Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to evaluate the short-term cost-utility of insulin degludec (degludec) versus insulin glargine 100 units/mL (glargine U100) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in the basal–bolus subgroup of the head-to-head cardiovascular (CV) outcome trial, DEVOTE.
Methods
A cost-utility analysis was conducted over a 2-year time horizon using a decision analytic model to compare costs in patients receiving once daily degludec or glargine U100, both as part of a basal–bolus regimen, in addition to standard care. Clinical outcomes and patient characteristics were taken exclusively from DEVOTE, whilst health-related quality of life utilities and UK-specific costs (expressed in 2016 GBP) were obtained from the literature. The analysis was conducted from the perspective of the National Health Service.
Results
Degludec was associated with mean cost savings of GBP 28.78 per patient relative to glargine U100 in patients with type 2 diabetes at high CV risk. Cost savings were driven by the reduction in risk of diabetes-related complications with degludec, which offset the higher treatment costs relative to glargine U100. Degludec was associated with a mean improvement of 0.0064 quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) compared with glargine U100, with improvements driven predominantly by lower rates of severe hypoglycemia with degludec versus glargine U100. Improvements in quality-adjusted life expectancy combined with cost neutrality resulted in degludec being dominant over glargine U100. Sensitivity analyses demonstrated that the incremental cost-utility ratio was stable to variations in the majority of model inputs.
Conclusion
The present short-term modeling analysis found that for the basal–bolus subgroup of patients in DEVOTE, with a high risk of CV events, degludec was cost neutral (no additional costs) compared with glargine U100 over a 2-year time horizon in the UK setting. Furthermore, there were QALY gains with degludec, particularly due to the reduction in the risk of severe hypoglycemia.
Funding
Novo Nordisk A/S.
Trial Registration
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier, NCT01959529.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Healthcare systems in many countries are under increasing financial pressure due to the demographic challenge of aging populations and the growing burden of chronic diseases, including diabetes [1]. Globally, one in 11 adults (425 million) has diabetes, of which type 2 diabetes makes up around 90% of cases, with the total cost of diabetes to healthcare systems estimated to be USD 727 billion in 2017 [2]. The cost of treating diabetes-related complications is substantial and in many healthcare systems exceeds the cost of blood-glucose-lowering medication [3]. With increasing constraints on healthcare budgets, health economic evaluations, including cost-utility analyses (CUA), are playing an increasingly important role in decisions to allocate resources between therapy areas and interventions. CUA, a special type of cost-effectiveness analysis, compares the costs of new interventions with their outcomes measured in utility-based units, most commonly the quality-adjusted life-year (QALY). This enables the comparison of alternative interventions according to cost per QALY gained, and assists in the efficient allocation of resources to achieve maximum healthcare gains within the constraints of a limited budget [4].
Episodes of severe hypoglycemia are becoming increasingly common, particularly as attention focuses on intensive glycemic control [5,6,7]. In the Hypoglycaemia Assessment Tool (HAT) study, 8.9% of patients with type 2 diabetes reported an episode of severe hypoglycemia during the 4-week prospective study [8]. Severe hypoglycemic events requiring hospitalization can pose a significant financial burden on healthcare systems: in the UK, the average direct medical cost of an event was estimated at over GBP 1300 in patients with type 2 diabetes [7]. Hypoglycemia has an acute, negative impact on clinical outcomes, including an increased risk of falls, fractures, cardiovascular (CV) events, coma, dementia, neurological conditions, and death, but can also have an adverse effect on longer-term diabetes management due to the fear of hypoglycemia [9,10,11,12,13,14].
Insulin degludec (degludec) is a basal insulin with an ultralong duration of action and a stable glucose-lowering profile [15]. Studies of the pharmacodynamics of degludec and another long-acting insulin analog, insulin glargine 100 units/mL (glargine U100), have confirmed the lower day-to-day and within-day variability in glucose-lowering effect with degludec compared with glargine U100 [16, 17]. Phase 3 clinical studies have established that similar improvements in glycemic control can be achieved with fewer hypoglycemic episodes, particularly nocturnal hypoglycemia, with degludec versus glargine U100 across a broad spectrum of patients with diabetes [18,19,20]. Recently, results from the first double-blind, active-comparator cardiovascular outcome trial (CVOT) of a specific antihyperglycemic therapy were published [21, 22]. DEVOTE (NCT01959529) evaluated the CV safety of degludec relative to glargine U100 in patients with type 2 diabetes at a heightened risk of CV complications [22]. In DEVOTE, degludec was noninferior to glargine U100 in terms of the incidence of CV events [22]. Furthermore, the trial demonstrated a significant reduction in the risk of severe hypoglycemia for degludec versus glargine U100 at a similar level of glycemic control [22].
