Abstract
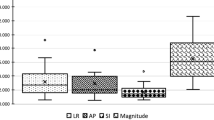
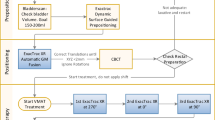
To perform implanted fiducial based real-time target position monitoring in pancreas stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) using the x-ray imaging system available in a Elekta linear accelerator. An in-house system was developed and clinically utilised for real-time target position monitoring of pancreas SBRT delivery. The developed system was used for the target position monitoring of a pancreas cancer patient treated in free breathing treatment within the study entitled ‘Mfolfirinox And STEreotactic Radiotherapy for Patients with Locally Advanced paNcreas cancer (MASTERPLAN): a feasibility study’ (ACTRN 12617001642370) consisting of five treatment fractions. The clinical efficacy of the system was studied by performing a retrospective cumulative dose assessment of delivered dose using observed position deviations. The developed system identified two events of baseline shifts in target position that exceeded the accepted tolerance level of ± 3 mm from reference planned position. The retrospective dose assessment study showed that if the position deviations were not detected and corrected for, the maximum dose to duodenum would have increased from 34.6 to 38.8 Gy. The first real-time position monitoring in pancreas SBRT on an Elekta linear accelerator was successfully performed. The developed system was shown to improve the safety and accuracy of SBRT delivery.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGuire S (2016) World cancer report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, international agency for research on cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv Nutr 7:419–419
Conlon KC, Klimstra DS, Brennan MF (1996) Long-term survival after curative resection for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 5-year survivors. Ann Surg 223:273
Assifi MM, Lu X, Eibl G, Reber HA, Li G, Hines OJ (2011) Neoadjuvant therapy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a meta-analysis of phase II trials. Surgery 150:466–473
Gillen S, Schuster T, Zum Büschenfelde CM, Friess H, Kleeff J (2010) Preoperative/neoadjuvant therapy in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of response and resection percentages. PLoS Med 7:e1000267
Boone BA, Steve J, Krasinskas AM, Zureikat AH, Lembersky BC, Gibson MK et al (2013) Outcomes with FOLFIRINOX for borderline resectable and locally unresectable pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol 108:236–241
Kharofa J, Kelly TR, Ritch PS, George B, Wiebe LA, Thomas JP et al (2012) 5-FU/leucovorin, irinotecan, oxaliplatin (FOLFIRINOX) induction followed by chemoXRT in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2012.30.15_suppl.e14613
Potters L, Kavanagh B, Galvin JM, Hevezi JM, Janjan NA, Larson DA et al (2010) American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) and American College of Radiology (ACR) practice guideline for the performance of stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:326–332
Abbas H, Chang B, Chen ZJ (2014) Motion management in gastrointestinal cancers. J Gastrointest Oncol 5:223
Chuong MD, Springett GM, Freilich JM, Park CK, Weber JM, Mellon EA et al (2013) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer is effective and well tolerated. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86:516–522
Minn AY, Schellenberg D, Maxim P, Suh Y, McKenna S, Cox B et al (2009) Pancreatic tumor motion on a single planning 4D-CT does not correlate with intrafraction tumor motion during treatment. Am J Clin Oncol 32:364–368
Suker M, Nuyttens JJ, Eskens FALM, Haberkorn BCM, Coene PPLO, van der Harst E et al (2019) Efficacy and feasibility of stereotactic radiotherapy after folfirinox in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC-1 trial). EClinicalMedicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2019.10.013
Brunner TB, Nestle U, Grosu AL, Partridge M (2015) SBRT in pancreatic cancer: what is the therapeutic window? Radiother Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2014.10.015
Akimoto M, Nakamura M, Nakamura A, Mukumoto N, Kishi T, Goto Y et al (2017) Inter-and intrafractional variation in the 3-dimensional positions of pancreatic tumors due to respiration under real-time monitoring. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 98:1204–1211
Chang DT, Schellenberg D, Shen J, Kim J, Goodman KA, Fisher GA et al (2009) Stereotactic radiotherapy for unresectable adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Cancer 115:665–672
Rudra S, Jiang N, Rosenberg SA, Olsen JR, Roach MC, Wan L et al (2019) Using adaptive magnetic resonance image-guided radiation therapy for treatment of inoperable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2100
