Abstract
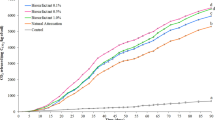
The production of biosurfactants and lipases through solid-state fermentation (SSF) processes remains relatively unexplored, especially in bacterial applications. The use of solid matrices, eliminating the need for precipitation and recovery processes, holds significant potential for facilitating bioremediation. This study aimed to simultaneously produce biocompounds via SSF using Bacillus methylotrophicus and employ the fermented substrate for remediating soil contaminated with 20% biodiesel. Initial efforts focused on determining optimal conditions for concurrent lipase and biosurfactant production during an 8-day fermentation period. The selected conditions, including a substrate mix of wheat bran and corn cob (80/20), 75% moisture, 1% glycerol inducer, 2% nitrogen, and 1% sugarcane molasses, resulted in a 24.61% reduction in surface tension and lipase activity of 3.54 ± 1.20 U. Subsequently, a 90-day bioremediation of clayey soil contaminated with biodiesel showcased notable biodegradation, reaching 72.08 ± 0.36% within the initial 60 days. The incorporation of biocompounds, biostimulation, and bioaugmentation (Test E2) contributed to this efficacy. The use of the fermented substrate as a biostimulant and bioaugmentation agent facilitated in situ biocompound production in the soil, leading to a 23.97% reduction in surface tension and lipase production of 1.52 ± 0.19 U.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Almeida AF, Taulk-Tornisielo SM, Carmona EC (2013) Influence of carbon and nitrogen sources on lipase production by a newly isolated Candida viswanathii strain. Ann Microbiol 63(4):1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0580-y
American Society for Testing and Materials (2013) Standard specification for woven wire test sieve cloth and test sieves. ASTM, West Conshohocken
Ananthi S, Ramasubburayan R, Palavesam A, Immanuel G (2014) Optimization and purification of lipase through solid state fermentation by bacillus cereus MSU as isolated from the gut of a marine fish Sardinella longiceps. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 6(5):291–298
Ángeles MT, Refugio RV (2013) In situ biosurfactant production and hydrocarbon removal by Pseudomonas putida CB-100 in bioaugmented and biostimulated oil-contaminated soil. Braz J Microbiol 44:595–605. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-8382201300020004
Azhdarpoor A, Mortazavi B, Moussavi G (2014) Oily wastewaters treatment using Pseudomonas sp. isolated from the compost fertilizer. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336X-12-77
Banat IM, Satpute SK, Cameotra SS, Patil R, Nyayanit NV (2014) Cost effective technologies and renewable substrates for biosurfactants’ production. Front Microbiol 5:697. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00697
Burkert JFM, Maugeri F, Rodrigues MI (2004) Optimization of extracellular lipase production by Geotrichum sp. using factorial design. Bioresour Technol 91(1):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(03)00152-4
Cecchin I, Reginatto C, Thomé A, Colla LM, Reddy KR (2016) Influence of physicochemical factors on biodiesel retention in clayey residual soil. J Environ Eng 142(4):04015093. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001060
Chaprão MJ, Ferreira IN, Correa PF, Rufino RD, Luna JM, Silva EJ, Sarubbo LA (2015) Application of bacterial and yeast biosurfactants for enhanced removal and biodegradation of motor oil from contaminated sand. Electron J Biotechnol 18(6):471–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2015.09.005
Chu W, Chan KH (2003) The mechanism of the surfactant-aided soil washing system for hydrophobic and partial hydrophobic organics. Sci Total Environ 307(1–3):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00461-8
Colla LM, Rizzardi J, Pinto MH, Reinehr CO, Bertolin TE, Costa JAV (2010) Simultaneous production of lipases and biosurfactants by submerged and solid-state bioprocesses. Bioresour Technol 101(21):8308–8314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.086
Colla LM, Primaz AL, Benedetti S, Loss RA, Lima MD, Reinehr CO, Bertolin TE, Costa JAV (2016) Surface response methodology for the optimization of lipase production under submerged fermentation by filamentous fungi. Braz J Microbiol 47:461–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2016.01.028
Contesini FJ, Lopes DB, Macedo GA, da Graça NM, Carvalho PO (2010) Aspergillus sp. lipase: potential biocatalyst for industrial use. J Mol Catal Enzym 67(3–4):163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2010.07.021