The present evaluation focused on the subgroup of patients who started DEVOTE on a basal–bolus regimen. Guidelines recommend that patients with advanced or very poorly controlled diabetes are managed by basal–bolus therapy [23]. Basal–bolus regimens most closely mimic the natural pattern of insulin secretion found in individuals without diabetes but are complex and costly, as they require multiple injections per day and therefore an elevated use of consumables such as needles and self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) tests. This subgroup of patients have advanced type 2 diabetes, and are thus at an increased risk of complications relative to patients with a shorter duration of disease [24]. Zoungas et al. report that for every 5-year increase in diabetes duration, the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and all-cause death increased by 49 and 78%, respectively, when accounting for age at diagnosis [24]. Patients on basal–bolus regimens also have an increased incidence of hypoglycemia relative to those using basal insulin only [25, 26], which can negatively impact quality of life whilst imposing a significant economic burden through increased healthcare resource utilization and loss of productivity [27,28,29]. The aim of this analysis was therefore to report the clinical outcomes for the basal–bolus subgroup of DEVOTE, and to evaluate the cost-utility of degludec versus glargine U100 in patients treated with a basal–bolus regimen at baseline, over the 2-year trial duration using a simple and transparent decision analytic model in the UK setting.
Methods
The DEVOTE Trial
DEVOTE was a multinational, treat-to-target, randomized, double-blind, active comparator-controlled CVOT conducted in 20 countries [22]. A total of 7637 patients with type 2 diabetes and at high risk of CV events were randomly assigned to receive either degludec (100 units/mL) or glargine U100, both once daily in addition to standard care [22]. The event-driven trial was designed to continue until the occurrence of at least 633 first MACE—a combined endpoint of non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), non-fatal stroke, and CV death [22]. Severe hypoglycemia was self-recorded, defined according to the American Diabetes Association as an episode requiring the assistance of another person to actively administer carbohydrate or glucagon or to take other corrective actions [30]. All outcomes, including severe hypoglycemia, were confirmed by central, blinded review by an independent event adjudication committee. Data on nonsevere hypoglycemia were not collected in DEVOTE.
Basal–Bolus Subgroup Analysis
This analysis used data on clinical outcomes derived from the basal–bolus subgroup of DEVOTE (Table 1, [22]). The basal–bolus subgroup was defined as using basal–bolus (or premix or bolus insulin only) at baseline (before switching to degludec or glargine U100) and constituted 46% (n = 3515; degludec, 1760; glargine U100, 1755) of the patients in DEVOTE. Patients on premix regimens were switched to appropriate bolus injections at the start of the trial. Time to first composite MACE, which was the primary outcome measure in DEVOTE and defined as the first occurrence of nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or CV mortality, was analyzed using a Cox proportional hazards regression model on the composite endpoint. The number of severe hypoglycemic episodes was analyzed using a negative binomial regression model with a log-link function and log(duration of observation time) as offset. Death from other causes, i.e., death from causes other than first MACE, was analyzed using a Cox proportional hazards regression model. Insulin dose (units/kg) was log-transformed and analyzed with a mixed model for repeated measures (MMRM) within subjects using an unstructured residual covariance matrix among visits. Visit interactions with age, dose at baseline, body mass index, alternative titration target (yes/no), and treatment were included in the model as fixed effect covariates. Change from baseline in HbA1c to the 24-month visit was analyzed using an MMRM within subjects using an unstructured residual covariance matrix among visits at 6, 12, and 24 months of the trial; interactions between visit and treatment and between visit and baseline HbA1c were included as fixed effects in the model.
