Abstract
Background
Elymus atratus (Nevski) Hand.-Mazz. is perennial hexaploid wheatgrass. It was assigned to the genus Elymus L. sensu stricto based on morphological characters. Its genome constitution has not been disentangled yet.
Objective
To identify the genome constitution and origin of E. atratus.
Methods
In this study, genomic in situ hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization, and phylogenetic analysis based on the Acc1, DMC1 and matK sequences were performed.
Results
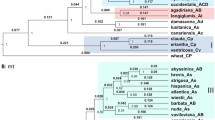
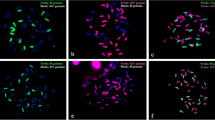
Genomic in situ hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization results reveal that E. atratus 2n = 6x = 42 is composed of 14 St genome chromosomes, 14 H genome chromosomes, and 14 Y genome chromosomes including two H-Y type translocation chromosomes, suggesting that the genome formula of E. atratus is StStYYHH. The phylogenetic analysis based on Acc1 and DMC1 sequences not only shows that the Y genome originated in a separate diploid, but also suggests that Pseudoroegneria (St), Hordeum (H), and a diploid species with Y genome were the potential donors of E. atratus. Data from chloroplast DNA showed that the maternal donor of E. atratus contains the St genome.
Conclusion
Elymus atratus is an allohexaploid species with StYH genome, which may have originated through the hybridization between an allotetraploid Roegneria (StY) species as the maternal donor and a diploid Hordeum (H) species as the paternal donor.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adderley S, Sun GL (2014) Molecular evolution and nucleotide diversity of nuclear plastid phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) gene in Triticeae (Poaceae). Gene 533:142–148
Assadi M, Runemark H (1995) Hybridisation, genomic constitution and generic delimitation in Elymus s. l. (Poaceae: Triticeae). Plant Syst Evol 194:189–205
Barkworth ME, Jacobs SWL (2009) Connorochloa: a new genus in Triticeae. Breed Sci 59:685–686
Baum BR, Yang JL, Yen C (1995) Taxonomic separation of Kengyilia (Poaceae: Triticeae) in relation to nearest related Roegneria, Elymus, and Agropyron, based on some morphological characters. Plant Syst Evol 194:123–132
Baum BR, Yang JL, Yen C, Agafonov AV (2011) A taxonomic synopsis of the genus Campeiostachys Drobov. J Syst Evol 49:146–159
Cai LB (1997) A taxonomical study on the genus Roegneria C. Koch from China. Acta Phytotax Sin 35:148–177
Dewey DR (1984) The genomic system of classification as a guide to intergeneric hybridization with the perennial Triticeae. In: Gustafson JP (ed) Gene manipulation in plant improvement: 16th Stadler genetics symposium. Springer US, Boston, pp 209–279
Dong ZZ, Fan X, Sha LN, Wang Y, Zeng J, Kang HY, Zhang HQ, Wang XL, Zhang L, Ding CB (2015) Phylogeny and differentiation of the St genome in Elymus L. sensu lato (Triticeae; Poaceae) based on one nuclear DNA and two chloroplast genes. BMC Plant Biol 15:179
Dou QW, Zhang TL, Tsujimoto H (2011) Physical mapping of repetitive sequences and genome analysis in six Elymus species by in situ hybridization. J Syst Evol 49:347–352
Doyle JJT, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Gao G, Gou XM, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Deng JB, Ding CB, Zhang L, Zhou YH, Yang RW (2014) Phylogenetic relationships and Y genome origin in Chinese Elymus (Triticeae: Poaceae) based on single copy gene DMC1. Biochem Syst Ecol 57:420–426
Guindon S, Delsuc F, Dufayard JF, Gascuel O (2009) Estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies with PhyML. Methods Mol Biol 537:113–137
