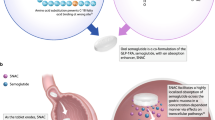
Abstract
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are a well-established class of glucose-lowering drugs. GLP-1 RAs can be classified according to their structure, duration of action and mode of administration. This review describes the basic and clinical pharmacology of orally administered semaglutide. It highlights the PIONEER clinical trial programme results, and reviews the efficacy, safety and tolerability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
GLP-1 RAs (glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists) are a preferred class of glucose-lowering drug. |
Subcutaneous treatment with GLP-1 RAs is limited by their injectable mode of administration. |
Orally administered semaglutide, a recently developed GLP-1 RA formulation, offers good glucose control in a safe and well-tolerated manner. |
This review describes the basic and clinical pharmacology of orally administered semaglutide. |
Introduction
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing worldwide; 31 and 60 million adults live with type 2 diabetes in USA and Europe, respectively. India has 77 million people with diabetes mellitus (DM); currently India has the second highest number of diabetes cases in the world preceded only by China [1]. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complex and progressive disease associated with significant morbidity and mortality; four million deaths worldwide are attributable to diabetes, with half of these in people aged under 60 years. The risk of death among people with diabetes (aged 20–59 years) is at least double that in those without diabetes [2]. A key factor underlying the global rise in diabetes is the increasing prevalence of obesity, which is a significant risk factor for diabetes. Different terms have been used to describe the association of obesity and diabetes. Metabolic syndrome is considered as a diagnostic entity; the word ‘diabesity’ highlights the etiologic effect of obesity on type 2 diabetes. A body mass index (BMI) greater than 35 kg/m2 is associated with an increased risk of diabetes of more than 40-fold in men and more than 70-fold in women. When combined with overweight/obesity, the risks of serious long-term complications and overall mortality associated with diabetes are further increased [3,4,5].
The pathophysiology of T2D is progressive and involves multiple defects that contribute to chronic hyperglycaemia. At least eight distinct pathophysiological abnormalities, commonly known as the ominous octet, contribute to impaired glucose homeostasis and are present early in the natural history of T2D [6]. A decreased incretin effect also plays an important role in the progressive β-cell failure of T2D. β-cell resistance to glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) contributes to progressive failure in the function of β-cells [7]. The incretin effect is significantly impaired in people with T2D, greatly reducing the capacity for insulin release in response to food intake [8].
Incretin-based therapies work either by preventing enzymatic degradation of GLP-1, thus maintaining plasma levels of endogenous GLP-1 (dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, DPP4is) or by directly activating GLP-1 receptors and mimicking the action of native GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, GLP-1 RAs) [9]. GLP-1 RAs are preferred second-line agents in patients with T2DM with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (ASCVD) in light of their demonstrated ASCVD benefit, high efficacy, low potential for hypoglycaemia and potential for weight loss. More recently, the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) has deemed GLP-1 RAs to be the first-line therapy for cardiovascular risk reduction in patients with T2DM with very high/high risk [10].
Despite the benefits of GLP-1 RAs, subcutaneous administration is still a major barrier in adopting this therapy. Development of a co-formulation of orally administered semaglutide with the absorption enhancer sodium N-(8-[2-hydroxybenzoyl]amino)caprylate (SNAC) has overcome the barrier of poor absorption and degradation in the stomach [11]. This review article will discuss the pharmacology of orally administered semaglutide with a focus on role of SNAC in enhancing the absorption of semaglutide, in addition to efficacy and safety from the PIONEER trials to determine its potential therapeutic role. This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Classification of GLP-1 RA
Classification of GLP-1 RAs is based on their basic structure and pharmacokinetic (PK) properties. By altering the amino acid in the peptide chain they resist degradation by the DPP4 enzyme. Another group was synthetically developed by replicating the structure of a naturally occurring protein isolated from saliva of the gila monster, exendin-4 (Ex-4), with substantial homology to native GLP-1. This naturally occurring protein has GLP-1 receptor-activating properties, and it is resistant to degradation by the DPP4 enzyme. Apart from structural classification, they can also be classified on the basis of their duration of action (short-acting and long-acting GLP-1 RAs). Short-acting GLP-1 RAs are resistant to DPP4 owing to their structural modifications, and longer-acting molecules have undergone some structural modifications to enhance their duration of action, e.g. exenatide once weekly, dulaglutide, albiglutide, liraglutide [12]. GLP-1 RAs can also be classified on the basis of structure, duration of action and mode of delivery, as shown in Table 1 [13].