Model Overview
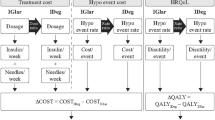
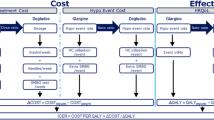
A decision analytic model (Fig. 1, [30]) was developed to evaluate the cost-utility of degludec versus glargine U100 using clinical data from the basal–bolus subgroup of patients with type 2 diabetes from DEVOTE. The analysis was conducted for the UK setting from the perspective of the National Health Service (NHS). Baseline characteristics for the simulated patient cohort were based on the DEVOTE basal–bolus subgroup (Table S1 in the Electronic supplementary material, ESM). The model was a short-term cohort model with two annual cycles capturing first MACE, death from other causes, severe hypoglycemic events, and insulin dose. HbA1c was not captured in the analysis given the short time horizon and the treat-to-target trial design of DEVOTE, resulting in similar end-of-trial HbA1c levels in both treatment arms [22]. The model used relative rates (hazard, rate, and dose ratios) from regression analyses to estimate differences between the degludec and glargine U100 treatment arms (Table 1). In line with previous evaluations of degludec, the model only included treatment effects for which a statistically significant difference between treatment arms was documented, and assumed that all other differences were due to random variation (i.e., the null hypothesis could not be rejected). However, nonsignificant differences were explored in the sensitivity analyses. An annual discount rate of 3.5% was applied to the costs and clinical benefits in the second cycle [31]. Model outputs include the average cost in pounds sterling (GBP), utility outcomes in QALYs for each arm, the inter-arm differences in cost and QALYs, and the incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR; cost per QALY gained).
Schematic of the cost-utility model. Diagram shows the model as run for each treatment arm (degludec and glargine U100). The model used relative rates (hazard, rate, and dose ratios) from regression analyses to derive the rates and doses in the degludec arm (see the ”Model Overview” section). * Severe hypoglycemia was defined according to the American Diabetes Association as an episode requiring the assistance of another person to actively administer carbohydrate or glucagon or to take other corrective actions [30]. CV cardiovascular, glargine U100 insulin glargine 100 units/mL, MACE major adverse cardiovascular event, MI myocardial infarction, U units
Cost Data and Resource Use
Treatment unit costs were based on UK list prices (Table 2, [32,33,34,35,36,37]). It was assumed that four injections per day were administered for the basal–bolus regimen (same in both arms) and a new needle and SMBG test strip and lancet were used per injection. Mean doses of basal and bolus insulin were estimated for each of the annual cycles and adjusted for survival. Insulin treatment costs were modeled as the unit cost multiplied by the mean annual dose, calculated as the arithmetic mean of the start- and end-of-year doses captured from the clinical trial data to approximate the average under the curve (Table 1b). Costs of complications were derived from the literature and inflation-adjusted to 2016 prices using the hospital and community health services index from the Personal Social Services Research Unit [37] (Table 2). For nonfatal MI and nonfatal stroke, an event cost was captured in the cycle in which the event took place and a state cost was captured in the subsequent year, reflecting ongoing excess healthcare resource use after the event (only relevant for first-year events given the 2-year time-horizon). Costs of severe hypoglycemia were captured exclusively in the year of the event, and were a summary of direct costs for patients who were treated by a family member or friend, or received emergency treatment from a paramedic or general practitioner, or received treatment in a hospital [34]. Cost estimates of severe hypoglycemia included immediate direct treatment costs (attendance by a healthcare professional, ambulance callout, and administration of medications) and follow-up treatment costs (additional visits to see a general practitioner, extra blood glucose test strips, and patient/family education).
Event Rates
Rates from DEVOTE for first MACE, death from other causes, and severe hypoglycemic events were captured in the model. Adopting a conservative approach, subsequent CV events after first MACE were not incorporated into the CUA. The model used CV death from first MACE as well as death from other causes to estimate annual survival, which was applied in each of the two annual cycles. Annual nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, and severe hypoglycemic event rates were applied to the surviving proportion of the cohort in the two annual cycles (Fig. 1).
Utility Data
Baseline utility and disutility values were identified in the literature (Table 2). For nonfatal MI and nonfatal stroke, the utilities were half-cycle-corrected in the first year and applied fully in the subsequent year (only relevant for first-year events given the 2-year time horizon). The severe hypoglycemia disutility was an annualized disutility for the year of the event. The model was developed to optionally capture an “extension period,” allowing additional costs and quality of life estimates over a longer time horizon to be attached to the events that occurred in the within-trial period, i.e., four scenarios based on a nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, no MACE, or death in the trial. Extending the analysis with additional costs was explored in a sensitivity analysis.
