Abstract
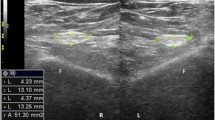
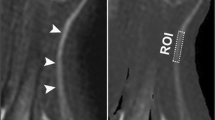
Ultrasound is an effective tool for peripheral disease with direct imaging of morphological and echogenic changes, but it has limitations when applied to evaluation of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The aim of this study was to assess the role of ultrasound to quantitatively evaluate diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rat sciatic nerve. In our experiments, ultrasound imaging and electrophysiological examination testing of sciatic nerves were monitored in diabetic and control rats at the period of 1st and 4th month of hyperglycemia. Cross sectional area, intraneural echo intensity, inner diameter, motor nerve conduction velocity, and histological changes were measured and compared between diabetic and control groups. Intraneural hyperechoic were observed in the diabetic rats, and the echo intensity of the sciatic nerve was increased in diabetic rats rather than control lean rats at 4th month of hyperglycemia (p < 0.05), which has shown a similar correlation with functional deficit and histological changes based on the severity of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. We conclude that the echo intensity is potentially useful in detecting diabetic peripheral neuropathy, which can pave the way for more accurate and efficient diagnosis in clinical study.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vinik AI, Mehrabyan A (2004) Diabetic neuropathies. Med Clin N Am 88(4):947–949, xi
Bloomgarden ZT (2008) Diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 31(3):616–621
Dyck PJ (1988) Detection, characterization, and staging of polyneuropathy: assessed in diabetics. Muscle Nerve 11(1):21–32
Tesfaye S, Boulton AJ, Dyck PJ, Freeman R, Horowitz M, Kempler P, Lauria G, Malik RA, Spallone V, Vinik A, Bernardi L, Valensi P, Toronto Diabetic Neuropathy Expert Group (2010) Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 33:2285–2293
Dyck PJ, Overland CJ, Low PA, Litchy WJ, Davies JL, Dyck PJ, O’Brien PC, Cl vs. NPhys Trial Investigators, Albers JW, Andersen H, Bolton CF, England JD, Klein CJ, Llewelyn JG, Mauermann ML, Russell JW, Singer W, Smith AG, Tesfaye S, Vella A (2010) Signs and symptoms versus nerve conduction studies to diagnose diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy: Cl vs. NPhys trial. Muscle Nerve 42(2):157–164
Valensi P, Attali JR, Gagant S (1993) Reproducibility of parameters for assessment of diabetic neuropathy. Diabet Med 10(10):933–939
Vinik AI, Suwanwalaikorn S, Stansberry KB, Holland MT, McNitt PM, Colen LE (1995) Quantitative measurement of cutaneous perception in diabetic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 18(6):574–584
Shy ME, Frohman EM, So YT, Arezzo JC, Cornblath DR, Giuliani MJ, Kincaid JC, Ochoa JL, Parry GJ, Weimer LH, Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology (2003) Quantitative sensory testing: report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 60(6):898–904
Rahman M, Griffin SJ, Rathmann W, Wareham NJ (2003) How should peripheral neuropathy be assessed in people with diabetes in primary care? A population-based comparison of four measures. Diabet Med 20(5):368–374
Boulton AJ, Malik RA, Arezzo JC, Sosenko JM (2004) Diabetic somatic neuropathies. Diabetes Care 27(6):1458–1486
Beekman R, Visser LH (2004) High-resolution sonography of the peripheral nervous system—a review of the literature. Eur J Neurol 11(5):305–314
Hollister AM, Simoncini A, Sciuk A, Jordan J (2012) High frequency ultrasound evaluation of traumatic peripheral nerve injuries. Neurol Res 34(1):98–103
Watanabe T, Ito H, Sekine A, Katano Y, Nishimura T, Kato Y, Takeda J, Seishima M, Matsuoka T (2010) Sonographic evaluation of the peripheral nerve in diabetic patients: the relationship between nerve conduction studies, echo intensity, and cross-sectional area. J Ultrasound Med 29(5):697–708
Zheng Y, Wang L, Krupka TM, Wang Z, Lu G, Zhang P, Zuo G, Li P, Ran H, Jian H (2013) The feasibility of using high frequency ultrasound to assess nerve ending neuropathy in patients with diabetic foot. Eur J Radiol 82(3):512–517
Liu F, Zhu J, Wei M, Bao Y, Hu B (2012) Preliminary evaluation of the sural nerve using 22-MHz ultrasound: a new approach for evaluation of diabetic cutaneous neuropathy. PLoS One 7(4):e32730
Lee D, Dauphinee DM (2005) Morphological and functional changes in the diabetic peripheral nerve: using diagnostic ultrasound and neurosensory testing to select candidates for nerve decompression. J Am Pediatr Med Assoc 95(5):433–437