Boldrini L, Cusumano D, Cellini F, Azario L, Mattiucci GC, Valentini V (2019) Online adaptive magnetic resonance guided radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer: State of the art, pearls and pitfalls. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-019-1275-3
Vinogradskiy Y, Goodman KA, Schefter T, Miften M, Jones BL (2019) The clinical and dosimetric impact of real-time target tracking in pancreatic SBRT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 103:268–275
Arumugam S, Sidhom M, Xing A, Holloway L (2016) An online x-ray based position validation system for prostate hypofractionated radiotherapy. Med Phys 43:961–974
Arumugam S, Sidhom M, Truant D, Xing A, Udovitch M, Holloway L (2017) Variable angle stereo imaging for rapid patient position correction in an in-house real-time position monitoring system. Phys Med 33:170–178
Pishvaian AC, Collins B, Gagnon G, Ahlawat S, Haddad NG (2006) EUS-guided fiducial placement for CyberKnife radiotherapy of mediastinal and abdominal malignancies. Gastrointest Endosc 64:412–417
Sothmann T, Blanck O, Poels K, Werner R, Gauer T (2016) Real time tracking in liver SBRT: comparison of CyberKnife and Vero by planning structure-based γ-evaluation and dose-area-histograms. Phys Med Biol 61:1677
Depuydt T, Poels K, Verellen D, Engels B, Collen C, Buleteanu M et al (2014) Treating patients with real-time tumor tracking using the vero gimbaled linac system: implementation and first review. Radiother Oncol 112:343–351
Feng M, Balter JM, Normolle D, Adusumilli S, Cao Y, Chenevert TL et al (2009) Characterization of pancreatic tumor motion using cine MRI: surrogates for tumor position should be used with caution. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.003
Zeng C, Xiong W, Li X, Reyngold M, Gewanter RM, Cuaron JJ et al (2019) Intrafraction tumor motion during deep inspiration breath hold pancreatic cancer treatment. J Appl Clin Med Phys. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12577
Batista V, Richter D, Chaudhri N, Naumann P, Herfarth K, Jäkel O (2018) Significance of intra-fractional motion for pancreatic patients treated with charged particles. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-1060-8
Ge J, Santanam L, Noel C, Parikh PJ (2013) Planning 4-dimensional computed tomography (4DCT) cannot adequately represent daily intrafractional motion of abdominal tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.09.014
James SS, Mishra P, Hacker F, Berbeco RI, Lewis JH (2012) Quantifying ITV instabilities arising from 4DCT: a simulation study using patient data. Phys Med Biol. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/57/5/L1
Friend G, O’Connor P, Charles P (2020) The effect of megavoltage field size on intrafraction cone-beam CT image quality. Phys Eng Sci Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-020-00870-7
Poulsen PR, Jonassen J, Schmidt ML, Jensen C (2015) Improved quality of intrafraction kilovoltage images by triggered readout of unexposed frames. Med Phys. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4933248
Ruan D, Fessler JA, Balter JM, Sonke J (2006) Exploring breathing pattern irregularity with projection-based method. Med Phys 33:2491–2499
Rankine L, Wan H, Parikh P, Maughan N, Poulsen P, DeWees T et al (2016) Cone-beam computed tomography internal motion tracking should be used to validate 4-dimensional computed tomography for abdominal radiation therapy patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95:818–826
Hoogeman M, Prévost J-B, Nuyttens J, Pöll J, Levendag P, Heijmen B (2009) Clinical accuracy of the respiratory tumor tracking system of the cyberknife: assessment by analysis of log files. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:297–303
Falk M, af Rosenschöld PM, Keall P, Cattell H, Cho BC, Poulsen P et al (2010) Real-time dynamic MLC tracking for inversely optimized arc radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 94:218–223
Bae SH, Kim M-S, Cho CK, Kang J-K, Lee SY, Lee K-N et al (2012) Predictor of severe gastroduodenal toxicity after stereotactic body radiotherapy for abdominopelvic malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:e469–e474
Verma V, Lazenby AJ, Zheng D, Bhirud AR, Ly QP, Are C et al (2017) Dosimetric parameters correlate with duodenal histopathologic damage after stereotactic body radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer: secondary analysis of a prospective clinical trial. Radiother Oncol 122:464–469
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by a human research ethics committee, South Western Sydney Local Health District, Australia.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugam, S., Pavey, D., Oar, A. et al. The first real-time intrafraction target position monitoring in pancreas SBRT on an Elekta linear accelerator. Phys Eng Sci Med 44, 625–638 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-021-01007-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-021-01007-0