Sensitivity Analyses
Deterministic sensitivity analyses (of the effects of individual changes in model parameters on clinical and cost outcomes) were performed based on no discounting, the inclusion of nonsignificant differences between treatment arms, the use of the same MACE distribution for degludec and glargine U100, alternative unit costs and disutilities, the inclusion of a utility for flexible dosing, and the inclusion of long-term additional costs and effects based on scenarios run in the IQVIA CORE Diabetes Model version 9.0 (IQVIA, Basel, Switzerland) [using updated UKPDS 82 CV risk equations], assuming the same rescue medication in both arms (Fig. S1 in the ESM) and extension parameters detailed in Table S2 of the ESM.
A probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) was performed to quantify the effect of statistical uncertainty around the input parameters on the model results. Uncertainty was captured based on standard errors around the DEVOTE outcomes, which were used to inform the shape of a series of normal and lognormal distributions around model parameters (Table S3 of the ESM). PSA outcomes were based on 1000 model iterations, sampling from all modeled distributions in each iteration without capturing covariance.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article does not contain any new studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Results
Basal–Bolus Subgroup Analysis
The risk of experiencing the primary composite outcome of 3-component MACE was 19% lower with degludec versus glargine U100 (hazard ratio, 0.81; 95% CI 0.66–0.98; P = 0.035) (Table 1a). This hazard ratio was applied to the annual rate of first MACE observed in the glargine U100 arm of 0.0607 events/patient-year of exposure (PYE) to estimate a rate of 0.0489 events/PYE for the degludec arm. The distribution of components within the composite MACE endpoint for degludec versus glargine U100 (events/PYE) was nonfatal MI (0.0208 [42%] vs. 0.0292 [48%]), nonfatal stroke (0.0099 [20%] vs. 0.0124 [20%]), and CV death (0.0182 [37%] vs. 0.0191 [31%]). There was a 37% lower risk of severe hypoglycemia with degludec versus glargine U100 (estimated rate ratio, 0.63; 95% CI 0.47–0.85; P = 0.002) (Table 1a). This ratio was applied to the annual rate of severe hypoglycemia observed in the glargine U100 arm of 0.085 to result in an estimated annual rate of 0.0536 episodes of severe hypoglycemia for degludec. There was no significant difference in the incidence of death from other causes (excluding first MACE) between treatment arms (Table 1a). The only significant difference in insulin dose between treatment arms was for basal insulin dose at 24 months, which was higher in the degludec arm (Table 1b). There was no significant difference in change from baseline in HbA1c after 24 months between treatment arms (Table S4 of the ESM).
Base Case
In our evaluation of discounted costs, the mean cost per patient was GBP 4002.36 in the degludec arm compared with GBP 4031.13 in the glargine U100 arm. This resulted in a negligible cost saving of GBP 28.78 per patient with degludec over the 2-year time horizon. Savings were driven by a reduction in the risk of diabetes-related complications with degludec, particularly nonfatal MI, which more than offset the higher acquisition costs compared with glargine U100 (Table 3). Total discounted QALYs were estimated at 1.4778 and 1.4715 for degludec and glargine U100, respectively, with an increment of 0.0064 in favor of degludec. The main drivers of this were the risk reductions for severe hypoglycemia and (to a smaller extent) nonfatal MI and nonfatal stroke with degludec compared with glargine U100 (Table 3). An ICUR is not shown, per convention, as the result was “dominant,” meaning that an improvement in health is observed together with cost savings/cost neutrality.
Sensitivity Analyses
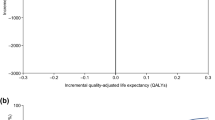
The deterministic sensitivity analyses demonstrated that the base-case findings remained largely unchanged despite variation in a range of model input values, with ICURs showing dominance or close to cost neutrality in most cases. Using the same MACE distribution (the glargine U100 MACE distribution) in both treatment arms changed the results, lowering CV mortality at the expense of the nonfatal MI reduction, which increased the QALYs gained in the degludec arm but lowered the cost offsets. Changing the treatment costs (a 15% lower glargine U100 cost) resulted in an ICUR in the lower range of £20,000–£30,000 per QALY gained, although when long-term extension costs and effects were included, degludec was still highly cost-effective (Table 4, [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]). The probabilistic sensitivity analyses showed that degludec is likely to be cost-effective with 96.5 and 97.7% probabilities for willingness-to-pay thresholds of £20,000 and £30,000 per QALY gained, respectively (Fig. 2).