Hobson-Webb LD, Massey JM, Juel VC (2013) Nerve ultrasound in diabetic polyneuropathy: correlation with clinical characteristics and electrodiagnostic testing. Muscle Nerve 47(3):379–384
Boom J, Visser LH (2012) Quantitative assessment of nerve echogenicity: comparison of methods for evaluating nerve echogenicity in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Clin Neurophysiol 123(7):1446–1453
Lee H, Brekelmans GJF, Visser LH (2016) Quantitative assessment of nerve echogenicity as an additional tool for evaluation of common fibular neuropathy. Clin Neurophysiol 127(1):874–879
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53(1):55–63
Brussee V, Guo G, Dong Y, Cheng C, Martinez JA, Smith D, Glazner GW, Fernyhough P, Zochodne DW (2008) Distal degenerative sensory neuropathy in a long-term type 2 diabetes rat model. Diabetes 57(6):1664–1673
Cameron NE, Cotter MA, Robertson S (1989) The effect of aldose reductase inhibition on the pattern of nerve conduction deficits in diabetic rats. Q J Exp Physiol 74(6):917–926
Klauser AS, Abd Ellah MM, Halpern EJ, Siedentopf C, Auer T, Eberle G, Bellmann-Weiler R, Kremser C, Sojer M, Löscher WN, Gabl MF, Feuchtner GM, Jaschke WR (2015) Sonographic cross-sectional area measurement in carpal tunnel syndrome patients: can delta and ratio calculations predict severity compared to nerve conduction studies? Eur Radiol 25(8):2419–2427
Shevalye H, Watcho P, Stavniichuk R, Dyukova E, Lupachyk S, Obrosova IG (2012) Metanx alleviates multiple manifestations of peripheral neuropathy and increases intraepidermal nerve fiber density in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Diabetes 61(8):2126–2133
De Visser A, Hemming A, Yang C, Zaver S, Dhaliwal R, Jawed Z, Toth C (2014) The adjuvant effect of hypertension upon diabetic peripheral neuropathy in experimental type 2 diabetes. Neurobiol Dis 62:18–30
Schreiber S, Oldag A, Kornblum C, Kollewe K, Kropf S, Schoenfeld A, Feistner H, Jakubiczka S, Kunz WS, Scherlach C, Tempelmann C, Mawrin C, Dengler R, Schreiber F, Goertler M, Vielhaber S (2013) Sonography of the median nerve in CMT1A, CMT2A, CMTX, and HNPP. Muscle Nerve 47(3):385–395
Rajabally YA, Morlese J, Kathuria D, Khan A (2012) Median nerve ultrasonography in distinguishing neuropathy sub-types: a pilot study. Acta Neurol Scand 125(4):254–259
Zaidman CM, Al-Lozi M, Pestronk A (2009) Peripheral nerve size in normals and patients with polyneuropathy: an ultrasound study. Muscle Nerve 40(6):960–966
Tagliafico A, Tagliafico G, Martinoli C (2010) Nerve density: a new parameter to evaluate peripheral nerve pathology on ultrasound. Preliminary study. Ultrasound Med Biol 36(10):1588–1593
Fazan VP, Rodrigues Filho OA, Jordão CE, Moore KC (2009) Phrenic nerve diabetic neuropathy in rats: unmyelinated fibers morphometry. J Peripher Nerv Syst 14(2):137–145
Kroin JS, Buvanendran A, Williams DK, Wagenaar B, Moric M, Tuman KJ, Kerns JM (2010) Local anesthetic sciatic nerve block and nerve fiber damage in diabetic rats. Reg Anesth Pain Med 35(4):343–350
Krishnan AV, Lin CS, Kiernan MC (2008) Activity-dependent excitability changes suggest Na+/K+ pump dysfunction in diabetic neuropathy. Brain 131(5):1209–1216
Malik RA (1997) The pathology of human diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 46(Suppl 2):S50–S53
Wang D, Zhang X, Lu L, Li H, Zhang F, Chen Y, Shen J (2015) Assessment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats with magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 25(2):463–471
Grant GA, Britz GW, Goodkin R, Jarvik JG, Maravilla K, Kliot M (2002) The utility of magnetic resonance imaging in evaluating peripheral nerve disorders. Muscle Nerve 25(3):314–331
Kim S, Choi JY, Huh YM, Song HT, Lee SA, Kim SM, Suh JS (2007) Role of magnetic resonance imaging in entrapment and compressive neuropathy-what, where, and how to see the peripheral nerves on the musculoskeletal magnetic resonance image: part 2. Upper extremity. Eur Radiol 17(2):509–522
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Key Programs of the Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Shanghai (11JC1409500). We are grateful to clinical fellows, Dr Lan Jiang, Dr Han Zhang, and Dr Huimei Dong, who have contributed to this electrophysiological work over the years.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Hu, B. & Zhu, J. Study on the use of quantitative ultrasound evaluation of diabetic neuropathy in the rat sciatic nerve. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 39, 997–1005 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0448-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0448-8