Abstract
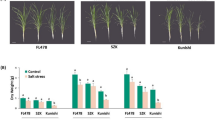
Herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) is easily injured by heat stress (HS), which greatly restricts its application and promotion. In this study, the thermo-tolerance of three representative P. lactiflora cultivars had been firstly assessed. ‘Zifengyu’ was identified as the thermo-tolerant cultivar with relatively lower values and smaller variations in malondialdehyde, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and proline contents under HS. Subsequently, their transcriptomes were sequenced by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) technology to construct a complete database. 81,599 unigenes were obtained, and 34,940 unigenes had been annotated. Moreover, through digital gene expression analysis of thermo-tolerant ‘Zifengyu’ and moderately thermo-tolerant ‘Hongyanzhenghui’, 161 heat stress response genes had been screened involving heat shock protein genes, plant hormone signal transduction related genes, fatty acid synthesis genes, reactive oxygen species-scavenging genes and secondary metabolites related genes. And the effectively and timely response of these genes to HS could endow thermo-tolerance to ‘Zifengyu’. Among these genes, 11 key thermo-tolerant related genes whose expressions were all significantly up-regulated in ‘Zifengyu’ and ‘Hongyanzhenghui’ during development and the former possessed higher levels could be regarded as the candidate genes, including isoprene synthase gene, 2 peroxidase genes, 3-oxoacyl-acyl carrier protein reductase gene (FabG), 3 transcription factor genes (bHLH, NAC and WRKY), HSP20 and 3 HSP70. These results could provide a better understanding of heat stress response in P. lactiflora, and pave for the breeding of thermo-tolerant cultivars.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Whaibi MH (2011) Plant heat-shock proteins: a mini review. J King Saud Univ Sci 23:139–150
Audic S, Claverie JM (1997) The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res 7:986–995
Barnabas B, Jaeger K, Feher A (2008) The effect of drought and heat stress on reproductive processes in cereals. Plant Cell Environ 31:11–38
Chauhan H, Khurana N, Agarwal P, Khurana P (2011) Heat shock factors in rice (Oryza sativa L.): genome-wide expression analysis during reproductive development and abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genomics 286:171–187
Chauhan H, Khurana N, Nijhavan A, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2012) The wheat chloroplastic small heat shock protein (sHSP26) is involved in seed maturation and germination and imparts tolerance to heat stress. Plant Cell Environ 35:1912–1931
Chen J, Huang P, McCarl BA, Shiva L (2014) Climate change, society, and agriculture: an economic and policy perspective. In: Alfen NKV (ed) Encyclopedia of agriculture and food systems. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 294–306
Chinnusamy V, Schumaker K, Zhu JK (2004) Molecular genetic perspectives on cross-talk and specificity in abiotic stress signalling in plants. J Exp Bot 55:225–236
Chung E, Kim KM, Lee JH (2013) Genome-wide analysis and molecular characterization of heat shock transcription fctor family in Glycine max. J Genet Genomics 40:127–135
Cruz RM, Vieira MC, Silva CL (2006) Effect of heat and thermosonication treatments on peroxidase inactivation kinetics in watercress (Nasturtium officinale). J Food Eng 72:8–15
Cvikrova M, Gemperlova L, Dobra J, Martincova O, Prasil IT, Gubis J, Vankova R (2012) Effect of heat stress on polyamine metabolism in proline-over-producing tobacco plants. Plant Sci 182:49–58
Gong SJ, Hao ZJ, Meng JS, Liu D, Wei MR, Tao J (2015) Digital gene expression analysis to screen disease resistance-relevant genes from leaves of herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) infected by Botrytis cinerea. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0133305
Guertin MJ, Lis JT (2010) Chromatin landscape dictates HSF binding to target DNA elements. PLoS Genet 6:e1001114. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001114
Guo J, Wu J, Ji Q, Wang C, Luo L, Yuan Y, Wang Y, Wang J (2008) Genome-wide analysis of heat shock transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. J Genet Genomics 35:105–118
Han CX (2013) Preliminary research on physiological mechanism of thermostability in herbaceous peony. Masters dissertation, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, pp 15–16 (in Chinese)