Han FP, Gao Z, Birchler JA (2009) Reactivation of an inactive centromere reveals epigenetic and structural components for centromere specification in Maize. Plant Cell 21:1929–1939
Heslop-Harrison JS (1992) Molecular cytogenetics, cytology and genomic comparisons in the Triticeae. Hereditas 116:93–99
Huang SX, Sirikhachornkit A, Su XJ, Faris J, Gill B, Haselkorn R, Gornicki P (2002) Genes encoding plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of the Triticum/Aegilops complex and the evolutionary history of polyploid wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:8133–8138
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MrBayes: bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Jensen KB (1990) Cytology, fertility, and morphology of Elymus kengii (Keng) Tzvelev and E. grandiglumis (Keng) A. Lve (Triticeae: Poaceae). Genome 33:563–570
Kellogg EA, Appels R, Mason-Gamer RJ (1996) When genes tell different stories: the diploid genera of Triticeae (Gramineae). Syst Bot 21:321–347
Kimber G, Alonso LC (1981) The analysis of meiosis in hybrids. III. Tetraploid hybrids. Can J Genet Cytol 23:235–254
Kuo PC (1987) Flora republicae popularis sinicae. Science Press, Beijing
Lei YX, Fan X, Sha LN, Wang Y, Kang HY, Zhou YH, Zhang HQ (2016) Phylogenetic relationships and the maternal donor of Roegneria (Triticeae: Poaceae) based on three nuclear DNA sequences (ITS, Acc1, and Pgk1) and one chloroplast region (trnL-F). J Syst Evol 65:185–191
Lei YX, Liu J, Fan X, Sha LN, Wang Y, Kang HY, Zhou YH, Zhang HQ (2018) Phylogeny and maternal donor of Roegneria and its affinitive genera (Poaceae: Triticeae) based on sequence data for two chloroplast DNA regions (ndhF and trnH–psbA). J Syst Evol 56:105–119
Lei YX, Fan X, Sha LN, Wang Y, Kang HY, Zhou YH, Zhang HQ (2022) Phylogenetic relationships and the maternal donor of Roegneria (Triticeae: Poaceae) based on three nuclear DNA sequences (ITS, Acc1, and Pgk1) and one chloroplast region (trnL-F). J Syst Evol 60:305–318
Li CB, Zhang DM, Ge S, Lu BR, Hong DY (2001) Identification of genome constitution of Oryza malampuzhaensis, O. minuta, and O. punctata by multicolor genomic in situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 103:204–211
Liu YH (1985) Studies on the karyotypes of 11 species of Elymus from China. Plant Sci J 3:325–330
Liu QL, Ge S, Tang HB, Zhang XL, Zhu GF, Lu BR (2006) Phylogenetic relationships in Elymus (Poaceae: Triticeae) based on the nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and chloroplast trnL-F sequences. New Phytol 170:411–420
Liu QL, Liu L, Ge S, Fu LP, Bai SQ, Lv X, Wang QK, Chen W, Wang FY, Wang LH et al (2022) Endo-allopolyploidy of autopolyploids and recurrent hybridization—A possible mechanism to explain the unresolved Y-genome donor in polyploid Elymus species (Triticeae: Poaceae). J Syst Evol 60:344–360
Löve Á (1984) Conspectus of the Triticeae. Feddes Repertorium 95:425–521
Lu BR (1993) Meiotic studies of Elymus nutans and E. jacquemontii (Poaceae, Triticeae) and their hybrids with Pseudoroegneria spicata and seventeen Elymus species. Plant Syst Evol 186:193–212
Lu BR, Yan J, Yang JL (1990) Cytological observations on Triticeae materials from Xinjiang. Acta Bot Yunnan 12:57–66
Lucía V, Enrique R, Anamthawat-Jónsson K, Martínez-Ortega MM (2019) Cytogenetic evidence for a new genus of Triticeae (Poaceae) endemic to the Iberian Peninsula: description and comparison with related genera. Bot J Linn Soc 4:523–546
Mason-Gamer RJ, Orme NL, Anderson CM (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of north American Elymus and the monogenomic Triticeae (Poaceae) using three chloroplast DNA data sets. Genome 45:991–1002
Mason-Gamer RJ, Burns MM, Naum M (2005) Polyploidy, introgression, and complex phylogenetic patterns within Elymus. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 41:21–26
