nested PCR assays. However, this method is time-consuming and expensive. Therefore, we developed a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay based detection protocol from a previously identified 16SrVI group phytoplasma strain in cherry samples. Three sets of primers based on the leucyl tRNA synthetase (leuS) and 16 S rRNA gene sequences were designed and evaluated to establish a rapid and efficient LAMP assay based detection system for 16SrVI-D subgroup associated cherry phytoplasma strains. The sweet cherry phytoplasma DNA was efficiently amplified by employing a set of leuS based LAMP detection primers in a reaction condition of 63o C for 70 min. The phytoplasma positive reactions were visualised by ladder like bands on 2% agarose gel, colour change from violet to blue with hydroxynaphthol blue and presence of fluorescence with ethidium bromide after an hour of LAMP reaction. Furthermore, the designed primers were tested for cross reactivity with other groups of phytoplasma strains belonging to 16SrI, 16SrII and 16SrV but could not amplify any of them. The lowest detection limit for the LAMP detection assay was 10 pg/µL. The developed LAMP method was found to be more robust, reliable and sensitive than the conventional nested PCR assay method. As a result, it has the potential to be used in phytoplasma indexing of sweet cherry germplasm and seedlings for disease free vegetative propagative materials.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeysinghe S, Kanatiwela-de Silva C, Abeysinghe PD, Udagama P,Warawichanee K, Aljafer N, Kawicha P, Dickinson M (2016) Refinement of the taxonomic structure of 16SrXI and 16SrXIV phytoplasmas of gramineous plants using multilocus sequence typing. PlDis 100(10):2001–2010.
Aljafer N, Dickinson M (2021) Evaluating LAMP assays for detection of phytoplasmas classified in different ribosomal groups. J Pl Pathol, 103(4):1315–1321.
Bekele B, Hodgetts J, Tomlinson J, Boonham N, Nikolic´ P, Swarbrick P, Dickinson M (2011) Use of a real-time LAMP isothermal assay for detecting 16SrII and XII phytoplasmas in fruit and weeds of the Ethiopian Rift Valley. Pl Pathol 60:345–355.
Cieślińska M, Smolarek T (2019) Multilocus sequence analysis of phytoplasmas detected in cherry trees in Poland. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture 106(1).
Deng S, Hiruki C (1991) Amplification of 16S rRNA genes from culturable and nonculturable mollicutes. J of Microbiol Meth 14: 53–61.
Donoso A, Valenzuela S (2018) In-field molecular diagnosis of plant pathogens: recent trends and future perspectives. Pl Pathol 67(7): 1451–1461.
Fiore N, Bertaccini A, Bianco PA, Cieślińska M, Ferretti L, Hoat TX, Quaglino F (2018). Fruit crop phytoplasmas. Rao GP, Bertaccini A, Fiore N, Liefting LW(eds) In Phytoplasmas: Plant pathogenic bacteria-I, Springer, Singapore. pp 153–190.
Goto M, Honda E, Ogura A, Nomoto A, Hanaki KI (2009) Colorimetric detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by using hydroxy naphthol blue. Biotechniq 46:167–172
Hu T, Subbiah V, Wu H, Amrit BK, Rauf A, Alhumaydhi FA, Suleria HAR (2021) Determination and characterization of phenolic compounds from Australia-grown sweet cherries (Prunus avium L.) and their potential antioxidant properties. ACS Omega 6 (50): 34687–34699
Kogovšek P, Hodgetts J, Hall J, Prezelj N, Nikolić P, Mehle N, Lenarčič R, Rotter A, Dickinson M, Boonham N, Dermastia M (2015) LAMP assay and rapid sample preparation method for on-site detection of favescence dorée phytoplasma in grapevine. Pl Pathol 64(2):286–296.
Kogovšek P, Mehle N, Pugelj A, Jakomin T, Schroers HJ, Ravnikar M, Dermastia M (2017) Rapid loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for grapevine yellows phytoplasmas on crude leafvein homogenate has the same performance as qPCR. Eur J Pl Pathol 148:75–84.
Lau HY, Botella JR (2017) Advanced DNA-based point-of-care diagnostic methods for plant diseases detection. Front Pl Sci 8: 2016.
Manimekalai R, Soumya VP, Sathish Kumar R, Selvarajan R, Reddy K, Thomas GV, Baranwal VK (2010) Molecular detection of 16SrXI group phytoplasma associated with root (wilt) disease of coconut (Cocos nucifera) in India. Pl Dis 94(5): 636
Mori Y, Nagamine K, Tomita N, Notomi T (2001) Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289: 150–154.
Nagamine K, Hase T, Notomi T (2002) Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol Cell Probes 16: 223–229.
Nair S, Manimekalai R, Ganga Raj P, Hegde V (2016) Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for detection of coconut root wilt disease and arecanut yellow leaf disease phytoplasma. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(7):1–7.
Nejat N, Vadamalai G (2010) Phytoplasma detection in coconut palm and other tropical crops. Pl Pathol J (Faisalabad) 9(3):112–121.
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K,Amino N, Hase T (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28(12):e63–e63.
Njiru ZK (2012) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology: towards point of care diagnostics. PLoS neglected tropical diseases, 6(6):e1572.
Parida M, Sannarangaiah S, Dash PK, Rao PVL, Morita K (2008) Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): a new generation of innovative gene amplification technique; perspectives in clinical diagnosis of infectious diseases. Rev Med Virol 18:407–421.
Schneider B, Seemüller E, Smart CD, Kirkpatrick BC (1995) Phylogenetic classification of plant pathogenic mycoplasma like organisms or phytoplasmas. In Razin S & Tully JG (eds). Molecular and diagnostic procedures in mycoplasmology. Academic Press pp 369–380
Tomlinson JA, Boonham N, Dickinson M (2010) Development and evaluation of a one-hour DNA extraction and loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of phytoplasmas. Pl Pathol 59: 465–471.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial help provided by the Director, ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi, India. We would also like to thank the Head, Division of Plant Pathology, Indian Agricultural Research Institute for providing laboratory facilities and Dr A I Bhat ICAR-Indian Institute of Spice Research, Kerala for his help in designing LAMP specific primers and corrections in the manuscript.
Table 1 LAMP primers designed for 16SrVI group phytoplasma based on 16SrRNA and leuS genes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors conceived the idea, analysed data and drafted manuscript for publication. The first author, Shreenath Y S did the survey, sample analysis, sequence analysis, sequence submission, design of primer and also contributed significantly in the preparation of draft of the manuscript. Sunil Kumar Sunani and M Dickinson have contributed for the design of primers and finalization of the manuscript and G P Rao contributed significantly in preparation of draft of the manuscript, finalization of the manuscript and formatting.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human studies and participants
The current study did not include any human or animal volunteers or animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shreenath, Y.S., Sunani, S.K., Rao, G.P. et al. Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for the detection of clover proliferation phytoplasma-associated with sweet cherry witches’ broom disease. Australasian Plant Pathol. 51, 467–474 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-022-00871-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-022-00871-y