GLP-1 RAs correct six of the eight components of the ominous octet. Direct activation by GLP-1 RAs has been shown widely to increase insulin and decrease glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner, resulting in reduced blood glucose levels combined with low risk of hypoglycaemia. GLP-1 RAs also have a series of beneficial multifactorial effects beyond glycaemic control that include reduction of body weight and improvement of cardiovascular (CV) outcomes [14]. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends GLP-1 RAs in patients with clinical characteristics like presence of established ASCVD and cardiac heart failure or chronic kidney diseases [15]. GLP-1 RAs are peptides and include exenatide, liraglutide, dulaglutide, lixisenatide and semaglutide. Oral peptide drug delivery is limited by low permeability of the gastrointestinal tract and rapid enzymatic and pH-induced degradation in the stomach. As a result, GLP-1 RAs require administration by subcutaneous injection on either a daily or weekly basis [11].
Semaglutide
Semaglutide was designed as a potent, long-acting GLP-1 analogue that could be administered subcutaneously (s.c.) once weekly, rather than s.c. once daily, to improve convenience and adherence. Semaglutide has 94% sequence homology with native GLP-1 and three key structural differences that provide extended pharmacokinetics [16] (Fig. 1):
-
1.
Substitution of Ala with Aib at position 8 increases enzymatic (DPP4) stability.
-
2.
Attachment of a linker and C18 di-acid chain at position 26 provides strong binding to albumin.
-
3.
Substitution of Lys with Arg at position 34 prevents C18 fatty acid binding at the wrong site.
Semaglutide subcutaneous formulation proved efficacious across SUSTAIN trials; semaglutide sc 0.5 mg and 1 mg reduced HbA1c levels by 1.8% from baseline and 57–74% of cases experienced a reduction of HbA1c levels to less than 7% with 0.5 mg and 67–79% with 1 mg. It also reduced the body weight by up to 6.5 kg from baseline. In addition, the SUSTAIN 6 trial demonstrated a significant reduction in major CV events with semaglutide versus placebo in patients with T2D at high CV risk. The hazard ratio (HR) for major adverse cardiac events (MACE) was 0.74 (95% CI 0.58, 0.95) in subjects treated with semaglutide versus placebo (p < 0.001 for non-inferiority) [17,18,19].
Barriers to Injectable GLP-1 RA Therapy
Quite a few barriers have been identified related to injectable GLP-1 RA therapy. Patients’ perception of injectable therapy include perceived difficultly to use and fear of injections. This can have effects on the acceptance of therapy or adherence in a patient with type 2 diabetes [20].
To overcome the barriers and to improve the adherence, oral GLP-1 RAs were needed, but oral protein-based drug absorption is limited because of degradation in the stomach due to low pH, proteolytic enzyme activity, and limited permeability across the gastrointestinal (GI) epithelium. The bioavailability of GLP-1 RAs administered orally alone is very low and, in order to avoid degradation, the active molecule has to be protected and delivered through the GI epithelium and into the bloodstream. Co-formulation of GLP-1 RA with an absorption enhancer is necessary to achieve adequate bioavailability after oral administration [11].
Orally Administered Semaglutide
The search for modifications which can enable oral therapy of currently injectable peptides has been ongoing for a long time. Various strategies which were developed include the use of biotin to form biotinylated GLP-1; another method tried was addition of polyethylene glycol (PEG) to form PEGylated GLP-1; the use of nanotechnology to develop non-peptidic receptor agonists was also tried, but the results were not very promising [21].