Middleton CP, Senerchia N, Stein N, Akhunov ED, Keller B, Wicker T, Kilian B (2014) Sequencing of chloroplast genomes from wheat, barley, rye and their relatives provides a detailed insight into the evolution of the Triticeae tribe. PLoS ONE 9:e85761
Nasernakhaei F, Rahiminejad MR, Saeidi H, Tavassoli M (2015) Phylogenetic relationships among the Iranian Triticum diploid gene pool as inferred from the loci Acc1 and Pgk1. Phytotaxa 201:111–121
Okito P, Mott IW, Wu YJ, Wang RC (2009) A Y genome specific STS marker in Pseudoroegneria and Elymus species (Triticeae: Gramineae). Genome 52:391–400
Ørgaard M, Heslop-Harrison JS (1994) Investigation of genome relationships between Leymus psathyrostachys and Hordeum inferred from genomic DNA: DNA in situ hybridization. Ann Botany 73:195–203
Petersen G, Seberg O (2002) Molecular evolution and phylogenetic application of DMC1. Mol Phylogenet Evol 22:43–50
Petersen G, Seberg O, Yde M, Berthelsen K (2006) Phylogenetic relationships of Triticum and Aegilops and evidence for the origin of the A, B, and D genomes of common wheat (Triticum aestivum). Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:70–82
Petersen G, Seberg O, Salomon B (2011) The origin of the H, St, W, and Y genomes in allotetraploid species of Elymus L. and Stenostachys Turcz. (Poaceae: Triticeae). Plant Syst Evol 291:197–210
Posada D, Crandall K (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Rauscher JT, Doyle JJ, Brown AH (2004) Multiple origins and nrDNA internal transcribed spacer homeologue evolution in the Glycine tomentella (Leguminosae) allopolyploid complex. Genetics 166:987–998
Sakamoto S, Muramatsu M (1966) Cytogenetic studies in the tribe Triticeae. II. Tetraploid and hexaploid hybrids of Agropyron. Japanese J Genet 41:155–168
Sears ER (1954) The aneuploids of common wheat. In, pp 1–59
Sha LN, Fan X, Yang RW, Kang HY, Ding CB, Zhang L, Zheng YL, Zhou YH (2010) Phylogenetic relationships between Hystrix and its closely related genera (Triticeae; Poaceae) based on nuclear Acc1, DMC1 and chloroplast trnL-F sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 54:327–335
Sha LN, Fan X, Wang XL, Dong ZZ, Zeng J, Zhang HQ, Kang HY, Wang Y, Liao JQ, Zhou YH (2017) Genome origin, historical hybridization and genetic differentiation in Anthosachne australasica (Triticeae; Poaceae), inferred from chloroplast rbc L, trn H- psb A and nuclear Acc1 gene sequences. Ann Botany 119:95–107
Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Tate JA (2004) Advances in the study of polyploidy since plant speciation. New Phytol 161:173–191
Sun G, Komatsuda T (2010) Origin of the Y genome in Elymus and its relationship to other genomes in Triticeae based on evidence from elongation factor G (EF-G) gene sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 56:727–733
Sun G, Ni Y, Daley T (2008) Molecular phylogeny of RPB2 gene reveals multiple origin, geographic differentiation of H genome, and the relationship of the Y genome to other genomes in Elymus species. Mol Phylogenet Evol 46:897–907
Tan L, Zhang HQ, Chen WH, Deng MQ, Zhou YH (2021) Genome composition and taxonomic revision of Elymus purpuraristatus and Roegneria calcicola (Poaceae: Triticeae) based on cytogenetic and phylogenetic analyses. Bot J Linn Soc 196:245–255
Tan L, Huang QX, Song Y, Wu DD, Cheng YR, Zhang CB, Sha LN, Fan X, Kang HY, Wang Y et al (2022) Biosystematics studies on Elymus breviaristatus and Elymus sinosubmuticus (Poaceae: Triticeae). BMC Plant Biol 22:57
Tang C, Qi J, Chen N, Sha LN, Wang Y, Zeng J, Kang HY, Zhang HQ, Zhou YH, Fan X (2017) Genome origin and phylogenetic relationships of Elymus villosus (Triticeae: Poaceae) based on single-copy nuclear Acc1, Pgk1, DMC1 and chloroplast trnL-F sequences. Biochem Syst Ecol 70:168–176