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis results: a cost-utility scatterplot; b cost-utility acceptability curve. In a, the orange square represents the average value for incremental cost and incremental quality-adjusted life expectancy. GBP pounds sterling, glargine U100 insulin glargine 100 units/mL, QALY quality-adjusted life-years
Discussion
In this analysis of the basal–bolus subgroup of DEVOTE, there was a 19% lower risk of MACE and a 37% lower risk of severe hypoglycemia with degludec versus glargine U100. The results of the CUA showed that for the basal–bolus subgroup of patients in DEVOTE, with a high risk of CV events, degludec was cost neutral (no additional cost) compared with glargine U100 over a 2-year trial horizon in the UK setting. The higher acquisition costs with degludec were more than offset by the lower costs associated with a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications, particularly MI, with degludec versus glargine U100. Furthermore, there were QALY gains with degludec, particularly due to the reduction in risk of severe hypoglycemia.
Limiting the risk of hypoglycemia is important for both patients and physicians [46, 47]. Severe hypoglycemia is associated with an increased frequency of various adverse outcomes in patients with diabetes, including CV disease, MACE, dementia (in older patients), major microvascular events, and death [10,11,12,13,14]. Hypoglycemia can have considerable negative effects on patient quality of life [48], with an increasing frequency and severity of events associated with a reduced quality of life [47]. The long-term effects of hypoglycemia may include behavioral changes and significant anxiety or fear of future episodes [47]. Fear of hypoglycemia can adversely affect diabetes management and clinical outcomes by compromising adherence to medications [9].
Previous health economic evaluations from a NHS perspective have reported similar results, with degludec considered dominant or cost-effective relative to glargine U100 in the UK setting across diabetes types and regimens (basal only or basal–bolus) [49,50,51]. These results were based mainly upon differences in event rates (and associated costs) of severe and nonsevere hypoglycemia, whilst CV events and death from other causes (excluding first MACE) were not captured by the models [49,50,51]. With the present analysis using data from a CVOT, CV outcomes and death from other causes were included. However, data on nonsevere hypoglycemia, a large driver of QALYs in other reported evaluations, were not collected and therefore could not be included in our evaluation. Hypoglycemia exerts significant societal costs through lost productivity related to absences from work [52] that were not reflected by our CUA from a NHS perspective.
In the overall trial population of DEVOTE, degludec was noninferior to glargine U100 with respect to the incidence of first MACE (hazard ratio, 0.91; 95% CI 0.78–1.06) [22]. Here, we report that the risk of first MACE was significantly lower with degludec versus glargine U100 in the basal–bolus subgroup of DEVOTE. The more pronounced treatment difference for MACE in the basal–bolus subgroup of DEVOTE compared with the full trial population may be explained by the more advanced disease in these patients and thus a higher risk of diabetes-related complications such as MACE [24]. This is evidenced by the higher proportion of patients that experienced first MACE who started DEVOTE on a basal–bolus regimen (9.8% with degludec vs. 12.0% with glargine) compared with the full trial population (8.5% with degludec vs. 9.3% with glargine U100) [22].
Recently published and currently ongoing CVOTs of antihyperglycemic therapies are usually placebo-controlled, noninferiority trials lacking an active comparator [53]. DEVOTE is the first published double-blind CVOT that compared the drug of interest head-to-head with an active comparator—in this case degludec versus glargine U100, both once daily in addition to standard care [21, 22]. This strategy allows a direct comparison of treatment effects, and represents an improvement in the design of CVOTs [53]. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first health economic analysis of a specific antihyperglycemic therapy to use data sourced from a double-blind, active-comparator CVOT. This enabled clinical data for the base-case analysis for both treatment arms to be derived from a single homogeneous source (the basal–bolus subgroup of the DEVOTE study population) including observed event rates for MACE, death from other causes, and severe hypoglycemia. Additional strengths of this CUA include the exclusive use of endpoints with significant differences between treatment arms; that the base-case findings remained largely unchanged despite variation in a range of model input values in the sensitivity analyses; and the conservative assumptions of the base-case analysis, which did not include long-term improvements.