Cooper DG, Goldenberg BG (1987) Surface-active agents from two Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(2):224–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2010.07.021
Cooper DG, Paddock D (1984) Production of a biosurfactant from Torulopsis bombicola. Appl Environ Microbiol 47(1):173–176. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.47.1.173-176.1984
Das K, Mukherjee AK (2007) Comparison of lipopeptide biosurfactants production by Bacillus subtilis strains in submerged and solid state fermentation systems using a cheap carbon source: some industrial applications of biosurfactants. Process Biochem 42(8):1191–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2007.05.011
Decesaro A, Rampel A, Machado TS, Thomé A, Reddy K, Margarites AC, Colla LM (2017) Bioremediation of soil contaminated with diesel and biodiesel fuel using biostimulation with microalgae biomass. J Environ Eng 143(4):04016091. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001165
Decesaro A, Rempel A, Machado TS, Cappellaro ÂC, Machado BS, Cechin I, Thomé A, Colla LM (2021) Bacterial biosurfactant increases ex situ biodiesel bioremediation in clayey soil. Biodegradation 32(4):389–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-021-09944-z
Elumalai P, Parthipan P, Huang M, Muthukumar B, Cheng L, Govarthanan M, Rajasekar A (2021) Enhanced biodegradation of hydrophobic organic pollutants by the bacterial consortium: impact of enzymes and biosurfactants. Environ Pollut 289:117956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117956
Eraqi WA, Yassin AS, Ali AE, Amin MA (2016) Utilization of crude glycerol as a substrate for the production of rhamnolipid by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biotechnol Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3464509
Fai AEC, Simiqueli APR, de Andrade CJ, Ghiselli G, Pastore GM (2015) Optimized production of biosurfactant from Pseudozyma tsukubaensis using cassava wastewater and consecutive production of galactooligosaccharides: an integrated process. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 4(4):535–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2015.10.001
Fontes GC, Amaral PFF, Coelho MAZ (2008) Produção de biossurfactante por levedura. Quim Nova 31:2091–2099. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422008000800033
Gharaei-Fathabad E (2011) Biosurfactants in pharmaceutical industry: a mini-review. Am J Drug Discov Dev 1(1):58–69. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajdd.2011.58.69
Ghribi D, Abdelkefi-Mesrati L, Mnif I, Kammoun R, Ayadi I, Saadaoui I, Maktouf S, Chaabouni-Ellouze S (2012) Investigation of antimicrobial activity and statistical optimization of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant production in solid-state fermentation. J Biomed Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/373682
Guerrero AB, Muñoz E (2018) Life cycle assessment of second generation ethanol derived from banana agricultural waste: environmental impacts and energy balance. J Clean Prod 174:710–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.298
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb Technol 39(2):235–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.016
Karanth NGK, Deo PG, Veenanadig NK (1999) Microbial production of biosurfactants and their importance. Curr Sci, pp 116–126. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24102919
Kirana S, Arshada Z, Nosheenb S, Kamala S, Gulzara T, Majeeda MS, Jannar M, Rafique MA (2016) Microbial lipases: production and applications: a review. J Biochem Biotechnol Biomater 1(2):7–20
Kreling NE, Simon V, Fagundes VD, Thomé A, Colla LM (2020) Simultaneous production of lipases and biosurfactants in solid-state fermentation and use in bioremediation. J Environ Eng 146(9):04020105. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001785
Larik IA, Qazi MA, Phulpoto AH, Haleem A, Ahmed S, Kanhar NA (2019) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain 5DMD: an efficient biosurfactant-producing bacterium for biodegradation of diesel oil and used engine oil. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(1):259–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1666-2
Li J, Wang Y, Zhou W, Chen W, Deng M, Zhou S (2020) Characterization of a new biosurfactant produced by an effective pyrene-degrading Achromobacter species strain AC15. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 152:104959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.104959
Lin X, Li X, Sun T, Li P, Zhou Q, Sun L, Hu X (2009) Changes in microbial populations and enzyme activities during the bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83(4):542–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9838-x