Torabinejad J, Mueller RJ (1993) Genome analysis of intergeneric hybrids of apomictic and sexual Australian Elymus species with wheat, barley and rye: implication for the transfer of apomixis to cereals. Theor Appl Genet 86:288–294
Wang L, Shi QH, Su HD, Wang Y, Sha LN, Fan X, Kang HY, Zhang HQ, Zhou YH (2017) St2-80 - a new FISH marker for St genome and genome analysis in Triticeae. Genome 60:553–563
Wang L, Jiang YY, Shi QH, Wang Y, Sha LN, Fan X, Kang HY, Zhang HQ, Sun GL, Zhang L et al (2019) Genome constitution and evolution of Elytrigia lolioides inferred from Acc1, EF-G, ITS, TrnL-F sequences and GISH. BMC Plant Biol 19:158
Yan C, Hu Q, Sun G (2014) Nuclear and chloroplast DNA phylogeny reveals complex evolutionary history of Elymus pendulinus. Genome 57:97–109
Yang CR, Zhang HQ, Zhao FQ, Liu XY, Fan X, Sha LN, Kang HY, Wang Y, Zhou YH (2015) Genome constitution of Elymus tangutorum (Poaceae: Triticeae)inferred from meiotic pairing behavior and genomic in situ hybridization. J Syst Evol 53:529–534
Yang C-R, Baum B-R, Chen W-H, Zhang H-Q, Liu X-Y, Fan X, Sha L-N, Kang H-Y, Wang Y, Zhou Y-H (2016) Genomic constitution and taxonomy of the Chinese hexaploids Elymus cylindricus and E. breviaristatus (Poaceae: Triticeae). Bot J Linn Soc 182:650–657
Yen C, Yang JL (1990) Kengyilia gobicola, a new taxon from West China. Can J Bot 68:1894–1897
Yen C, Yang JL, Baum BR (2005) Douglasdeweya: a new genus, with a new species and a new combination (Triticeae: Poaceae). Can J Bot 83:413–419
Yen C, Yang JL, Baum BR (2006) Biosystematics of Triticeae: volume I. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Yen C, Yang JL, Baum BR (2011) Biosystematics of Triticeae: volume III. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Yen C, Yang JL, Baum BR (2013) Biosystematics of Triticeae: volume V. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Yu HQ, Zhang C, Ding CB, Zhang HQ, Zhou YH (2010) Genome constitutions of Roegneria alashanica, R. elytrigioides, R. magnicaespes and R. grandis (Poaceae: Triticeae) via genomic in-situ hybridization. Nord J Bot 28:1–6
Zhang HQ, Zhou YH (2007) Meiotic analysis of the interspecific and intergeneric hybrids between Hystrix patula Moench and H. Duthiei ssp. longearistata, Pseudoroegneria, Elymus, Roegneria, and Psathyrostachys species (Poaceae, Triticeae). Bot J Linn Soc 153:213–219
Zhang HQ, Yang RW, Dou QW, Tsujimoto H, Zhou YH (2006) Genome constitutions of Hystrix patula, H. duthiei ssp. duthiei and H. duthiei ssp. longearistata (Poaceae: Triticeae) revealed by meiotic pairing behavior and genomic in-situ hybridization. Chromosome Res 14:595–604
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our appreciation to Xuehua Deng for her management of the experimental plants. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32270388 and 32200180) and the Science and Technology Bureau of Sichuan Province (23NSFSC1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1 The accession numbers of Acc1 gene sequences used in phylogenetic analysis; Table S2 The accession numbers of DMC1 gene sequences used in phylogenetic analysis; Table S3 The accession numbers of matK gene sequences used in phylogenetic analysis. Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, L., Wu, DD., Zhang, CB. et al. Genome constitution and evolution of Elymus atratus (Poaceae: Triticeae) inferred from cytogenetic and phylogenetic analysis. Genes Genom 46, 589–599 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-024-01496-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-024-01496-9