This study also has several limitations. Foremost, the evaluation is based on a subgroup of patients, which affects the generalizability of the results beyond patients at high risk of CV events and treated with basal–bolus regimens. Notwithstanding, the internal validity for this group of patients is high. Decision analytic models, such as the one used in the present analysis, bring together evidence from various sources to model cost-utility in a specific setting, in this case the UK cost setting, and are always associated with some uncertainty arising from the model design and input parameters. Many of the factors contributing to the uncertainty have been explored in sensitivity analyses, which supported the results of the base-case model and suggest that the findings are robust. A further limitation is the omission of microvascular complications from the analysis. While microvascular complications can have a sizeable effect on diabetes-related treatment costs and patient quality of life, no microvascular endpoints were included in the DEVOTE trial. The rationale for their exclusion was driven primarily by the desire to maintain the homogeneity of the clinical data [33, 54]. Finally, the time horizon in this analysis was limited by the duration of the trial. It could be perceived as being overly conservative to limit a CV benefit to only two years. However, a longer-term (lifetime) perspective was explored in a sensitivity analysis which assumed rescue medication in both arms and no continued benefits after the trial period beyond differences in the modeled history of events in the two model arms. Further analyses would be required to quantify the potential long-term costs and benefits based on possible scenarios of the protective effects of degludec on CV risk and severe hypoglycemia.
Conclusion
Based on this short-term modeling analysis, degludec provides improvements in clinical outcomes at no additional cost in the UK setting, as compared with glargine U100 in patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk of CV events who are treated with a basal–bolus insulin regimen.
References
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387:1513–30.
International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. Brussels: IDF; 2017.
Kanavos P, Van den Aardweg S, Schurer W. Diabetes expenditure, burden of disease and management in 5 EU countries. London: London School of Economics; 2012.
Robinson R. Cost-utility analysis. BMJ. 1993;307:859–62.
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1577–89.
Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, et al. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000;321:405–12.
Holbrook T, Tang Y, Das R, et al. Direct medical costs of severe hypoglycaemic events in patients with type 2 diabetes in England: a retrospective database study. Int J Clin Pract. 2017;71:e12958.
Khunti K, Alsifri S, Aronson R, et al. Rates and predictors of hypoglycaemia in 27 585 people from 24 countries with insulin-treated type 1 and type 2 diabetes: the global HAT study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016;18:907–15.
Leiter LA, Yale JF, Chiasson J-L, Harris SB, Kleinstiver P, Sauriol L. Assessment of the impact of fear of hypoglycemic episodes on glycemic and hypoglycemic management. Can J Diabetes. 2005;29:186–92.
Goto A, Arah OA, Goto M, Terauchi Y, Noda M. Severe hypoglycaemia and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis with bias analysis. BMJ. 2013;347:f4533.
Johnston SS, Conner C, Aagren M, Ruiz K, Bouchard J. Association between hypoglycaemic events and fall-related fractures in Medicare-covered patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:634–43.
Zoungas S, Patel A, Chalmers J, et al. Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1410–8.
Whitmer RA, Karter AJ, Yaffe K, Quesenberry CP Jr, Selby JV. Hypoglycemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 2009;301:1565–72.
Bloomfield HE, Greer N, Newman D, et al. Predictors and consequences of severe hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes—a systematic review of the evidence. VA-ESP Project #09-009. Washington, DC: Department of Veterans Affairs; 2012.
Heise T, Nosek L, Bottcher SG, Hastrup H, Haahr H. Ultra-long-acting insulin degludec has a flat and stable glucose-lowering effect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:944–50.
Heise T, Kaplan K, Haahr HL. Day-to-day and within-day variability in glucose-lowering effect between insulin degludec and insulin glargine (100 U/mL and 300 U/mL): a comparison across studies. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2018;12(2):356–63.
Heise T, Hermanski L, Nosek L, Feldman A, Rasmussen S, Haahr H. Insulin degludec: four times lower pharmacodynamic variability than insulin glargine under steady-state conditions in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:859–64.
Ratner R, Gough SC, Mathieu C, et al. Hypoglycaemia risk with insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine in type 2 and type 1 diabetes: a pre-planned meta-analysis of phase 3 trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:175–84.
Wysham C, Bhargava A, Chaykin L, et al. Effect of insulin degludec vs insulin glargine U100 on hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes: the SWITCH 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:45–56.
Lane W, Bailey TS, Gerety G, et al. Effect of insulin degludec vs insulin glargine U100 on hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes: the SWITCH 1 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:33–44.
Marso SP, McGuire DK, Zinman B, et al. Design of DEVOTE (trial comparing cardiovascular safety of insulin degludec vs insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk of cardiovascular events)—DEVOTE 1. Am Heart J. 2016;179:175–83.
