Abstract
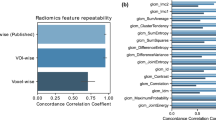
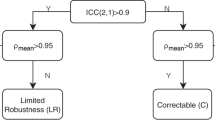
Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging using the amino acid tracer O-[2-(18F)fluoroethyl]-L-tyrosine (FET) has gained increased popularity within the past decade in the management of glioblastoma (GBM). Radiomics features extracted from FET PET images may be sensitive to variations when imaging at multiple time points. It is therefore necessary to assess feature robustness to test-retest imaging. Eight patients with histologically confirmed GBM that had undergone post-surgical test-retest FET PET imaging were recruited. In total, 1578 radiomic features were extracted from biological tumour volumes (BTVs) delineated using a semi-automatic contouring method. Feature repeatability was assessed using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The effect of both bin width and filter choice on feature repeatability was also investigated. 59/106 (55.7%) features from the original image and 843/1472 (57.3%) features from filtered images had an ICC ≥ 0.85. Shape and first order features were most stable. Choice of bin width showed minimal impact on features defined as stable. The Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG, σ = 5 mm) and Wavelet filters (HLL and LHL) significantly improved feature repeatability (p ≪ 0.0001, p = 0.003, p = 0.002, respectively). Correlation of textural features with tumour volume was reported for transparency. FET PET radiomic features extracted from post-surgical images of GBM patients that are robust to test-retest imaging were identified. An investigation with a larger dataset is warranted to validate the findings in this study.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, Van Den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. New Engl J Med 352:987–996
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJB, Janzer RC et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Shukla G, Alexander GS, Bakas S, Nikam R, Talekar K, Palmer JD et al (2017) Advanced magnetic resonance imaging in glioblastoma: a review. Chin Clin Oncol 6:40
Galldiks N, Langen KJ (2017) Amino acid PET in neuro-oncology: applications in the clinic. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 17:395–397
Langen KJ, Hamacher K, Weckesser M, Floeth F, Stoffels G, Bauer D et al (2006) O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine: uptake mechanisms and clinical applications. Nucl Med Biol 33:287–294
Overcast WB, Davis KM, Ho CY, Hutchins GD, Green MA, Graner BD et al (2021) Advanced imaging techniques for neuro-oncologic tumor diagnosis, with an emphasis on PET-MRI imaging of malignant brain tumors. Curr Oncol Rep 23:34
Verger A, Stoffels G, Bauer EK, Lohmann P, Blau T, Fink GR et al (2018) Static and dynamic (18)F-FET PET for the characterization of gliomas defined by IDH and 1p/19q status. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45:443–451
Vomacka L, Unterrainer M, Holzgreve A, Mille E, Gosewisch A, Brosch J et al (2018) Voxel-wise analysis of dynamic (18)F-FET PET: a novel approach for non-invasive glioma characterisation. EJNMMI Res 8:91
Weckesser M, Langen KJ, Rickert CH, Kloska S, Straeter R, Hamacher K et al (2005) O-(2-[18F]fluorethyl)-L-tyrosine PET in the clinical evaluation of primary brain tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:422–429
Song S, Cheng Y, Ma J, Wang L, Dong C, Wei Y et al (2020) Simultaneous FET-PET and contrast-enhanced MRI based on hybrid PET/MR improves delineation of tumor spatial biodistribution in gliomas: a biopsy validation study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 47:1458–1467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04656-2
Rapp M, Heinzel A, Galldiks N, Stoffels G, Felsberg J, Ewelt C et al (2013) Diagnostic performance of 18F-FET PET in newly diagnosed cerebral lesions suggestive of glioma. J Nucl Med 54:229–235
Harat M, Malkowski B, Makarewicz R (2016) Pre-irradiation tumour volumes defined by MRI and dual time-point FET-PET for the prediction of glioblastoma multiforme recurrence: A prospective study. Radiother Oncol 120:241–247
Niyazi M, Geisler J, Siefert A, Schwarz SB, Ganswindt U, Garny S et al (2011) FET-PET for malignant glioma treatment planning. Radiother Oncol 99:44–48
Henriksen OM, Larsen VA, Muhic A, Hansen AE, Larsson HBW, Poulsen HS et al (2016) Simultaneous evaluation of brain tumour metabolism, structure and blood volume using [(18)F]-fluoroethyltyrosine (FET) PET/MRI: feasibility, agreement and initial experience. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43:103–112
Vees H, Senthamizhchelvan S, Miralbell R, Weber DC, Ratib O, Zaidi H (2009) Assessment of various strategies for 18F-FET PET-guided delineation of target volumes in high-grade glioma patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:182–193
