Abstract
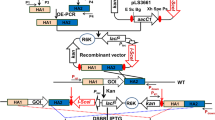
Rhodococcus strains not only have been widely used in industries but also have a potential ability of producing new structural natural products. Integration of heterologous genes into chromosomes of Rhodococcus strains for gene expression can facilitate the studies and applications of these strains. A conjugation system was optimized in order to transfer enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) encoding gene as a reporter from Escherichia coli into Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1. The influence of three native ribosome binding sites (RBSs) and two designed RBSs on the target protein production in R. erythropolis D-1 was also characterized. An efficient conjugation system of R. erythropolis D-1 was established to integrate EGFP gene into its chromosome. Among of five RBSs, RBS3 showed the highest translational activity in R. erythropolis D-1.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai N, Wang S, Abuduaini R, Zhang M, Zhu X, Zhao Y (2017) Rhamnolipid-aided biodegradation of carbendazim by Rhodococcus sp. D-1: characteristics, products, and phytotoxicity. Sci Total Environ 590-591:343–351
Bai C et al (2015) Exploiting a precise design of universal synthetic modular regulatory elements to unlock the microbial natural products in Streptomyces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:12181–12186
Benoit S, Benachour A, Taouji S, Auffray Y, Hartke A (2002) H(2)O(2), which causes macrophage-related stress, triggers induction of expression of virulence-associated plasmid determinants in Rhodococcus equi. Infect Immun 70:3768–3776
Bentley SD et al (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Bhasarkar JB, Dikshit PK, Moholkar VS (2015) Ultrasound assisted biodesulfurization of liquid fuel using free and immobilized cells of Rhodococcus rhodochrous MTCC 3552: a mechanistic investigation. Bioresour Technol 187:369–378
Bosello M, Mielcarek A, Giessen TW, Marahiel MA (2012) An enzymatic pathway for the biosynthesis of the formylhydroxyornithine required for rhodochelin iron coordination. Biochemistry 51:3059–3066
Bosello M, Robbel L, Linne U, Xie X, Marahiel MA (2011) Biosynthesis of the siderophore rhodochelin requires the coordinated expression of three independent gene clusters in Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. J Am Chem Soc 133:4587–4595
Bosello M, Zeyadi M, Kraas FI, Linne U, Xie X, Marahiel MA (2013) Structural characterization of the heterobactin siderophores from Rhodococcus erythropolis PR4 and elucidation of their biosynthetic machinery. J Nat Prod 76:2282–2290
Ceniceros A, Dijkhuizen L, Petrusma M, Medema MH (2017) Genome-based exploration of the specialized metabolic capacities of the genus Rhodococcus. BMC Genomics 18:593
Crespi M, Vereecke D, Temmerman W, Van Montagu M, Desomer J (1994) The fas operon of Rhodococcus fascians encodes new genes required for efficient fasciation of host plants. J Bacteriol 176:2492–2501
Desomer J, Crespi M, Van Montagu M (1991) Illegitimate integration of non-replicative vectors in the genome of Rhodococcus fascians upon electrotransformation as an insertional mutagenesis system. Mol Microbiol 5:2115–2124
Dhungana S et al (2007) Purification and characterization of rhodobactin: a mixed ligand siderophore from Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain OFS. Biometals 20:853–867
Fernandes PJ, Powell JA, Archer JA (2001) Construction of Rhodococcus random mutagenesis libraries using Tn5 transposition complexes. Microbiology 147:2529–2536
Fischbach MA, Walsh CT (2006) Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: logic, machinery, and mechanisms. Chem Rev 106:3468–3496
Hart S, Kirby R, Woods DR (1990) Structure of a Rhodococcus gene encoding pigment production in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol 136:1357–1363
Ivshina I et al (2016) Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil spiked with model mixtures of petroleum hydrocarbons and heterocycles using biosurfactants from Rhodococcus ruber IEGM 231. J Hazard Mater 312:8–17
Jiang H et al (2013) Improvement of natamycin production by engineering of phosphopantetheinyl transferases in Streptomyces chattanoogensis L10. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3346–3354