Marso SP, McGuire DK, Zinman B, et al. Efficacy and safety of degludec versus glargine in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:723–32.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes 2017. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:S64–74.
Zoungas S, Woodward M, Li Q, et al. Impact of age, age at diagnosis and duration of diabetes on the risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications and death in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2014;57:2465–74.
Elliott L, Fidler C, Ditchfield A, Stissing T. Hypoglycemia event rates: a comparison between real-world data and randomized controlled trial populations in insulin-treated diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2016;7:45–60.
Meneghini L, Mersebach H, Kumar S, Svendsen AL, Hermansen K. Comparison of 2 intensification regimens with rapid-acting insulin aspart in type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled by once-daily insulin detemir and oral antidiabetes drugs: the step-wise randomized study. Endocr Pract. 2011;17:727–36.
Barendse S, Singh H, Frier BM, Speight J. The impact of hypoglycaemia on quality of life and related patient-reported outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a narrative review. Diabet Med. 2012;29:293–302.
Brod M, Christensen T, Thomsen TL, Bushnell DM. The impact of non-severe hypoglycemic events on work productivity and diabetes management. Value Health. 2011;14:665–71.
Bron M, Marynchenko M, Yang H, Yu AP, Wu EQ. Hypoglycemia, treatment discontinuation, and costs in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on oral antidiabetic drugs. Postgrad Med. 2012;124:124–32.
Seaquist ER, Anderson J, Childs B, et al. Hypoglycemia and diabetes: a report of a workgroup of the American Diabetes Association and the Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:1384–95.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. NICE process and methods guides. Guide to the methods of technology appraisal. 2013. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg9/chapter/the-reference-case. Accessed November 2017.
MIMS. MIMS monthly index of medical specialities. 2017. Available at: https://www.mims.co.uk/. Accessed October 2017.
Alva ML, Gray A, Mihaylova B, Leal J, Holman RR. The impact of diabetes-related complications on healthcare costs: new results from the UKPDS (UKPDS 84). Diabet Med. 2015;32:459–66.
Hammer M, Lammert M, Mejias SM, Kern W, Frier BM. Costs of managing severe hypoglycaemia in three European countries. J Med Econ. 2009;12:281–90.
Clarke P, Gray A, Holman R. Estimating utility values for health states of type 2 diabetic patients using the EQ-5D (UKPDS 62). Med Decis Making. 2002;22:340–9.
Evans M, Khunti K, Mamdani M, et al. Health-related quality of life associated with daytime and nocturnal hypoglycaemic events: a time trade-off survey in five countries. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013;11:90.
Personal Social Services Research Unit. The hospital and community health services index. 2016. Available at: http://www.pssru.ac.uk/pub/uc/uc2016/sources-of-information.pdf. Accessed October 2017.
Hunt B, Ye Q, Valentine WJ, Ashley D. Evaluating the long-term cost-effectiveness of daily administered GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in the United Kingdom. Diabetes Ther. 2017;8:129–47.
Sullivan PW, Ghushchyan VH. EQ-5D scores for diabetes-related comorbidities. Value Health. 2016;19:1002–8.
Palmer AJ, Roze S, Valentine WJ, et al. The CORE diabetes model: projecting long-term clinical outcomes, costs and cost-effectiveness of interventions in diabetes mellitus (types 1 and 2) to support clinical and reimbursement decision-making. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004;20(Suppl 1):S5–26.
Hayes A, Arima H, Woodward M, et al. Changes in quality of life associated with complications of diabetes: results from the ADVANCE study. Value Health. 2016;19:36–41.
Boye KS, Matza LS, Walter KN, Van BK, Palsgrove AC, Tynan A. Utilities and disutilities for attributes of injectable treatments for type 2 diabetes. Eur J Health Econ. 2011;12:219–30.
Evans M, Jensen HH, Bogelund M, Gundgaard J, Chubb B, Khunti K. Flexible insulin dosing improves health-related quality-of-life (HRQoL): a time trade-off survey. J Med Econ. 2013;16:1357–65.
Waugh N, Cummins E, Royle P, et al. Newer agents for blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14:1–248.
Currie CJ, Morgan CL, Poole CD, Sharplin P, Lammert M, McEwan P. Multivariate models of health-related utility and the fear of hypoglycaemia in people with diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006;22:1523–34.