Orally administered semaglutide is co-formulated with an absorption enhancer, SNAC (Fig. 2), which promotes absorption of semaglutide across gastric mucosa. SNAC has previously been co-formulated with heparin, ibandronate and vitamin B12 to increase drug absorption [22,23,24].
Clinical Pharmacology
Gamma scintigraphy was used in healthy men to study the anatomical site of erosion following absorption of orally administered semaglutide and its erosion kinetics. A randomised, open-label crossover study (Study 3957; NCT01619345) was conducted in 26 healthy men in a fasting state who received a single dose of 10 mg orally administered semaglutide containing a labelled ion exchange resin. Complete tablet erosion occurred in the stomach. Scintigraphic images showed that no erosion had occurred 2 min after dosing, whereas no intact tablet core remained after 140 min. Measurement of semaglutide plasma concentrations confirmed early systemic absorption and an apparently slow elimination phase once present in the systemic circulation (Fig. 3) [25].
Estimated mean semaglutide plasma concentration–time profile after a single dose of orally administered semaglutide 10 mg [26]
Role of SNAC in Absorption of Orally Administered Semaglutide
A series of in vitro studies were conducted in dogs to investigate the mechanism via which SNAC enhances the absorption of semaglutide. The trans-epithelial transport of semaglutide was examined in cell monolayers of gastric epithelium (NCI-N87) with and without SNAC exposure. The absorption-enhancing action of SNAC on semaglutide was found to require concentrations in the millimolar range, as reflected by a significant increase in the apparent permeability coefficient of semaglutide across gastric epithelial cell monolayers in the presence of 80 mM SNAC. The fold change in the apparent permeability coefficient of semaglutide elicited by SNAC was rapidly reduced following the removal of SNAC (within 60 min), emphasising its relatively short window of action. There was a substantial increase in intracellular uptake of semaglutide by gastric epithelial cells with SNAC exposure compared with control, which was not apparent with EDTA, a modulator of tight junction function; these divergent patterns indicate that SNAC mediates absorption via the transcellular route. The authors concluded that SNAC prevented gastric degradation by neutralizing a low pH microenvironment surrounding the tablet, resulting in an increased concentration-dependent flux of semaglutide across the gastric mucosa [26, 27] (Fig. 4).
Because SNAC protects semaglutide from pH-dependent degradation and the consumption of food leads to an increase in gastric pH, the effect of food and water on systemic semaglutide exposure was investigated. Semaglutide absorption was compared in a fed group that ate 30 min before dosing, a fasting group that did not eat until 4 h post dosing, and a reference group that ate 30 min post dosing. The fed group experienced significantly lower systemic semaglutide exposure after the 10th dose, whereas both the fasting and reference groups achieved therapeutic concentrations [26]. Two volumes of water (50 and 120 mL) consumed with semaglutide 10 mg/SNAC 300 mg were also examined. Neither amount of water made significant differences to the PK parameters of orally administered semaglutide. On the basis of these studies, food intake impacts the pharmacokinetics of semaglutide and it is necessary to advise patients to fast before administration of the drug [28]. The PK parameters of orally administered semaglutide and subcutaneously administered semaglutide are listed in Table 2 [29, 30]. Orally administered semaglutide was administered for 10 consecutive days with dose escalation on the 5th day (5 days of 5 mg dosing followed by five days of 10 mg dosing) to avoid gastrointestinal side effects in both normal and renally impaired subjects. After 10 days PK samples were taken for 21 days. Cmax was 15 nM with a Tmax of 1 h and a half-life of 1 week [29]. In comparison, subcutaneously administered semaglutide given as a single injection (0.5 mg) has shown a Cmax of 10 nM with Tmax of 24 h with a similar 1-week half life [30]. In both studies no difference was seen in normal vs renally impaired subjects.
