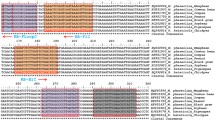
Abstract
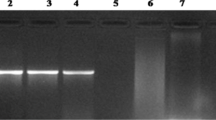
The coconut root wilt disease (RWD) and the arecanut yellow leaf disease (YLD) are two major phytoplasma associated diseases affecting palms in South India. Greatly debilitating the palm health, these diseases cause substantial yield reduction and economic loss to farmers. A rapid and robust diagnostic technique is crucial in efficient disease management. We established phytoplasma 16S rDNA targeted loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) and real time LAMP based diagnostics for coconut RWD and arecanut YLD. The LAMP reaction was set at 65 °C and end point detection made using hydroxynaphthol blue (HNB) and agarose gel electrophoresis. Molecular typing of LAMP products were made with restriction enzyme HpyCH4 V. Conventional PCR with LAMP external primers and sequencing of amplicons was carried out. Real time LAMP was performed on the Genei II platform (Optigene Ltd., UK). An annealing curve analysis was programmed at the end of the incubation to check the fidelity of the amplicons. The phytoplasma positive samples produced typical ladder like bands on agarose gel, showed colour change from violet to blue with HNB and produced unique annealing peak at 85 ± 0.5 °C in the real time detection. Restriction digestion produced predicted size fragments. Sequencing and BLASTN analysis confirmed that the amplification corresponded to phytoplasma 16S rRNA gene. LAMP method devised here was found to be more robust compared to conventional nested PCR and hence has potential applications in detection of phytoplasma from symptomatic palm samples and in rapid screening of healthy seedlings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens U, Seemuller E (1992) Detection of DNA of plant pathogenic mycoplasma like organisms by a polymerase chain reaction which amplifies a sequence of the 16S rRNA gene. Phytopathology 82:828–832
Alhudaib K, Arocha Y, Wilson M, Jones P (2007) “Al-Wijam”, a new phytoplasma disease of date palm in Saudi Arabia. Bull Insectology 60:285–286
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bekele B, Hodgetts J, Tomlinson J et al (2011) Use of a real-time LAMP isothermal assay for detecting 16SrII and XII phytoplasmas in fruit and weeds of the Ethiopian Rift Valley. Plant Pathol 60:345–355
Butler EJ (1908) Report on coconut palm disease in Travancore (Agriculture Research Institute PUSA). Bulletin No. 9:23
Daquan L, Murong C, Shabin Y, Tsai JH (2001) Identification of pathogens of yellow leaf disease of arecanut in Hainan Islands. Chin J Trop Crops (2):43–46 (in Chinese)
Goto M, Honda E, Ogura A, Nomoto A, Ken-Ichi Hanaki KI (2009) Colorimetric detection of loop mediated isothermal amplification reaction by using hydroxy naphthol blue. Biotechniques 46:167–172
Harrison NA, Richardson PA, Kramer JB, Tsai JH (1994) Detection of the mycoplasma-like organism associated with lethal yellowing disease of palms in Florida by polymerase chain reaction. Plant Pathol 43:998–1008
Harrison NA, Davis RE, Helmick EE (2013) DNA extraction from arboriscent monocots and how to deal with other challenging hosts. In: Hodgetts J, Dickinson M (eds) Phytoplasma: methods and protocols, methods in molecular biology. Springer, New York, pp 147–158
Hodgetts J, Tomlinson J, Boonham N et al (2011) Development of rapid in-field loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays for phytoplasmas. Bull Insectology 64:41–42
Kochu Babu KM, Nair KR, Solomon JJ, Nambiar KKN, Geetha L (2004) Studies on spear rot disease of oil palm in Kerala, India I. Establishment of phytoplasma etiology and yellow leaf disease affected arecanut as the source of inoculum. J Plant Crop 32:298–300
Kogovsek P, Hodgetts J, Hall J et al (2015) LAMP assay and rapid sample preparation method for on-site detection of flavescence doree phytoplasma in grapevine. Plant Pathol 64:286–296