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Li J, Liu J, Chen J, Wang Y, Luo G, Yu H (2015) Multiple reuses of Rhodococcus ruber TH3 free cells to produce acrylamide in a membrane dispersion microreactor. Bioresour Technol 187:198–204
Luo H, Tao Y, Wang W, Lin T, Wang Y, Jiang H (2017) Design of ribosome binding sites in Streptomyces coelicolor. Curr Proteomics 14:287–292
Lynch SA, Gallivan JP (2009) A flow cytometry-based screen for synthetic riboswitches. Nucleic Acids Res 37:184–192
McLeod MP et al (2006) The complete genome of Rhodococcus sp. RHA1 provides insights into a catabolic powerhouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:15582–15587
Miranda-Casoluengo R, Coulson GB, Miranda-Casoluengo A, Vazquez-Boland JA, Hondalus MK, Meijer WG (2012) The hydroxamate siderophore rhequichelin is required for virulence of the pathogenic actinomycete Rhodococcus equi. Infect Immun 80:4106–4114
Miranda-CasoLuengo R, Prescott JF, Vazquez-Boland JA, Meijer WG (2008) The intracellular pathogen Rhodococcus equi produces a catecholate siderophore required for saprophytic growth. J Bacteriol 190:1631–1637
Murakami S, Kodama N, Shinke R, Aoki K (1997) Classification of catechol 1,2-dioxygenase family: sequence analysis of a gene for the catechol 1,2-dioxygenase showing high specificity for methylcatechols from gram+ aniline-assimilating Rhodococcus erythropolis AN-13. Gene 185:49–54
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2007) Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod 70:461–477
Omotajo D, Tate T, Cho H, Choudhary M (2015) Distribution and diversity of ribosome binding sites in prokaryotic genomes. BMC Genomics 16:604
Osawa A, Kasahara A, Mastuoka S, Gassel S, Sandmann G, Shindo K (2011) Isolation of a novel carotenoid, OH-chlorobactene glucoside hexadecanoate, and related rare carotenoids from Rhodococcus sp. CIP and their antioxidative activities. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:2142–2147
Peng L et al (2014) Characterization and application of bioflocculant prepared by Rhodococcus erythropolis using sludge and livestock wastewater as cheap culture media. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:6847–6858
Sattely ES, Fischbach MA, Walsh CT (2008) Total biosynthesis: in vitro reconstitution of polyketide and nonribosomal peptide pathways. Nat Prod Rep 25:757–793
Steitz JA, Jakes K (1975) How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3′ terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 72:4734–4738
Sun J, Kelemen GH, Fernandez-Abalos JM, Bibb MJ (1999) Green fluorescent protein as a reporter for spatial and temporal gene expression in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 145(Pt 9):2221–2227
Thakur N, Kumar V, Sharma NK, Thakur S, Bhalla TC (2016) Aliphatic amidase of Rhodococcus rhodochrous PA-34: purification, characterization and application in synthesis of acrylic acid. Protein Pept Lett 23:152–158
Thanapimmetha A, Suwaleerat T, Saisriyoot M, Chisti Y, Srinophakun P (2016) Production of carotenoids and lipids by Rhodococcus opacus PD630 in batch and fed-batch culture. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng
Wang YY et al (2016) Characterization of discrete phosphopantetheinyl transferases in streptomyces tsukubaensis L19 unveils a complicate phosphopantetheinylation network. Sci Rep 6:24255
Zhang X et al (2013) Isolation and characterization of carbendazim-degrading Rhodococcus erythropolis djl-11. PLoS One 8:e74810
Zhang D et al (2015) Complete genome sequence of Rhodococcus sp. B7740, a carotenoid-producing bacterium isolated from the Arctic Sea. Genome Announc 3
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LR16H300001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670008), and the State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism, School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University (MMLKF17-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Y., Wang, WG., Lu, SH. et al. Conjugational delivery of chromosomal integrative constructs for gene expression in the carbendazim-degrading Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1. Ann Microbiol 68, 773–780 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1382-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1382-7