Semaglutide is primarily metabolized via proteolytic cleavage of the peptide backbone by DPP4 and neutral endopeptidases and sequential beta-oxidation of the fatty di-acid side chain. These degradation products are then excreted in the urine and faeces [29]. There was no apparent effect of renal impairment, hepatic impairment or upper GI disease on the PK and tolerability of orally administered semaglutide, suggesting that dose adjustment is not necessary in these special populations [11, 31,32,33]. Since orally administered semaglutide absorption depends on localized SNAC buffering, co-administration with other agents has the potential for drug–drug interactions. Omeprazole, lisinopril, warfarin, metformin, digoxin, the combined oral contraceptive ethinyl estradiol/levonorgestrel, rosuvastatin and furosemide have all been evaluated for drug interactions with semaglutide. None of these agents significantly affected orally administered semaglutide concentrations [34].
Orally Administered Semaglutide Clinical Data: Summary of PIONEER Trials
PIONEER is the phase 3 trial programme of orally administered semaglutide designed to evaluate the risk–benefit profile of orally administered semaglutide. The orally administered semaglutide phase 3a programme evaluated the efficacy, safety and tolerability of once-daily orally administered semaglutide in 9543 randomised subjects with T2D, of whom 5707 were exposed to orally administered semaglutide. In the ten phase 3a trials comprising the programme, relevant contemporary T2D treatment options were used as comparators in head-to-head comparisons. The programme also included a long-term safety trial, trials to evaluate the use of orally administered semaglutide in individuals with moderate renal impairment and as add-on to insulin as well as a cardiovascular outcome trial (CVOT) to evaluate the CV safety profile. Table 3 summarizes the PIONEER trial programmes [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44].
Cardiovascular Outcomes with Orally Administered Semaglutide
PIONEER 6 (NCT02692716) was an event-driven CVOT designed to confirm that treatment with orally administered semaglutide does not result in an unacceptable increase in CV risk compared with placebo. It was a pre-approval cardiac safety assessment trial with a primary objective of non-inferiority to placebo, which was basically done to get early approval as per regulatory guidance. A total of 3183 patients with T2D at high risk of CV events were enrolled; PIONEER 6 achieved its primary endpoint by demonstrating non-inferiority (p < 0.001) of MACE (composite of CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) and non-fatal stroke) for orally administered semaglutide compared with placebo, both in addition to standard of care. An HR of 0.79 in favour of orally administered semaglutide compared with placebo was observed, but this 21% reduction in MACE did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.17 for superiority). Among the individual components of the primary endpoint, there was a reduction in CV death of 51% (HR 0.49; 95% CI 0.27, 0.92) in the orally administered semaglutide group. The HR for non-fatal MI was 1.18 (95% CI 0.73, 1.90) and for non-fatal stroke was 0.74 (95% CI 0.35, 1.57). In addition, a statistically significant reduction in all-cause mortality of 49% (HR 0.51; 95% CI 0.31, 0.84) in favour of orally administered semaglutide was observed. The HR for the expanded MACE outcome was similar to that of the primary outcome (HR 0.82; 95% CI 0.61, 1.10) [40]. In comparison, the subcutaneously administered once-weekly semaglutide CVOT, SUSTAIN 6 has shown superiority over placebo with a significant 26% risk reduction for MACE [19].
The PIONEER 6 trial was aimed at proving CV safety of orally administered semaglutide only. Another trial, SOUL (NCT03914326), has now been initiated to overcome the shortcomings of PIONEER 6 with a primary endpoint focused at proving CV superiority vs placebo.
Safety of Orally Administered Semaglutide
The most common adverse effect observed in all PIONEER studies are gastrointestinal-related, dose-dependent and manifested as nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea. Across the PIONEER trials around 15–23% of patients experienced nausea with orally administered semaglutide 14 mg, and approximately 7–15% of patients on 14 mg orally administered semaglutide discontinued the trial. Approximately 5–7% of patients experienced decrease in appetite, which was consistent across the PIONEER trials [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44].