Kurian A, Peter KV (2007) Commercial crops technology. Horticulture science series, vol 8. New India Publishing Agency, New Delhi
Manimekalai R, Sathish Kumar R, Soumya VP, Thomas GV (2010a) Molecular detection of phytoplasma associated with yellow leaf disease in areca palms (Areca catechu) in India. Plant Dis 94:1376
Manimekalai R, Soumya VP, Sathish Kumar R, Selvarajan R, Krishna Reddy M, Thomas GV, Sasikala M, Rajeev G, Baranwal VK (2010b) Molecular detection of 16SrXI group phytoplasma associated with root (wilt) disease of coconut (Cocos nucifera) in India. Plant Dis 94:636
Manimekalai R, Nair S, Soumya VP, Roshna OM, Thomas GV (2011) Real-time PCR technique-based detection of coconut root (wilt) phytoplasma. Curr Sci 101:1209–1213
Manimekalai R, Nair S, Soumya VP, Thomas GV (2013) Phylogenetic analysis identifies a ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma oryzae’-related strain associated with yellow leaf disease of areca palm (Areca catechu L.) in India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1376–1382
Manimekalai R, Soumya VP, Nair S, Thomas GV, Baranwal VK (2014) Molecular characterization identifies 16SrXI-B group phytoplasma(‘Candidatus Phytoplasma oryzae’-related strain) associated with root wilt disease of coconut in India. Sci Hortic 165:288–294
Marzachi C (2004) Molecular diagnosis of phytoplasmas. Phytopathol Mediterr 43:228–231
Mehdi A, Baranwal VK, Kochu Babu M, Praveena D (2011) Sequence analysis of 16S rRNA and secA genes confirms the association of 16SrI-B subgroup phytoplasma with oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) stunting disease in India. J Phytopathol 160:6–12
Nagamine K, Hase T, Notomi T (2002) Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol Cell Probes 16:223–229
Nair S, Roshna OM, Soumya VP et al (2014) Real-time PCR technique for detection of arecanut yellow leaf disease phytoplasma. Australas Plant Pathol. doi:10.1007/s13313-014-0278-7
Nayar R, Selsikar CE (1978) Mycoplasma-like organisms associated with yellow leaf disease of Areca catechu. Eur J For Pathol 8:125–128
Nejat N, Vadamalai G (2010) Phytoplasma detection in coconut palm and other tropical crops. Plant Pathol J 9:112–121
Nejat N, Sijam K, Abdullah SNA, Vadamalai G, Dickinson M (2009) Molecular characterization of a phytoplasma associated with coconut yellow decline (CYD) in Malaysia. Am J Appl Sci 6:1331–1340
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H et al (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28:E63
Perera L, Meegahakumbura MK, Wijesekara HRT, Fernando WBS, Dickinson MJ (2012) A phytoplasma is associated with the Weligama coconut leaf wilt disease in Sri Lanka. J. Plant Pathol. doi:10.4454/jpp.fa.2012.009
Rawther TSS (1982) Yellow leaf disease of arecanut. Indian Cocoa Arecanut Spices J 6:41–42
Sasikala M, Mathen K, Govindankutty MP, Solomon JJ, Geetha L (1989) Transmission of a mycoplasma-like organism from Cocos nucifera with root wilt disease to Catharanthus roseus by Cassytha filiformis. Eur J Plant Pathol 94:191–194
Sasikala M, Prakash VR, Sapna VP, Mayilvaganan M, Leena SN (2005) Refinement of ELISA and its use in early detection of coconut root (wilt) disease. Cord 212:37–44
Solomon JJ, Nair CPR, Srinivasan N, Gunasekaran M, Sasikala M (1999) Coconut root wilt—the malady and remedy. J Plant Crops 27:71–92
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant from National Agricultural Science Fund (NASF), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, S., Manimekalai, R., Ganga Raj, P. et al. Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for detection of coconut root wilt disease and arecanut yellow leaf disease phytoplasma. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32, 108 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2078-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2078-4