Pauleit D, Floeth F, Hamacher K, Riemenschneider MJ, Reifenberger G, Muller HW et al (2005) O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET combined with MRI improves the diagnostic assessment of cerebral gliomas. Brain 128:678–687
Pauleit D, Stoffels G, Bachofner A, Floeth FW, Sabel M, Herzog H et al (2009) Comparison of (18)F-FET and (18)F-FDG PET in brain tumors. Nucl Med Biol 36:779–787
Jansen NL, Suchorska B, Wenter V, Schmid-Tannwald C, Todica A, Eigenbrod S et al (2015) Prognostic significance of dynamic 18F-FET PET in newly diagnosed astrocytic high-grade glioma. J Nucl Med 56:9–15
Poulsen SH, Urup T, Grunnet K, Christensen IJ, Larsen VA, Jensen ML et al (2017) The prognostic value of FET PET at radiotherapy planning in newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44:373–381
Galldiks N, Dunkl V, Ceccon G, Tscherpel C, Stoffels G, Law I et al (2018) Early treatment response evaluation using FET PET compared to MRI in glioblastoma patients at first progression treated with bevacizumab plus lomustine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45:2377–2386
Galldiks N, Langen KJ, Holy R, Pinkawa M, Stoffels G, Nolte KW et al (2012) Assessment of treatment response in patients with glioblastoma using O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET in comparison to MRI. J Nucl Med 53:1048–1057
Galldiks N, Dunkl V, Stoffels G, Hutterer M, Rapp M, Sabel M et al (2015) Diagnosis of pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma using O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42:685–695
Albert NL, Weller M, Suchorska B, Galldiks N, Soffietti R, Kim MM et al (2016) Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology working group and European Association for Neuro-Oncology recommendations for the clinical use of PET imaging in gliomas. Neuro Oncol 18:1199–1208
Galldiks N, Langen KJ, Albert NL, Chamberlain M, Soffietti R, Kim MM et al (2019) PET imaging in patients with brain metastasis-report of the RANO/PET group. Neuro Oncol 21:585–595
Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout RG, Granton P et al (2012) Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer 48:441–446
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278:563–577
Kebir S, Khurshid Z, Gaertner FC, Essler M, Hattingen E, Fimmers R et al (2017) Unsupervised consensus cluster analysis of [18F]-fluoroethyl-L-tyrosine positron emission tomography identified textural features for the diagnosis of pseudoprogression in high-grade glioma. Oncotarget 8:8294
Carles M, Popp I, Starke MM, Mix M, Urbach H, Schimek-Jasch T et al (2021) FET-PET radiomics in recurrent glioblastoma: prognostic value for outcome after re-irradiation? Radiat Oncol 16:46
Lohmann P, Elahmadawy MA, Gutsche R, Werner JM, Bauer EK, Ceccon G et al (2020) FET PET radiomics for differentiating pseudoprogression from early tumor progression in glioma patients post-chemoradiation. Cancers (Basel) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123835
Lohmann P, Kocher M, Ceccon G, Bauer EK, Stoffels G, Viswanathan S et al (2018) Combined FET PET/MRI radiomics differentiates radiation injury from recurrent brain metastasis. Neuroimage Clin 20:537–542
Lohmann P, Lerche C, Bauer EK, Steger J, Stoffels G, Blau T et al (2018) Predicting IDH genotype in gliomas using FET PET radiomics. Sci Rep 8:13328
Yip SS, Aerts HJ (2016) Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys Med Biol 61:R150–R166
Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich SA, Schabath MB et al (2012) Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging 30:1234–1248
Zwanenburg A (2019) Radiomics in nuclear medicine: robustness, reproducibility, standardization, and how to avoid data analysis traps and replication crisis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46:2638–2655
Lambin P, Leijenaar RTH, Deist TM, Peerlings J, de Jong EEC, van Timmeren J et al (2017) Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:749–762
Unterrainer M, Vettermann F, Brendel M, Holzgreve A, Lifschitz M, Zahringer M et al (2017) Towards standardization of (18)F-FET PET imaging: do we need a consistent method of background activity assessment? EJNMMI Res 7:48
Forghani R, Savadjiev P, Chatterjee A, Muthukrishnan N, Reinhold C, Forghani B (2019) Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence for Biomarker and Prediction Model Development in Oncology. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 17:995–1008
van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, Hosny A, Aucoin N, Narayan V et al (2017) Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res 77:e104–e107
Zwanenburg A, Vallières M, Abdalah MA, Aerts HJ, Andrearczyk V, Apte A et al (2020) The image biomarker standardization initiative: standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping. Radiology 295:328–338
Tixier F, Hatt M, Le Rest CC, Le Pogam A, Corcos L, Visvikis D (2012) Reproducibility of tumor uptake heterogeneity characterization through textural feature analysis in 18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med 53:693–700