Lizardi-Jiménez MA, Hernández-Martínez R (2017) Solid state fermentation (SSF): diversity of applications to valorize waste and biomass. 3 Biotech 7(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0692-y
Machado TS, Decesaro A, Cappellaro AC, Machado BS, van Schaik RK, Reinehr CO, Thomé A, Colla LM (2020) Effects of homemade biosurfactant from Bacillus methylotrophicus on bioremediation efficiency of a clay soil contaminated with diesel oil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 201:110798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110798
Mahadik ND, Puntambekar US, Bastawde KB, Khire JM, Gokhale DV (2002) Production of acidic lipase by Aspergillus niger in solid state fermentation. Process Biochem 38(5):715–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00194-2
Margesin R, Zimmerbauer A, Schinner F (1999) Soil lipase activity–a useful indicator of oil biodegradation. Biotechnol Tech 13(12):859–863. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008928308695
Martins VG, Kalil SJ, Costa JAV (2008) Co-produção de lipase e biossurfactante em estado sólido para utilização em biorremediação de óleos vegetais e hidrocarbonetos. Quim Nova 31:1942–1947. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422008000800005
Mazhar H, Abbas N, Hussain Z, Sohail A, Ali SS (2016) Extracellular lipase production from Bacillus subtilis using agro-industrial waste and fruit peels. Punjab Univ J Zool 31(2):261–267
Mulligan CN (2009) Recent advances in the environmental applications of biosurfactants. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 14(5):372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2009.06.005
Nehal N, Singh P (2022) Role of nanotechnology for improving properties of biosurfactant from newly isolated bacterial strains from Rajasthan. Mater Today Proc 50:2555–2561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.682
Nievas ML, Commendatore MG, Esteves JL, Bucalá V (2008) Biodegradation pattern of hydrocarbons from a fuel oil-type complex residue by an emulsifier-producing microbial consortium. J Hazard Mater 154(1–3):96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.112
Nitschke M, Pastore GM (2002) Biossurfactantes: propriedades e aplicações. Quim Nova 25:772–776. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422002000500013
Oliveira F, Souza CE, Peclat VR, Salgado JM, Ribeiro BD, Coelho MA, Venâncio A, Belo I (2017) Optimization of lipase production by Aspergillus ibericus from oil cakes and its application in esterification reactions. Food Bioprod Process 102:268–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2017.01.007
Pandey A (2003) Solid-state fermentation. Biochem Eng J 13(2–3):81–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-703X(02)00121-3
Parthipan P, Cheng L, Dhandapani P, Elumalai P, Huang M, Rajasekar A (2022) Impact of biosurfactant and iron nanoparticles on biodegradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Environ Pollut 306:119384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119384
Perfumo A, Banat IM, Marchant R (2018) Going green and cold: biosurfactants from low-temperature environments to biotechnology applications. Trends Biotechnol 36(3):277–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.10.016
Quintella CM, Mata AM, Lima LC (2019) Overview of bioremediation with technology assessment and emphasis on fungal bioremediation of oil contaminated soils. J Environ Manage 241:156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.019
Rufino DR, Moura de Luna J, de Campos Takaki GM, AsforaSarubbo L (2014) Characterization and properties of the biosurfactant produced by Candida lipolytica UCP 0988. Electron J Biotechnol 17(1):6–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2013.12.006
Salgado JM, Abrunhosa L, Venâncio A, Domínguez JM, Belo I (2016) Combined bioremediation and enzyme production by Aspergillus sp. in olive mill and winery wastewaters. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 110:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.12.011
Salim AA, Grbavčić S, Šekuljica N, Stefanović A, Tanasković SJ, Luković N, Knežević-Jugović Z (2017) Production of enzymes by a newly isolated Bacillus sp. TMF-1 in solid state fermentation on agricultural by-products: the evaluation of substrate pretreatment methods. Bioresour Technol 228:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.081