When it comes to outcomes and safety measures in different age groups, an exploratory analysis of seven PIONEER trials was done; including PIONEER 1–5, 7 and 8, a total of 5657 patients were included in the analysis. This exploratory analysis evaluated the effect of age at baseline on efficacy (< 45, ≥ 45 to < 65, or ≥ 65 years) and safety (< 65 years and ≥ 65 years). In terms of safety, generally more events and events leading to discontinuation were reported in the patient group aged of 65 years or more. This is in line with what has been seen with other GLP-1 RAs [45].
Cost of Oral vs Injectable and Other Therapies
No new drug adoption is possible without the proper cost-related analysis in relation to already available options. In a cost of control analysis by Hansen et al. for the US market, orally administered semaglutide was found to be cost effective in comparison to dulaglutide, exenatide, liraglutide and lixisenatide. Cost of a 14 mg dose of orally administered semaglutide came out the least at USD 15,430 and USD 17,383 for patients achieving glycaemic targets of < 7% and ≤ 6.5%, respectively [46]. In another cost-effectiveness analysis done for the UK market, orally administered semaglutide 14 mg was found to be cost effective relative to sitagliptin 100 mg and empagliflozin 25 mg and dominant in comparison to liraglutide 1.8 mg daily dose for the treatment of T2DM. The cost-effectiveness ratio per quality-adjusted life year (QUALY) was reported as GBP 11,006 versus empagliflozin and GBP 4930 versus sitagliptin [47].
Dosing and Administration
Currently orally administered semaglutide is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency, Health Canada, Australia and Japan as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycaemic control in adults with T2DM. It is available as 3, 7 and 14 mg oral tablet formulations.
-
Orally administered semaglutide should be taken on an empty stomach.
-
Orally administered semaglutide should be swallowed whole with up to half a glass of water equivalent to 120 mL.
-
Do not split, crush or chew the tablet.
-
Wait at least 30 min before the first meal or drink of the day or taking other oral medicinal products. Waiting less than 30 min may decrease the absorption of semaglutide.
If a dose is missed, the missed dose should be skipped, and the next dose should be taken the following day [48]. Patient counselling on the administration of the drug is crucial for the effectiveness of orally administered semaglutide.
Oral GLP-1 RA in Development
The success of orally administered semaglutide in clinical trials has led to the development of other oral formulations. OWL833 is a new orally active non-peptide GLP-1 RA licensed by Eli Lilly. In preclinical studies conducted on cynomolgus monkeys it has shown agonistic activity to human and cynomolgus GLP-1 receptors and improved glucose tolerance by stimulating insulin secretion, and it exhibited an anti-feeding activity like exenatide. Further human clinical trials will help in better understanding the drug in the treatment of diabetes [49]. Another oral GLP-1 RA, which is a non-peptide molecule, under development is TTP273 from vTv Therapeutics; this drug has recently completed phase 2a clinical trials with promising results in reducing HbA1c without any nausea [50].
Conclusion
GLP-1 RAs are an important class of glucose-lowering drugs. Though their use is supported by various professional guidelines, their injectable route of administration has been considered a barrier to widespread adoption. The development of semaglutide, an oral GLP-1 RA, overcomes this barrier. Already approved for prescription in Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Japan and Switzerland, orally administered semaglutide has been shown to be effective, safe and well tolerated. The drug should emerge as a first-line therapy for persons with type 2 diabetes and associated overweight/obesity as well as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. It should also be helpful in persons at high risk of hypoglycaemia, and those who prefer the advantage of oral over injectable administration. Further clinical trials and experience will help improve our understanding of the benefits of this drug.
References
International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 9th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2019.
Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett PH, et al. The burden of mortality attributable to diabetes: realistic estimates for the year 2000. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(9):2130–5.
World Health Organization. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases, 2014. https://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-status-report-2014/en/. Accessed May 31, 2020.
Lau DC, Teoh H. Benefits of modest weight loss on the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Can J Diabetes. 2013;37(2):128–34.
Kalra S. Diabesity. J Pak Med Assoc. 2013;63(4):532–4.