Havaux M (1998) Carotenoids as membrane stabilizers in chloroplasts. Trends Plant Sci 3:147–151
Horváth I, Glatza A, Nakamotob H, Mishkindd M, Munnike T, Saidif Y, Goloubinofff P, Harwoodg J, Vigha L (2012) Heat shock response in photosynthetic organisms: membrane and lipid connections. Prog Lipid Res 51:208–220
Hu W, Hu G, Han B (2009) Genome-wide survey and expression profiling of heat shock proteins and heat shock factors revealed overlapped and stress specific response under abiotic stresses in rice. Plant Sci 176:583–590
Janka E, Korner O, Rosenqvist E, Ottosen CO (2013) High temperature stress monitoring and detection using chlorophyll a fluorescence and infrared thermography in chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflora). Plant Physiol Bioch 67:87–94
Joyce SM, Cassells AC, Jain SM (2003) Stress and aberrant phenotypes in in vitro culture. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 74:103–121
Kawanishi T, Shima K, Hayashi H, Douzono M, Hisamatsu T (2012) Effect of short-term rising temperature treatment performed around the end of the day on the growth, flowering, and cut-flower quality of spray-type chrysanthemums. Hortic Res 11:241–249
Kim OT, Cha SW, Park HW, Hyun DY, Bang KH, Jung SJ, Kim YC, Shin YS, Kim DH, Kim SW, Seong NS, Cha SW, Park HW (2007) Thermotolerant transgenic ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) by introducing isoprene synthase gene through Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Korean J Med Crop Sci 15:95–99
Kotak S, Larkindale J, Lee U, von Koskull-Doering P, Vierling E, Scharf KD (2007) Complexity of the heat stress response in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:310–316
Li R, Yu C, Li Y, Lam TW, Yiu SM, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2009) SOAP2: an improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 25:1966–1967
Liang WD, Bi YT, Wang HY, Dong S, Li KS, Li JS (2013) Gene expression profiling of Clostridium botulinum under heat shock stress. BioMed Res Int 2013:760904
Liu XZ, Huang BR (2000) Heat stress injury in relation to membrane lipid peroxidation in creeping bentgrass. Crop Sci 40:503–510 (in Chinese)
Lockhart DJ, Winzeler EA (2000) Genomics, gene expression and DNA arrays. Nature 405:827–836
Lv C, Liu L (2008) Effects of high temperature on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Paeonia lactiflora. J Hunan Agric Univ (Nat Sci) 34:664–667 (in Chinese)
Maestri E, Klueva N, Perrotta C, Gulli M, Nguyen HT, Marmiroli N (2002) Molecular genetics of heat tolerance and heat shock proteins in cereals. Plant Mol Biol 48:667–681
Meehl GA, Tebaldi C (2004) More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 305:994–997
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5:621–628
Niu L, Fu X, Liu A (2010) Application of herbaceous peony in flower border. North Hortic 4:97–100 (in Chinese)
Nover L, Bharti K, Doring P, Mishra SK, Ganguli A, Scharf KD (2001) Arabidopsis and the heat stress transcription factor world: how many heat stress transcription factors do we need? Cell Stress Chaperon 6:177–189
Ranney TG, Blazich FA, Warren SL (1995) Heat tolerance of selected species and populations of rhododendron. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 120:423–428
Rivero RM, Ruiz JM, Garcia PC, Lopez-Lefebre LR, Sanchez E, Romero L (2001) Resistance to cold and heat stress: accumulation of phenolic compounds in tomato and watermelon plants. Plant Sci 160:315–321
Santos TBD, Budzinski IG, Marur CJ, Petkowicz CL, Pereira LF, Vieira LG (2011) Expression of three galactinol synthase isoforms in Coffea arabica L. and accumulation of raffinose and stachyose in response to abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:441–448
Savchenko G, Klyuchareva E, Abramchik L, Serdyuchenko E (2002) Effect of periodic heat shock on the inner membrane system of etioplasts. Russ J Plant Physiol 49:349–359
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3(6):1101–1108
Somerville C (1991) Plant lipids: metabolism, mutants, and membranes. Science 252:80
Sun J, Ren L, Cheng Y, Gao J, Dong B, Chen S, Chen F, Jiang J (2014) Identification of differentially expressed genes in Chrysanthemum nankingense (Asteraceae) under heat stress by RNA Seq. Gene 552:59–66
Suzuki N, Mittler R (2006) Reactive oxygen species and temperature stresses: a delicate balance between signaling and destruction. Physiol Plant 126:45–51