Santos RDS, Muruci LNM, Santos LO, Antoniassi R, da Silva JPL, Damaso MCT (2014) Characterization of different oil soapstocks and their application in the lipase production by Aspergillus niger under solid state fermentation. J Food Nutr Res 2(9):561–566. https://doi.org/10.12691/jfnr-2-9-6
Satpute SK, Banpurkar AG, Dhakephalkar PK, Banat IM, Chopade BA (2010) Methods for investigating biosurfactants and bioemulsifiers: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 30(2):127–144. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388550903427280
Scherhaufer S, Moates G, Hartikainen H, Waldron K, Obersteiner G (2018) Environmental impacts of food waste in Europe. Waste Manage 77:98–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.04.038
Sella SRBR, Guizelini BP, Vandenberghe LPDS, Medeiros ABP, Soccol CR (2009) Lab-Scale production of Bacillus atrophaeus’ spores by solid state fermentation in fifferent types of bioreactors. Braz Arch Biol Technol 52:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132009000700021
Sharma A, Kumar P, Rehman MB (2014) Biodegradation of diesel hydrocarbon in soil by bioaugmentation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a laboratory scale study. Int J Environ Bioremediat Biodegrad 2(4):202–212. https://doi.org/10.12691/ijebb-2-4-8
Slivinski CT, Mallmann E, de Araújo JM, Mitchell DA, Krieger N (2012) Production of surfactin by Bacillus pumilus UFPEDA 448 in solid-state fermentation using a medium based on okara with sugarcane bagasse as a bulking agent. Process Biochem 47(12):1848–1855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.06.014
Sperb JGC, Costa TM, Vaz DA, Valle JAB, Valle RDCSC, Tavares LBB (2015) Análise qualitativa da produção de lipases e biossurfactantes por fungos isolados de resíduos oleosos. Engevista 17(3):385–397
Tanyol M, Uslu G, Yönten V (2015) Optimization of lipase production on agro-industrial residue medium by Pseudomonas fluorescens (NRLL B-2641) using response surface methodology. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 29(1):64–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2014.991635
Thomas L, Larroche C, Pandey A (2013) Current developments in solid-state fermentation. Biochem Eng J 81:146–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.10.013
Thomé A, Reginatto C, Cecchin I, Colla LM (2014) Bioventing in a residual clayey soil contaminated with a blend of biodiesel and diesel oil. J Environ Eng 140(11):06014005. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000863
Tsuji M, Yokota Y, Shimohara K, Kudoh S, Hoshino T (2013) An application of wastewater treatment in a cold environment and stable lipase production of Antarctic basidiomycetous yeast Mrakia blollopis. PLoS ONE 8(3):e59376. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059376
Urum K, Pekdemir T (2004) Evaluation of biosurfactants for crude oil contaminated soil washing. Chemosphere 57(9):1139–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.07.048
USEPA (1996) Method 3550B: ultrasonic extraction. http://www.trincoll.edu/~henderso/textfi~1/416%20notes/3550b.pdf. Accessed Sept 2015
Utami TS, Hariyani I, Alamsyah G, Hermansyah H (2017) Production of dry extract extracellular lipase from Aspergillus niger by solid state fermentation method to catalyze biodiesel synthesis. Energy Proc 136:41–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.10.275
Uzoigwe C, Burgess JG, Ennis CJ, Rahman PK (2015) Bioemulsifiers are not biosurfactants and require different screening approaches. Front Microbiol 6:245. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00245
Zarinviarsagh M, Ebrahimipour G, Sadeghi H (2017) Lipase and biosurfactant from Ochrobactrum intermedium strain MZV101 isolated by washing powder for detergent application. Lipids Health Dis 16(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-017-0565-8
Zouari R, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi-Aydi D (2014) Optimization of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant production under solid-state fermentation using by-products of a traditional olive mill factory. Achiev Life Sci 8(2):162–169. https://www.scipedia.com/public/Zouari_et_al_2015a
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for the financial support, project number 408866/2016-0, Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS), BSBIOS Company for supplying the biodiesel used in this work and Universidade de Passo Fundo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kreling, N.E., Fagundes, V.D., Simon, V. et al. Co-production of lipases and biosurfactants by Bacillus methylotrophicus in solid-state fermentation. 3 Biotech 14, 78 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03910-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03910-7