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1(1):1–22.
DeFronzo RA. Banting lecture. From the triumvirate to the ominous octet: a new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 2009;58(4):773–95.
Holst JJ, Knop FK, Vilsbøll T, Krarup T, Madsbad S. Loss of incretin effect is a specific, important, and early characteristic of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(2):S251–S257257.
Vilsbøll T. Liraglutide: a once-daily GLP-1 analogue for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;16(2):231–7.
Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, et al. 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: the task force for diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J. 2020;41(2):255–32323.
Baekdal TA, Thomsen M, Kupčova V, Hansen CW, Anderson TW. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of oral semaglutide in subjects with hepatic impairment. J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;58(10):1314–23.
Kalra S, Baruah MP, Sahay RK, Unnikrishnan AG, Uppal S, Adetunji O. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: past, present, and future. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2016;20(2):254.
Kalra S, Das AK, Sahay RK, al. Consensus recommendations on GLP-1 RA use in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: South Asian Task Force. Diabetes Ther. 2019;1:1–73.
Ghani AM, Defronzo AR. Is it time to change the type 2 diabetes treatment paradigm? Yes! GLP-1 RAs should replace metformin in the type 2 diabetes algorithm. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(8):1121–7.
American Diabetes Association. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S73–S85.
Lau J, Bloch P, Schäffer L, et al. Discovery of the once-weekly glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) analogue semaglutide. J Med Chem. 2015;58(18):7370–80.
Ahmann A, Chow F, Vivian F, et al. Semaglutide provides superior glycemic control across SUSTAIN 1–5 clinical trials. Int J Nutrol. 2018;11(S 01):Trab722.
Pratley RE, Aroda VR, Lingvay I, et al. Semaglutide versus dulaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): a randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(4):275–86.
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;10(375):1834–44.
Romera I, Cebrián-Cuenca A, Álvarez-Guisasola F, Gomez-Peralta F, Reviriego J. A review of practical issues on the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2019;10(1):5–19.
Araújo F, Fonte P, Santos HA, Sarmento B. Oral delivery of glucagon-like peptide-1 and analogs: alternatives for diabetes control? J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012;6(6):1486–97.
Pineo G, Hull R, Marder V. Oral delivery of heparin: SNAC and related formulations. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2004;17(1):153–60.
Bittner B, McIntyre C, Tian H, Tang K, Shah N, Phuapradit W, et al. Phase I clinical study to select a novel oral formulation for ibandronate containing the excipient sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] caprylate (SNAC). Die Pharmazie-Int J Pharm Sci. 2012;67(3):233–41.
Castelli MC, Wong DF, Friedman K, Riley MG. Pharmacokinetics of oral cyanocobalamin formulated with sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino]caprylate (SNAC): an open-label, randomized, single-dose, parallel-group study in healthy male subjects. Clin Ther. 2011;33(7):934–45.
Buckley ST, Bækdal TA, Vegge A, et al. Transcellular stomach absorption of a derivatized glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(467).
Baekdal TA, Borregaard J, Donsmark M, Breitschaft A, Sondergaard FL. Evaluation of the effects of water volume with dosing and post-dose fasting period on pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide. InDiabetes. 2017;66:A315–A315315.
Buckley ST, Bækdal TA, Vegge A, et al. Transcellular stomach absorption of a derivatized glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(467).
Jensen L, Helleberg H, Roffel A, et al. Absorption, metabolism and excretion of the GLP-1 analogue semaglutide in humans and nonclinical species. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;15(104):31–41.
Granhall C, Søndergaard FL, Thomsen M, Anderson TW. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of oral semaglutide in subjects with renal impairment. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018;57(12):1571–80.
Marbury TC, Flint A, Jacobsen JB, Karsbøl JD, Lasseter K. Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of a single dose of semaglutide, a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, in subjects with and without renal impairment. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56(11):1381–90.