Leijenaar RT, Nalbantov G, Carvalho S, van Elmpt WJ, Troost EG, Boellaard R et al (2015) The effect of SUV discretization in quantitative FDG-PET Radiomics: the need for standardized methodology in tumor texture analysis. Sci Rep 5:11075
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86:420
McGraw KO, Wong SP (1996) Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychol Methods 1:30
Traverso A, Wee L, Dekker A, Gillies R (2018) Repeatability and Reproducibility of Radiomic Features: A Systematic Review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 102:1143–1158
Koo TK, Li MY (2016) A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropractic Med 15:155–163
Brooks FJ, Grigsby PW (2014) The effect of small tumor volumes on studies of intratumoral heterogeneity of tracer uptake. J Nucl Med 55:37–42
Hatt M, Majdoub M, Vallieres M, Tixier F, Le Rest CC, Groheux D et al (2015) 18F-FDG PET uptake characterization through texture analysis: investigating the complementary nature of heterogeneity and functional tumor volume in a multi-cancer site patient cohort. J Nucl Med 56:38–44
Altazi BA, Zhang GG, Fernandez DC, Montejo ME, Hunt D, Werner J et al (2017) Reproducibility of F18-FDG PET radiomic features for different cervical tumor segmentation methods, gray-level discretization, and reconstruction algorithms. J Appl Clin Med Phys 18:32–48
van Timmeren JE, Leijenaar RTH, van Elmpt W, Wang J, Zhang Z, Dekker A et al (2016) Test-Retest Data for Radiomics Feature Stability Analysis: Generalizable or Study-Specific? Tomography 2:361–365
Gutsche R, Scheins J, Kocher M, Bousabarah K, Fink GR, Shah NJ et al (2021) Evaluation of FET PET radiomics feature repeatability in glioma patients. Cancers (Basel) 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040647
Shiri I, Hajianfar G, Sohrabi A, Abdollahi H, S PS, Geramifar P et al (2020) Repeatability of radiomic features in magnetic resonance imaging of glioblastoma: Test-retest and image registration analyses. Med Phys 47:4265–4280
Schwier M, van Griethuysen J, Vangel MG, Pieper S, Peled S, Tempany C et al (2019) Repeatability of Multiparametric Prostate MRI Radiomics Features. Sci Rep 9:9441
Peerlings J, Woodruff HC, Winfield JM, Ibrahim A, Van Beers BE, Heerschap A et al (2019) Stability of radiomics features in apparent diffusion coefficient maps from a multi-centre test-retest trial. Sci Rep 9:4800
Li Z, Duan H, Zhao K, Ding Y (2019) Stability of MRI Radiomics Features of Hippocampus: An Integrated Analysis of Test-Retest and Inter-Observer Variability. IEEE Access 7:97106–97116
van Timmeren JE, Cester D, Tanadini-Lang S, Alkadhi H, Baessler B (2020) Radiomics in medical imaging-“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 11:91
Ferjančič P, Ebert MA, Francis R, Nowak AK, Jeraj R (2021) Repeatability of quantitative 18F-FET PET in glioblastoma. Biomed Phys Eng Express 7:035020
Larue R, Van De Voorde L, van Timmeren JE, Leijenaar RTH, Berbee M, Sosef MN et al (2017) 4DCT imaging to assess radiomics feature stability: An investigation for thoracic cancers. Radiother Oncol 125:147–153
Zwanenburg A, Leger S, Agolli L, Pilz K, Troost EGC, Richter C et al (2019) Assessing robustness of radiomic features by image perturbation. Sci Rep 9:614
Hatt M, Tixier F, Le ChezeRest C, Pradier O, Visvikis D (2013) Robustness of intratumour 18F-FDG PET uptake heterogeneity quantification for therapy response prediction in oesophageal carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 40:1662–1671
van Velden FH, Kramer GM, Frings V, Nissen IA, Mulder ER, de Langen AJ et al (2016) Repeatability of Radiomic Features in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer [(18)F]FDG-PET/CT Studies: Impact of Reconstruction and Delineation. Mol Imaging Biol 18:788–795
Leijenaar RT, Carvalho S, Velazquez ER, van Elmpt WJ, Parmar C, Hoekstra OS et al (2013) Stability of FDG-PET Radiomics features: an integrated analysis of test-retest and inter-observer variability. Acta Oncol 52:1391–1397
Whybra P, Parkinson C, Foley K, Staffurth J, Spezi E (2019) Assessing radiomic feature robustness to interpolation in (18)F-FDG PET imaging. Sci Rep 9:9649
Funding
This work was supported by Pfizer Australia and the Australian and New Zealand Society of Nuclear Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Ethical Approval
The study used in this paper was performed in accordance with the “NHMRC Statement on Ethical Conduct in Human Research” (Commonwealth of Australia, 2007), the principles laid down by the 18th World Medical Assembly (Helsinki, 1964), and subsequent amendments.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barry, N., Rowshanfarzad, P., Francis, R.J. et al. Repeatability of image features extracted from FET PET in application to post-surgical glioblastoma assessment. Phys Eng Sci Med 44, 1131–1140 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-021-01049-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-021-01049-4