Peyrot M, Barnett AH, Meneghini LF, Schumm-Draeger PM. Insulin adherence behaviours and barriers in the multinational global attitudes of patients and physicians in insulin therapy study. Diabet Med. 2012;29:682–9.
Fidler C, Elmelund CT, Gillard S. Hypoglycemia: an overview of fear of hypoglycemia, quality-of-life, and impact on costs. J Med Econ. 2011;14:646–55.
Nicolucci A, Kovacs Burns K, Holt RI, et al. Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes and Needs second study (DAWN2): cross-national benchmarking of diabetes-related psychosocial outcomes for people with diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013;30:767–77.
Evans M, Wolden M, Gundgaard J, Chubb B, Christensen T. Cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine in a basal-bolus regimen in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in the UK. J Med Econ. 2015;18:56–68.
Evans M, Chubb B, Gundgaard J. Cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2017;8:275–91.
Evans M, Wolden M, Gundgaard J, Chubb B, Christensen T. Cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine for patients with type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin—from the UK health care cost perspective. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:366–75.
Brod M, Wolden M, Christensen T, Bushnell DM. Understanding the economic burden of nonsevere nocturnal hypoglycemic events: impact on work productivity, disease management, and resource utilization. Value Health. 2013;16:1140–9.
Schnell O, Ryden L, Standl E, Ceriello A. Current perspectives on cardiovascular outcome trials in diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016;15:139.
Bagust A, Beale S. Modelling EuroQol health-related utility values for diabetic complications from CODE-2 data. Health Econ. 2005;14:217–30.
Acknowledgements
We thank the trial investigators, staff, and patients for their participation in the DEVOTE trial.
Funding
Sponsorship for the DEVOTE clinical trial, this study, and article processing charges were funded by Novo Nordisk A/S. All authors had full access to all of the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Medical Writing and Editorial Assistance
Medical writing support was provided by Anna Campbell, Ph.D., and editorial assistance was provided by Beverly La Ferla, of Watermeadow Medical, an Ashfield company, part of UDG Healthcare plc, and was funded by Novo Nordisk.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval to the version to be published.
Disclosures
Richard F. Pollock is a full-time employee of Ossian Health Economics and Communications GmbH, which received consultancy fees from Novo Nordisk to construct the model and conduct the analyses. William J. Valentine is also a full-time employee of Ossian Health Economics and Communications GmbH, which received consultancy fees from Novo Nordisk to construct the model and conduct the analyses. Steven P. Marso has received personal fees from Abbott Vascular, Novo Nordisk, University of Oxford, AstraZeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and research support from Novo Nordisk, The Medicines Company, and Terumo Medical. Jens Gundgaard is an employee of Novo Nordisk and also holds shares/stocks in Novo Nordisk. Nino Hallén is an employee of Novo Nordisk. Lars L. Hansen is an employee of Novo Nordisk. Deniz Tutkunkardas is an employee of Novo Nordisk. John B. Buse reports grant and consultation fees to the University of North Carolina (UNC) under contract and travel/meals/lodging for contracted activities from Novo Nordisk during the conduct of the study; grants and fees for consultation to UNC under contract and travel/meals/lodging for contracted activities from Eli Lilly, GI Dynamics, Amylin, Orexigen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Transtech Pharma, AstraZeneca, Takeda, Sanofi, and Lexicon; fees for consultation to UNC under contract and travel/meals/lodging for contracted activities from Hoffmann-La Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Liposcience, Elcelyx, Metavention, Dance Biopharm Inc, and Quest; grants from Medtronic Minimed, Tolerex, Osiris, Halozyme, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Andromeda, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Astellas, MacroGenics, Intarcia Therapeutics, and Scion NeuroStim; stock options in PhaseBio outside the submitted work; and is or has been a member of a variety of nonprofit boards: American Diabetes Association, DiabetesSisters, Taking Control of Your Diabetes, AstraZeneca Healthcare Foundation, Bristol-Myers Squib Together on Diabetes Foundation, and the National Diabetes Education Program.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article does not contain any new studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced Digital Features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.6128024.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Pollock, R.F., Valentine, W.J., Marso, S.P. et al. DEVOTE 5: Evaluating the Short-Term Cost-Utility of Insulin Degludec Versus Insulin Glargine U100 in Basal–Bolus Regimens for Type 2 Diabetes in the UK. Diabetes Ther 9, 1217–1232 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0430-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0430-4