Turoczy Z, Kis P, Toeroek K, Cserhati M, Lendvai A, Dudits D, Horvath GV (2011) Overproduction of a rice aldo-keto reductase increases oxidative and heat stress tolerance by malondialdehyde and methylglyoxal detoxification. Plant Mol Biol 75:399–412
Vicente AR, Martínez GA, Chaves AR, Civello PM (2006) Effect of heat treatment on strawberry fruit damage and oxidative metabolism during storage. Postharvest Biol Technol 40:116–122
Wahid A (2007) Physiological implications of metabolite biosynthesis for net assimilation and heat-stress tolerance of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) sprouts. J Plant Res 120:219–228
Wahid A, Ghazanfar A (2006) Possible involvement of some secondary metabolites in salt tolerance of sugarcane. J Plant Physiol 163:723–730
Wahid A, Gelani S, Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Heat tolerance in plants: an overview. Environ Exp Bot 61:199–223
Wan XL, Zhou Q, Wang YY, Wang WE, Bao MZ, Zhang JW (2015) Identification of heat-responsive genes in carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.) by RNA-seq. Front. Plant Sci 6:519
Wang L, Li P, Brutnell TP (2010) Exploring plant transcriptomes using ultra high-throughput sequencing. Brief Funct Genomics 9:118–128
Webb L, Darbyshire R, Goodwin I (2014) Climate change: horticulture. In: Alfen NKV (ed) Encyclopedia of agriculture and food systems. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 266–283
Wu X, Kishitani S, Ito Y, Toriyama K (2009) Accumulation of raffinose in rice seedlings overexpressing OsWRKY11 in relation to desiccation tolerance. Plant Biotech 26:431–434
Xu S, Li JL, Zhang XQ, Wei H, Cui LJ (2006) Effects of heat acclimation pretreatment on changes of membrane lipid peroxidation, antioxidant metabolites, and ultrastructure of chloroplasts in two cool-season turfgrass species under heat stress. Environ Exp Bot 56:274–285
Yin H, Chen Q, Yi M (2008) Effects of short-term heat stress on oxidative damage and responses of antioxidant system in Lilium longiflorum. Plant Growth Regul 54:45–54
Zhang X, Li J, Liu A, Zou J, Zhou X, Xiang J, Rerksiri W, Peng Y, Xiong X, Chen X (2012) Expression profile in rice panicle: insights into heat response mechanism at reproductive stage. PLoS One 7:e49652. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049652
Zhang XW, Rerksiri W, Liu A, Zhou X, Xiong H, Xiang J, Chen X, Xiong X (2013) Transcriptome profile reveals heat response mechanism at molecular and metabolic levels in rice flag leaf. Gene 530:185–192
Zhao TY, Martin D, Meeley RB, Downie B (2004) Expression of the maize GALACTINOL SYNTHASE gene family: (II) Kernel abscission, environmental stress and myo-inositol influences accumulation of transcript in developing seeds and callus cells. Physiol Plant 121:647–655
Zhao DQ, Zhou CH, Tao J (2011) Carotenoid accumulation and carotenogenic genes expression during two types of persimmon fruit (Diospyros kaki L.) development. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:646–654
Zhao DQ, Tao J, Han CX, Ge JT (2012) An actin gene as the internal control for gene expression analysis in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). Afr J Agric Res 7(14):2153–2159
Zhao DQ, Jiang Y, Ning CL, Meng JS, Lin S, Ding W, Tao J (2014) Transcriptome sequencing of a chimaera reveals coordinated expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes mediating yellow formation in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). BMC Genom 15:689
Zhao DQ, Han CX, Zhou CH, Tao J (2015) Shade ameliorates high temperature-induced inhibition of growth in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora). Int J Agric Biol 17:911–919
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the College Natural Science Research of Jiangsu Province (14KJB210011), the Opening Project of Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Horticultural Crop Genetic Improvement (2014014), the Natural Science Foundation of Yangzhou City (YZ2014033), and the Priority Academic Program Development from Jiangsu Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Zhaojun Hao, Mengran Wei, Saijie Gong, Daqiu Zhao and Jun Tao declares no conflict of interest.
Studies with human or animal research
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Z., Wei, M., Gong, S. et al. Transcriptome and digital gene expression analysis of herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) to screen thermo-tolerant related differently expressed genes. Genes Genom 38, 1201–1215 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0465-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0465-8