Davies M, Chatterjee S, Khunti K. The treatment of type 2 diabetes in the presence of renal impairment: what we should know about newer therapies. Clin Pharmacol. 2016;8:61–81.
Meier JJ, Granhall C, Hoevelmann U, et al. Effect of upper gastrointestinal disease on the pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide in subjects with type 2 diabetes. American Diabetes Association, 79th Scientific Sessions 2019; poster number 1013-P.
Bækdal TA, Breitschaft A, Navarria A, Hansen CW. A randomized study investigating the effect of omeprazole on the pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2018;14(8):869–77.
Bækdal TA, Borregaard J, Hansen CW, Thomsen M, Anderson TW. Effect of oral semaglutide on the pharmacokinetics of lisinopril, warfarin, digoxin, and metformin in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019;58(9):1193–203.
Aroda VR, Rosenstock J, Terauchi Y, et al. PIONEER 1: randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in comparison with placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(9):1724–32.
Rodbard HW, Rosenstock J, Canani LH, et al. Oral semaglutide versus empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on metformin: the PIONEER 2 trial. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(12):2272–81.
Rosenstock J, Allison D, Birkenfeld AL, et al. Effect of additional oral semaglutide vs sitagliptin on glycated hemoglobin in adults with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with metformin alone or with sulfonylurea: the PIONEER 3 randomized clinical trial. J Am Med Assoc. 2019;321(15):1466–80.
Pratley R, Amod A, Hoff ST, et al. Oral semaglutide versus subcutaneous liraglutide and placebo in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 4): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3a trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10192):39–50.
Mosenzon O, Blicher TM, Rosenlund S, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (PIONEER 5): a placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(7):515–27.
Husain M, Birkenfeld AL, Donsmark M, et al. Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(9):841–51.
Pieber TR, Bode B, Mertens A, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide with flexible dose adjustment versus sitagliptin in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 7): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(7):528–39.
Zinman B, Aroda VR, Buse JB, et al. 985-P: Oral semaglutide as add-on to insulin in T2D: PIONEER 8. Diabetes. 2019;68(suppl 1):985-P.
Yamada Y, Katagiri H, Hamamoto Y, et al. Dose-response, efficacy, and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 9): a 52-week, phase 2/3a, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(5):377–91.
Yabe D, Nakamura J, Kaneto H, et al. Safety and efficacy of oral semaglutide versus dulaglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 10): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(5):392–406.
Aroda VR, Bauer R, Hertz CL, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide by baseline age in the PIONEER clinical trial program. Poster presented at- American Diabetes Association 2020.
Hansen BB, Nuhoho S, Ali SN, et al. Oral semaglutide versus injectable glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a cost of control analysis. J Med Econ. 2020;23(6):650–8.
Bain SC, Hansen BB, Malkin SJ, et al. Oral semaglutide versus empagliflozin, sitagliptin and liraglutide in the UK: long-term cost-effectiveness analyses based on the PIONEER clinical trial programme. Diabetes Ther. 2020;11(1):259–77.
Rybelsus (semaglutide tablets) [package insert]. Plainsboro, NJ; Novo Nodisk; Published September 2019. https://www.novo-pi.com/rybelsus.pdf. Accessed May 27, 2020.
Kawai T, Tanino F, Fukazawa M, et al. OWL833, an orally active nonpeptide GLP-1 receptor agonist, improves glucose tolerance by increasing insulin secretion and reduces food intake of cynomolgus monkeys. Diabetes 2018;67(Suppl 1).
Zhao P, Liang YL, Belousoff MJ, et al. Activation of the GLP-1 receptor by a non-peptidic agonist. Nature. 2020;8:1–5.
Acknowledgements
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Disclosures
Sanjay Kalra has received speaker fees from Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi and is a member of the journal’s Editorial Board. Rakesh Sahay has received speaker fees from Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Digital Features
To view digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12661451.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalra, S., Sahay, R. A Review on Semaglutide: An Oral Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist in Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Ther 11, 1965–1982 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-020-00894-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-020-00894-y